关于binary log那些事——认真码了好长一篇
本文介绍binlog的作用以及几个重要参数的使用方法,同时通过实验来描述binlog内部记录内容:row 、statement跟mixed的设置下,记录了哪些东西,最后会简单介绍下binlog server的搭建以及一些关于binlog使用的小Tips。
理解跟熟悉binlog相关内容,对复制原理及故障处理会有很大帮助的。
如果转载,请注明博文来源: www.cnblogs.com/xinysu/ ,版权归 博客园内 苏家小萝卜 所有。望各位支持!
1 what's binary log
Binary log 用来记录数据库中发生的修改情况,比如数据的修改、表格的创建及修改等,它既可以记录涉及修改的SQL,也可以记录数据修改的行变化记录,同时也记录了执行时间。比如,执行sql:update tabname set cola='a' where id between 1 and 5,修改了5行记录。当开启binlog记录的时候,根据设置的binlog格式,可能记录的是这一条SQL语句,也可能记录的是5行数据记录的修改情况,也可能两者都有,这部分详情可以看本博文的第3部分:binlog formats。
这里注意跟general log区分下,binnary log是记录数据库内部的修改情况,而general log是记录所有数据库的SQL操作情况,比如像select或者show这种语句,不会发生数据修改,则不会记录到binnary log,但是属于数据库操作记录,会记录到general log。
那么,开启它,有什么好处,有什么确定呢 ?
首先,好处有3个:
- 搭建复制架构的时候,需要binary log 来记录数据库的修改event;
- 数据库宕机恢复使用;
- 异常操作,紧急恢复数据使用;
那么,当开启binlog记录日志的时候,也就以为着有一定的IO量被占用,相对而言,数据库会比不开启的时候稍微慢些。但是由于带来的好处比较多且重要,这点性能影响在大多数情况下可以忽略。
2 Binary Logging Options and Variables
2.1 基础参数
- 文件大小
- max_binlog_size
- 范围4k-1G,默认为1G;这里注意下,并非设置了 max_binlog_size=1G,binlog文件最大就为1G,当事务短且小的情况下,binlog接近1G的时候,就会flush log,生成新的binlog文件,但是,但是,但是,但是同个事务是不能够跨多个binlog文件存储,一个事务只能存储在一个binlog文件。如果这个时候,有个大事务,假设单个SQL UPDATE了100w行数据,SQL产生的binlog日志记录有5G,那么当前的binlog文件则会出现大于5G的情况,该事务结束后,才会切换binlog文件。
- max_binlog_size
- 缓存大小
- binlog_cache_size
- binlog写缓冲区设置大小,由于是内存,写速度非常快,可以有效提高binlog的写效率,如果数据库中经常出现大事务,可以酌情提高该参数。
- 那么,如果观察自家DB实例的binlog_cache_size设置是否合理呢?可以通过show status like 'Binlog_cache%';查看Binlog_cache_use and Binlog_cache_disk_use的使用情况,Binlog_cache_use表示用到binlog缓冲区的次数,Binlog_cache_disk_use ,使用临时文件来存放binlog cache的次数,如果Binlog_cache_disk_use的次数过多,可以酌情提高该参数。详见下图。
- binlog_stmt_cache_size
- 保留一个事务内,非事务语句文本的缓存大小。默认32k。
- 与binlog_cache_size一样,也可以通过show status like 'binlog_stmt_cache%'来查看是否设置合理。查看参数为:Binlog_stmt_cache_use (使用缓存区的次数),Binlog_stmt_cache_disk_use(使用临时文件的次数)
- max_binlog_cache_size
- 默认为4G,如果发生大事务占用binlog cache超过设置值,则会报错 : multi-statement transaction required more than 'max_binlog_cache_size' bytes of storage。
- 这时候,就有个疑问了,为啥存在了 binlog_cache_size的设置,还需要 max_binlog_cache_size呢?
- 其实是这样,当一个线程连接进来并开始执行事务的时候,数据库会按照binlog_cache_size的大小分配给它一个缓冲区域,如果使用到的空间要大于binlog_cache_size,则会使用临时文件来存储,线程结束后再删除临时文件。
- 而max_binlog_cache_size则是严格限制了一个多SQL事务总的使用binlog cache的大小,保留分配缓冲区域跟临时文件,总大小不能超过max_binlog_cache_size的限制值,一旦超过,则会报错multi-statement transaction required more than 'max_binlog_cache_size' bytes of storage。
- max_binlog_stmt_cache_size
- 默认4G。超过则报错。注意事项跟 max_binlog_cache_size 类似。
- binlog_cache_size
- binlog文件相关
- log_bin_basename
- binlog文件的命名方式
- log_bin_index
- binlog索引文件的绝对路径
- expire_logs_days
- binlog保留的有效天数,过期的会自动删除
- 这里有个小tips,假设当前binlog文件过多且大占用磁盘空间,可以修改小改参数,改参数只有在切换新的binlog文件时,才会删除过期文件,也就是可以等数据库把当前binlog写满后切换到新文件的时候删除,也可以手动执行flush logs,手动切换binlog,同时会触发对过期binlog文件的删除。
- log_bin_basename
2.2 重要参数(sync_binlog=0丢失数据的描述有疑问,目前查阅相关资料跟咨询业界人士中....)
