透视 n 点问题,简称 PnP,源自相机标定,是计算机视觉的经典问题,广泛应用在机器人定位、SLAM、AR/VR、摄影测量等领域
1 PnP 问题
1.1 定义
已知:相机的内参和畸变系数;世界坐标系中,n 个空间点坐标,以及投影在像平面上的像素坐标
求解:相机在世界坐标系下的位姿 R 和 t,即 {W} 到 {C} 的变换矩阵 $\;^w_c\bm{T} $,如下图:
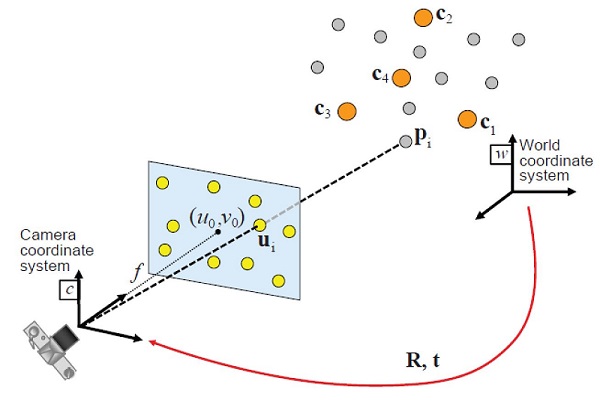
世界坐标系中的 3d 空间点,与投影到像平面的 2d 像素点,两者之间的关系为:
$\quad s \begin{bmatrix} u \\ v \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} f_x & 0 & c_x \\ 0 & f_y & c_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} r_{11} & r_{12} & r_{13} & t_1 \\ r_{21} & r_{22} & r_{23} & t_2 \\ r_{31} & r_{32} & r_{33} & t_3 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} X_w \\ Y_w \\ Z_w\\ 1 \end{bmatrix} $
1.2 分类
根据给定空间点的数量,可将 PnP 问题分为两类:
第一类 3≤n≤5,选取的空间点较少,可通过联立方程组的方式求解,精度易受图像噪声影响,鲁棒性较差
第二类 n≥6,选取的空间点较多,可转化为求解超定方程的问题,一般侧重于鲁棒性和实时性的平衡
2 求解方法
2.1 DLT 法
2.1.1 转化为 Ax=0
令 $P = K\;[R\;\, t]$,$K$ 为相机内参矩阵,则 PnP 问题可简化为:已知 n 组 3d-2d 对应点,求解 $P_{3\times4}$
DLT (Direct Linear Transformation,直接线性变换),便是直接利用这 n 组对应点,构建线性方程组来求解
$\quad s \begin{bmatrix} u \\ v \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} p_{11} & p_{12} & p_{13} & p_{14} \\ p_{21} & p_{22} & p_{23} & p_{23} \\ p_{31} & p_{32} & p_{33} & p_{33} \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} X_w \\ Y_w \\ Z_w\\ 1 \end{bmatrix} $
简化符号 $X_w, Y_w, Z_w$ 为 $X, Y, Z$,展开得:
$\quad \begin{equation} \begin{cases} su= p_{11}X + p_{12}Y + p_{13}Z + p_{14}\\ \\sv=p_{21}X + p_{22}Y + p_{23}Z + p_{24} \\ \\s\;=p_{31}X + p_{32}Y + p_{33}Z + p_{34} \end{cases}\end{equation} \;\bm{=>} \; \begin{cases} Xp_{11} + Yp_{12} + Zp_{13} + p_{14} - uXp_{31} - uYp_{32} - uZp_{33} - up_{34} = 0 \\ \\ Xp_{21} + Yp_{22} + Zp_{23} + p_{24} - vXp_{31} - vYp_{32} - vZp_{33} - vp_{34} = 0 \end{cases}$
未知数有 11 个 ($p_{34}$可约掉),则至少需要 6 组对应点,写成矩阵形式如下:
$\quad \begin{bmatrix} X_1&Y_1&Z_1&1 &0&0&0&0&-u_1X_1&-u_1Y_1&-u_1Z_1&-u_1 \\ 0&0&0&0& X_1&Y_1&Z_1&1&-v_1X_1&-v_1Y_1&-v_1Z_1&-v_1 \\ \vdots &\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots \\ \vdots &\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots&\vdots\\ X_n&Y_n&Z_n&1 &0&0&0&0&-u_nX_n&-u_nY_1&-u_nZ_n&-u_n \\ 0&0&0&0& X_n&Y_n&Z_n&1&-v_nX_n&-v_nY_n&-v_nZ_n&-v_n\end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix}p_{11}\\p_{12}\\p_{13}\\p_{14}\\ \vdots\\p_{32}\\p_{33}\\p_{34}\end{bmatrix}=\begin{bmatrix}0\\ \vdots\\ \vdots\\0\end{bmatrix}$
因此,求解 $P_{3\times4}$ 便转化成了 $Ax=0$ 的问题
2.1.2 SVD 求 R t
给定相机内参矩阵,则有 $K \begin{bmatrix} R & t \end{bmatrix} = \lambda \begin{bmatrix} p_1 & p_2 &p_3&p_4 \end{bmatrix}$
考虑 $\lambda$ 符号无关,得 $\lambda R = K^{-1}\begin{bmatrix} p_1 & p_2&p_3 \end{bmatrix}$
SVD 分解 $K^{-1}\begin{bmatrix} p_1&p_2&p_3\end{bmatrix}=\bm{U}\begin{bmatrix}d_{11} && \\ &d_{22}&\\&&&d_{33}\end{bmatrix} \bm{V^T}$
$\quad=> \lambda \approx d_{11}$ 和 $\begin{cases}\bm{R=UV^T} \\ \bm{t=\dfrac{K^{-1}p_4}{d_{11}}} \end{cases}$
2.2 P3P 法
当 n=3 时,PnP 即为 P3P,它有 4 个可能的解,求解方法是 余弦定理 + 向量点积
2.2.1 余弦定理
根据投影几何的消隐点和消隐线,构建 3d-2d 之间的几何关系,如下:
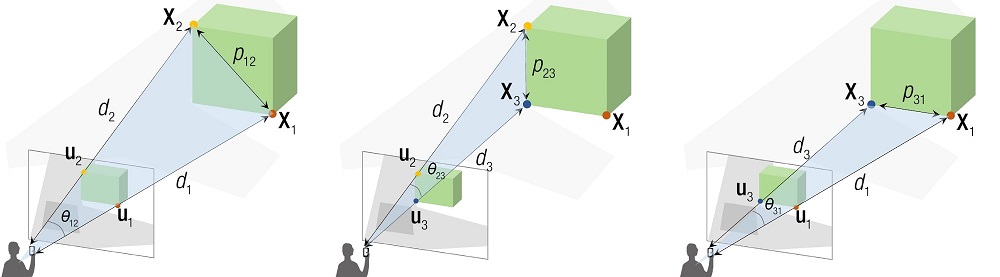
根据余弦定理,则有
$\begin{cases} d_1^2 + d_2^2 - 2d_1d_2\cos\theta_{12} = p_{12}^2 \\ \\ d_2^2 + d_3^2 - 2d_2d_3\cos\theta_{23} = p_{23}^2 \\ \\ d_3^2 + d_1^2 + 2d_3d_2\cos\theta_23 = p_{31}^2 \end{cases}$
只有 $d_1,\, d_2,\,d_3$ 是未知数,求解方程组即可
其中,有个关键的隐含点:给定相机内参,以及 3d-2d 的投影关系,则消隐线之间的夹角 $\theta_{12}\; \theta_{23}\; \theta_{31}$ 是可计算得出的
2.2.2 向量点积
相机坐标系中,原点即为消隐点,原点到 3d-2d 的连线即为消隐线,如图所示:
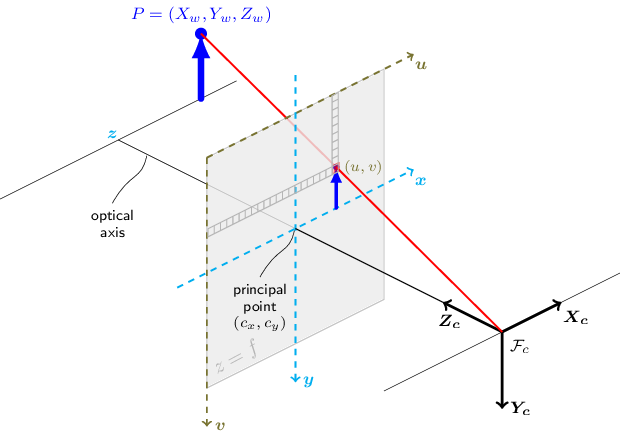

如果知道 3d点 投影到像平面的 2d点,在相机坐标系中的坐标 $U_1,\,U_2,\,U_3$,则 $\cos\theta_{23}= \dfrac {\overrightarrow{OU_2}\cdot \overrightarrow{OU_3}} {||\overrightarrow{OU_2}||\;||\overrightarrow{OU_3}||} $
具体到运算,可视为 世界坐标系 {W} 和 相机坐标系 {C} 重合,且 $Z = f$,则有
$\quad \begin{bmatrix} R & t \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} 1 &0&0&0 \\ 0&1&0&0 \\ 0&0&1&0 \end{bmatrix} =>$ $\; s \begin{bmatrix} u \\ v \\ 1 \end{bmatrix} = \begin{bmatrix} f_x & 0 & c_x \\ 0 & f_y & c_y \\ 0 & 0 & 1 \end{bmatrix} \begin{bmatrix} X_c \\ Y_c \\ Z_c \end{bmatrix} $
