Spark核心编程模型之RDD(二)
承接上一篇,key-value类型RDD
ShuffleRDD
上篇文章里讲到,combineByKey有参数支持设置分区器,它返回的结果就是ShuffleRDD,对于shuffle过程,父RDD会先对map计算的结果聚合(mapSideCombine参数默认为true,会进行聚合),然后按照分区器对结果进行分区,中间数据会以文件的形式写入磁盘,reduce端就会对已经分区好的中间数据进行读数据然后聚合
这些特点都没理解。。。。

记住aggregateByKey和reduceByKey,foldByKey,groupByKey都基于combineByKey实现的,只是参数函数不同而已,其中distinct是用reduceByKey实现的,groupBy是用groupByKey实现
其他的看代码
import org.apache.spark.serializer.JavaSerializer
import org.apache.spark.{HashPartitioner, SparkConf, SparkContext}
import scala.collection.mutable.ArrayBuffer
import scala.reflect.ClassTag
val pairRDD = sc.parallelize[(Int, Int)](Seq((1, 2), (3, 4), (3, 6), (5, 6)), 2)
// 指定初始值 累加 统计次数,多元操作
pairRDD.aggregateByKey((0, 0))( // createCombiner = mergeValue((0, 0), v)
(acc: (Int, Int), v) => (acc._1 + v, acc._2 + 1), //mergeValue
(acc1: (Int, Int), acc2: (Int, Int)) => (acc1._1 + acc2._1, acc1._2 + acc2._2) // mergeCombiners
).collect()
// 效果和下面的是一样的
def createCombinerAggregate = (value: Int) => mergeValueAggregate((0, 0), value)
def mergeValueAggregate = (acc: (Int, Int), v: Int) => (acc._1 + v, acc._2 + 1)
def mergeCombinersAggregate = (acc1: (Int, Int), acc2: (Int, Int)) =>
(acc1._1 + acc2._1, acc1._2 + acc2._2)
pairRDD.combineByKey(createCombinerAggregate,
mergeValueAggregate, mergeCombinersAggregate).collect()
// createCombiner = (v: V) => v
// mergeValue = (x, y) => x + y
// mergeCombiners = (x, y) => x + y
// 基于key 对值累加
pairRDD.reduceByKey((x, y) => x + y).collect()
//效果和下面的是一样的
def createCombinerReduce = (value: Int) => value
def mergeValueReduce = (v: Int, value: Int) => v + value
def mergeCombinersReduce = (v: Int, value: Int) => v + value
pairRDD.combineByKey(createCombinerReduce, mergeValueReduce, mergeCombinersReduce).collect()
// createCombiner = (v: V) => mergeValue(0, v)
// mergeValue = (x, y) => x + y
// mergeCombiners = (x, y) => x + y
// 和reduceByKey效果差不多,只是给定了累加的起始值
pairRDD.foldByKey(0)((x, y) => x + y).collect()
//效果和下面的是一样的
def createCombinerFold = (value: Int) => mergeValueFold(0, value)
def mergeValueFold = (v: Int, value: Int) => v + value
def mergeCombinersFold = (v: Int, value: Int) => v + value
pairRDD.combineByKey(createCombinerFold, mergeValueFold, mergeCombinersFold).collect()
//createCombiner = (v: V) => CompactBuffer(v)
//mergeValue = (buf: CompactBuffer[V], v: V) => buf += v
//mergeCombiners = (c1: CompactBuffer[V], c2: CompactBuffer[V]) => c1 ++= c2
// 基于key相同的 分组
pairRDD.groupByKey().collect()
//效果和下面的是一样的
def createCombinerGroup = (value: Int) => ArrayBuffer(value)
def mergeValueGroup = (buf: ArrayBuffer[Int], value: Int) => buf += value
def mergeCombinersGroup = (buf1: ArrayBuffer[Int], buf2: ArrayBuffer[Int]) => buf1 ++= buf2
pairRDD.combineByKey(createCombinerGroup, mergeValueGroup, mergeCombinersGroup,
new HashPartitioner(2), false).collect()
val rdd = sc.parallelize(Seq(1,2,2,3,1))
val distinctRDD = rdd.distinct() //对rdd数据去重
distinctRDD.collect()
pairRDD.reduceByKeyLocally((x, y) => x + y) //效果和reduceByKey差不多,只是返回值类型 变成了map类型
CombineByKey练习:按key聚合统计值的正负个数
package com.twq.spark.rdd.keyvalue
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/8/19.
*/
object CombineByKeyPractice {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("word count")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val pairStrRDD = sc.parallelize[(String, Double)](Seq(("coffee", 0.6),
("coffee", -0.1), ("panda", -0.3), ("coffee", 0.1)), 2)
def createCombiner = (label: Double) => new BinaryLabelCounter(0L, 0L) += label
def mergeValue = (c: BinaryLabelCounter, label: Double) => c += label
def mergeCombiners = (c1: BinaryLabelCounter, c2: BinaryLabelCounter) => c1 += c2
// 统计相同key对应的所有值中是正数值的个数以及是负数值的个数
//需要的三个参数:
//createCombiner: V => C,
//mergeValue: (C, V) => C,
//mergeCombiners: (C, C) => C
val testCombineByKeyRDD =
pairStrRDD.combineByKey(createCombiner, mergeValue, mergeCombiners)
testCombineByKeyRDD.collect()
}
}
class BinaryLabelCounter(var numPositives: Long = 0L,
var numNegatives: Long = 0L) extends Serializable {
def +=(label: Double): BinaryLabelCounter = {
if (label > 0) numPositives += 1L else numNegatives += 1L
this
}
def +=(other: BinaryLabelCounter): BinaryLabelCounter = {
numPositives += other.numPositives
numNegatives += other.numNegatives
this
}
override def toString: String = s"{numPos: $numPositives, numNeg: $numNegatives}"
}
reduceByKey和foldByKey的区别
//1 rdd action api reduce and fold
val emptyRdd = sc.emptyRDD[Int]
emptyRdd.reduce(_ + _) // 如果空的rdd reduce会报错
//java.lang.UnsupportedOperationException: empty collection
// at org.apache.spark.rdd.RDD$$anonfun$reduce$1$$anonfun$apply$36.apply(RDD.scala:1027)
emptyRdd.fold(0)(_ + _) // res1: Int = 0 而fold在计算空RDD不会报错
val testRdds = sc.parallelize(Seq(ArrayBuffer(0, 1, 3), ArrayBuffer(2, 4, 5)))
// fold由于要指定初始值的特点,在下面的这种场景非常合适: 可变数组 ++ ++=
// 会产生很多的中间临时对象 因为ArrayBuffer ++ ArrayBuffer会创建一个新的ArrayBuffer对象
ArrayBuffer(0, 1, 3) ++ ArrayBuffer(0, 1, 3)
testRdds.reduce(_ ++ _)
// ArrayBuffer只初始化一次,每次都是将ArrayBuffer append到之前的ArrayBuffer中,不会产生中间临时对象
ArrayBuffer(0, 1, 3) ++= ArrayBuffer(0, 1, 3)
testRdds.fold(ArrayBuffer.empty[Int])((buff, elem) => buff ++= elem)
//2 key-value rdd transformations api reduceByKey and foldByKey
//空的RDD的行为是一样的
val emptyKeyValueRdd = sc.emptyRDD[(Int, Int)]
emptyKeyValueRdd.reduceByKey(_ + _).collect // key-value的 不会报错
// scala> emptyKeyValueRdd.reduceByKey(_+_).collect
// res2: Array[(Int, Int)] = Array()
emptyKeyValueRdd.foldByKey(0)(_ + _).collect
// 同样适用 可变数组的场景
val testPairRdds = sc.parallelize(Seq(("key1", ArrayBuffer(0, 1, 3)),
("key2", ArrayBuffer(2, 4, 5)), ("key1", ArrayBuffer(2, 1, 3))))
testPairRdds.reduceByKey(_ ++ _).collect()
testPairRdds.foldByKey(ArrayBuffer.empty[Int])((buff, elem) => buff ++= elem).collect()
reduceByKey和groupByKey对比:
reduceByKey默认会在map端汇总的,汇总后可以达到减少网络传输,而GroupByKey则不会在map端汇总,它把所有的map端计算结果shuffle发送到reduce端进行汇总计算
好像这么说reduceByKey性能好,那groupByKey有什么使用场景呢?reduceByKey既然是在map端先汇总,那对于汇总计算场景性能好,比如求和,统计个数,求平均,但是对于不是聚合操作的场景,groupByKey就更适用了,比如对同一key的值进行排序
groupByKey还要注意的地方就是:它会把所有的数据拿到reduce端再计算,如果数据量大,可能会撑爆内存,这种情况,就需要我们重新设计key了
package com.twq.spark.rdd.keyvalue
import org.apache.spark.{HashPartitioner, SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/8/19.
