逻辑设计, 顾名思义, 只要理清了 逻辑 和 时序, 剩下的设计只是做填空题而已。
下面给出了有限状态机的标准设计,分别为 VHDL 和 Verilog 代码
1 有限状态机
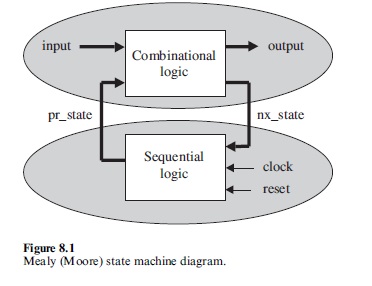
2 VHDL模板一
library IEEE; use ieee.std_logic_1164.all; --! 1) 端口定义 entity <entity_name> is port ( DIN : in <data_type>; RST : in std_logic; CLK : in std_logic; DOUT : out <data_type> ); end <entity_name>; --! 2) 状态定义 architecture <arch_name> of <entity_name> is type state is (IDLE, ST1, ST2, ...); signal c_state, n_state : state; begin --! 3) 时序逻辑 pfsmsyn: process (rst, clk) begin if (rst = '1') then c_state <= IDLE; elsif (clk'event and clk='1') then c_state <= n_state; endif; end process; --! 4) 组合逻辑 pfsmlogic: process (din, c_state) begin case c_state is when IDLE => if (din = ...) then dout <= <value>; -- 输出 c_state <= state1; -- 状态 else ... end if; when ST1 => ... ... ... ... ... ... when others => ... ... end case; end process; end <arch_name>;
3 Verilog模板一
// 1) 端口声明 module fsm(clk, rst, ctrl, dout); input clk, rst, ctrl; output [n-1:0] dout; // n 取决于输出值的位数 reg [n-1:0] dout; // 2) 状态定义 parameter IDLE = 0, ST1 = 1, ST2 = 2, ST3 = 3, ....; reg [m-1:0] c_state, n_state; // m 取决于‘“状态”数量的位数 // 3) 时序逻辑 always @ (posedge clk or posedge rst) begin: SEQ if (rst) c_state = IDLE; else c_state = n_state; end // 4) 组合逻辑 module @ (ctrl or c_state) begin: COMB case (c_state) IDLE: begin dout = <value0>; n_state = ST1; end ST1: begin dout = <value1>; n_state = ST2; end ST2: . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . endcase end endmodule
参考资料:
<Circuit Design with VHDL> chapter 8 State Machines
<HDL Chip Design>
原文链接: http://www.cnblogs.com/xinxue/
专注于机器视觉、OpenCV、C++ 编程



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号