java从入门到精通
1. 进制转换
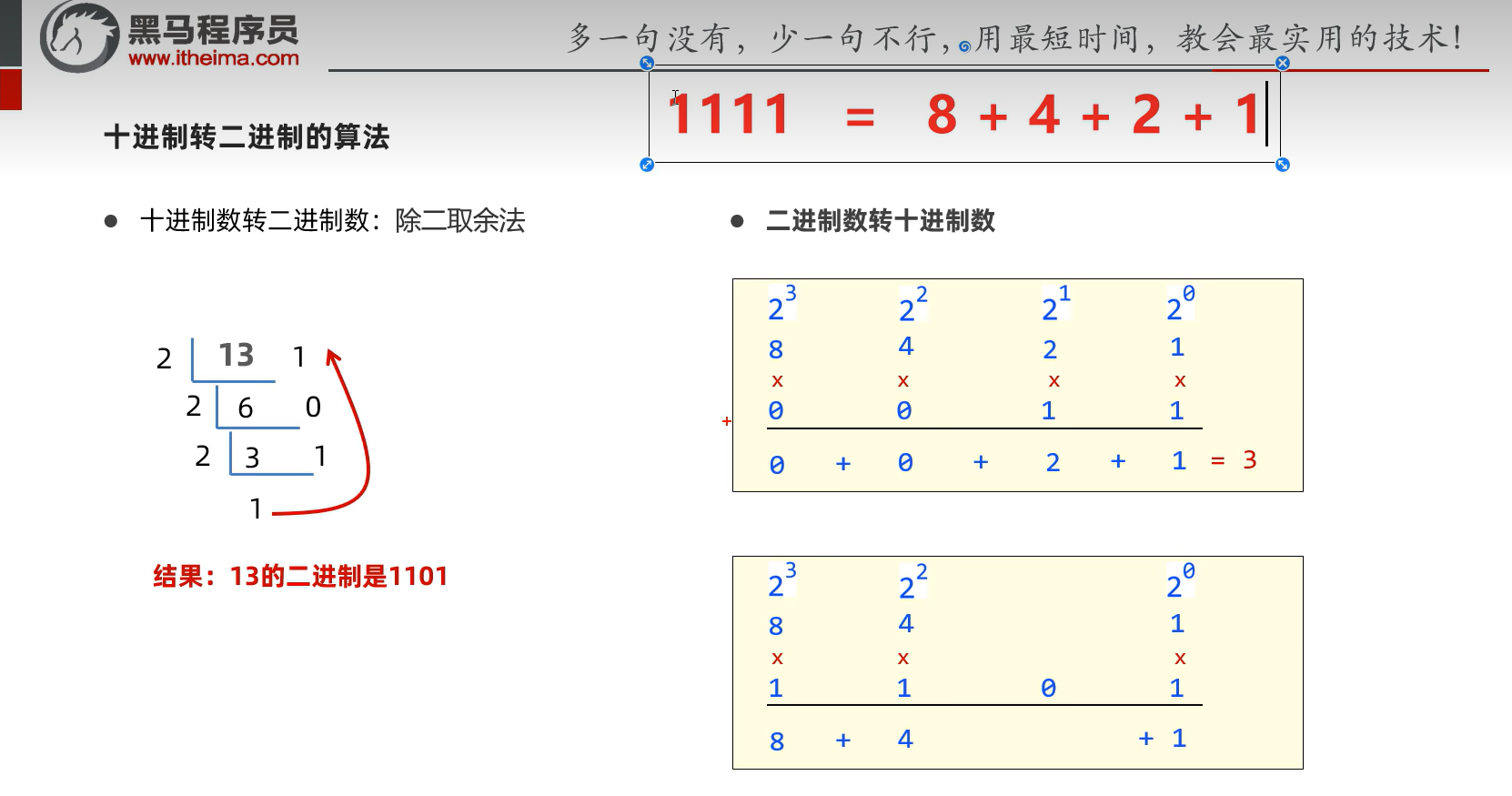
1.1 二进制和十进制
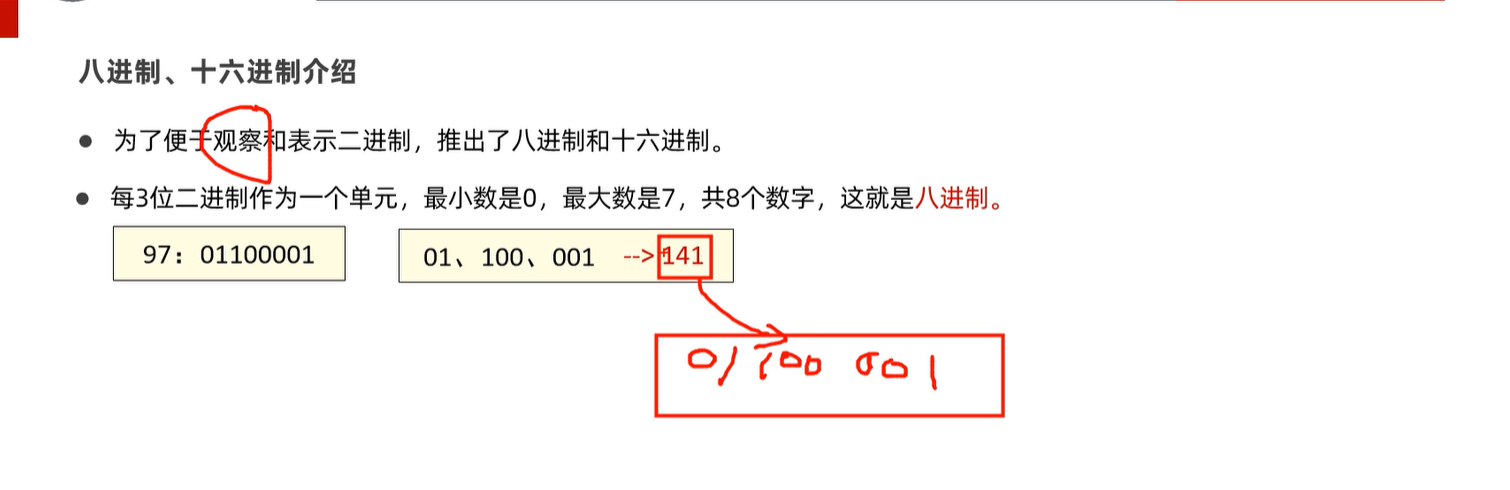
1.2 八进制
package com.itheima.variable;
public class ASCIIDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:掌握ASCII编码表的编码特点。
System.out.println('a' + 10); // 97 + 10 = 107
System.out.println('A' + 10); // 65 + 10 = 75
System.out.println('0' + 10); // 48 + 10 = 58