*/
object ReduceAndGroupByKeyCompare {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("word count")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val pairRDD = sc.parallelize(Seq(("a", 1), ("b", 2), ("c", 1), ("a", 2),
("c", 4), ("b", 1), ("a", 1), ("a", 1)), 3)
//结果都是 res1: Array[(String, Int)] = Array((b,3), (a,5), (c,5))
pairRDD.reduceByKey(new HashPartitioner(2), _ + _).collect() //先map端汇总,再shuffle重分区,reduce端再汇总
pairRDD.groupByKey(new HashPartitioner(2)).map(t => (t._1, t._2.sum)).collect() //直接shuffle重分区,再reduce端汇总
//需要对同一个key下的所有value值进行排序
pairRDD.groupByKey().map { case (key, iter) =>
val sortedValues = iter.toArray.sorted
(key, sortedValues)
}.collect()
//对于一个key对应的value有很多数据的话,groupByKey可能发生OOM,可以通过重新设计key来消除这个OOM
}
}
总结:对combineByKey的儿子们进行总结-- aggregateByKey和reduceByKey,foldByKey,groupByKey
- aggregateByKey,多维度统计key对应的数据
- reduceByKey 和 foldByKey 都是针对key统计数据,foldByKey需要指定初始值,因为这个,foldByKey在某些场景会比reduceByKey更好,比如防止空指针异常(这个在非key-value RDD有体现)和GC优化
- reduceByKey和groupByKey,reduceByKey会在map端聚合,主要用于汇总计算,而groupByKey不会在map端聚合,主要用于汇总会排序场景
cogroup 主要 对两个RDD进汇总,主要是把同一key的元素收集到一个元组里
其中groupWith,join,rightOuterJoin,leftOuterJoin,fullOuterJoin都是由cogroup实现
package com.twq.spark.rdd.keyvalue
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/8/19.
*/
object CogroupApiTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("word count")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val pairRDD = sc.parallelize[(Int, Int)](Seq((1, 2), (3, 4), (3, 6), (5, 6)), 4)
val otherRDD = sc.parallelize(Seq((3, 9), (4, 5)))
//res0: Array[(Int, (Iterable[Int], Iterable[Int]))]
// = Array((4,(CompactBuffer(),CompactBuffer(5))), (1,(CompactBuffer(2),CompactBuffer())),
// (5,(CompactBuffer(6),CompactBuffer())), (3,(CompactBuffer(6, 4),CompactBuffer(9))))
pairRDD.cogroup(otherRDD).collect() // 按照键进行汇总,把两个RDD中 key对应的值,分别封装在 两个CompactBuffer对象中
//groupWith是cogroup的别名,效果和cogroup一摸一样
pairRDD.groupWith(otherRDD).collect()
// Array[(Int, (Int, Int))] = Array((3,(4,9)), (3,(6,9)))
pairRDD.join(otherRDD).collect() //相当sql中的inner join, 只有key在两个RDD都有的,才会join,主要对两个RDD key对应的值,随机组合呈现
// Array[(Int, (Int, Option[Int]))]
// = Array((1,(2,None)), (5,(6,None)), (3,(4,Some(9))), (3,(6,Some(9))))
pairRDD.leftOuterJoin(otherRDD).collect() //以左RDD为准所有的展示,右RDD没有的 以None显示
// Array[(Int, (Option[Int], Int))] = Array((4,(None,5)), (3,(Some(4),9)), (3,(Some(6),9)))
pairRDD.rightOuterJoin(otherRDD).collect() //以右RDD为准所有的展示,左RDD没有的 以None显示
// Array[(Int, (Option[Int], Option[Int]))]
// = Array((4,(None,Some(5))), (1,(Some(2),None)), (5,(Some(6),None)),
// (3,(Some(4),Some(9))), (3,(Some(6),Some(9))))
pairRDD.fullOuterJoin(otherRDD).collect()
// 减掉相同的key, 这个示例减掉了为3的key
// Array[(Int, Int)] = Array((1,2), (5,6))
pairRDD.subtractByKey(otherRDD).collect() //理解为取差集,otherRDD有的key 就不返回
}
}
cogroup实现原理:
这里假如RDD1是没有分区器的,而RDD2是有HashPartitioner(2)分区器的
而RDD3=RDD1.cogroup(RDD2),这种场景RDD3分区器也是HashPartitioner(2),由于RDD1没有分区器,所以RDD1 group的时候按照HashPartitioner(2)会发生shuffle重分区,而重分区会尽量保持和RDD2分区情况保持协同,减少已经分区好RDD2的数据进行传输,保证计算的本地性,至于分区器的实现细节,我们可以看下源码
如果cogroup时没传分区器,这里默认使用的是一个defaultPartitioner
def cogroup[W](other: RDD[(K, W)]): RDD[(K, (Iterable[V], Iterable[W]))] = self.withScope {
cogroup(other, defaultPartitioner(self, other))
}
这个默认分区器,最后会从RDD和spark默认配置取最大的值,作为分区器的分区数,所以在上面这种场景,会RDD2的分区器
def defaultPartitioner(rdd: RDD[_], others: RDD[_]*): Partitioner = {
val rdds = (Seq(rdd) ++ others)
// 循环所有的rdd,获取进行分区过的rdd,判断依据就是分区器的分区数 >0
val hasPartitioner = rdds.filter(_.partitioner.exists(_.numPartitions > 0))
// 获取设置有分区器的RDD是最大分区数的RDD
val hasMaxPartitioner: Option[RDD[_]] = if (hasPartitioner.nonEmpty) {
Some(hasPartitioner.maxBy(_.partitions.length))
} else {
None
}
// 如果spark程序里设置了spark.default.parallelism,那么就取这个默认值,如果没有就取上面RDD的最大分区数
val defaultNumPartitions = if (rdd.context.conf.contains("spark.default.parallelism")) {
rdd.context.defaultParallelism
} else {
rdds.map(_.partitions.length).max
}
// If the existing max partitioner is an eligible one, or its partitions number is larger
// than or equal to the default number of partitions, use the existing partitioner.