- binlog开关
- log_bin
- 需要在数据库配置文件中添加或者指定--log-bin=[base-name]启动DB服务,重启后修改才生效
- 需要在数据库配置文件中添加或者指定--log-bin=[base-name]启动DB服务,重启后修改才生效
- log_bin
- 日志记录内容相关
- binlog_format
- 多么重要的参数,以至于本文开了一节来细讲,详见 第三部分
- 设置binlog的记录格式
- 5.7.6前默认statement,5.7.7后默认row,可选row,mixed,statement
- binlog_row_image
- 主要针对当binlog_format=row格式 下的设置,
- 默认full,可选full,minimal,noblob
- binlog_rows_query_log_events
- 主要针对当binlog_format=row格式 下的设置,如果基于row记录binlog日志,默认是只记录变化的行数据,不记录涉及执行的SQL语句,如果开启此参数,则会一同记录执行的SQL语句
- 默认false
- binlog_gtid_simple_recovery
- GTID复制会使用到,该参数控制 配置了的GTID复制到实例,在重启时或者清理binlog文件时,数据库只需要打开最老跟最新两个binlog文件取出gtid_purged and gtid_executed,不需要打开所有文件
- 默认为false,这个参数是社区反馈给官方添加,调整这个选项设置为True,对性能会有所提高,但是在某些环境下,由于只打开两个文件来计算,所以计算gtids值可能会出错。而保持这个选项值为false,能确保计算总是正确。
- 组提交(提高binary log并发提交的数据量)
- binlog_group_commit_sync_delay
- 默认为0
- 结合binlog_group_commit_sync_no_delay_count来理解,见下文
- binlog_group_commit_sync_no_delay_count
- 默认为0
- MySQL等待binlog_group_commit_sync_delay毫秒的时间直到 binlog_group_commit_sync_no_delay_count个数时进行一次组提交,如果binlog_group_commit_sync_delay毫秒内也还没有到达指定的个数,也会提交。
- flush disk相关
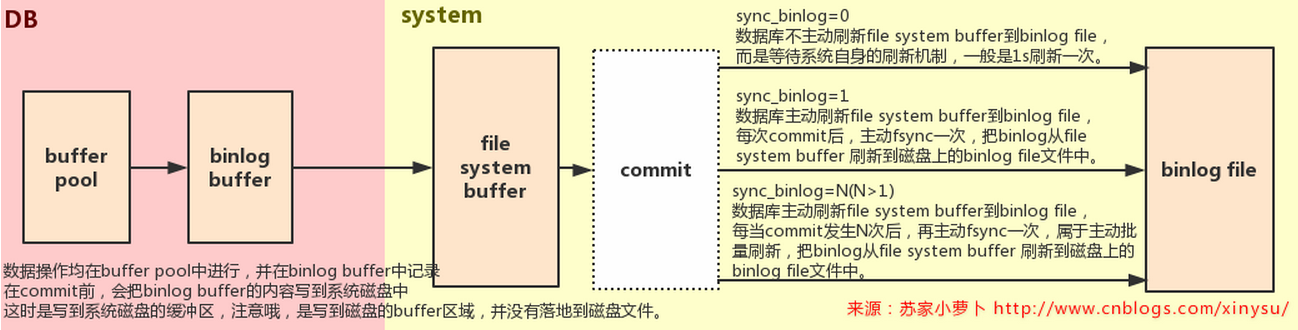
- sync_binlog
- 5.7.7前默认为0,之后默认为1,范围0-4294967295
- binlog_format
-
-
- sync_binlog =0,则是依赖操作系统刷新文件的机制,MySQL不会主动同步binlog内容到磁盘文件中去,而是依赖操作系统来刷新binary log。
-
-
-
- sync_binlog =N (N>0) ,则是MySQL 在每写 N次 二进制日志binary log时,会使用fdatasync()函数将它的写二进制日志binary log同步到磁盘中去。
-
-
-
- 注: 如果启用了autocommit,那么每一个语句statement就会有一次写操作;否则每个事务对应一个写操作。
-
-
-
- 如果设置sync_binlog =0 ,发生crash事件(服务器),数据库最高丢失binlog内容为1s内写在file system buffer的内容;
-
-
-
- 如果设置sync_binlog =N ,发生crash事件(服务器),数据库最高丢失binlog内容为写在file system buffer内 N个binlog events;
- 如果设置sync_binlog =N ,发生crash事件(服务器),数据库最高丢失binlog内容为写在file system buffer内 N个binlog events;
-
-
-
- 这个参数经常跟innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit结合调整,提高性能或者提高安全性(详细可查看上周博文:http://www.cnblogs.com/xinysu/p/6555082.html 中 “redo参数” 一节),这里提2个推荐的配置:
-
-
-
-
- innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit和sync_binlog 都为 1(俗称双一模式),在mysqld 服务崩溃或者服务器主机crash的情况下,binary log 只有可能丢失最多一个语句或者一个事务。但是有得必有舍,这个设置是最安全但也是最慢的。适合数据一致性要求较高,核心业务使用。
-
-
-
-
-
- innodb_flush_log_at_trx_commit=2 ,sync_binlog=N (N为500 或1000) ,但是但是但是,服务器一定要待用蓄电池后备电源来缓存cache,在服务器crash后,还能支持把file system buffer中的内容写入到binlog file中,防止系统断电异常。这种适合当磁盘IO无法满足业务需求时,比如节假日或者周年活动产生的数据库IO压力,则推荐这么设置。
-
-
3 Binary Logging Formats
这一部分,将通过实验来说明。我们会使用到mysqlbinlog指令,其具体用法详见:https://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/mysqlbinlog.html 。