// 二进制 八进制 十六进制在程序中的写法。
int a1 = 0B01100001;
System.out.println(a1); //97
int a2 = 0141; // 0开头的数据当成八进制看待!
System.out.println(a2); //97
int a3 = 0XFA; // 0X开头的数据是十六进制
System.out.println(a3);
}
}
1.3 十六进制

2. 类型及转换
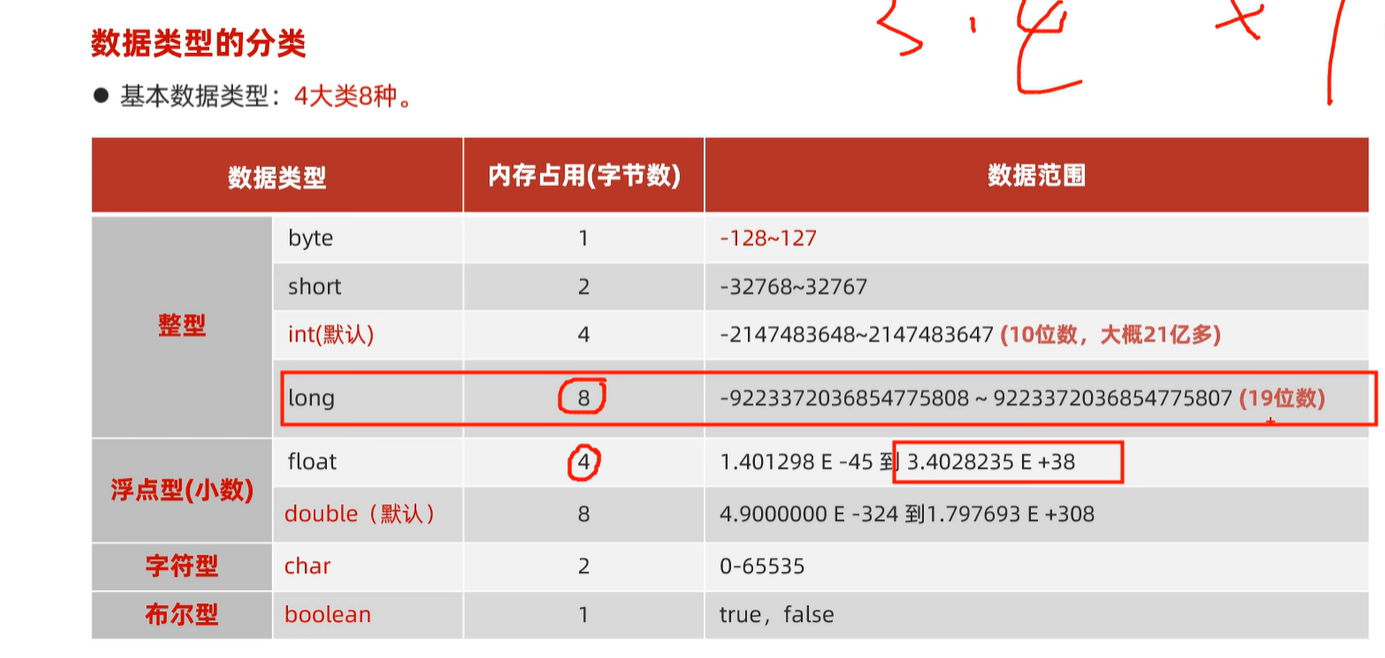
2.1 基本数据类型
1字节等于8位(2进制)
2.2 自动类型转换

package com.itheima.type;
public class TypeConversionDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:理解自动类型转换机制。