// 最后 比较spark默认规则下的分区数 和 最大分区数RDD的分区数 取最大
if (hasMaxPartitioner.nonEmpty && (isEligiblePartitioner(hasMaxPartitioner.get, rdds) ||
defaultNumPartitions <= hasMaxPartitioner.get.getNumPartitions)) {
hasMaxPartitioner.get.partitioner.get
} else {
new HashPartitioner(defaultNumPartitions)
}
}
继续往下看cogroup的源码,会发现主要把所有的值汇总过来的动作在CoGroupedRDD中做的,我们可以看下这个RDD的实现,它是RDD的一个实现类
首先看到getDependencies,由于会把分区器传过来,所以判断是什么依赖的时候是依据循环的RDD分区器和传过来的分区器是否相等,相等就是窄依赖,不相等就是宽依赖,就当前场景下,RDD2有分区器,在这里就会判断成窄依赖,而RDD1则会判断宽依赖,也确实是,RDD1是 需要shuffle重分区的,最终返回这么两个依赖的Seq
getPartitions,根据传进来的分区器的分区数量,实例化这个长度的数组,然后循环取获取每个分区的依赖,其中如果是宽依赖就是获取所有的分区,窄依赖就是获取依赖的那个分区(分区也有依赖,获取方式还没确定)
override def getPartitions: Array[Partition] = {
val array = new Array[Partition](part.numPartitions)
for (i <- 0 until array.length) {
// Each CoGroupPartition will have a dependency per contributing RDD
array(i) = new CoGroupPartition(i, rdds.zipWithIndex.map { case (rdd, j) =>
// Assume each RDD contributed a single dependency, and get it
dependencies(j) match {
case s: ShuffleDependency[_, _, _] =>
None
case _ =>
Some(new NarrowCoGroupSplitDep(rdd, i, rdd.partitions(i)))
}
}.toArray)
}
array
}
最后再说下compute的逻辑,它主要把分区循环,读取数据,读取的过程会判断窄依赖还是宽依赖,这个不同读取的方式不同,最后读取出来的key-value数据,会交给insertAll处理,其中 createExternalMap也是通过createCombiner,mergeValue,mergeCombiners来实现的
val map = createExternalMap(numRdds)
for ((it, depNum) <- rddIterators) {
map.insertAll(it.map(pair => (pair._1, new CoGroupValue(pair._2, depNum))))
}
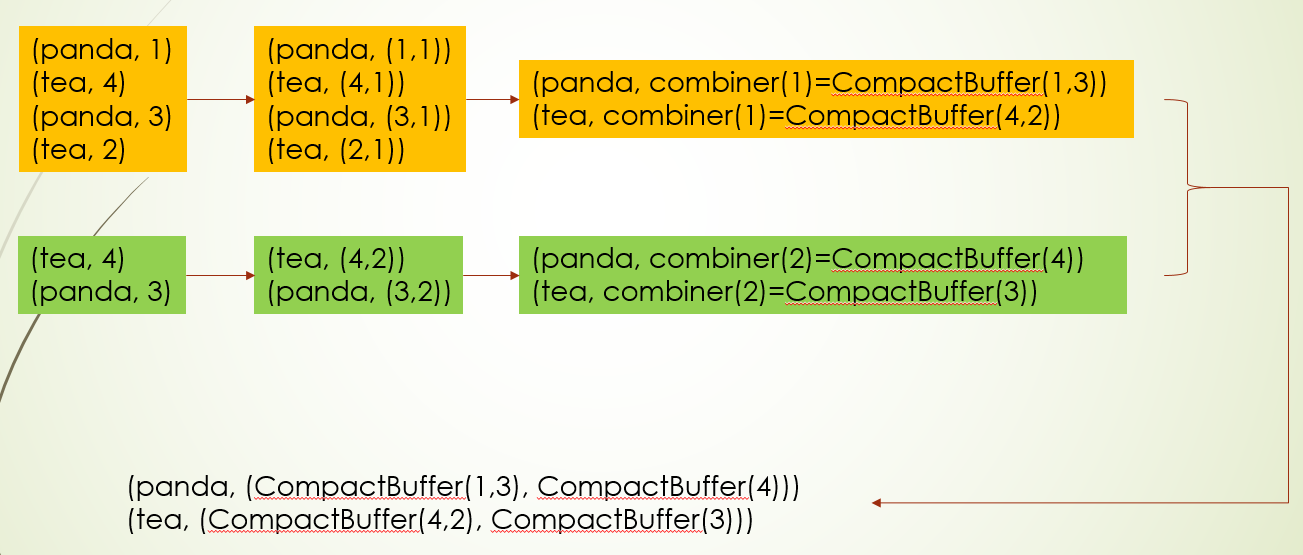
mapValues,flatMapValues,sortBy,sortByKey,filterByRange,其中两个sort接口使用了RangePartitioner,因为RangePartitioner能保证分区间是有序,排序动作只要对分区内的数据进行排序,filterByRange也是基于这个分区器,在过滤范围的时候可以减少扫描分区,提高性能
package com.twq.spark.rdd.keyvalue
import org.apache.spark.{HashPartitioner, RangePartitioner, SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/8/19.
*/
object OtherApiTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("word count")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val rdd = sc.parallelize(Seq(2, 3, 3, 6, 2))
rdd.distinct().collect()
val pairRDD =
sc.parallelize[(Int, Int)](Seq((5, 2), (7, 4), (3, 3), (2, 4)), 4).partitionBy(new HashPartitioner(2))
val mapValuesRDD = pairRDD.mapValues(x => x + 1)
mapValuesRDD.collect()
mapValuesRDD.partitioner //会记住父亲RDD的分区器
val flatMapValuesRDD = pairRDD.flatMapValues(x => (x to 5))
flatMapValuesRDD.collect()
flatMapValuesRDD.partitioner
pairRDD.keys.collect()
pairRDD.values.collect()
pairRDD.sortByKey().collect()
pairRDD.sortByKey(false).collect()
pairRDD.sortBy(_._1).collect()
pairRDD.sortBy(_._1, false).collect()
val rangeTestRDD =
sc.parallelize[(Int, Int)](Seq((5, 2), (7, 4), (3, 6), (2, 6), (3, 6), (2, 6)), 4)
rangeTestRDD.filterByRange(3, 5).collect() //把key在 3-5的取出来
}
}
count api
package com.twq.spark.rdd.keyvalue
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/8/19.
*/
object CountApiTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("word count")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
//
val numberRDD = sc.parallelize(1 to 10000 , 200)
//RDD a内容 union 5次,其中有50000个元素
val numbersRDD = numberRDD ++ numberRDD ++ numberRDD ++ numberRDD ++ numberRDD
numbersRDD.count()
//第一个参数是超时时间
//第二个参数是期望达到近似估计的准确度
// 如果你不断用0.9来调用countApprox,则我们期望90%的结果数据是正确的count值
//如果count统计在超时时间内执行完,则不会近视估值,而是取正确的值
//如果count统计在超时时间内没有执行完,则根据执行完的task的返回值和准确度进行近似估值
val resultCount = numbersRDD.countApprox(200, 0.9)
resultCount.initialValue.mean
resultCount.initialValue.low
resultCount.initialValue.high
resultCount.initialValue.confidence
resultCount.getFinalValue().mean
numbersRDD.countByValue()
val resultCountValue = numbersRDD.countByValueApprox(200, 0.9)
resultCountValue.initialValue(1).mean
//结果是9760,不传参数,默认是0.05
numbersRDD.countApproxDistinct()
//结果是9760
numbersRDD.countApproxDistinct(0.05)
//8224
numbersRDD.countApproxDistinct(0.1)
//10000 参数越小值越精确
numbersRDD.countApproxDistinct(0.006)
val pair = sc.parallelize((1 to 10000).zipWithIndex)
pair.collect()
val pairFive = pair ++ pair ++ pair ++ pair ++ pair
pairFive.countByKey()
pairFive.countByKeyApprox(10, 0.95)
//用HyperLogLogPlus来实现的
//也是调用combineByKey来实现的
//val createCombiner = (v: V) => {
// val hll = new HyperLogLogPlus(p, sp)
// hll.offer(v)
// hll
//}
//val mergeValue = (hll: HyperLogLogPlus, v: V) => {
// hll.offer(v)
// hll
//}
//val mergeCombiner = (h1: HyperLogLogPlus, h2: HyperLogLogPlus) => {
// h1.addAll(h2)
// h1
//}
pairFive.countApproxDistinctByKey(0.1).collect().size
pairFive.collectAsMap() // 这种 操作很容易把内存打爆,不建议
pairFive.lookup(5)
}
}
union 等同把两个RDD ++的效果,主要两种场景的分区器,如果所有的父RDD分区器一致,那么分区数就是分区器的分区数
如果是父RDD的分区器不相同,那么分区数就是所有的父RDD分区数加总

intersection 取两个RDD的交集
cartesian 笛卡尔积,可以理解为 RDD的元素随机组合,分区数是每个RDD分区数相乘
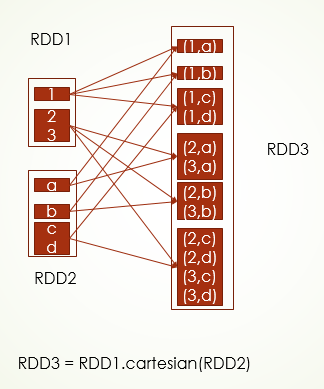
package com.twq.spark.rdd
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/8/19.