$K^{-1}$ 可用增广矩阵求得,且 $Z_c = f$,则有
$\quad \begin{bmatrix} X_c \\Y_c\\f \end{bmatrix} = s K^{-1}\begin{bmatrix} u\\v\\1 \end{bmatrix}$
记 $\vec u = \begin{bmatrix} X_c \\ Y_c \\ Z_c \end{bmatrix}$,则 $\cos\theta_{12}=\dfrac{(K^{-1}\vec{u_1})^T (K^{-1}\vec{u_2})}{||K^{-1}\vec{u_1}||\,||K^{-1}\vec{u_2}||}$,以此类推 $\cos\theta_{23}$ 和 $\cos\theta_{31}$
3 OpenCV 函数
OpenCV 中解 PnP 的方法有 9 种,目前实现了 7 种,还有 2 种未实现,对应论文如下:
- SOLVEPNP_P3P Complete Solution Classification for the Perspective-Three-Point Problem
- SOLVEPNP_AP3P An Efficient Algebraic Solution to the Perspective-Three-Point Problem
- SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE 基于 L-M 最优化方法,求解重投影误差最小的位姿
- SOLVEPNP_EPNP EPnP: An Accurate O(n) Solution to the PnP Problem
- SOLVEPNP_SQPNP A Consistently Fast and Globally Optimal Solution to the Perspective-n-Point Problem
- SOLVEPNP_IPPE Infinitesimal Plane-based Pose Estimation 输入的 3D 点需要共面且 n ≥ 4
- SOLVEPNP_IPPE_SQUARE SOLVEPNP_IPPE 的一种特殊情况,要求输入 4 个共面点的坐标,并且按照特定的顺序排列
- SOLVEPNP_DLS (未实现) A Direct Least-Squares (DLS) Method for PnP 实际调用 SOLVEPNP_EPNP
- SOLVEPNP_UPLP (未实现) Exhaustive Linearization for Robust Camera Pose and Focal Length Estimation 实际调用 SOLVEPNP_EPNP
3.1 solveP3P()
solveP3P() 的输入是 3 组 3d-2d 对应点,定义如下:
// P3P has up to 4 solutions, and the solutions are sorted by reprojection errors(lowest to highest).
int solveP3P (
InputArray objectPoints, // object points, 3x3 1-channel or 1x3/3x1 3-channel. vector<Point3f> can be also passed
InputArray imagePoints, // corresponding image points, 3x2 1-channel or 1x3/3x1 2-channel. vector<Point2f> can be also passed
InputArray cameraMatrix, // camera intrinsic matrix
InputArray distCoeffs, // distortion coefficients.If NULL/empty, the zero distortion coefficients are assumed.