byte a = 12;
int b = a; // 发生了自动类型转换了
System.out.println(a);
System.out.println(b);
int c = 100; // 4
double d = c;// 8 发生了自动类型转换了
System.out.println(d);
char ch = 'a'; // 'a' 97 => 00000000 01100001
int i = ch; // 发生了自动类型转换了 => 00000000 00000000 00000000 01100001
System.out.println(i); //97
}
}
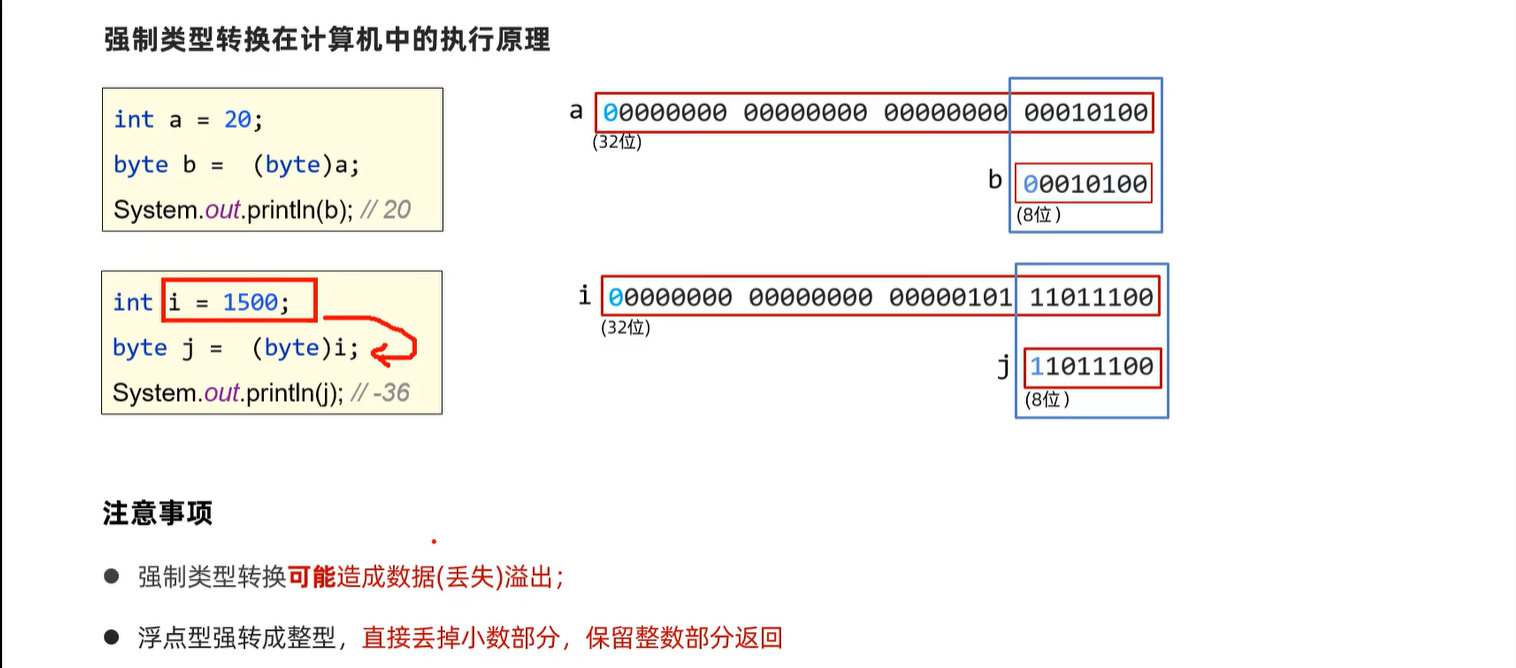