*/
object TwoRDDApiTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("word count")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val oneRDD = sc.parallelize[Int](Seq(1, 2, 3), 3)
val otherRDD = sc.parallelize(Seq(3, 4, 5), 3)
val unionRDD = oneRDD.union(otherRDD)
unionRDD.collect() // Array[Int] = Array(1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5)
val plusPlusRDD = oneRDD ++ otherRDD
plusPlusRDD.collect() // Array[Int] = Array(1, 2, 3, 3, 4, 5)
val thirdRDD = sc.parallelize(Seq(5, 5, 5), 3)
val unionAllRDD = sc.union(Seq(oneRDD, otherRDD, thirdRDD))
oneRDD.union(otherRDD).union(thirdRDD).collect()
unionAllRDD.collect()
val intersectionRDD = oneRDD.intersection(otherRDD)
intersectionRDD.collect() // Array[Int] = Array(3)
val subtractRDD = oneRDD.subtract(otherRDD)
subtractRDD.collect() // Array[Int] = Array(1, 2)
// Array[(Int, Int)] = Array((1,3), (1,4), (1,5), (2,3), (2,4), (2,5), (3,3), (3,4), (3,5))
val cartesianRDD = oneRDD.cartesian(otherRDD)
cartesianRDD.collect()
//要求两个RDD有相同的元素个数, 分区也得是一样的
val zipRDD = oneRDD.zip(otherRDD)
zipRDD.collect() // Array[(Int, Int)] = Array((1,3), (2,4), (3,5))
//要求两个rdd需要有相同的分区数,但是每一个分区可以不需要有相同的元素个数
val zipPartitionRDD =
oneRDD.zipPartitions(otherRDD)((iterator1, iterator2)
=> Iterator(iterator1.sum + iterator2.sum))
zipPartitionRDD.collect() // Array[Int] = Array(0, 4, 6, 8)
val zipPartition3RDD =
oneRDD.zipPartitions(otherRDD, thirdRDD)((iterator1, iterator2, iterator3)
=> Iterator(iterator1.sum + iterator2.sum + iterator3.sum))
zipPartition3RDD.collect()
}
}
zip的使用及其原理
zip 两个RDD相同索引的分区相同索引位置的元素对应成元组,注意:两个RDD分区数必须相同,分区里的元素个数都要相同,否则在进行操作的时候就会报错
zipPartitions 两个RDD相同索引分区的所有元素按照某个计算函数求得结果项,注意:两个RDD分区数必须相同,否则也会报错
zip是基于zipPartitions实现的
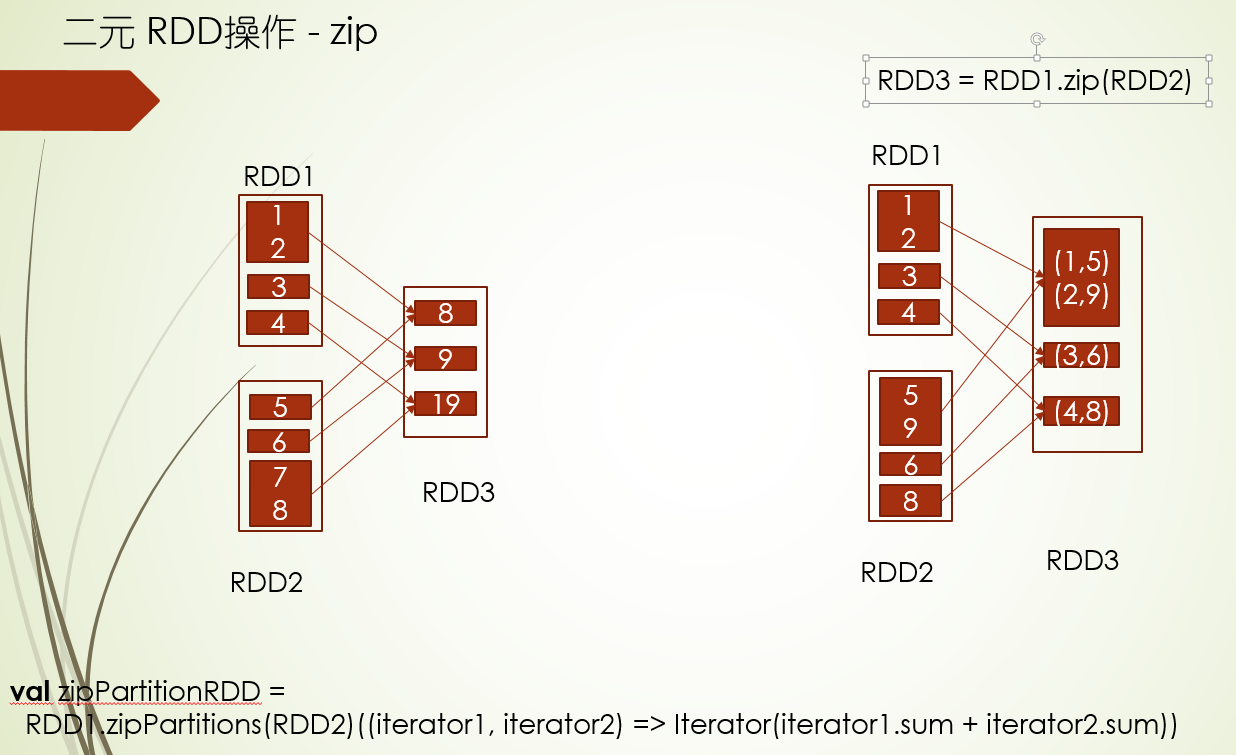
val oneRDD = sc.parallelize[Int](Seq(1, 2, 3), 3)
val otherRDD = sc.parallelize(Seq(3, 4, 5), 3)
//要求两个RDD有相同的元素个数, 分区也得是一样的
val zipRDD = oneRDD.zip(otherRDD)
zipRDD.collect() // Array[(Int, Int)] = Array((1,3), (2,4), (3,5))
//要求两个rdd需要有相同的分区数,但是每一个分区可以不需要有相同的元素个数
val zipPartitionRDD =
oneRDD.zipPartitions(otherRDD)((iterator1, iterator2)
=> Iterator(iterator1.sum + iterator2.sum))
zipPartitionRDD.collect() // Array[Int] = Array(0, 4, 6, 8)
val zipPartition3RDD =
oneRDD.zipPartitions(otherRDD, thirdRDD)((iterator1, iterator2, iterator3)
=> Iterator(iterator1.sum + iterator2.sum + iterator3.sum))
zipPartition3RDD.collect()
RDD的缓存机制
RDD的缓存机制,你就可以理解成把RDD的数据缓存到内存或者磁盘中
persist(StorageLevel) 其中StorageLevel就是缓存级别,决定缓存在哪,其中persist的源码里,就是把缓存级别赋值给一个storageLevel的成员变量,为什么赋值给这个成员变量,就可以达到缓存的效果?那这里还要看下在读取数据时的Iterator方法,因为在compute方法,会调用这方法读取数据,在iterator方法中,会获取这个存储级别进行判断,比如不为None,就是设置了存储级别,就会调用getOrCompute方法,这个方法中,主要去blockManager获取数据,能获取到就返回,获取不到就进行计算,然后放到blockManager中,下次获取时,直接从这个缓存对象里面获取
cache 缓存在内存中,它调用就是persist方法,因为persist默认缓存级别就是内存中
unpersist 从缓存中移除掉,不让其缓存
package com.twq.spark.rdd
import org.apache.spark.storage.StorageLevel
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/8/19.