OutputArrayOfArrays rvecs, // rotation vectors
OutputArrayOfArrays tvecs, // translation vectors
int flags // solving method
);
3.2 solvePnP() 和 solvePnPGeneric()
solvePnP() 实际上调用的是 solvePnPGeneric(),内部实现如下:
bool solvePnP(InputArray opoints, InputArray ipoints, InputArray cameraMatrix, InputArray distCoeffs, OutputArray rvec, OutputArray tvec, bool useExtrinsicGuess, int flags)
{
CV_INSTRUMENT_REGION();
vector<Mat> rvecs, tvecs;
int solutions = solvePnPGeneric(opoints, ipoints, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, rvecs, tvecs, useExtrinsicGuess, (SolvePnPMethod)flags, rvec, tvec);
if (solutions > 0)
{
int rdepth = rvec.empty() ? CV_64F : rvec.depth();
int tdepth = tvec.empty() ? CV_64F : tvec.depth();
rvecs[0].convertTo(rvec, rdepth);
tvecs[0].convertTo(tvec, tdepth);
}
return solutions > 0;
}
solvePnPGeneric() 除了求解相机位姿外,还可得到重投影误差,其定义如下:
bool solvePnPGeneric (
InputArray objectPoints, // object points, Nx3 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, N is the number of points. vector<Point3d> can be also passed
InputArray imagePoints, // corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, N is the number of points. vector<Point2d> can be also passed
InputArray cameraMatrix, // camera intrinsic matrix
InputArray distCoeffs, // distortion coefficients
OutputArrayOfArrays rvec, // rotation vector
OutputArrayOfArrays tvec, // translation vector
bool useExtrinsicGuess = false, // used for SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE. If true, use the provided rvec and tvec as initial approximations, and further optimize them.
SolvePnPMethod flags = SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE, // solving method
InputArray rvec = noArray(), // initial rotation vector when using SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE and useExtrinsicGuess is set to true
InputArray tvec = noArray(), // initial translation vector when using SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE and useExtrinsicGuess is set to true
OutputArray reprojectionError = noArray() // optional vector of reprojection error, that is the RMS error
);
3.3 solvePnPRansac()
solvePnP() 的一个缺点是鲁棒性不强,对异常点敏感,这在相机标定中问题不大,因为标定板的图案已知,并且特征提取较为稳定
然而,当相机拍摄实际物体时,因为特征难以稳定提取,会出现一些异常点,导致位姿估计的不准,因此,需要一种处理异常点的方法
RANSAC 便是一种高效剔除异常点的方法,对应 solvePnPRansac(),它是一个重载函数,共有 2 种参数形式,第 1 种形式如下:
bool solvePnPRansac (
InputArray objectPoints, // object points, Nx3 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, N is the number of points. vector<Point3d> can be also passed
InputArray imagePoints, // corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel, N is the number of points. vector<Point2d> can be also passed
InputArray cameraMatrix, // camera intrinsic matrix
InputArray distCoeffs, // distortion coefficients
OutputArray rvec, // rotation vector
OutputArray tvec, // translation vector
bool useExtrinsicGuess = false, // used for SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE. If true, use the provided rvec and tvec as initial approximations, and further optimize them.
int iterationsCount = 100, // number of iterations
float reprojectionError = 8.0, // inlier threshold value. It is the maximum allowed distance between the observed and computed point projections to consider it an inlier
double confidence = 0.99, // the probability that the algorithm produces a useful result
OutputArray inliers = noArray(), // output vector that contains indices of inliers in objectPoints and imagePoints