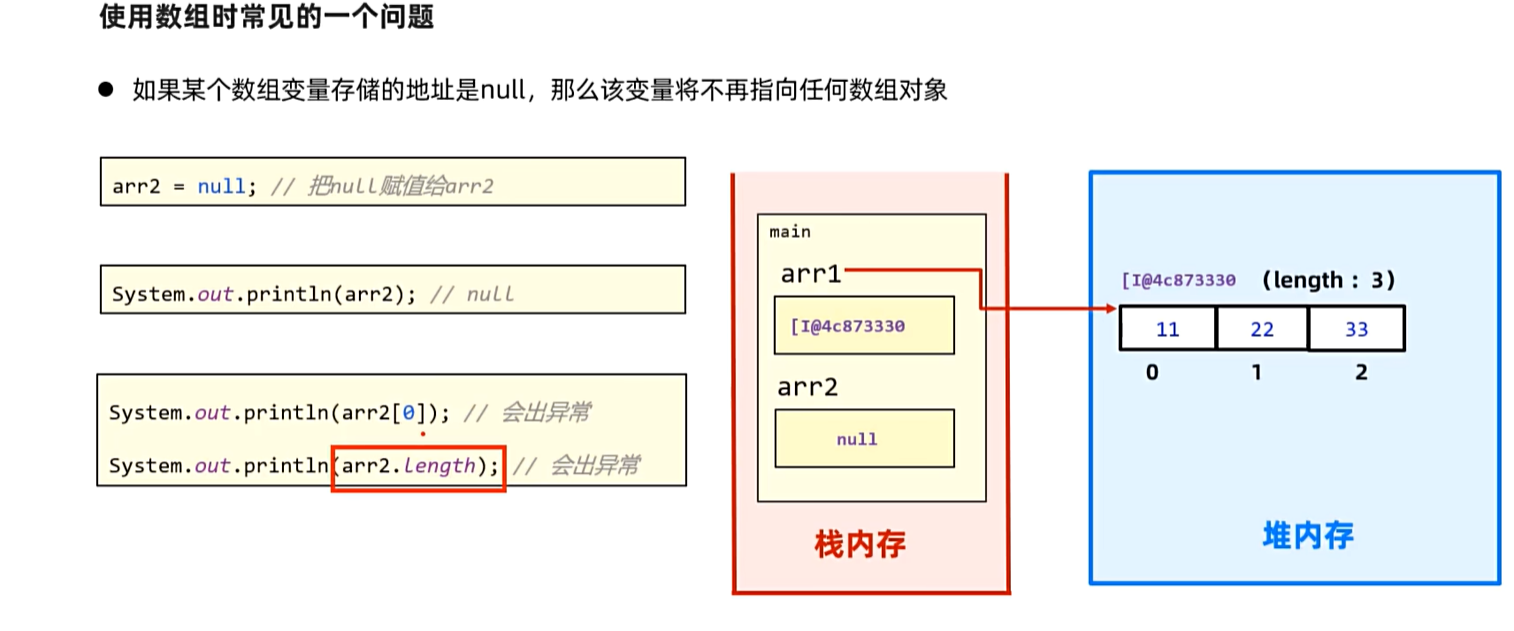
3. 数组
3.1数组在内存中的执行原理
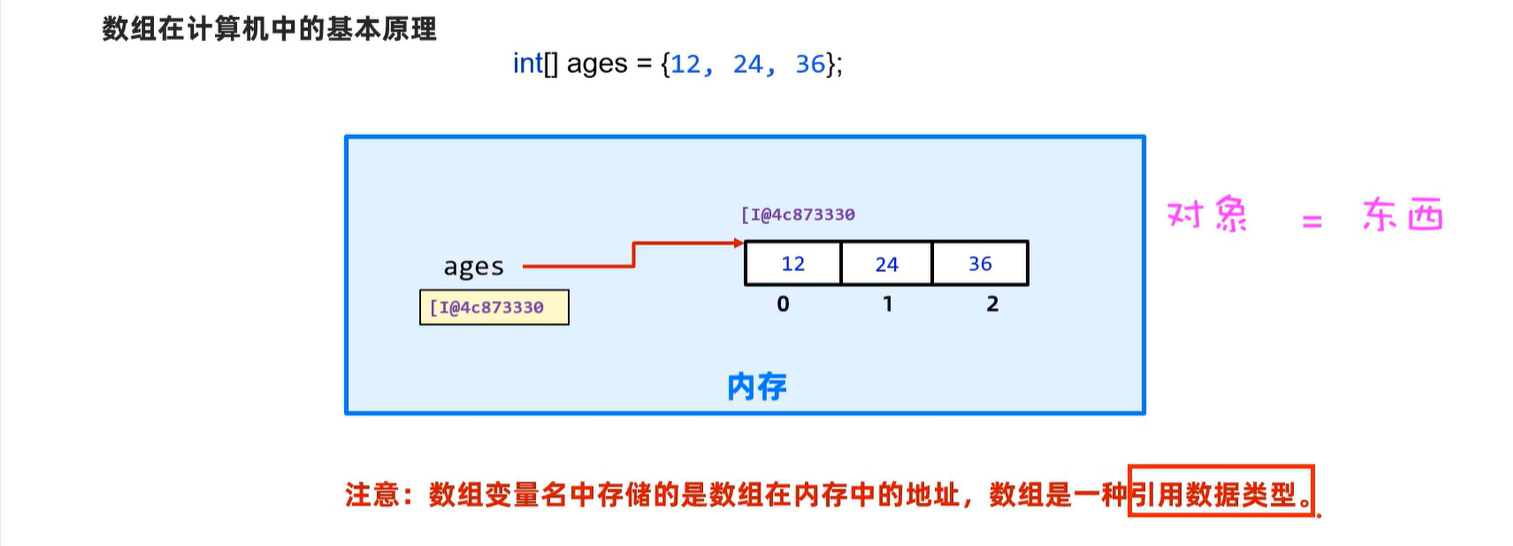
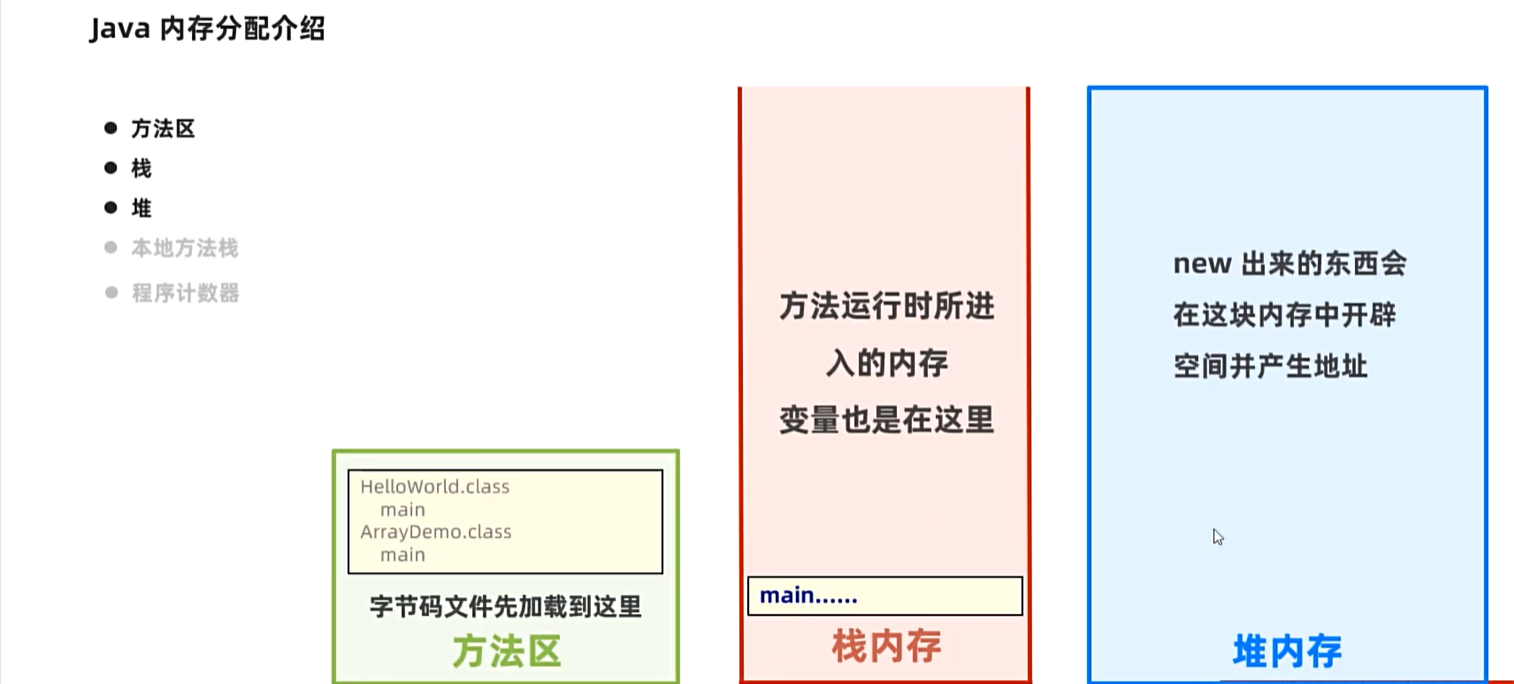
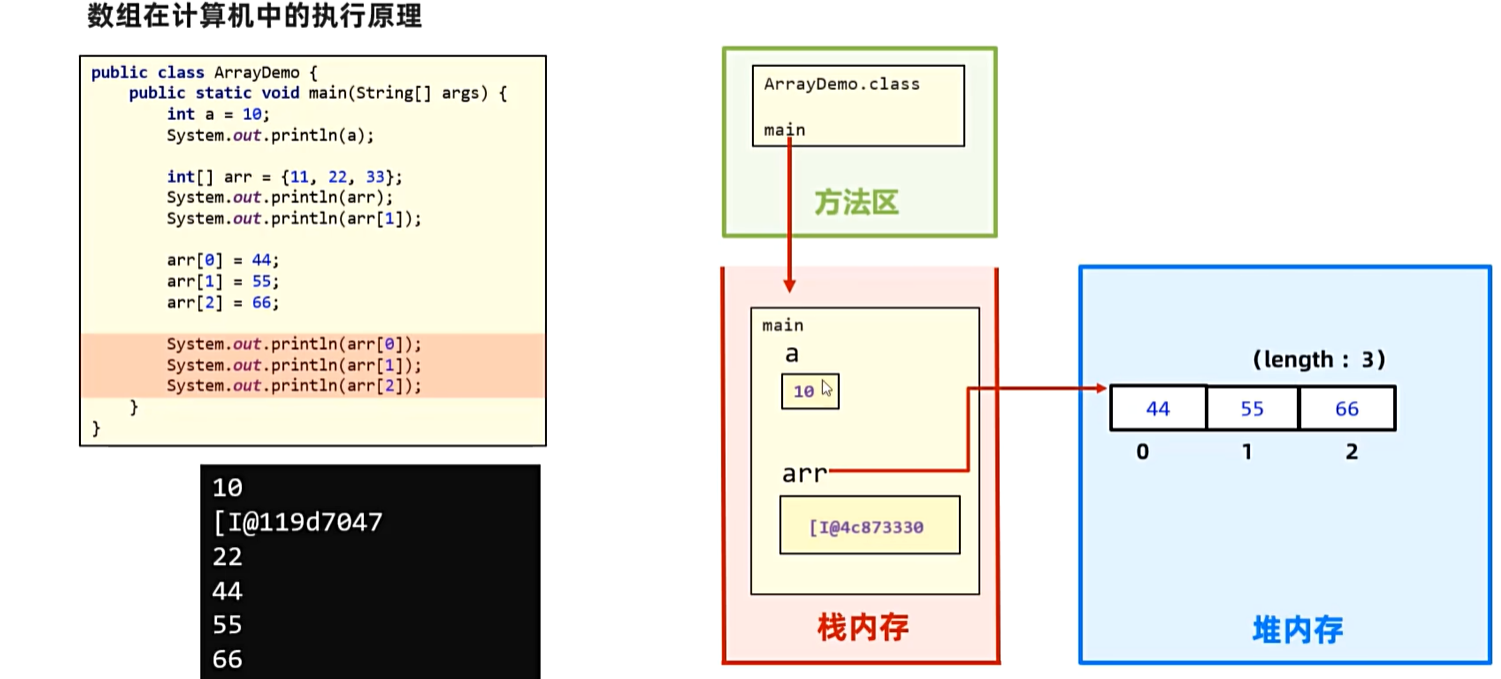
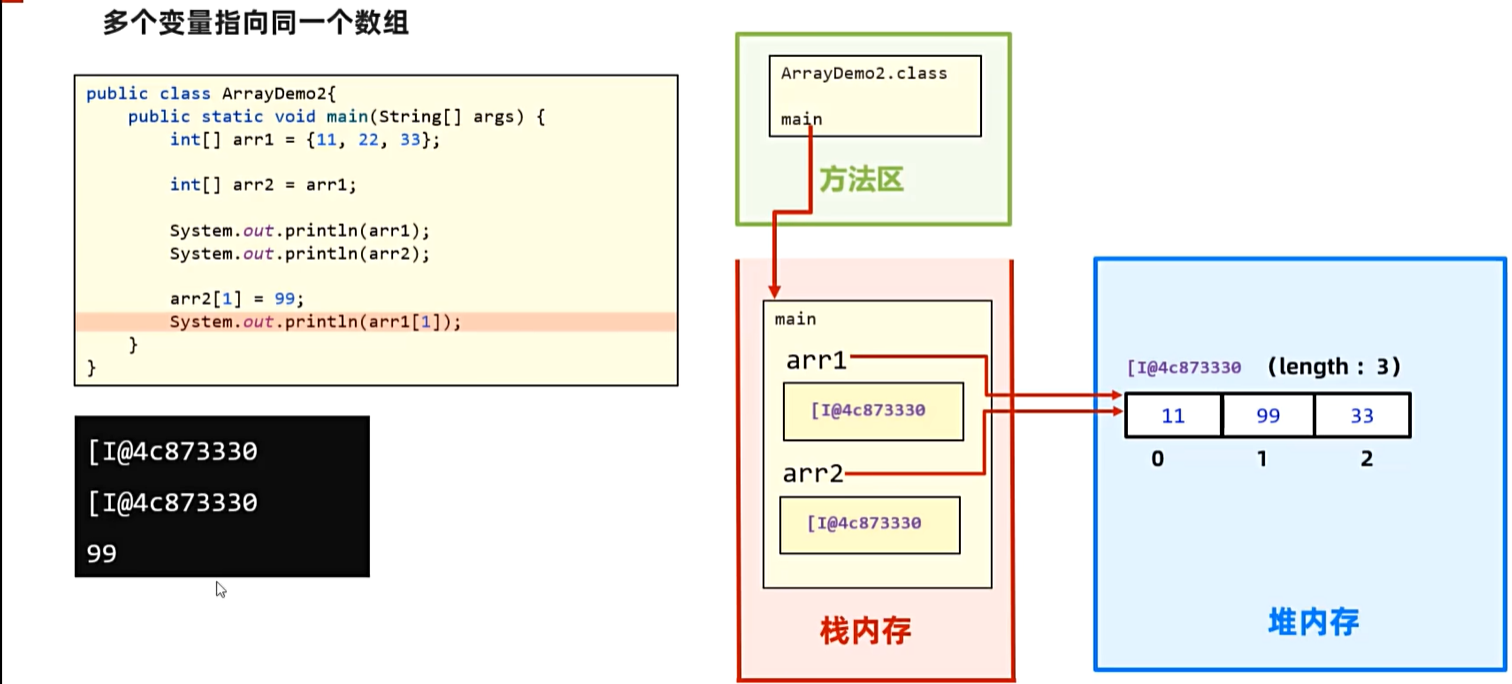
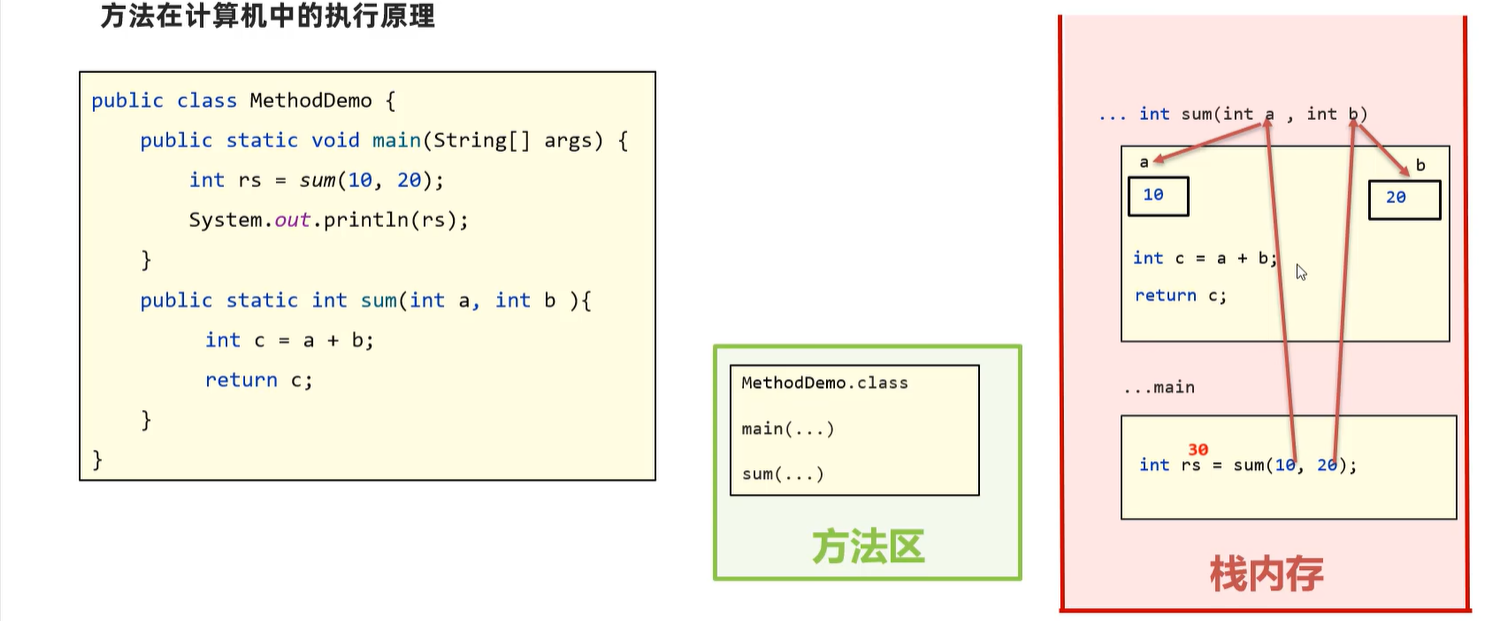
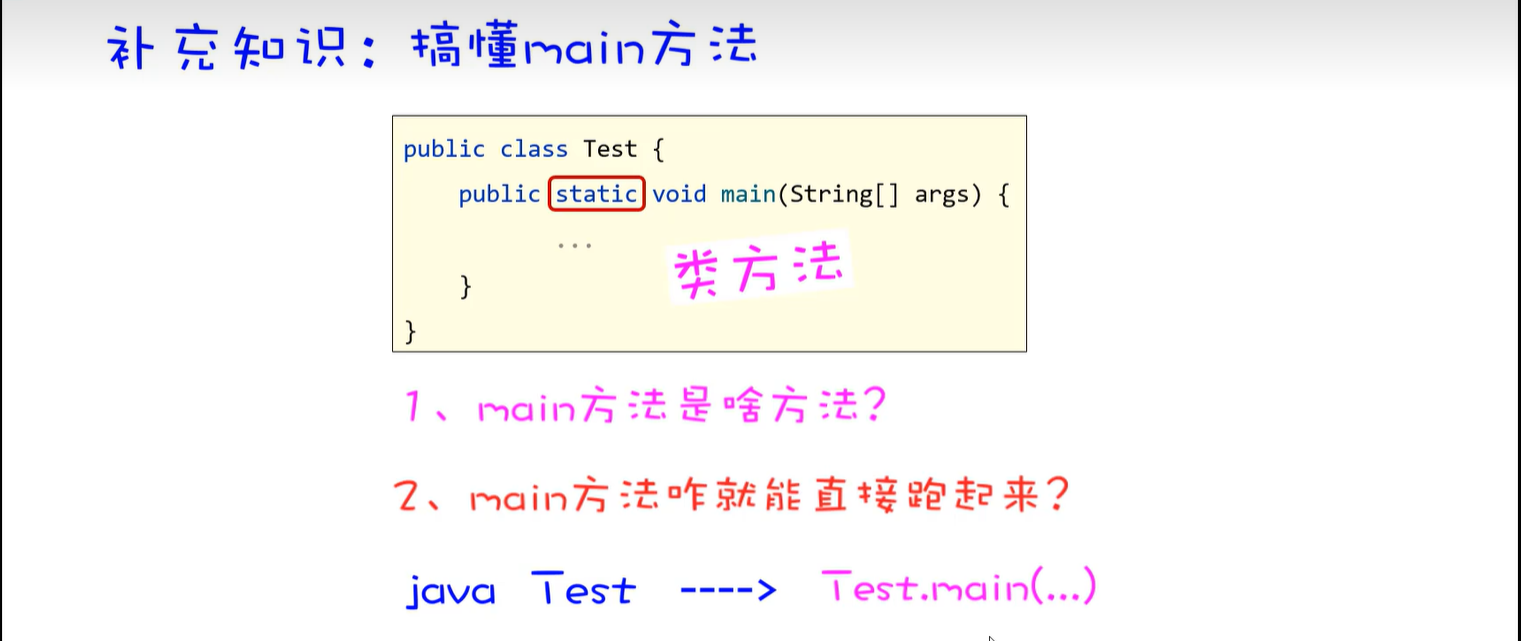
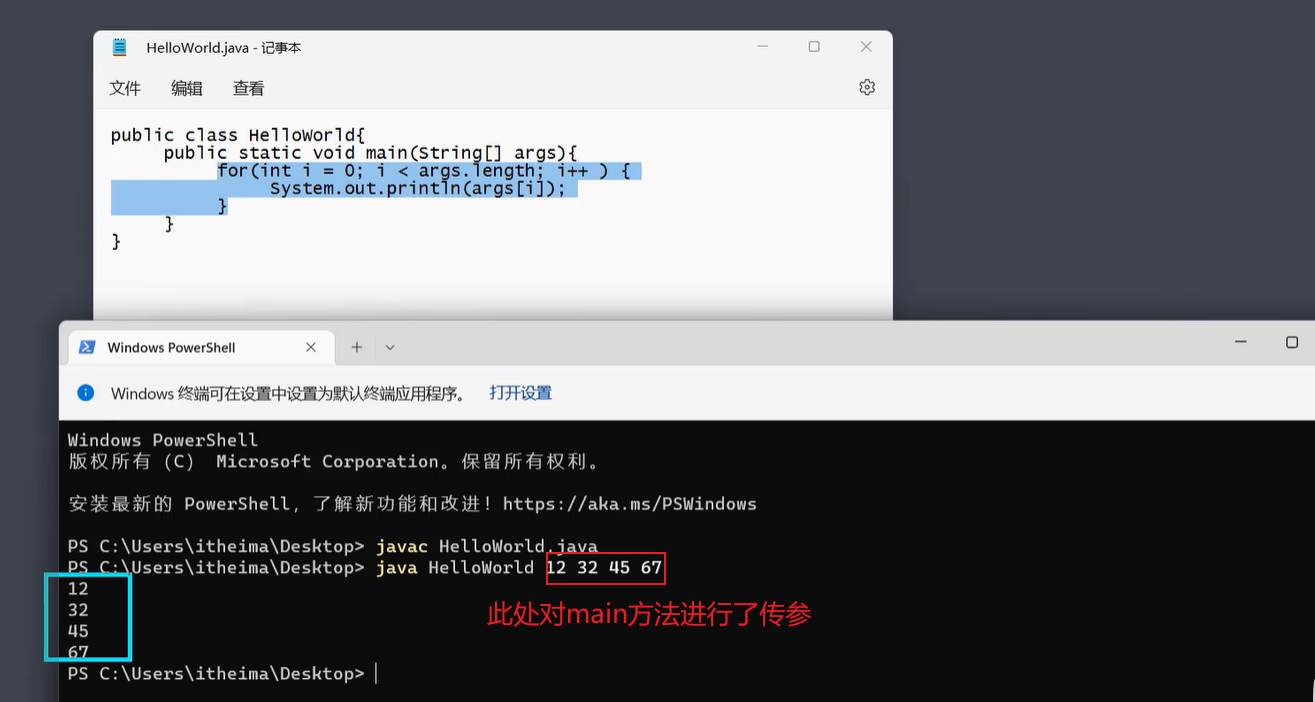
4. 方法
4.1在内存中的执行原理

4.2 java中的方法传递

4.2.1 基本数据类型传递