还记得你刚刚看到“日志记录内容相关 ” 小节里那三个红灿灿喜洋洋的参数吗?哈哈哈,见下文:
- binlog_format
- 多么重要的参数,以至于本文开了一节来细讲,详见 第三部分
- 设置binlog的记录格式
- 5.7.6前默认statement,5.7.7后默认row,可选row,mixed,statement
- binlog_row_image
- 主要针对当binlog_format=row格式 下的设置,
- 默认full,可选full,minimal,noblob
- binlog_rows_query_log_events
- 主要针对当binlog_format=row格式 下的设置,如果基于row记录binlog日志,默认是只记录变化的行数据,不记录涉及执行的SQL语句,如果开启此参数,则会一同记录执行的SQL语句
- 默认false
实验内容:
- 设置binlog format格式;设置隔离级别;
- 创建表格
- INSERT操作(重点查看UUID()函数使用情况)
- UPDATE操作(检查自动更新时间列)
- DELETE操作
3.1 binlog_format=statement
1 #测试前环境准备及清理: 2 mysql> set binlog_format='statement'; 3 mysql> SET session tx_isolation='REPEATABLE-READ'; 4 mysql> SELECT @@GLOBAL.tx_isolation, @@tx_isolation; 5 mysql> show variables like 'binlog_format' ; 6 mysql> flush logs; 7 mysql> show master status;
测试前环境准备及清理:
模拟DDL操作及DML操作:
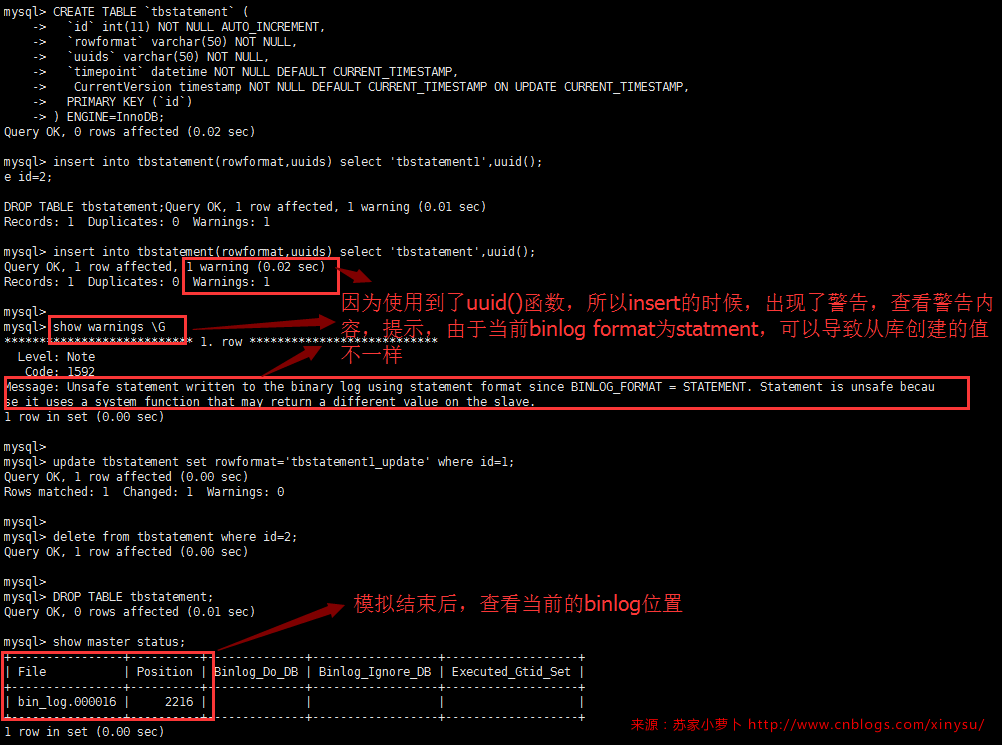
DDL跟DML模拟结束后,得到当前的binlog文件是 ,结束的position是,所以直接读取整个文件从position=154到i2216之间的操作记录,使用mysqlbinlog读取。
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqlbinlog --start-position=154 --stop-position=2216

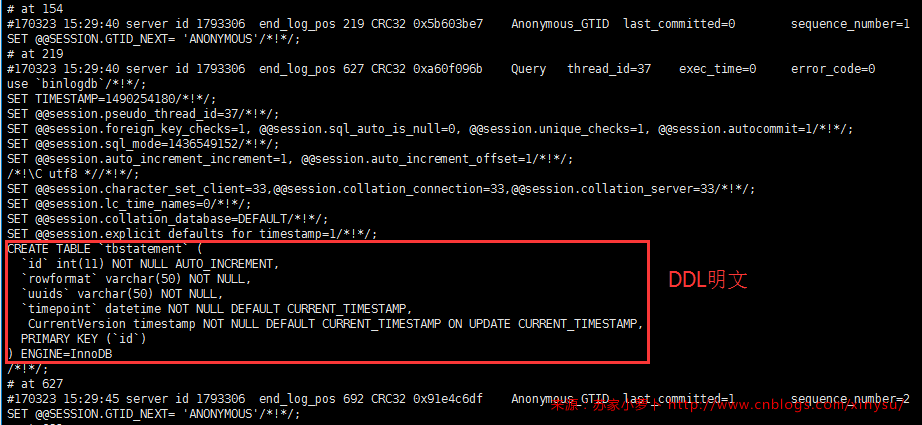
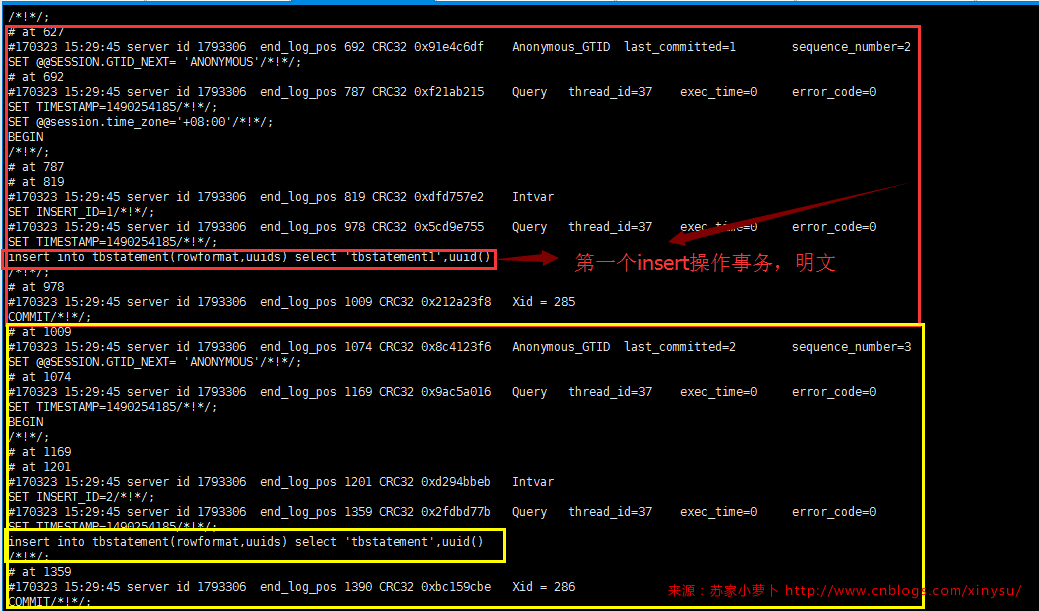
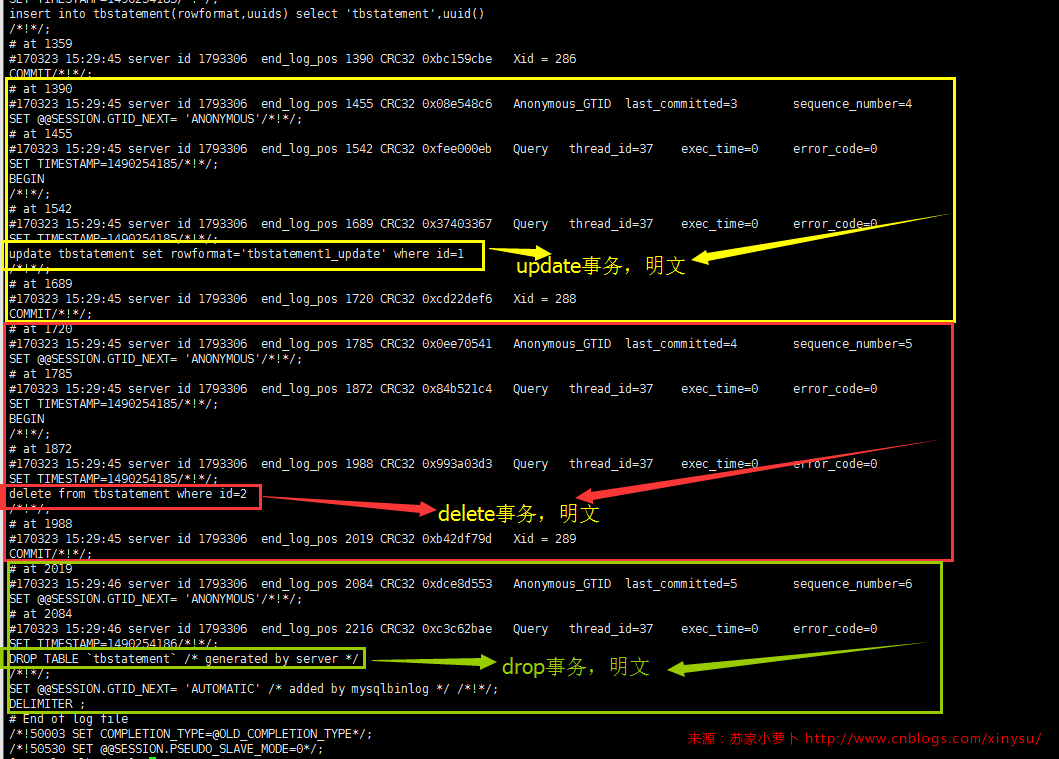
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqlbinlog --start-position=154 --stop-position=2216 /data/mysql/mysql3306/logs/bin_log.000016 /*!50530 SET @@SESSION.PSEUDO_SLAVE_MODE=1*/; /*!50003 SET @OLD_COMPLETION_TYPE=@@COMPLETION_TYPE,COMPLETION_TYPE=0*/; DELIMITER /*!*/; # at 4 #170323 15:29:32 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 123 CRC32 0xea8ce874 Start: binlog v 4, server v 5.7.14-log created 170323 15:29:32 # Warning: this binlog is either in use or was not closed properly. BINLOG ' XHnTWA8aXRsAdwAAAHsAAAABAAQANS43LjE0LWxvZwAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAA AAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAAEzgNAAgAEgAEBAQEEgAAXwAEGggAAAAICAgCAAAACgoKKioAEjQA AXTojOo= '/*!*/; # at 154 #170323 15:29:40 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 219 CRC32 0x5b603be7 Anonymous_GTID last_committed=0 sequence_number=1 SET @@SESSION.GTID_NEXT= 'ANONYMOUS'/*!*/; # at 219 #170323 15:29:40 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 627 CRC32 0xa60f096b Query thread_id=37 exec_time=0 error_code=0 use `binlogdb`/*!*/; SET TIMESTAMP=1490254180/*!*/; SET @@session.pseudo_thread_id=37/*!