int flags = SOLVEPNP_ITERATIVE // solving method
);
3.4 solvePnPRefineLM() 和 solvePnPRefineVVS()
OpenCV 中还有 2 个位姿细化函数:通过迭代不断减小重投影误差,从而求得最佳位姿,solvePnPRefineLM() 使用 L-M 算法,solvePnPRefineVVS() 则用虚拟视觉伺服 (Virtual Visual Servoing)
solvePnPRefineLM() 的定义如下:
void solvePnPRefineLM (
InputArray objectPoints, // object points, Nx3 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 3-channel, N is the number of points
InputArray imagePoints, // corresponding image points, Nx2 1-channel or 1xN/Nx1 2-channel
InputArray cameraMatrix, // camera intrinsic matrix
InputArray distCoeffs, // distortion coefficients
InputOutputArray rvec, // input/output rotation vector
InputOutputArray tvec, // input/output translation vector
TermCriteria criteria = TermCriteria(TermCriteria::EPS+TermCriteria::COUNT, 20, FLT_EPSILON) // Criteria when to stop the LM iterative algorithm
);
4 应用实例
4.1 位姿估计 (静态+标定板)
当手持标定板旋转不同角度时,利用相机内参 + solvePnP(),便可求出相机相对标定板的位姿
#include "opencv2/imgproc.hpp"
#include "opencv2/highgui.hpp"
#include "opencv2/calib3d.hpp"
using namespace std;
using namespace cv;
Size kPatternSize = Size(9, 6);
float kSquareSize = 0.025;
// camera intrinsic parameters and distortion coefficient
const Mat cameraMatrix = (Mat_<double>(3, 3) << 5.3591573396163199e+02, 0.0, 3.4228315473308373e+02,
0.0, 5.3591573396163199e+02, 2.3557082909788173e+02,
0.0, 0.0, 1.0);
const Mat distCoeffs = (Mat_<double>(5, 1) << -2.6637260909660682e-01, -3.8588898922304653e-02, 1.7831947042852964e-03,
-2.8122100441115472e-04, 2.3839153080878486e-01);
int main()
{
// 1) read image
Mat src = imread("left07.jpg");
if (src.empty())
return -1;
// prepare for subpixel corner
Mat src_gray;
cvtColor(src, src_gray, COLOR_BGR2GRAY);
// 2) find chessboard corners and subpixel refining
vector<Point2f> corners;
bool patternfound = findChessboardCorners(src, kPatternSize, corners);
if (patternfound) {
cornerSubPix(src_gray, corners, Size(11, 11), Size(-1, -1), TermCriteria(TermCriteria::EPS + TermCriteria::MAX_ITER, 30, 0.1));
}
else {
return -1;
}
// 3) object coordinates
vector<Point3f> objectPoints;
for (int i = 0; i < kPatternSize.height; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < kPatternSize.width; j++)
{
objectPoints.push_back(Point3f(float(j * kSquareSize), float(i * kSquareSize), 0));
}
}
// 4) Rotation and Translation vectors
Mat rvec, tvec;
solvePnP(objectPoints, corners, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, rvec, tvec);
// 5) project estimated pose on the image
drawFrameAxes(src, cameraMatrix, distCoeffs, rvec, tvec, 2*kSquareSize);
imshow("Pose estimation", src);
waitKey();
}
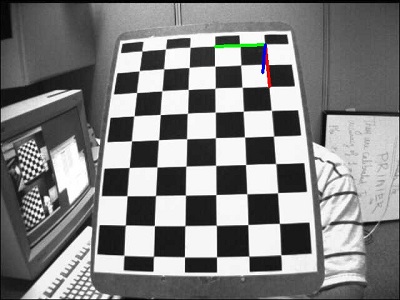
当标定板旋转不同角度时,相机所对应的位姿如下:



4.2 位姿估计 (实时+任意物)
OpenCV 中有一个实时目标跟踪例程,位于 "opencv\samples\cpp\tutorial_code\calib3d\real_time_pose_estimation" 中,实现步骤如下:
1) 读取目标的三维模型和网格 -> 2) 获取视频流 -> 3) ORB 特征检测 -> 4) 3d-2d 特征匹配 -> 5) 相机位姿估计 -> 6) 卡尔曼滤波
例程中设计了一个 PnPProblem 类来实现位姿估计,其中 2 个重要的函数 estimatePoseRANSAC() 和 backproject3DPoint() 定义如下:
class PnPProblem
{
public:
explicit PnPProblem(const double param[]); // custom constructor
virtual ~PnPProblem();
cv::Point2f backproject3DPoint(const cv::Point3f& point3d);
void estimatePoseRANSAC(const std::vector<cv::Point3f>& list_points3d, const std::vector<cv::Point2f>& list_points2d,
int flags, cv::Mat& inliers, int iterationsCount, float reprojectionError, double confidence);
// ...