package com.itheima.parameter;
public class MethodDemo1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:理解方法的参数传递机制:值传递。
int a = 10;
change(a); // change(10);
System.out.println("main:" + a); // 10
}
public static void change(int a){
System.out.println("change1:" + a); // 10
a = 20;
System.out.println("change2:" + a); // 20
}
}
4.2.2 引用数据类型传递
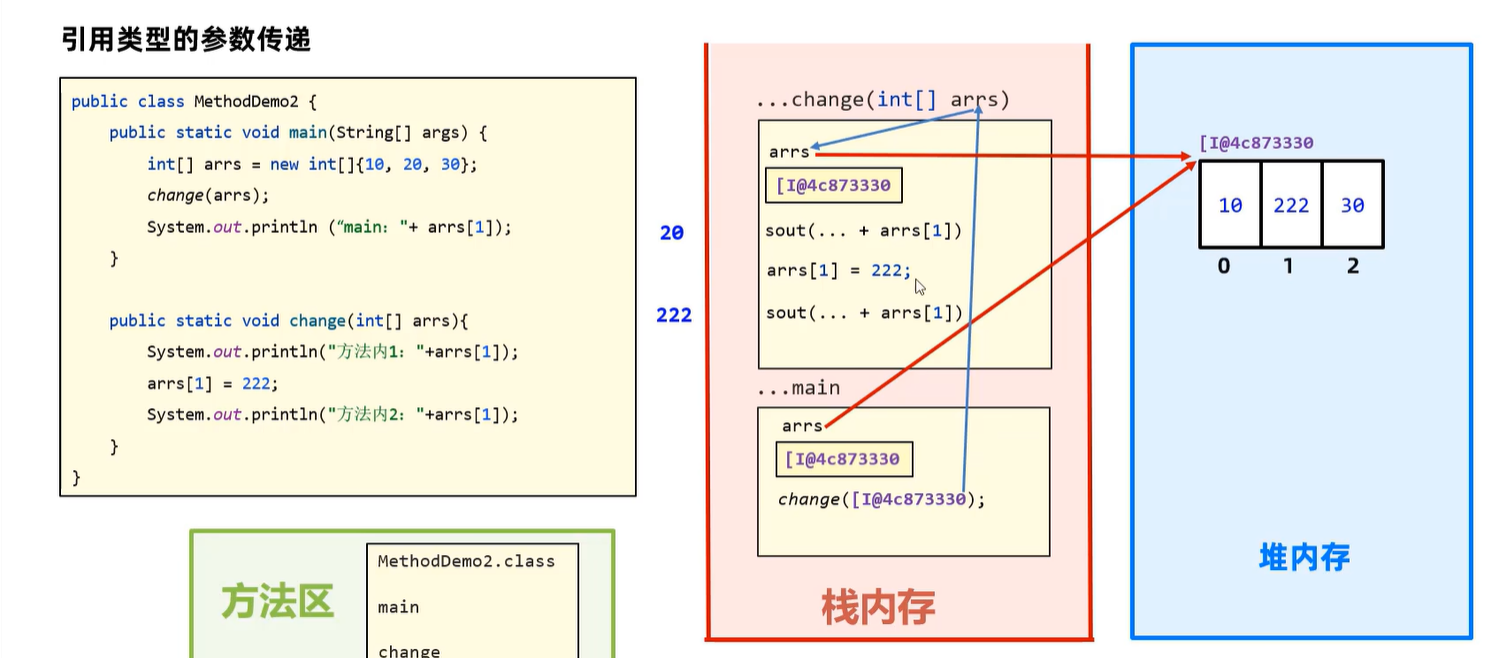