*/; SET @@session.foreign_key_checks=1, @@session.sql_auto_is_null=0, @@session.unique_checks=1, @@session.autocommit=1/*!*/; SET @@session.sql_mode=1436549152/*!*/; SET @@session.auto_increment_increment=1, @@session.auto_increment_offset=1/*!*/; /*!\C utf8 *//*!*/; SET @@session.character_set_client=33,@@session.collation_connection=33,@@session.collation_server=33/*!*/; SET @@session.lc_time_names=0/*!*/; SET @@session.collation_database=DEFAULT/*!*/; SET @@session.explicit_defaults_for_timestamp=1/*!*/; CREATE TABLE `tbstatement` ( `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, `rowformat` varchar(50) NOT NULL, `uuids` varchar(50) NOT NULL, `timepoint` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, CurrentVersion timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, PRIMARY KEY (`id`) ) ENGINE=InnoDB /*!*/; # at 627 #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 692 CRC32 0x91e4c6df Anonymous_GTID last_committed=1 sequence_number=2 SET @@SESSION.GTID_NEXT= 'ANONYMOUS'/*!*/; # at 692 #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 787 CRC32 0xf21ab215 Query thread_id=37 exec_time=0 error_code=0 SET TIMESTAMP=1490254185/*!*/; SET @@session.time_zone='+08:00'/*!*/; BEGIN /*!*/; # at 787 # at 819 #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 819 CRC32 0xdfd757e2 Intvar SET INSERT_ID=1/*!*/; #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 978 CRC32 0x5cd9e755 Query thread_id=37 exec_time=0 error_code=0 SET TIMESTAMP=1490254185/*!*/; insert into tbstatement(rowformat,uuids) select 'tbstatement1',uuid() /*!*/; # at 978 #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 1009 CRC32 0x212a23f8 Xid = 285 COMMIT/*!*/; # at 1009 #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 1074 CRC32 0x8c4123f6 Anonymous_GTID last_committed=2 sequence_number=3 SET @@SESSION.GTID_NEXT= 'ANONYMOUS'/*!*/; # at 1074 #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 1169 CRC32 0x9ac5a016 Query thread_id=37 exec_time=0 error_code=0 SET TIMESTAMP=1490254185/*!*/; BEGIN /*!*/; # at 1169 # at 1201 #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 1201 CRC32 0xd294bbeb Intvar SET INSERT_ID=2/*!*/; #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 1359 CRC32 0x2fdbd77b Query thread_id=37 exec_time=0 error_code=0 SET TIMESTAMP=1490254185/*!*/; insert into tbstatement(rowformat,uuids) select 'tbstatement',uuid() /*!