}
// Custom constructor given the intrinsic camera parameters
PnPProblem::PnPProblem(const double params[])
{
// intrinsic camera parameters
_A_matrix = cv::Mat::zeros(3, 3, CV_64FC1);
_A_matrix.at<double>(0, 0) = params[0]; // [ fx 0 cx ]
_A_matrix.at<double>(1, 1) = params[1]; // [ 0 fy cy ]
_A_matrix.at<double>(0, 2) = params[2]; // [ 0 0 1 ]
_A_matrix.at<double>(1, 2) = params[3];
_A_matrix.at<double>(2, 2) = 1;
// rotation matrix, translation matrix, rotation-translation matrix
_R_matrix = cv::Mat::zeros(3, 3, CV_64FC1);
_t_matrix = cv::Mat::zeros(3, 1, CV_64FC1);
_P_matrix = cv::Mat::zeros(3, 4, CV_64FC1);
}
// Estimate the pose given a list of 2D/3D correspondences with RANSAC and the method to use
void PnPProblem::estimatePoseRANSAC (
const std::vector<Point3f>& list_points3d, // list with model 3D coordinates
const std::vector<Point2f>& list_points2d, // list with scene 2D coordinates
int flags, Mat& inliers, int iterationsCount, // PnP method; inliers container
float reprojectionError, float confidence) // RANSAC parameters
{
// distortion coefficients, rotation vector and translation vector
Mat distCoeffs = Mat::zeros(4, 1, CV_64FC1);
Mat rvec = Mat::zeros(3, 1, CV_64FC1);
Mat tvec = Mat::zeros(3, 1, CV_64FC1);
// no initial approximations
bool useExtrinsicGuess = false;
// PnP + RANSAC
solvePnPRansac(list_points3d, list_points2d, _A_matrix, distCoeffs, rvec, tvec, useExtrinsicGuess, iterationsCount, reprojectionError, confidence, inliers, flags);
// converts Rotation Vector to Matrix
Rodrigues(rvec, _R_matrix);
_t_matrix = tvec; // set translation matrix
this->set_P_matrix(_R_matrix, _t_matrix); // set rotation-translation matrix
}
// Backproject a 3D point to 2D using the estimated pose parameters
cv::Point2f PnPProblem::backproject3DPoint(const cv::Point3f& point3d)
{
// 3D point vector [x y z 1]'
cv::Mat point3d_vec = cv::Mat(4, 1, CV_64FC1);
point3d_vec.at<double>(0) = point3d.x;
point3d_vec.at<double>(1) = point3d.y;
point3d_vec.at<double>(2) = point3d.z;
point3d_vec.at<double>(3) = 1;
// 2D point vector [u v 1]'
cv::Mat point2d_vec = cv::Mat(4, 1, CV_64FC1);
point2d_vec = _A_matrix * _P_matrix * point3d_vec;
// Normalization of [u v]'
cv::Point2f point2d;
point2d.x = (float)(point2d_vec.at<double>(0) / point2d_vec.at<double>(2));
point2d.y = (float)(point2d_vec.at<double>(1) / point2d_vec.at<double>(2));
return point2d;
}
PnPProblem 类的调用如下:实例化 -> estimatePoseRansac() 估计位姿 -> backproject3DPoint() 画出位姿
// Intrinsic camera parameters: UVC WEBCAM
double f = 55; // focal length in mm
double sx = 22.3, sy = 14.9; // sensor size
double width = 640, height = 480; // image size
double params_WEBCAM[] = { width * f / sx, // fx
height * f / sy, // fy
width / 2, // cx
height / 2 }; // cy
// instantiate PnPProblem class
PnPProblem pnp_detection(params_WEBCAM);
// RANSAC parameters
int iterCount = 500; // number of Ransac iterations.
float reprojectionError = 2.0; // maximum allowed distance to consider it an inlier.
float confidence = 0.95; // RANSAC successful confidence.
// OpenCV requires solvePnPRANSAC to minimally have 4 set of points
if (good_matches.size() >= 4)
{
// -- Step 3: Estimate the pose using RANSAC approach
pnp_detection.estimatePoseRANSAC(list_points3d_model_match, list_points2d_scene_match,
pnpMethod, inliers_idx, iterCount, reprojectionError, confidence);
// ... ..
}
// ... ...
float fp = 5;
vector<Point2f> pose2d;
pose2d.push_back(pnp_detect_est.backproject3DPoint(Point3f(0, 0, 0))); // axis center
pose2d.push_back(pnp_detect_est.backproject3DPoint(Point3f(fp, 0, 0))); // axis x
pose2d.push_back(pnp_detect_est.backproject3DPoint(Point3f(0, fp, 0))); // axis y
pose2d.push_back(pnp_detect_est.backproject3DPoint(Point3f(0, 0, fp))); // axis z
draw3DCoordinateAxes(frame_vis, pose2d); // draw axes
// ... ...
实时目标跟踪的效果如下:

参考资料
OpenCV-Python Tutorials / Camera Calibration and 3D Reconstruction / Pose Estimation
OpenCV Tutorials / Camera calibration and 3D reconstruction (calib3d module) / Real time pose estimation of a textured object
Perspective-n-Point, Hyun Soo Park
原文链接: http://www.cnblogs.com/xinxue/
专注于机器视觉、OpenCV、C++ 编程


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号