*/
object RDDPersistApiTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("word count")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val hdfsFileRDD = sc.textFile("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/person.json")
val mapRDD = hdfsFileRDD.flatMap(str => str.split(" "))
//存储级别:
//MEMORY_ONLY: 只存在内存中
//DISK_ONLY: 只存在磁盘中
//MEMORY_AND_DISK: 先存在内存中,内存不够的话则存在磁盘中
//OFF_HEAP: 存在堆外内存中
hdfsFileRDD.persist(StorageLevel.MEMORY_ONLY)
hdfsFileRDD.getStorageLevel
mapRDD.getStorageLevel // None
mapRDD.cache() //表示只存在内存中
mapRDD.count()
mapRDD.collect()
mapRDD.unpersist()
hdfsFileRDD.unpersist()
}
}
Checkpoint机制

那么上图已经很明显说了checkpoint机制的作用,和persist一样都做持久化,但是persist不会切断RDD之前的依赖关系,RDD依赖关系太长,会影响计算性能,所以checkpoint机制在某些场景下,可以提高性能
需要注意的是:只有触发了action动作,才会checkpoint,并且触发过action动作,立即checkpoint没有用
package com.twq.spark.rdd.checkpoint
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/8/23.
*/
object CheckPointTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("word count")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val pairRDD = sc.parallelize[(Int, Int)](Seq((1, 2), (3, 4), (3, 6)), 2)
val filterRDD = pairRDD.filter { case (key, value) => key > 2 }
val mapRDD = filterRDD.map { case (key, value) => (key + 1, value + 1) }
mapRDD.toDebugString
mapRDD.localCheckpoint()
mapRDD.collect()
mapRDD.toDebugString
val otherFilterRDD = mapRDD.filter {case (key, value) => key + value > 1}
val otherMapRDD = otherFilterRDD.map { case (key, value) => (key + 1, value + 1) }
otherMapRDD.toDebugString
sc.setCheckpointDir("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/checkpoint") //hdfs上缓存需要设置 hdfs存储地址
otherMapRDD.checkpoint()
otherMapRDD.toDebugString
val someMapRDD = otherMapRDD.map { case (key, value) => (key + 1, value + 1) }
someMapRDD.toDebugString
someMapRDD.collect()
someMapRDD.checkpoint()//没有用,因为这个rdd已经执行了job了
someMapRDD.collect()
}
}
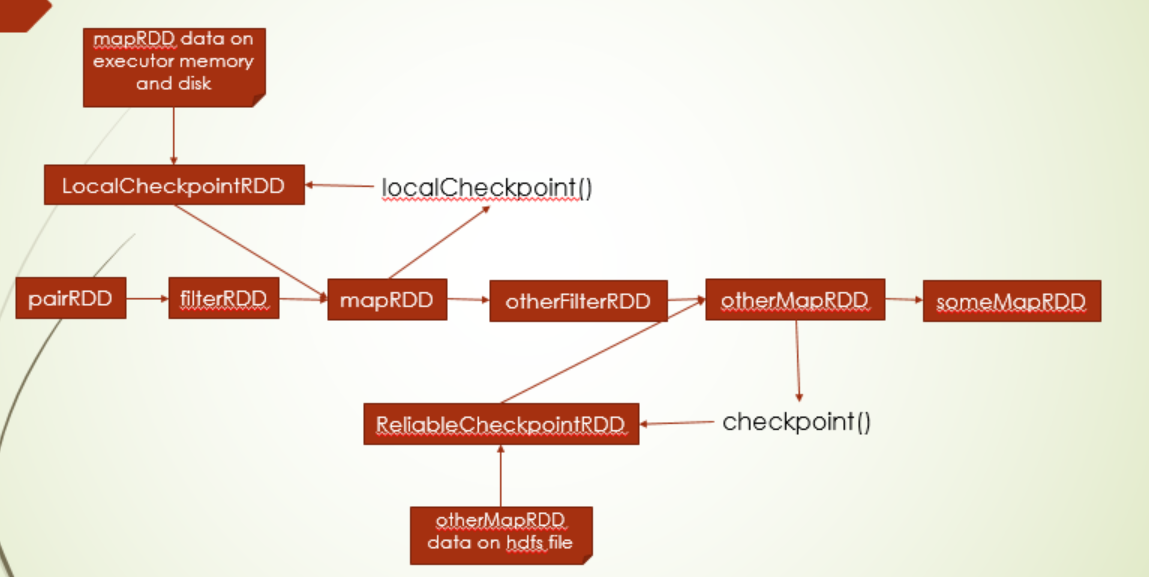
checkpoint原理
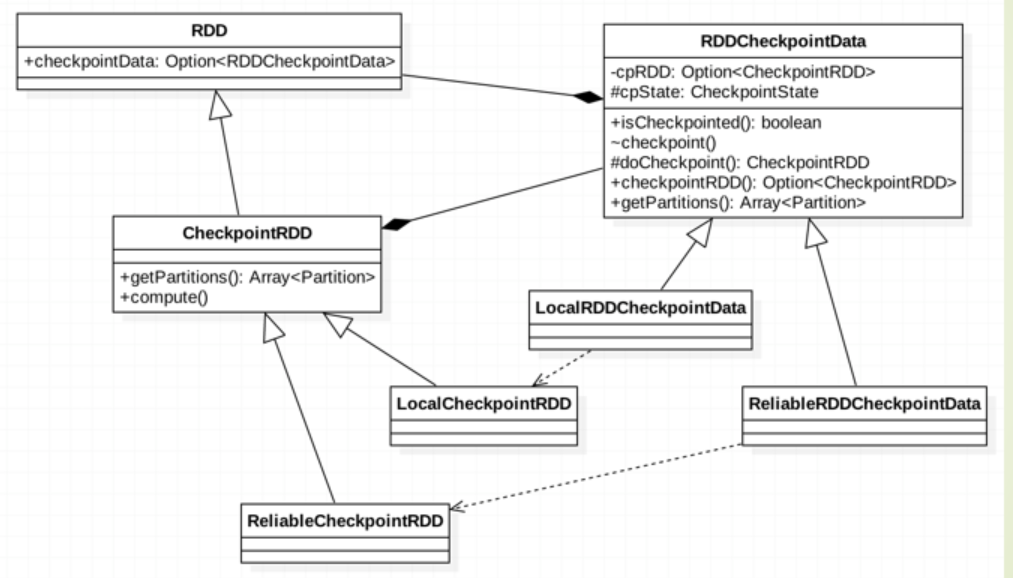
源码我们会发现,checkpoint api实现方式和persist一样,赋值给一个成员变量,checkpoint里是赋值给checkpointData,那它这里怎么触发checkpoint以及如何读取checkpoint的数据?
上面也说只有触发action动作才会触发checkpoint动作,比如collect动作,你往下看,它会调用RDD的doCheckpoint方法,在这里面会对checkpointData是否定义进行判断,如果定义了,就会调用checkpointData方法.get.checkpoint(),在这里面会checkpoint数据到对应的存储地方(实例化checkpoint RDD)并标记checkpoint过,以及清除依赖
说了触发,那读取checkpoint的数据呢?还是看iterator方法,之前说了,如果设置了storageLevel,那么就会走persist,没设置,那么就会走checkpoint,在这个分支下,会先判断是否checkpopint的标志,如果checkpoint过,直接读取checkpoint对应RDD的数据,如果没有,重新计算,并checkoutpoint

***broadcast的机制及其用法
broadcast翻译过来就是广播,它的应用场景是这样的,driver端负责放spark代码及其相关的数据,而Executor端是负责执行操作分区的task,其中driver还存有一些固定不变的配置数据,task执行时需要,如果采用传输的方式 ,性能低,所以就有了这么一个广播的机制,给到Executor端,前提是这个数据不能变

package com.twq.spark.rdd
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/9/3.
*/
object BroadcastTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("test")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val lookupTable = Map("plane" -> "sky", "fish" -> "sea", "people" -> "earth")
val lookupTableB = sc.broadcast(lookupTable)
val logData = sc.parallelize(Seq("plane", "fish", "duck", "dirty", "people", "plane"), 2)
logData.foreach(str => {
val replaceStrOpt = lookupTableB.value.get(str)
println("element is : " + str)
if (replaceStrOpt.isDefined) {
println(s"============找到了[${str}]对应的值[${replaceStrOpt.get}]")
}
})
}
}
总结:针对不变的少量的配置信息通过广播broadcast下发到Executor,可以提高性能
accumulator
这个可以监控task的运行情况,在driver端对task信息进行汇总,Accumutator运行在driver端,Executor端在运行task时可以直接访问Accumutator的数据
package com.twq.spark.rdd
import java.util.concurrent.ConcurrentHashMap
import java.util.function.BiConsumer
import org.apache.spark.util.AccumulatorV2
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/9/3.