*/; # at 1359 #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 1390 CRC32 0xbc159cbe Xid = 286 COMMIT/*!*/; # at 1390 #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 1455 CRC32 0x08e548c6 Anonymous_GTID last_committed=3 sequence_number=4 SET @@SESSION.GTID_NEXT= 'ANONYMOUS'/*!*/; # at 1455 #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 1542 CRC32 0xfee000eb Query thread_id=37 exec_time=0 error_code=0 SET TIMESTAMP=1490254185/*!*/; BEGIN /*!*/; # at 1542 #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 1689 CRC32 0x37403367 Query thread_id=37 exec_time=0 error_code=0 SET TIMESTAMP=1490254185/*!*/; update tbstatement set rowformat='tbstatement1_update' where id=1 /*!*/; # at 1689 #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 1720 CRC32 0xcd22def6 Xid = 288 COMMIT/*!*/; # at 1720 #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 1785 CRC32 0x0ee70541 Anonymous_GTID last_committed=4 sequence_number=5 SET @@SESSION.GTID_NEXT= 'ANONYMOUS'/*!*/; # at 1785 #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 1872 CRC32 0x84b521c4 Query thread_id=37 exec_time=0 error_code=0 SET TIMESTAMP=1490254185/*!*/; BEGIN /*!*/; # at 1872 #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 1988 CRC32 0x993a03d3 Query thread_id=37 exec_time=0 error_code=0 SET TIMESTAMP=1490254185/*!*/; delete from tbstatement where id=2 /*!*/; # at 1988 #170323 15:29:45 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 2019 CRC32 0xb42df79d Xid = 289 COMMIT/*!*/; # at 2019 #170323 15:29:46 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 2084 CRC32 0xdce8d553 Anonymous_GTID last_committed=5 sequence_number=6 SET @@SESSION.GTID_NEXT= 'ANONYMOUS'/*!*/; # at 2084 #170323 15:29:46 server id 1793306 end_log_pos 2216 CRC32 0xc3c62bae Query thread_id=37 exec_time=0 error_code=0 SET TIMESTAMP=1490254186/*!*/; DROP TABLE `tbstatement` /* generated by server */ /*!*/; SET @@SESSION.GTID_NEXT= 'AUTOMATIC' /* added by mysqlbinlog */ /*!*/; DELIMITER ; # End of log file /*!50003 SET COMPLETION_TYPE=@OLD_COMPLETION_TYPE*/; /*!50530 SET @@SESSION.PSEUDO_SLAVE_MODE=0*/;
逐个事务拆分开看如下图:
小结:
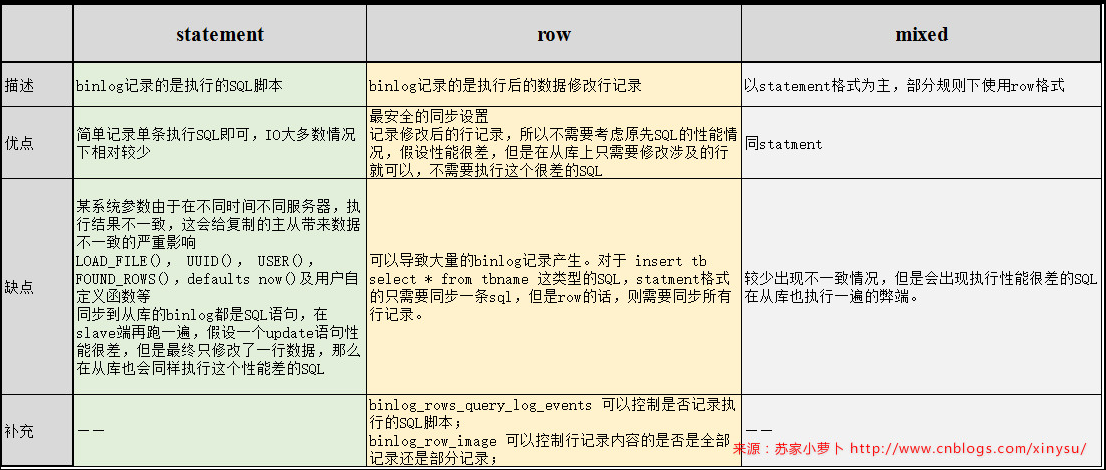
- 当binlog_format=statement的时候,DDL及DML都是明文按照SQL记录存储
- 对复制的影响
- 某系统参数由于在不同时间不同服务器,执行结果不一致,这会给复制的主从带来数据不一致的严重影响
- LOAD_FILE(), UUID(), USER(),FOUND_ROWS(),defaults now()及用户自定义函数等
- 同步到从库的binlog都是SQL语句,在slave端再跑一遍,假设一个update语句性能很差,但是最终只修改了一行数据,那么在从库也会同样执行这个性能差的SQL
- 而对于 insert tb select * from tbname 这类型的SQL,则只需要同步一行SQL语句即可