package com.itheima.parameter;
public class MethodDemo2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:理解引用类型的参数传递机制:值传递的。
int[] arrs = new int[]{10, 20, 30};
change(arrs);
System.out.println("main:" + arrs[1]); //222
}
public static void change(int[] arrs){
System.out.println("方法内1:" + arrs[1]); //20
arrs[1] = 222;
System.out.println("方法内2:" + arrs[1]); //222
}
}
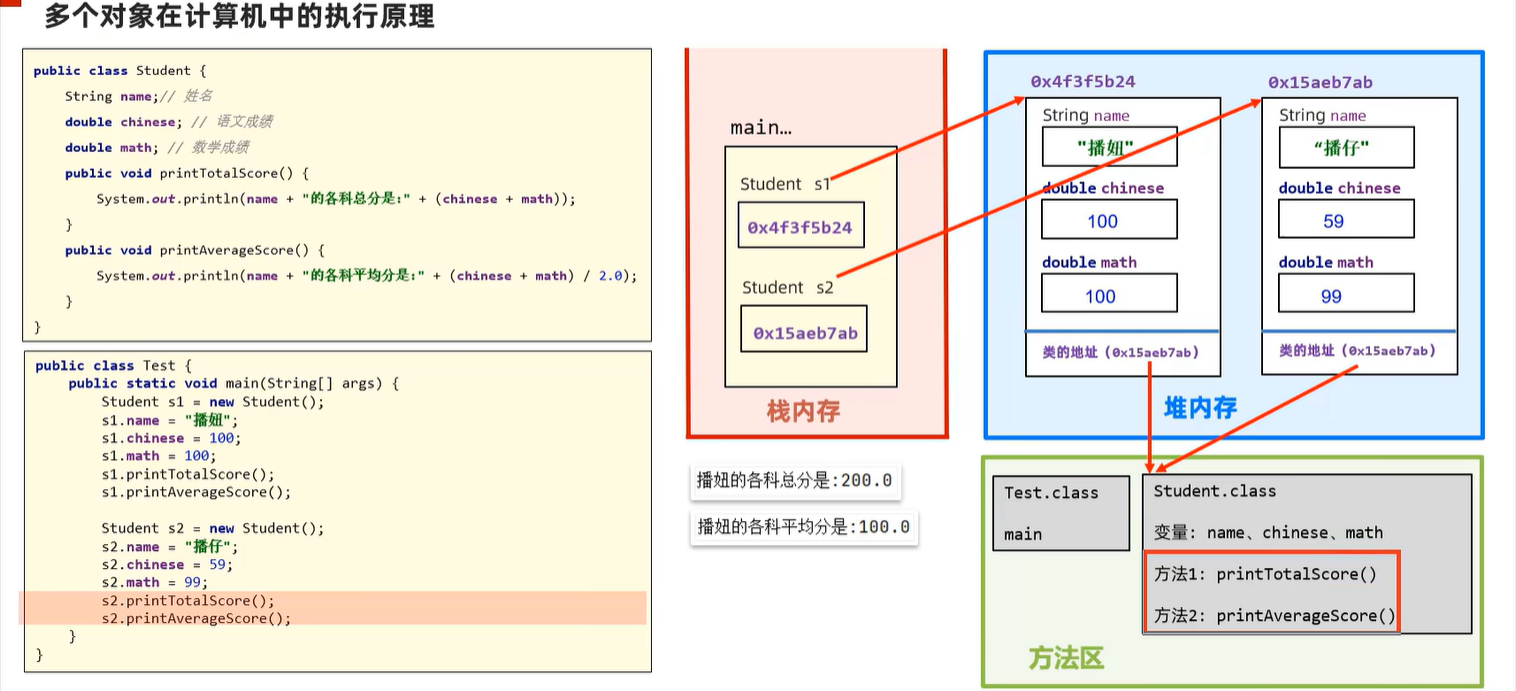
5. 对象
5.1 对象在内存中的执行原理
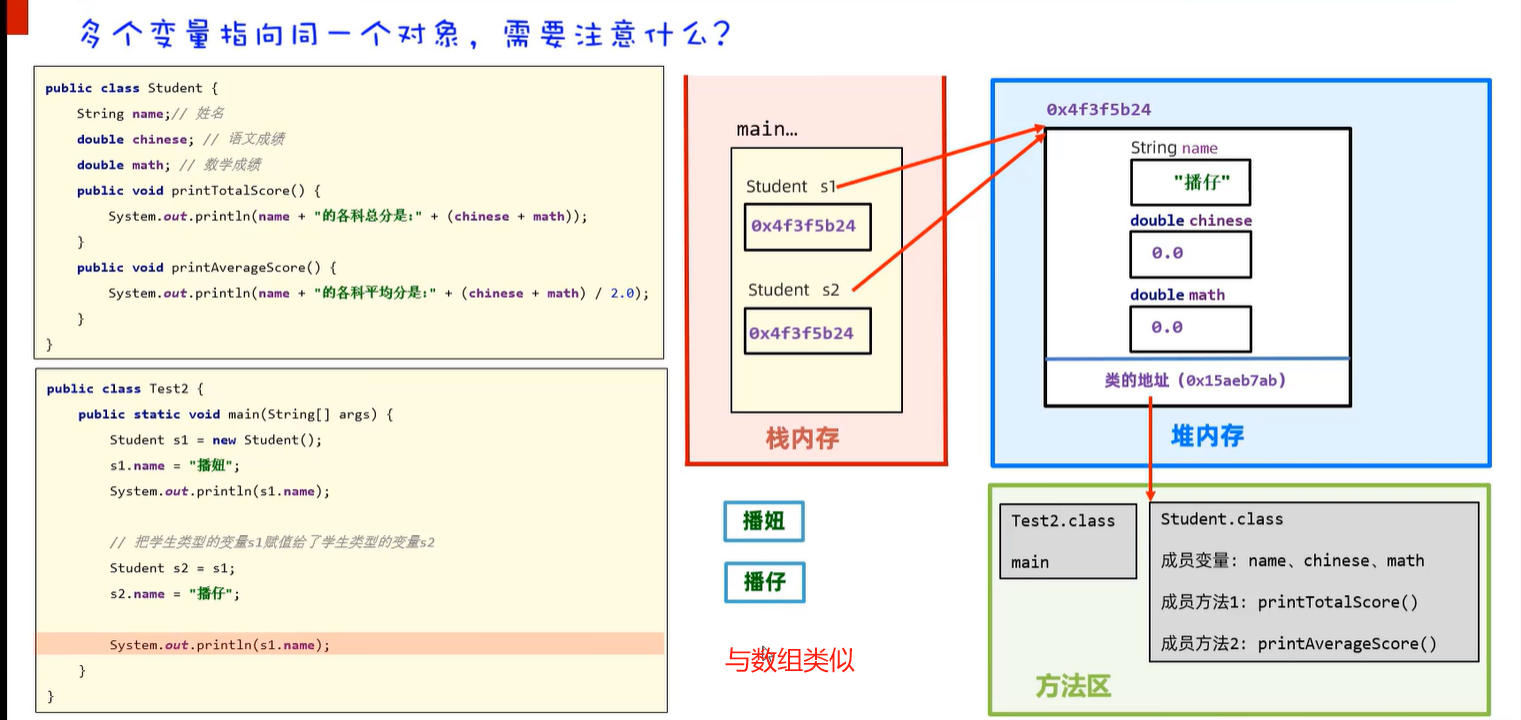
5.2 this的执行原理
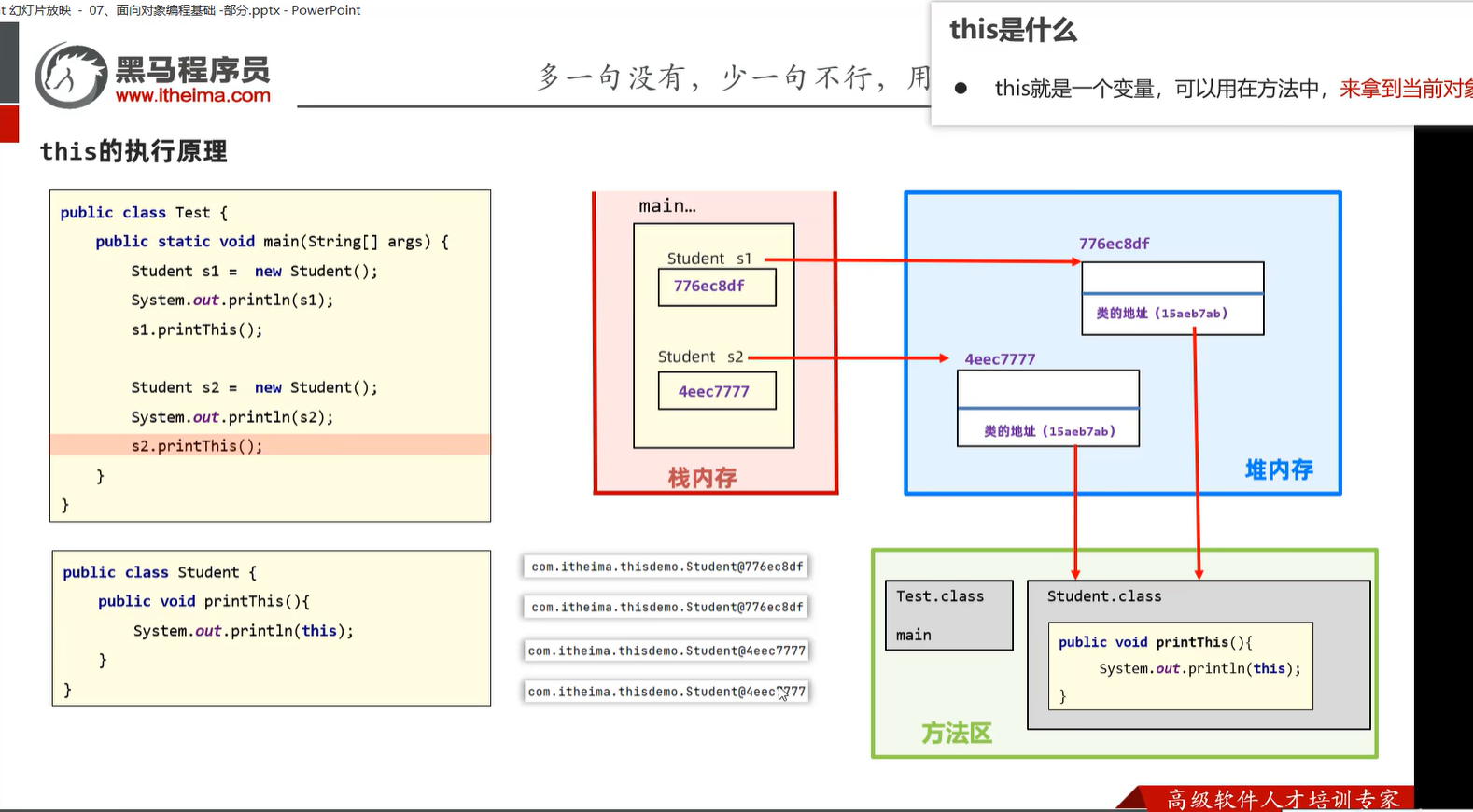
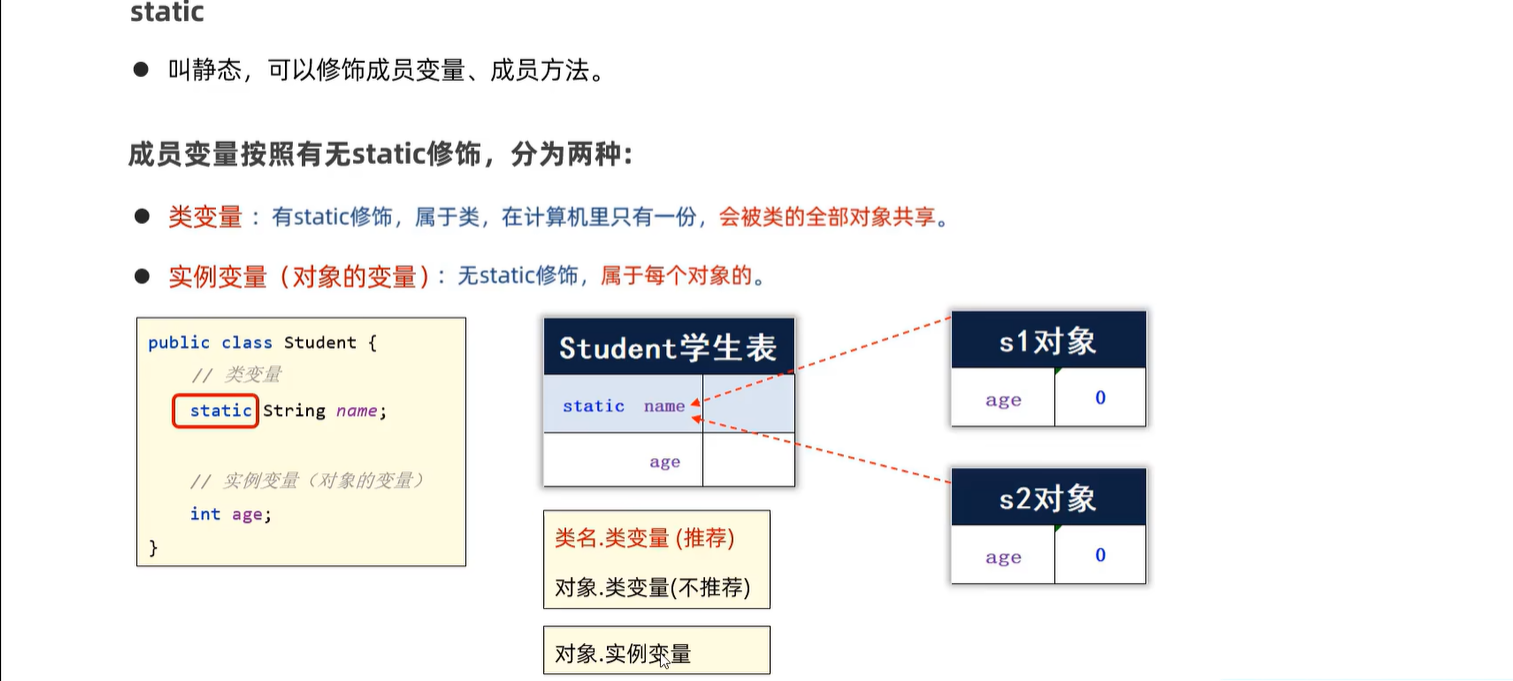
5.3 static的用法
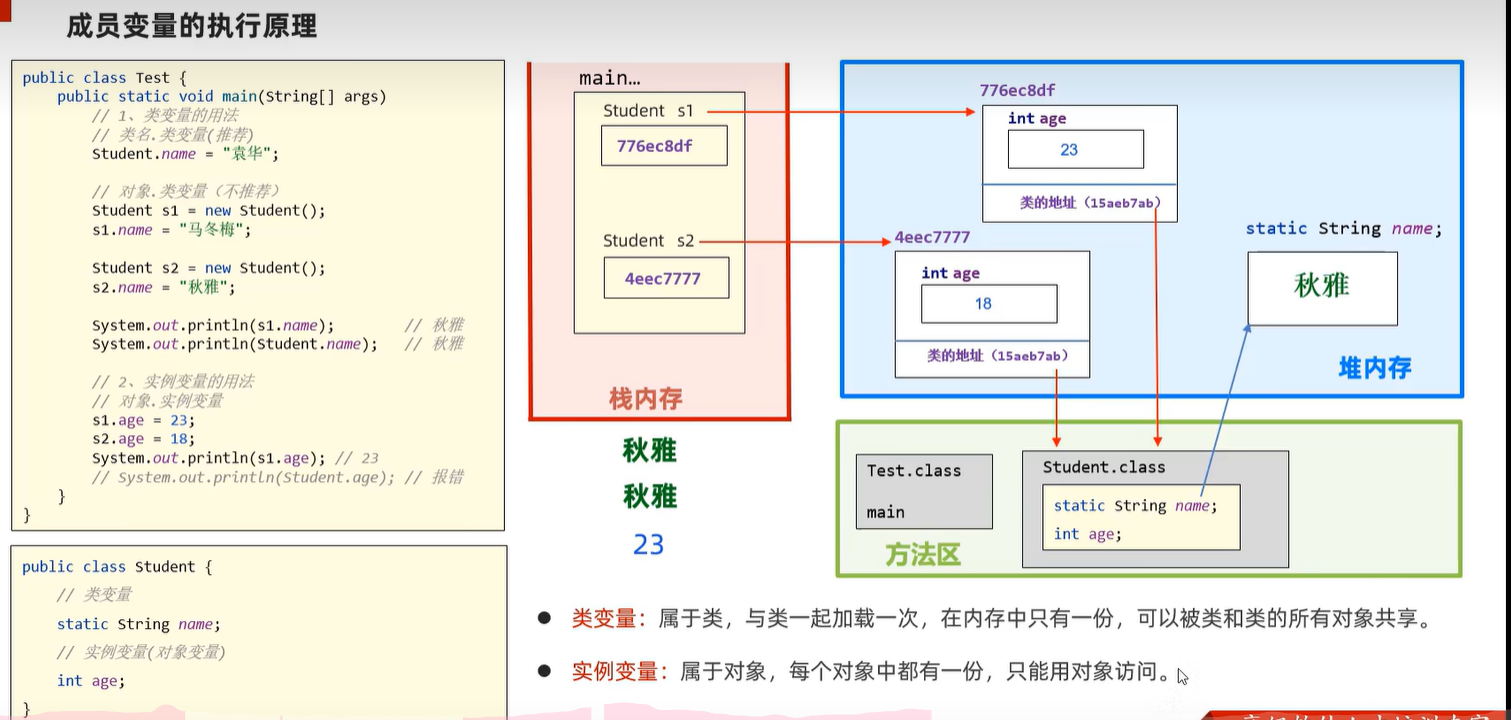
5.4 成员变量的执行原理
5.5 成员方法

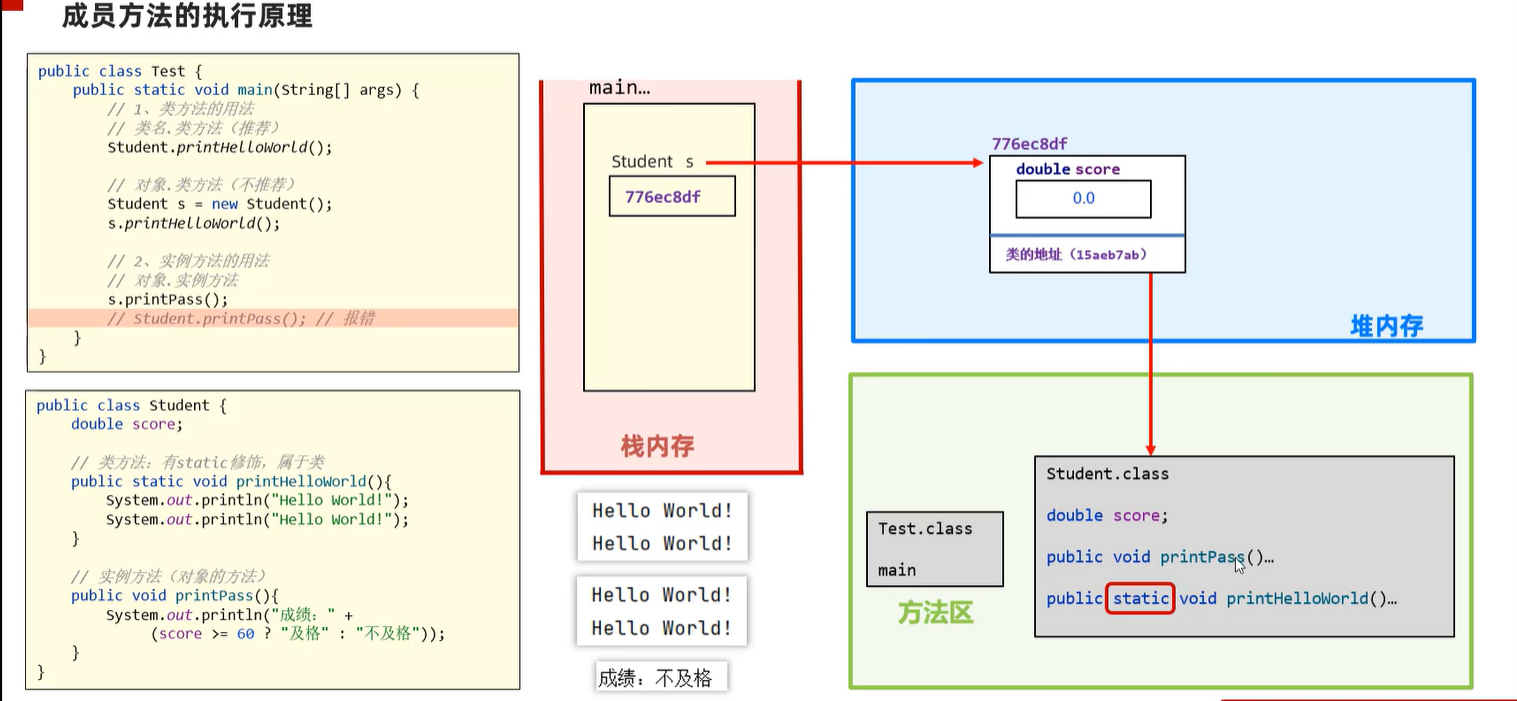
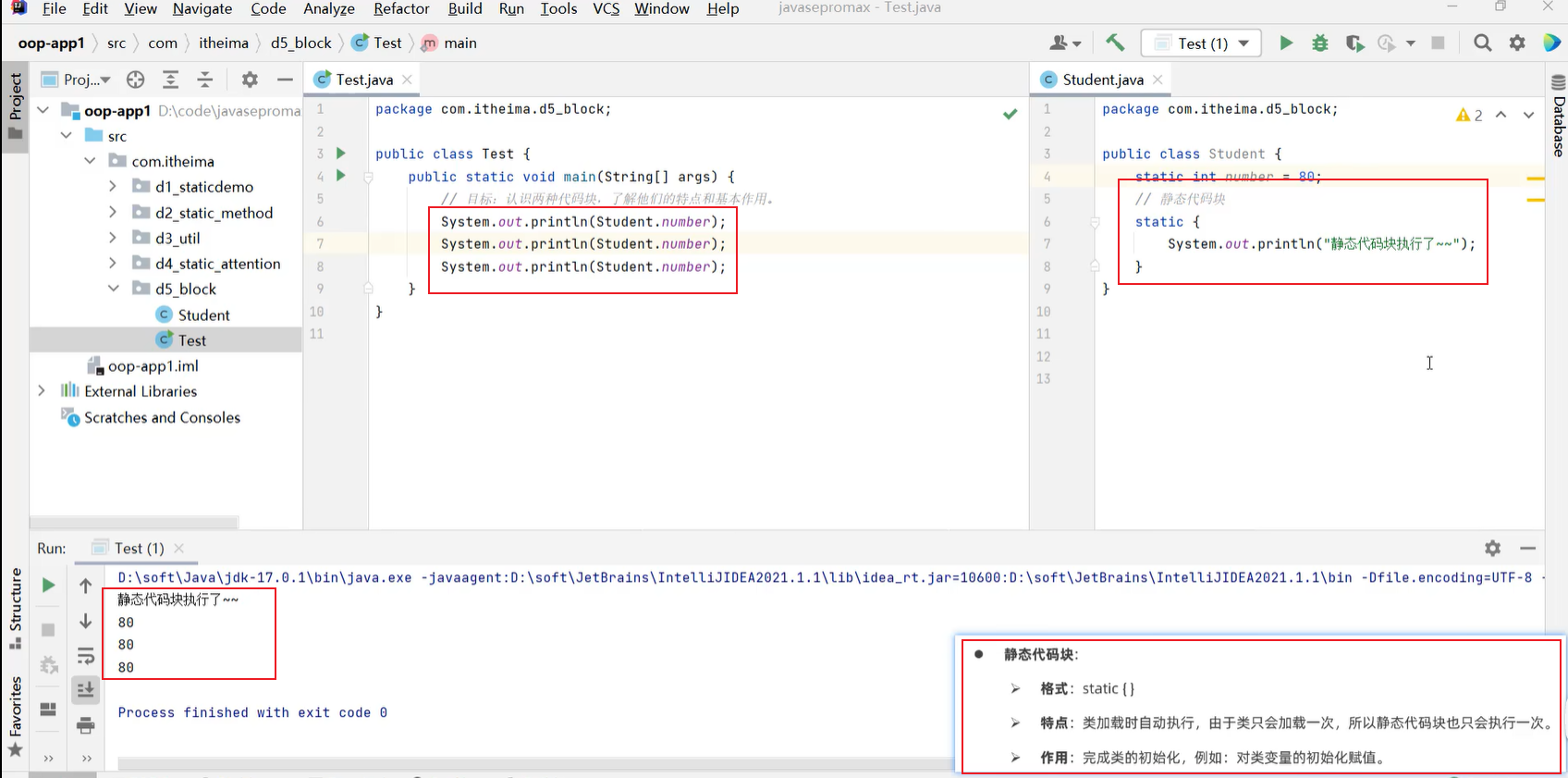