*/
object AccumulatorTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("test")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val longAccumulator = sc.longAccumulator("count mapped data")
val collectionAccumulator = sc.collectionAccumulator[String]("collect mapped data")
val mapAccumulator = new CustomAccumulator
sc.register(mapAccumulator) //自定义的 需要进行注册
val logData = sc.parallelize(Seq("plane", "fish", "duck", "dirty", "people", "plane"), 2)
// 上面代码在driver端执行
logData.foreach(str => { // 这里就在Executor端执行
if (str == "plane") {
longAccumulator.add(1L)
}
try {
// some code
} catch {
case e: Exception => {
collectionAccumulator.add(e.getMessage) //这里实例了 统计task发生异常信息
}
}
mapAccumulator.add(str)
})
longAccumulator.sum // 6
collectionAccumulator.value // "plane", "fish", "duck", "dirty", "people", "plane"
mapAccumulator.value //"plane -> 2", "fish -> 1", "duck -> 1", "dirty -> 1", "people -> 1",
}
}
class CustomAccumulator extends AccumulatorV2[String, ConcurrentHashMap[String, Int]] {
private val map = new ConcurrentHashMap[String, Int]()
override def isZero: Boolean = map.isEmpty
override def copy(): AccumulatorV2[String, ConcurrentHashMap[String, Int]] = {
val newAcc = new CustomAccumulator()
newAcc.map.putAll(map)
newAcc
}
override def reset(): Unit = map.clear()
// 在task端执行
override def add(v: String): Unit = {
map.synchronized {
if (map.containsKey(v)) {
map.put(v, map.get(v) + 1)
} else map.put(v, 1)
}
}
//在 driver端执行
override def merge(other: AccumulatorV2[String, ConcurrentHashMap[String, Int]]): Unit = other match {
case o: CustomAccumulator => {
o.map.forEach(new BiConsumer[String, Int] {
override def accept(key: String, value: Int): Unit = {
if (map.containsKey(key)) {
map.put(key, map.get(key) + value)
} else {
map.put(key, value)
}
}
})
}
case _ => throw new UnsupportedOperationException(
s"Cannot merge ${this.getClass.getName} with ${other.getClass.getName}")
}
override def value: ConcurrentHashMap[String, Int] = map
}
总结:accumulator用于统计Executor上task的执行情况,比如统计元素个数,定义driver端,可以在Executor上直接访问
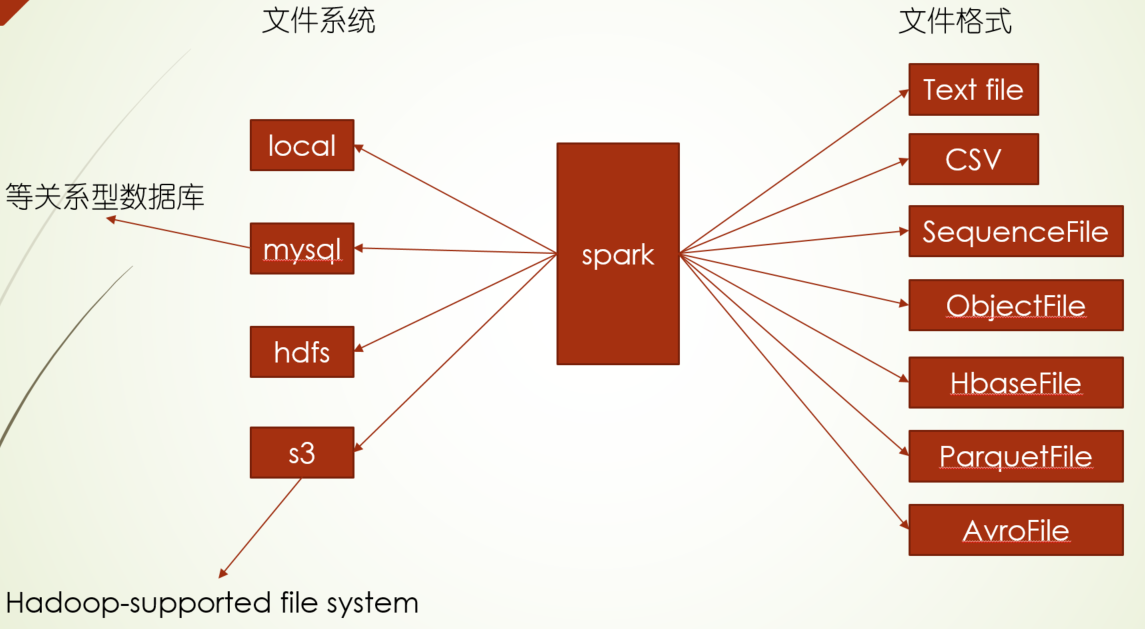
spark支持的读写存储系统
package com.twq.spark.rdd.sources
import java.sql.{DriverManager, ResultSet}
import org.apache.hadoop.io.{LongWritable, Text}
import org.apache.hadoop.mapred.TextInputFormat
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.{TextInputFormat => NewTextInputFormat}
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.{TextOutputFormat => NewTextOutputFormat}
import org.apache.spark.rdd.JdbcRDD
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/8/26.
*/
object FileSystemApiTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("test")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val data = sc.parallelize(Seq("just test", "hello world"), 1)
//jdbc mysql and oracle
def createConnection() = {
Class.forName("com.mysql.jdbc.Driver")
DriverManager.getConnection("jdbc:mysql://localhost/test?user=hhh")
}
def extractValues(r: ResultSet) = {
(r.getInt(1), r.getString(2))
}
val sql = "select * from test where ? <= id and id <= ?"
val dataJdbc = new JdbcRDD(sc, createConnection,
sql, lowerBound = 1, upperBound = 3, numPartitions = 2, mapRow = extractValues)
dataJdbc.collect()
data.saveAsTextFile("file:///home/hadoop-twq/spark-course/test")
//本地文件系统中写读文件
sc.textFile("file:///home/hadoop-twq/spark-course/echo.sh").collect()
//hdfs文件系统中读写文件
// use old api
data.saveAsTextFile("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/test")
val keyValueRDD = sc.hadoopFile("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/test/part-00000",
classOf[TextInputFormat], classOf[LongWritable], classOf[Text]).map {case (key, value) =>
(key.get(), value.toString)
}
keyValueRDD.collect()
// 当这里说 新老api 都是mapreduce 读写HDFS, spark会把这些api集成进去
// 新的api 使用抽象类代替了老的接口,这样的优点:在api演化方面更加灵活
// 新的api 有content的概念,参数可以在这里面,在兼容性方面更好,后面加参数往这里面加
val data2 = sc.hadoopFile("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/test/part-00000",
classOf[TextInputFormat], classOf[LongWritable], classOf[Text]) //需要注意的是 新的api读取的数据必须是key-value类型
// use new api
data2.saveAsNewAPIHadoopFile[NewTextOutputFormat[LongWritable, Text]](
"hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/test2")
sc.newAPIHadoopFile("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/test/part-00000",
classOf[NewTextInputFormat], classOf[LongWritable], classOf[Text]).