3.2 binlog_format=row
3.2.1 binlog_row_image默认full,binlog_rows_query_log_events默认false
1 set binlog_format='row'; 2 SET session tx_isolation='REPEATABLE-READ'; 3 SELECT @@GLOBAL.tx_isolation, @@tx_isolation; 4 show variables like 'binlog_format' ; 5 show master status; 6 flush logs; 7 show master status; 8 9 10 CREATE TABLE `tbrow` ( 11 `id` int(11) NOT NULL AUTO_INCREMENT, 12 `rowformat` varchar(50) NOT NULL, 13 `uuids` varchar(50) NOT NULL, 14 `timepoint` datetime NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, 15 CurrentVersion timestamp NOT NULL DEFAULT CURRENT_TIMESTAMP ON UPDATE CURRENT_TIMESTAMP, 16 PRIMARY KEY (`id`) 17 ) ENGINE=InnoDB; 18 insert into tbrow(rowformat,uuids) select 'row',uuid(); 19 insert into tbrow(rowformat,uuids) select 'row',uuid(); 20 update tbrow set rowformat='tbstatement1_update' where id=1; 21 delete from tbrow where id=2; 22 DROP TABLE tbrow; 23 show master status;
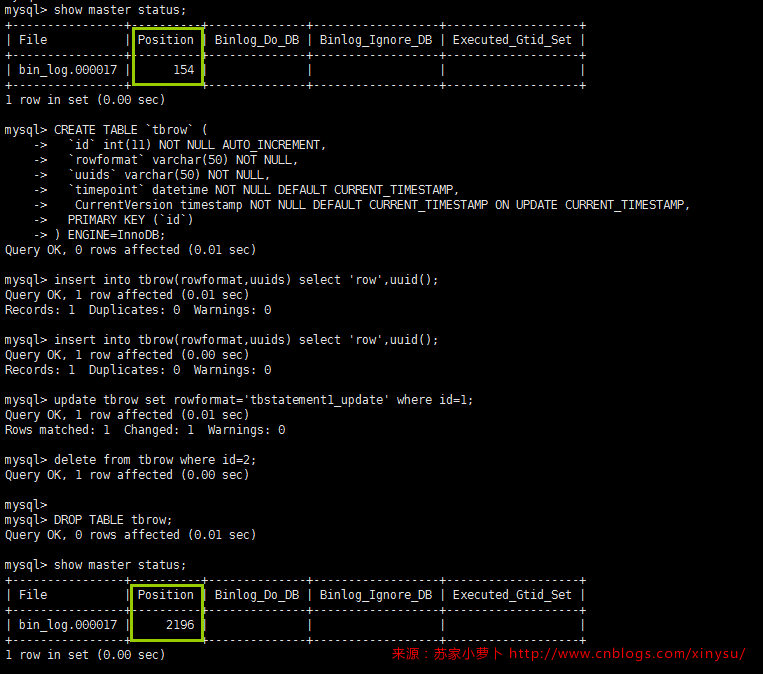
找到开始与结束的position点,查看这个区间的binlog日志内容:/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqlbinlog --start-position=154 --stop-position=2196 /data/mysql/mysql3306/logs/bin_log.000017
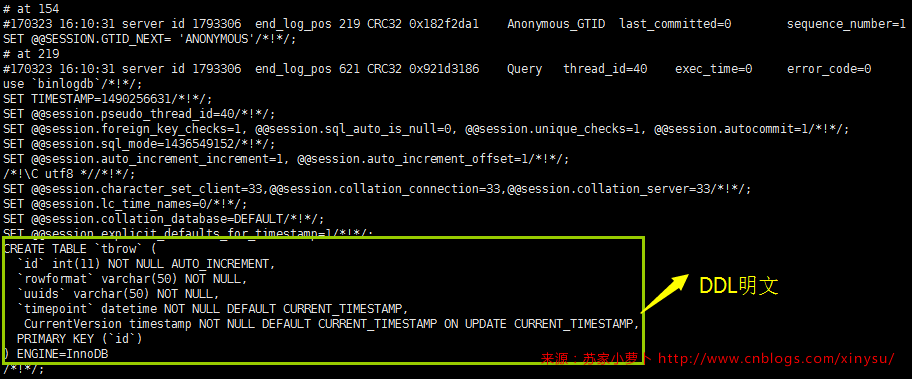

发现,在row格式下,DML是加密存储,好在mysqlbinlog提供参数-v 反解析查看,指令如下:
[root@localhost ~]# /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqlbinlog --base64-output=decode-rows -v -v --start-position=154 --stop-position=2196 /data/mysql/mysql3306/logs/bin_log.000017
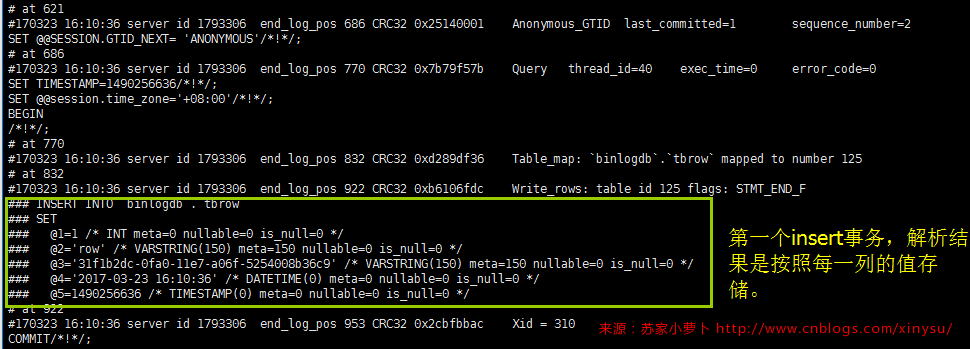
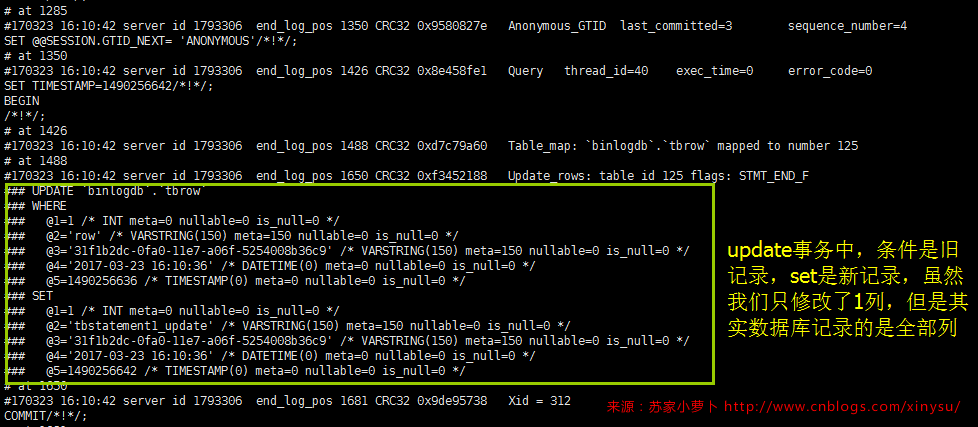
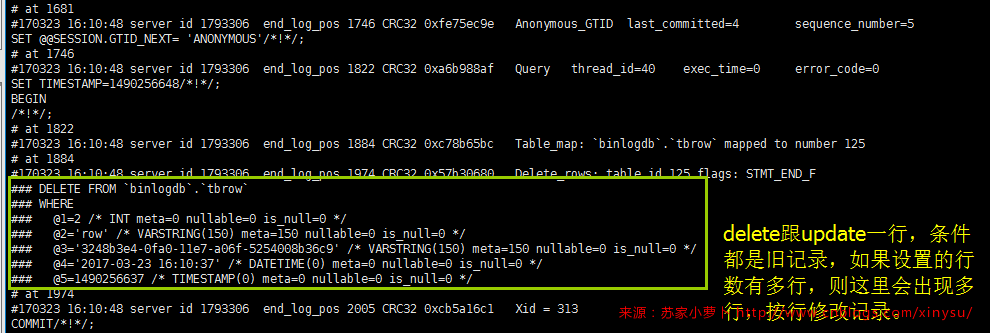
小结:
- 当binlog_format=row的时候,其他参数默认,DDL明文存储SQL脚本,DML都是加密存储且存储的是每一行的行记录修改情况
- 对复制的影响
- 最安全的同步设置
- 同步到从库的binlog都是按行记录修改的SQL,所以假设一个update语句性能很差,但是最终只修改了一行数据,那么在从库不需要执行这个性能差的SQL,只需要直接执行行记录的修改结果即可(注意,使用基于row格式复制的实例,请给所有表格添加主键或者唯一索引,不然每一行记录的修改都需要全表扫,会导致从库性能非常差而且可能延时较长)
- 而对于 insert tb select * from tbname 这类型的SQL,statment格式的只需要同步一条sql,但是row的话,则需要同步所有行记录。
3.2.2 binlog_rows_query_log_events 设置
从上小节可以看出,当binlog_format=row的时候,只记录行修改情况,不记录执行的SQL的。启动这个参数,则可在row格式下查看到执行的sql语句。
造数据中:
查看binlog日志如下:

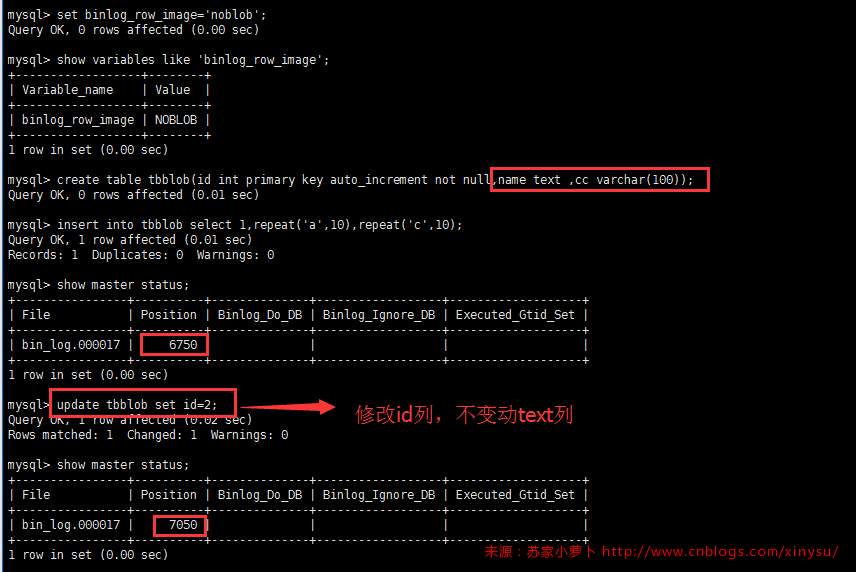
3.2.3 binlog_row_image设置
默认 full,可选full,minimal,noblob
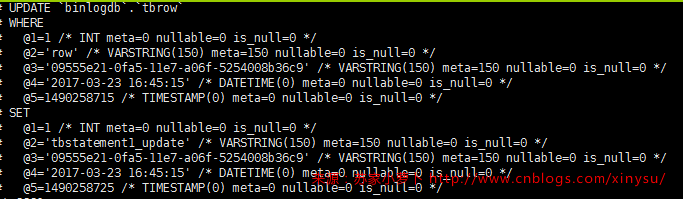
- full的结果可看上文的所有截图,update的时候,set是全部列的新纪录,where是全部的旧记录;
- noblob
- minimal
小结
- 设置为full,则update语句的set部分是新纪录内容,delete及update语句的where部分是全部旧记录内容
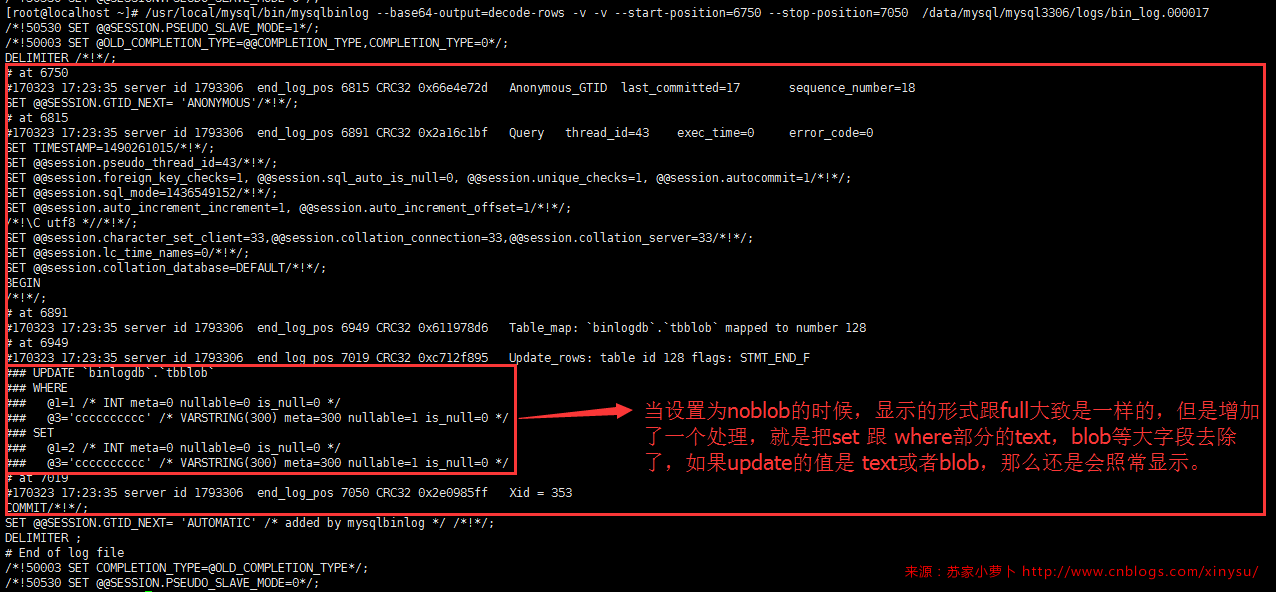
- 设置为noblob,则update语句的set部分是新纪录内容,delete及update语句的where部分是全部旧记录内容,但是,如果如果修改的列不是blob或者text字段,则set部分不会出现blob及text字段;where条件中无论涉不涉及,都不会出现;
- 这个截图表格有3列,( id int,name text, description varchar(50)),只update id为2,binlog记录如下:

- 设置为minimal ,则update语句的set部分只有修改的列内容,delete及update语句的where部分是主键或者唯一索引,如果都没有,才会使整行旧记录。
- 这个截图中,有5列,主键是id,第5列是根据行变动记录时间,update第二列的值,第5列值自动更新,binlog记录如下:
3.3 binlog_format=mixed
理解完statement跟row模式后,mixed混合模式就好理解了。
mixed模式下,大多数情况下,是以statement格式记录binlog日志,当隔离级别为RC模式的时候,则修改为row模式记录,以下几个形式,也是以row模式记录:
- When a function contains
UUID(). - When one or more tables with
AUTO_INCREMENTcolumns are updated and a trigger or stored function is invoked. Like all other unsafe statements, this generates a warning ifbinlog_format = STATEMENT - When the body of a view requires row-based replication, the statement creating the view also uses it. For example, this occurs when the statement creating a view uses the
UUID()function. - When a call to a UDF is involved.
- If a statement is logged by row and the session that executed the statement has any temporary tables, logging by row is used for all subsequent statements (except for those accessing temporary tables) until all temporary tables in use by that session are dropped
- This is true whether or not any temporary tables are actually logged.
- Temporary tables cannot be logged using row-based format; thus, once row-based logging is used, all subsequent statements using that table are unsafe. The server approximates this condition by treating all statements executed during the session as unsafe until the session no longer holds any temporary tables.
- When
FOUND_ROWS()orROW_COUNT()is used. (Bug #12092, Bug #30244) - When
USER(),CURRENT_USER(), orCURRENT_USERis used. (Bug #28086) - When a statement refers to one or more system variables. (Bug #31168)
不如做一个小小的总结,如下图:
4 binlog server的搭建
binlog server拿来干嘛?其实是一个实时备份binlog的配置,假设你有一台DB服务器的数据一致性及安全性非常高,你的备份策略可能是每周全备一次,每日差异备份一次,那么假设出现主从故障,需要使用备份来恢复,那么你可能丢失的数据最多可以达到一天。这个时候,其实可以搭建一个binlog server,来实时保存binlog文件在备份服务器上,它实时同步binlog文件内容,也就是当你发生宕机事故时,你可以通过备份文件+binlog server中的内容来恢复
- 搭建binlog
- 选定一台服务器,用来当做一个binlog server服务器
- 服务器上配置同个版本mysql
- 同一个binlog server 可以同步多台数据库实例的binlog文件
- 建立每个实例对应的文件夹,cd 文件夹,进入文件夹
- /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqlbinlog -R --raw --host=192.168.9.111 --port=3330 --user='repl' --password='replasslave' --stop-never --stop-never-slave-server-id=1113330 --start-position=14981 bin_log.000045