map { case (_, value) => value.toString } collect()
//s3文件系统中
sc.hadoopConfiguration.set("fs.s3n.awsAccessKeyId", "YOUR_KEY_ID")
sc.hadoopConfiguration.set("fs.s3n.awsSecretAccessKey", "YOUR_SECRET")
data.saveAsTextFile("s3n://bucket/test")
val s3FileInput = sc.textFile("s3n://bucket/*.log")
s3FileInput.collect()
}
}

package com.twq.spark.rdd.sources import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration import org.apache.hadoop.fs.Path import org.apache.hadoop.io.SequenceFile.CompressionType import org.apache.hadoop.io.compress.Lz4Codec import org.apache.hadoop.io.{NullWritable, Text} import org.apache.hadoop.mapred._ import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.TaskType /** * Created by tangweiqun on 2017/8/27. */ object MapReduceWriterOldApiTest { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { //1 设置配置的属性,包括写入key的类型、value的类型以及写入数据的文件格式 val conf = new Configuration() val jobConf = new JobConf(conf) jobConf.setOutputKeyClass(classOf[NullWritable]) jobConf.setOutputValueClass(classOf[Text]) jobConf.setOutputFormat(classOf[TextOutputFormat[NullWritable, Text]]) //2 写入数据的压缩设置 val codec = Some(classOf[Lz4Codec]) for (c <- codec) { jobConf.setCompressMapOutput(true) jobConf.set("mapred.output.compress", "true") jobConf.setMapOutputCompressorClass(c) jobConf.set("mapred.output.compression.codec", c.getCanonicalName) jobConf.set("mapred.output.compression.type", CompressionType.BLOCK.toString) } //3 设置数据写入到的文件夹 val path = "hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/test" val tempPath = new Path(path) val tempFs = tempPath.getFileSystem(conf) val finalOutputPath = tempPath.makeQualified(tempFs.getUri, tempFs.getWorkingDirectory) FileOutputFormat.setOutputPath(jobConf, finalOutputPath) //4 设置job相关的id等 val jobId = new JobID("jobtrackerID", 123) val jobContext = new JobContextImpl(jobConf, jobId) val taId = new TaskAttemptID(new TaskID(jobId, TaskType.MAP, 0), 0) conf.set("mapred.tip.id", taId.getTaskID.toString) conf.set("mapred.task.id", taId.toString) conf.setBoolean("mapred.task.is.map", true) conf.setInt("mapred.task.partition", 0) conf.set("mapred.job.id", jobId.toString) //5 设置数据写入文件的文件名称 val outputName = "part-" + System.currentTimeMillis() val outputPath = FileOutputFormat.getOutputPath(jobConf) val fs = outputPath.getFileSystem(jobConf) //6 构建一个写数据的writer,然后写文件 val writer = jobConf.getOutputFormat .asInstanceOf[OutputFormat[AnyRef, AnyRef]] .getRecordWriter(fs, jobConf, outputName, Reporter.NULL) val key = null val value = "test" writer.write(key, value) //7 关闭writer writer.close(Reporter.NULL) } }

package com.twq.spark.rdd.sources import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration import org.apache.hadoop.io.{NullWritable, Text} import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.{Job, RecordWriter, TaskAttemptID, TaskType} import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.TextOutputFormat import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.TaskAttemptContextImpl /** * Created by tangweiqun on 2017/8/27. */ object MapReduceWriterNewApiTest { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { //1 构建并配置写数据的一个job实例,包括写入key的类型、value的类型以及写入数据的文件格式 val conf = new Configuration() val job = Job.getInstance(conf) job.setOutputKeyClass(classOf[NullWritable]) job.setOutputValueClass(classOf[Text]) job.setOutputFormatClass(classOf[TextOutputFormat[NullWritable, Text]]) val jobConfiguration = job.getConfiguration jobConfiguration.set("mapred.output.dir", "hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/test") //2 构建job相关的id val attemptId = new TaskAttemptID("jobtrackerID", 0, TaskType.REDUCE, 0, 0) val hadoopContext = new TaskAttemptContextImpl(jobConfiguration, attemptId) //3 获取输出数据的文件类型 val format = job.getOutputFormatClass.newInstance //4 获取输出的committer val committer = format.getOutputCommitter(hadoopContext) committer.setupTask(hadoopContext) //5 获取写文件的writer,并写文件 val writer = format.getRecordWriter(hadoopContext).asInstanceOf[RecordWriter[NullWritable, Text]] val key = null val value = "test" writer.write(null, new Text("teet")) //6 关闭writer writer.close(hadoopContext) committer.commitTask(hadoopContext) } }

package com.twq.spark.rdd.sources import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration import org.apache.hadoop.io.{LongWritable, Text} import org.apache.hadoop.mapred._ import org.apache.hadoop.util.ReflectionUtils /** * Created by tangweiqun on 2017/8/22. */ object MapReduceFileReaderOldApi { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { //1 构建配置 val hadoopConf = new Configuration() val jobConf = new JobConf(hadoopConf) //2 设置数据存储的文件 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(jobConf, "hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/word.txt") //3 获取读取文件的格式 val inputFormat = ReflectionUtils.newInstance(classOf[TextInputFormat], jobConf) .asInstanceOf[InputFormat[LongWritable, Text]] //4 获取需要读取文件的数据块的分区信息 //4.1 获取文件被分成多少数据块了 val minSplit = 1 val inputSplits = inputFormat.getSplits(jobConf, minSplit) val firstSplit = inputSplits(0) //4.2 获取第一个数据块的存储信息 val splitInfoReflections = new SplitInfoReflections val lsplit = splitInfoReflections.inputSplitWithLocationInfo.cast(firstSplit) val preferLocations = splitInfoReflections.getLocationInfo.invoke(lsplit).asInstanceOf[Array[AnyRef]] val firstPreferLocation = preferLocations(0) val locationStr = splitInfoReflections.getLocation.invoke(firstPreferLocation).asInstanceOf[String] val isMemory = splitInfoReflections.isInMemory.invoke(firstPreferLocation).asInstanceOf[Boolean] //5 读取第一个数据块的数据 val reader = inputFormat.getRecordReader(firstSplit, jobConf, Reporter.NULL) val key = reader.createKey() val value = reader.createValue() val finished = !reader.next(key, value) } } class SplitInfoReflections { def classForName(className: String): Class[_] = { Class.forName(className, true, Thread.currentThread().getContextClassLoader) // scalastyle:on classforname } val inputSplitWithLocationInfo = classForName("org.apache.hadoop.mapred.InputSplitWithLocationInfo") val getLocationInfo = inputSplitWithLocationInfo.getMethod("getLocationInfo") val newInputSplit = classForName("org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.InputSplit") val newGetLocationInfo = newInputSplit.getMethod("getLocationInfo") val splitLocationInfo = classForName("org.apache.hadoop.mapred.SplitLocationInfo") val isInMemory = splitLocationInfo.getMethod("isInMemory") val getLocation = splitLocationInfo.getMethod("getLocation") }

package com.twq.spark.rdd.sources import org.apache.hadoop.conf.Configuration import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce._ import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.input.{FileInputFormat, TextInputFormat} import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.task.{JobContextImpl, TaskAttemptContextImpl} /** * Created by tangweiqun on 2017/8/22. */ object MapReduceFileReaderNewApi { def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = { //1 构建一个job实例 val hadoopConf = new Configuration() val job = Job.getInstance(hadoopConf) //2 设置需要读取的文件全路径 FileInputFormat.setInputPaths(job, "hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/word.txt") //3 获取读取文件的格式 val inputFormat = classOf[TextInputFormat].newInstance() val updateConf = job.getConfiguration //4 获取需要读取文件的数据块的分区信息 //4.1 获取文件被分成多少数据块了 val minSplit = 1 val jobId = new JobID("jobTrackerId", 123) val jobContext = new JobContextImpl(updateConf, jobId) val inputSplits = inputFormat.getSplits(jobContext).toArray val firstSplit = inputSplits(0).asInstanceOf[InputSplit] //4.2 获取第一个数据块的存储信息 val splitInfoReflections = new SplitInfoReflections val lsplit = splitInfoReflections.inputSplitWithLocationInfo.cast(firstSplit) val preferLocations = splitInfoReflections.getLocationInfo.invoke(lsplit).asInstanceOf[Array[AnyRef]] val firstPreferLocation = preferLocations(0) val locationStr = splitInfoReflections.getLocation.invoke(firstPreferLocation).asInstanceOf[String] val isMemory = splitInfoReflections.isInMemory.invoke(firstPreferLocation).asInstanceOf[Boolean] //5 读取第一个数据块的数据 val attemptId = new TaskAttemptID("jobTrackerId", 123, TaskType.MAP, 0, 0) val hadoopAttemptContext = new TaskAttemptContextImpl(updateConf, attemptId) val reader = inputFormat.createRecordReader(firstSplit, hadoopAttemptContext) reader.initialize(firstSplit, hadoopAttemptContext) val isFirst = reader.nextKeyValue() val key = reader.getCurrentKey val value = reader.getCurrentValue } }
HadoopRDD的原理和实现
后续 更新。。。。。
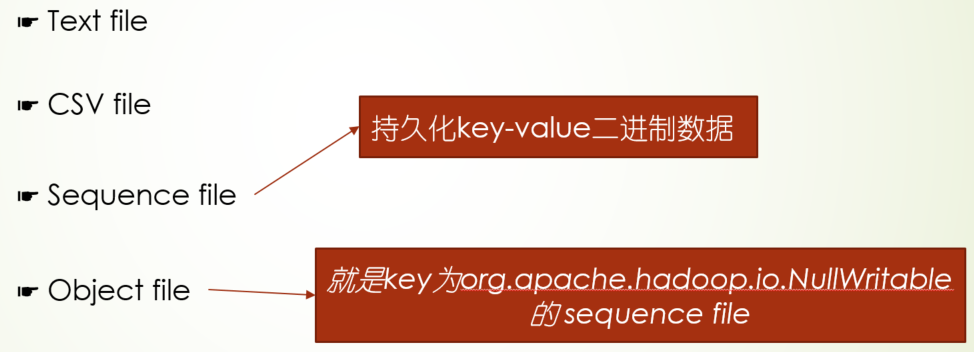
spark支持的通用文件格式
sequence file可以用于小文件处理的场景,key为文件名,value就是文件流
其中
package com.twq.spark.rdd.sources
import java.io.{StringReader, StringWriter}
import au.com.bytecode.opencsv.{CSVReader, CSVWriter}
import org.apache.hadoop.io.SequenceFile.CompressionType
import org.apache.hadoop.io.{IntWritable, Text}
import org.apache.hadoop.mapreduce.lib.output.FileOutputFormat
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/8/24.