- /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqlbinlog -R --raw --host=192.168.9.112 --port=3310 --user='repl' --password='replasslave' --stop-never --stop-never-slave-server-id=1443310 --start-position=154 bin_log.000044
5 Tips
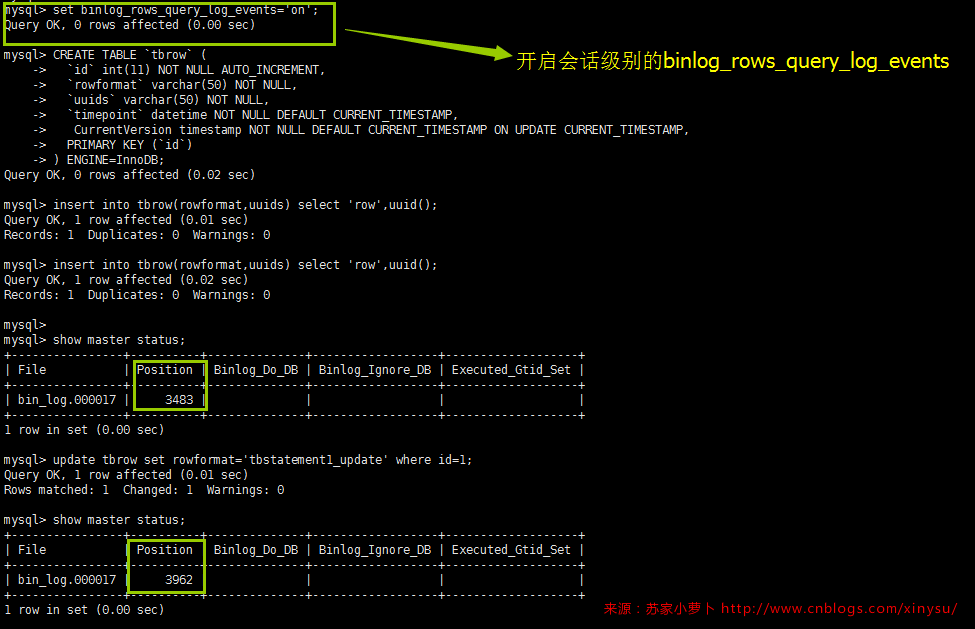
5.1 修改会话级别的binlog格式
一般情况下,我们不随意修改数据库级别的binlog格式,因为有可能会对程序不兼容。但是当人为导数的时候,比如insert into tb select * from .. 涉及100万行记录的时候,如果binlog_formant为row格式,那么产生的binlog文件将非常大,而且再传给从库落地为relay log也很大,这占用了一定量的IO资源,这个时候,可以在操作之前,先修改当前会话级别为 set binlog_formant='statement'; 再执行insert into tb select * from ..,那么它就仅记录这单条SQL,会话级别的binlog_format修改,不会影响整体的同步情况。
5.2 查看binlog中每个事务的开始跟结束
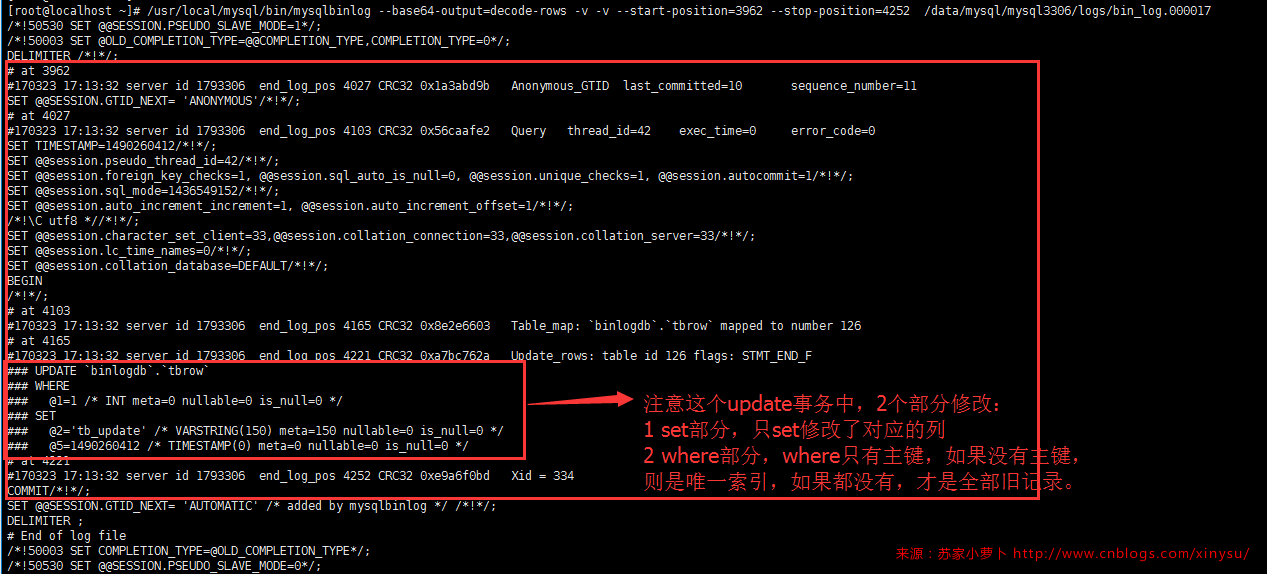
详细看上面的截图就会发现,都给大家把一个个事务画上了框框,细心可以发现,每个事务都会有一个last_committed,如下图。
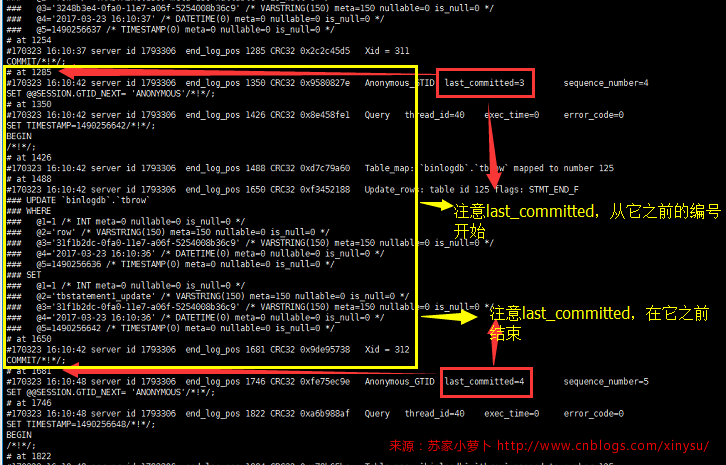
则可以发现这个update事务从1285开始,1681结束,通过/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqlbinlog --base64-output=decode-rows -v -v --start-position=1285 --stop-position=1681 /data/mysql/mysql3306/logs/bin_log.000017,可以正常读取这个事务。
但是假如结尾的position读错,读成1650,那么,会发生什么情况呢?
由于读出来的事务属于没有提交的事务,那么mysqlbinlog则会认为这个事务需要回滚,添加rollback语句,并提示这个rollbac是由mysqlbinlog自身添加的。
/usr/local/mysql/bin/mysqlbinlog --base64-output=decode-rows -v -v --start-position=1285 --stop-position=1650 /data/mysql/mysql3306/logs/bin_log.000017
5.3 根据binlog格式恢复数据(row格式)
通过mysqlbinlog正常读取行记录内容,按照一个事务一个事务来反推旧记录,insert的操作修改为delete,delete的修改为insert,update的set跟where兑换位置。
目前有不少python脚本可以用,本人也在试写中,大家感兴趣可以搜索下。
5.4 binlog文件清理(20170328修改)
- expire_logs_days+flush logs
-
- 设置expire_logs_days,假设当前binlog文件过多且大占用磁盘空间,可以修改小改参数,改参数只有在切换新的binlog文件时,才会删除过期文件,也就是可以等数据库把当前binlog写满后切换到新文件的时候删除,也可以手动执行flush logs,手动切换binlog,同时会触发对过期binlog文件的删除。注意从库的同步情况来设置。
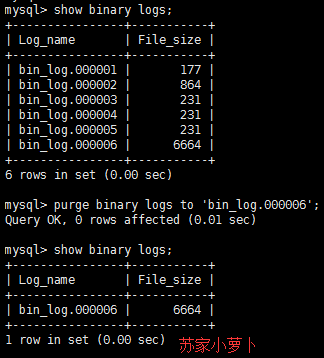
- purge binary logs to 'xxxx'
- 清理 'xxxx' 之前的 binary log文件,只保留 'xxxx' 之后的binary log文件
- 但是使用这个指令的时候,要注意主从同步情况,如果在主库执行,一定要去从库 SHOW SLAVE STATUS,看下当前同步到哪个binlog文件,防止清理报错
5.5 与binlog相关的指令
查看当前binlog文件情况:show binary logs;
查看当前使用的binlog文件及position:show master status;(复制随处可见到使用)
查看某个文件中的binlog事件:show binlog events in 'bin_log.000003';
重置所有binlog文件,会删除所有binlog文件哦,谨慎使用:reset master;
参考文档:
如果转载,请注明博文来源: www.cnblogs.com/xinysu/ ,版权归 博客园 苏家小萝卜 所有。望各位支持!
分类:
MySQL




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· 分享一个免费、快速、无限量使用的满血 DeepSeek R1 模型,支持深度思考和联网搜索!
· 使用C#创建一个MCP客户端
· 基于 Docker 搭建 FRP 内网穿透开源项目(很简单哒)
· ollama系列1:轻松3步本地部署deepseek,普通电脑可用
· 按钮权限的设计及实现