*/
object CommonFileFormatApiTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("test")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
// text file format
val data = sc.parallelize(Seq("i am the first test", "what about you", "hello world"), 3)
data.saveAsTextFile("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/text/")
val textFileInputFromHdfs = sc.textFile("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/text/part-00001")
textFileInputFromHdfs.collect()
// csv file format
val persons = sc.parallelize(Seq(Person("jeffy", 30), Person("tom", 24)), 1)
persons.map(person => List(person.name, person.age.toString).toArray).mapPartitions(people => {
import scala.collection.JavaConversions._
val stringWriter = new StringWriter()
val csvWriter = new CSVWriter(stringWriter)
csvWriter.writeAll(people.toList)
Iterator(stringWriter.toString)
}).saveAsTextFile("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/csv/")
val peopleWithCsv = sc.textFile("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/csv/part-00000").map(line => {
val reader = new CSVReader(new StringReader(line))
reader.readNext()
})
peopleWithCsv.collect()
// sequence file format
val sequenceFileData = sc.parallelize(List(("panda", 3), ("kay", 6), ("snail", 2)))
sc.hadoopConfiguration.setBoolean(FileOutputFormat.COMPRESS, true)
sc.hadoopConfiguration.set(FileOutputFormat.COMPRESS_TYPE, CompressionType.NONE.toString)
//sc.hadoopConfiguration.set(FileOutputFormat.COMPRESS_TYPE, CompressionType.RECORD.toString)
//sc.hadoopConfiguration.set(FileOutputFormat.COMPRESS_TYPE, CompressionType.BLOCK.toString)
sequenceFileData.saveAsSequenceFile("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/sequence/")
val sequenceFileInput = sc.sequenceFile("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/sequence/part-00003",
classOf[Text], classOf[IntWritable])
//sequenceFileInput.collect() //不支持直接collect
sequenceFileInput.map { case (x, y) => (x.toString, y.get()) }.collect()
// object file format
// 就是key为org.apache.hadoop.io.NullWritable的sequence file
persons.saveAsObjectFile("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/object")
val objectFileInput = sc.objectFile[Person]("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/object/part-00000")
objectFileInput.collect()
}
}
case class Person(name: String, age: Int)
binaryFiles和binaryRecords两者都是对二进制文件进行读取,其中binaryRecords要求读取的每条记录长度一致
binaryFiles因为读取的数据是流,基本不占空间,所以我可以用它通过广播的形式把一些脚本给到Executor端下载执行
package com.twq.spark.rdd.sources
import java.io.FileOutputStream
import org.apache.spark.{SparkConf, SparkContext}
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/9/2.
*/
object BinaryDataFileFormat {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val conf = new SparkConf().setAppName("test")
val sc = new SparkContext(conf)
val wholeTextFiles = sc.wholeTextFiles("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/text/")
wholeTextFiles.collect()
// 和wholeTextFiles效果类似,都是把文件名当key,而文件内容当value
// wholeTextFiles是读取出来的是文件的文本内容,而binaryFiles读取出来的是文件二进制数据流(如果要查看具体内容,可以将二进制流转化成String)
val binaryFilesRDD = sc.binaryFiles("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/text/")
binaryFilesRDD.collect()
binaryFilesRDD.map { case (fileName, stream) =>
(fileName, new String(stream.toArray()))
}.collect()
//可以用于将hdfs上的脚本同步到每一个executor上
val binaryFilesStreams = binaryFilesRDD.collect()
val binaryFilesStreamsB = sc.broadcast(binaryFilesStreams)
val data = sc.parallelize(Seq(2, 3, 5, 2, 1), 2)
data.foreachPartition(iter => {
val allFileStreams = binaryFilesStreamsB.value
allFileStreams.foreach { case (fileName, stream) =>
val inputStream = stream.open()
val fileOutputStream = new FileOutputStream(s"/local/path/fileName-${fileName}")
val buf = new Array[Byte](4096)
var hasData = true
while (true) {
val r = inputStream.read(buf)
if (r == -1) hasData = false
fileOutputStream.write(buf, 0, r)
}
}
})
val binaryFileData = sc.parallelize[Array[Byte]](List(Array[Byte](2, 3),
Array[Byte](3, 4), Array[Byte](5, 6)))
binaryFileData.saveAsTextFile("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/binary/")
val binaryRecordsRDD = sc.binaryRecords("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/binary/part-00002", 2)
binaryRecordsRDD.collect()
}
}
Avro file行式存储和Parquet file列式存储
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.parquet</groupId>
<artifactId>parquet-column</artifactId>
<version>1.8.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.parquet</groupId>
<artifactId>parquet-hadoop</artifactId>
<version>1.8.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.parquet</groupId>
<artifactId>parquet-avro</artifactId>
<version>1.8.1</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.avro</groupId>
<artifactId>avro</artifactId>
<version>1.7.7</version>
</dependency>
<dependency>
<groupId>org.apache.avro</groupId>
<artifactId>avro-mapred</artifactId>
<version>1.7.7</version>
</dependency>
package com.twq.spark.rdd.sources
import org.apache.spark.sql.{SaveMode, SparkSession}
import com.databricks.spark.avro._
/**
* Created by tangweiqun on 2017/8/24.
*
*/
object ParquetAvroApiTest {
def main(args: Array[String]): Unit = {
val spark = SparkSession
.builder()
.appName("Spark SQL basic example")
.config("spark.some.config.option", "some-value")
.getOrCreate()
import spark.implicits._
val personDf =
spark.sparkContext.parallelize(Seq(Person("jeffy", 30), Person("tomy", 23)), 1).toDF()
//avro
personDf.write.mode(SaveMode.Overwrite).avro("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/avro")
val avroPersonDf = spark.read.avro("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/avro")
avroPersonDf.show()
//parquet
personDf.write.mode(SaveMode.Overwrite).parquet("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/parquet")
val parquetPersonDF = spark.read.parquet("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/parquet")
parquetPersonDF.show()
//json
personDf.write.mode(SaveMode.Overwrite).json("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/json")
val jsonPersonDf = spark.read.json("hdfs://master:9999/users/hadoop-twq/json")
jsonPersonDf.show()
}
}
问题:文件格式特点以及使用场景,以及和spark sql存储有啥区别