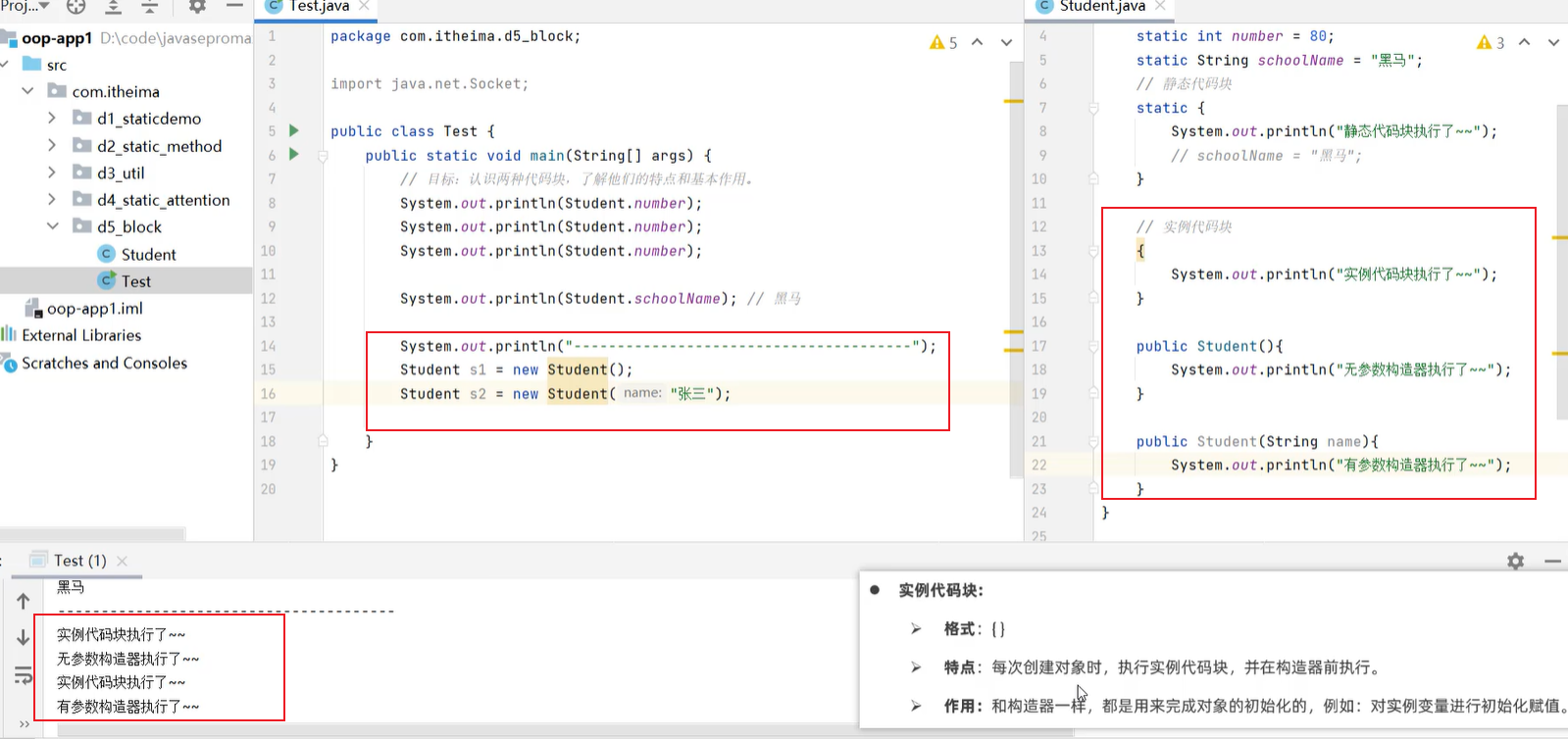
5.6 静态代码块

5.7 实例代码块

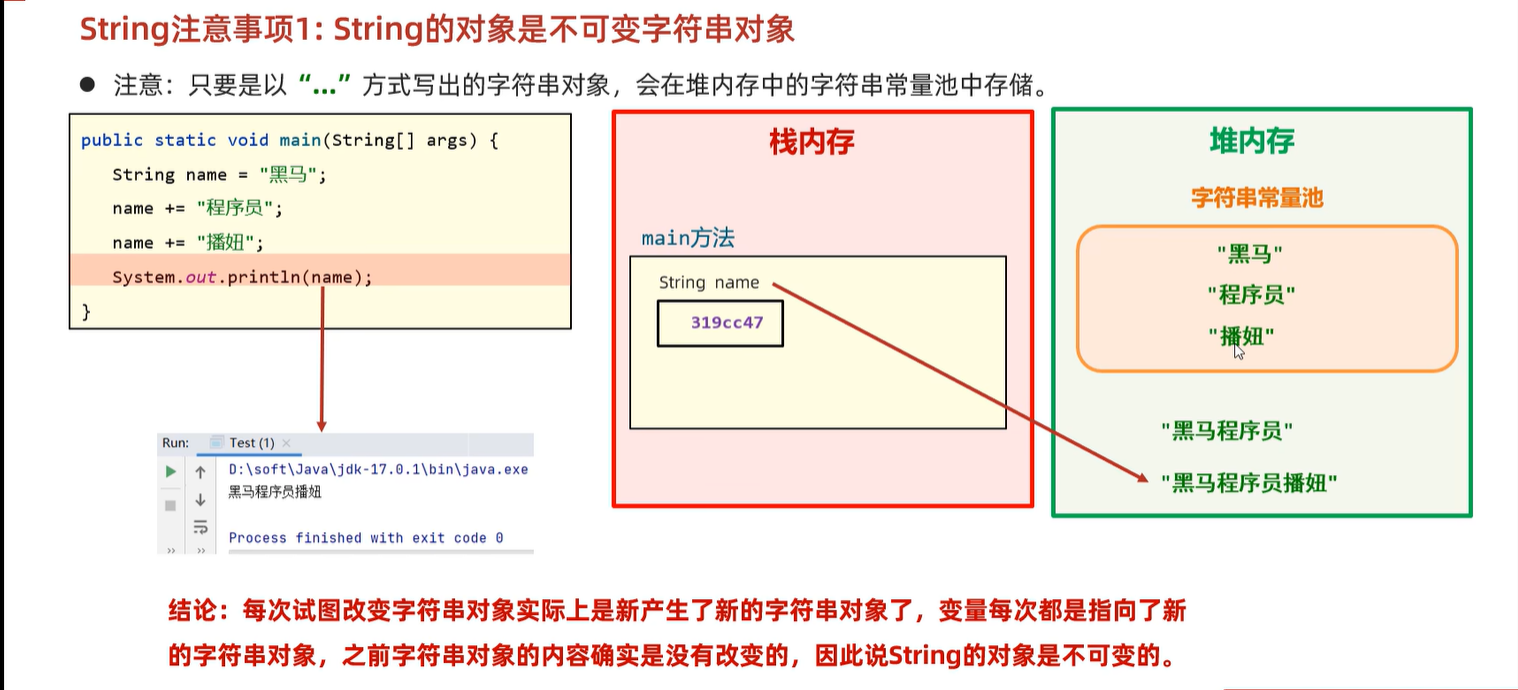
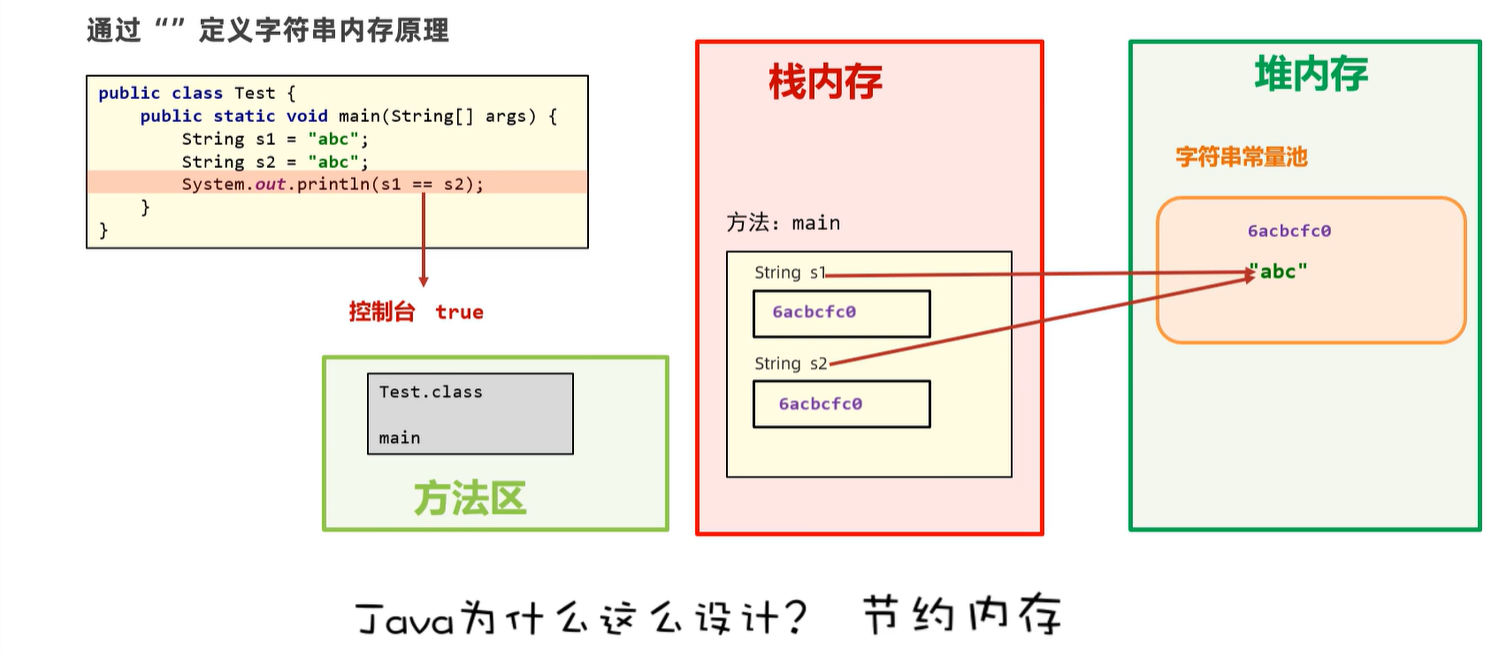
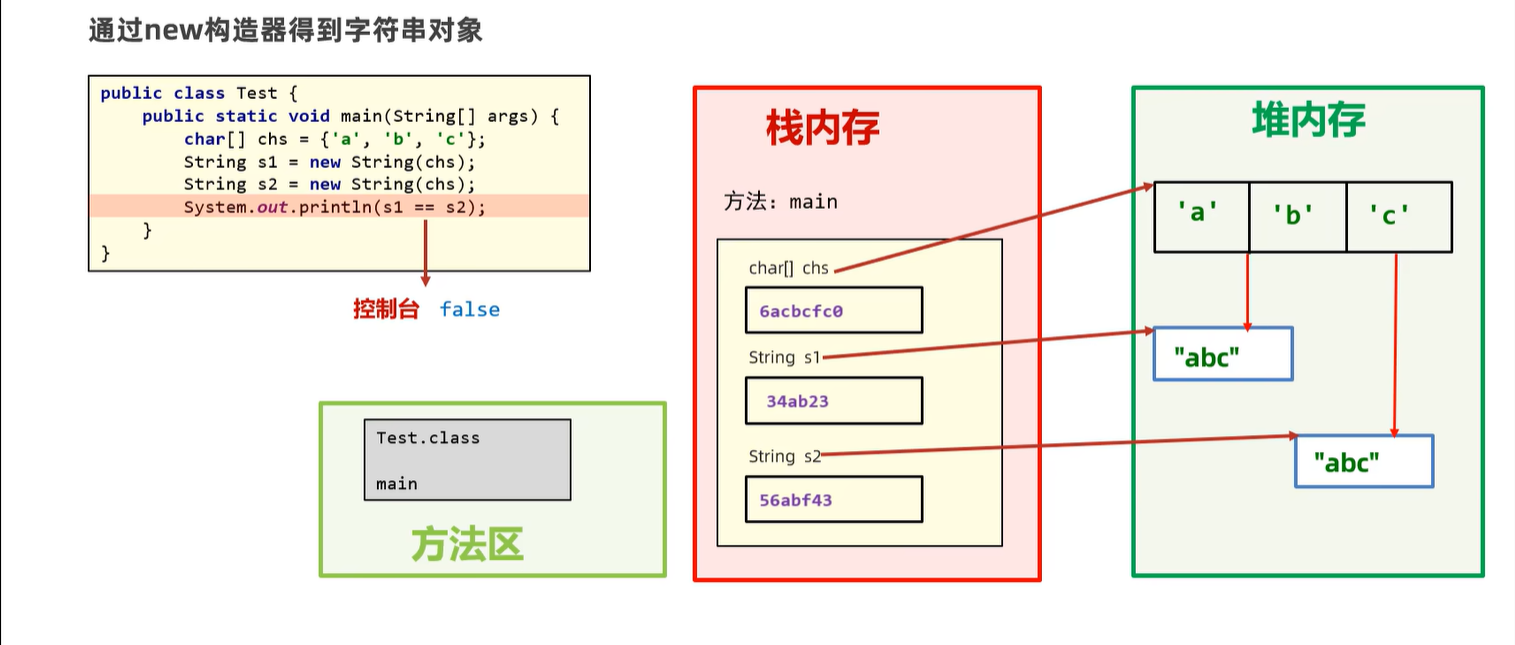
6. string


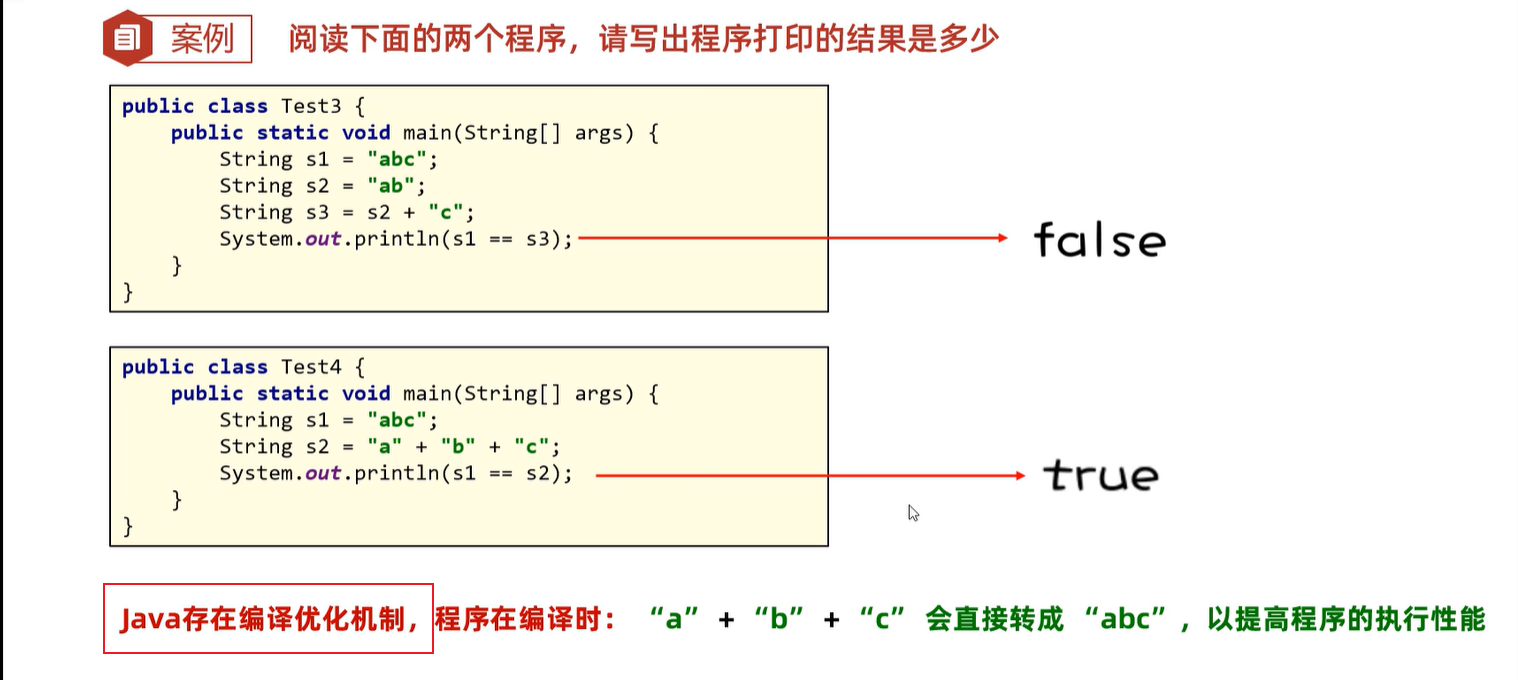
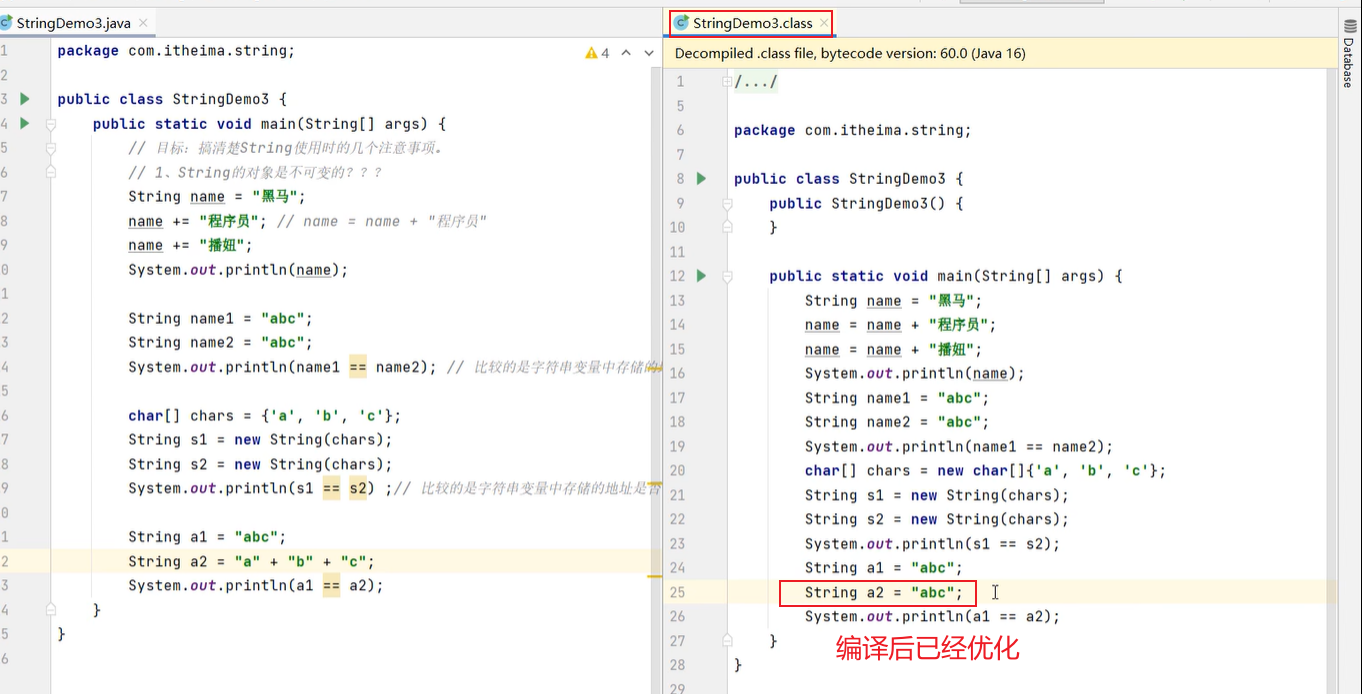
7. 继承

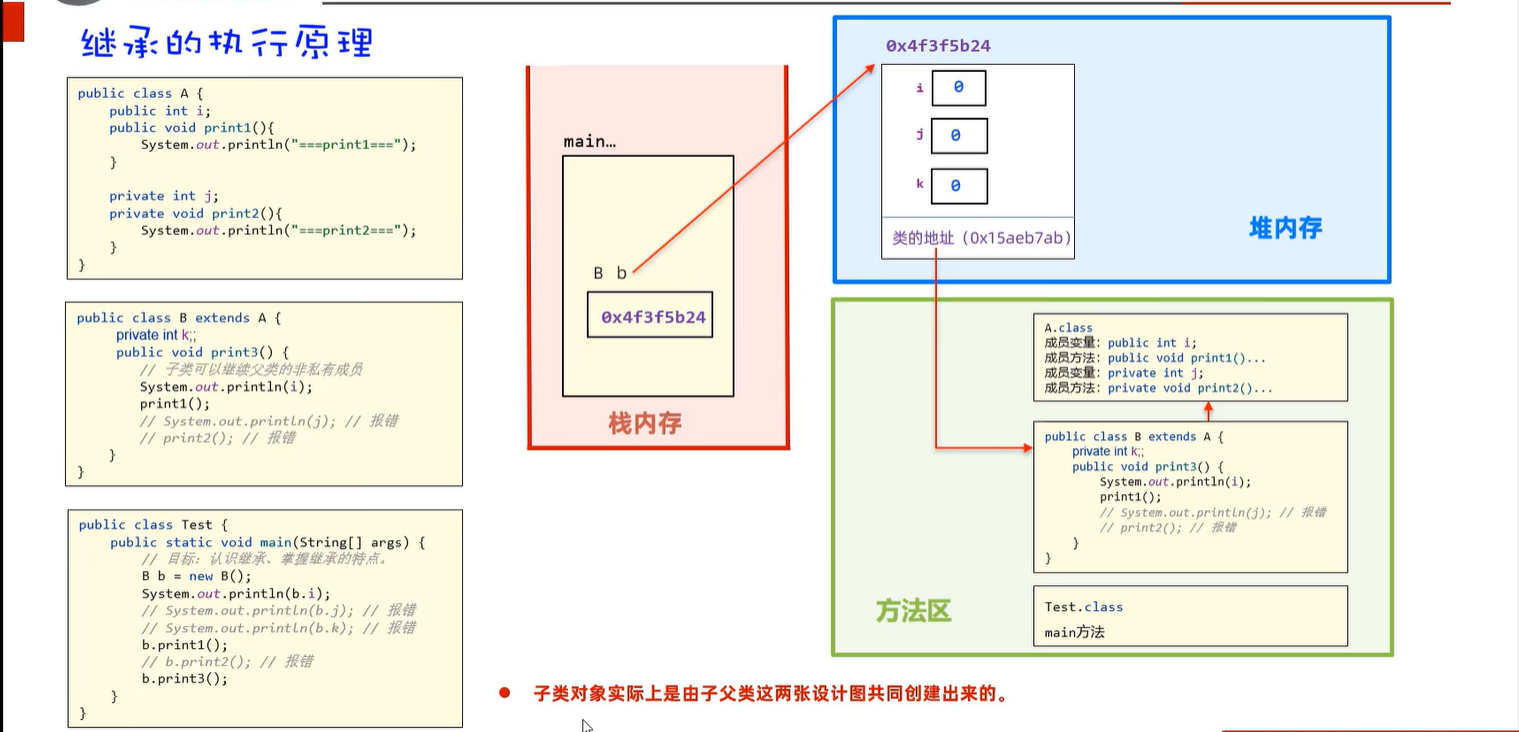
7.1 继承的执行原理
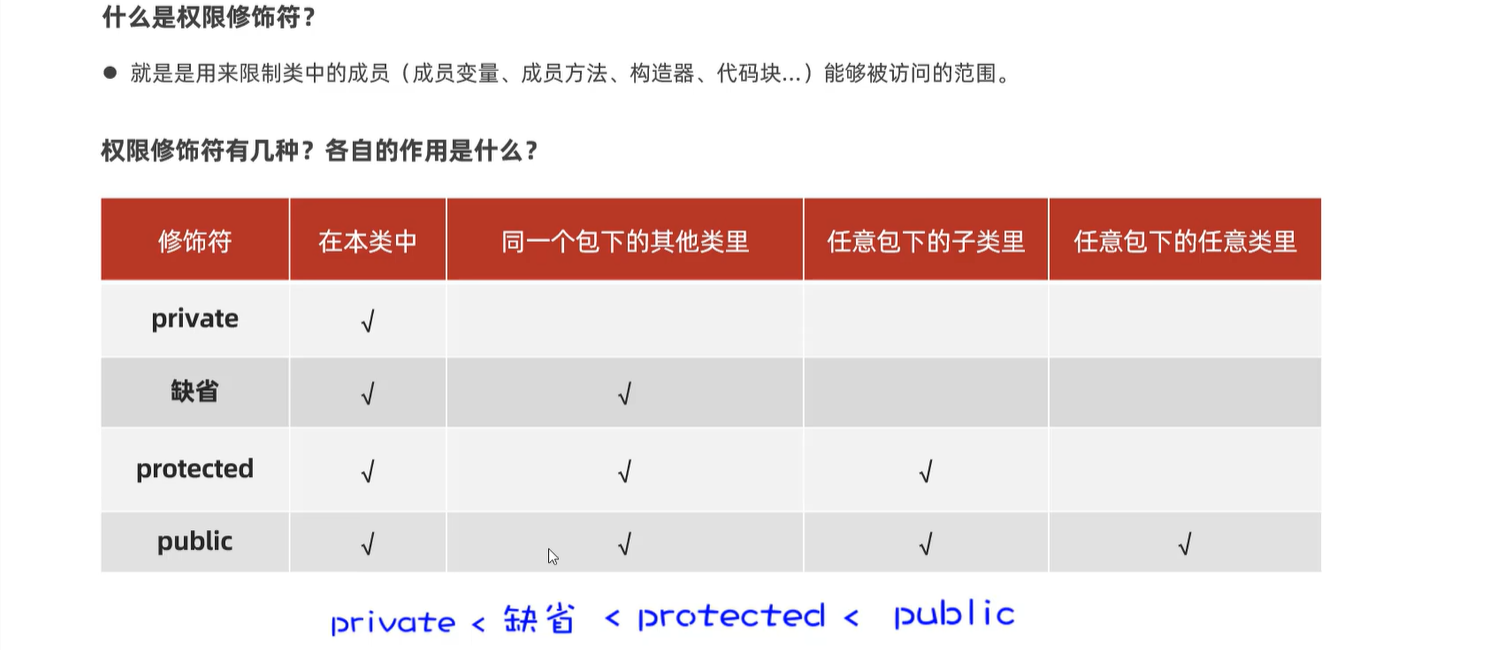
7.2 权限修饰符

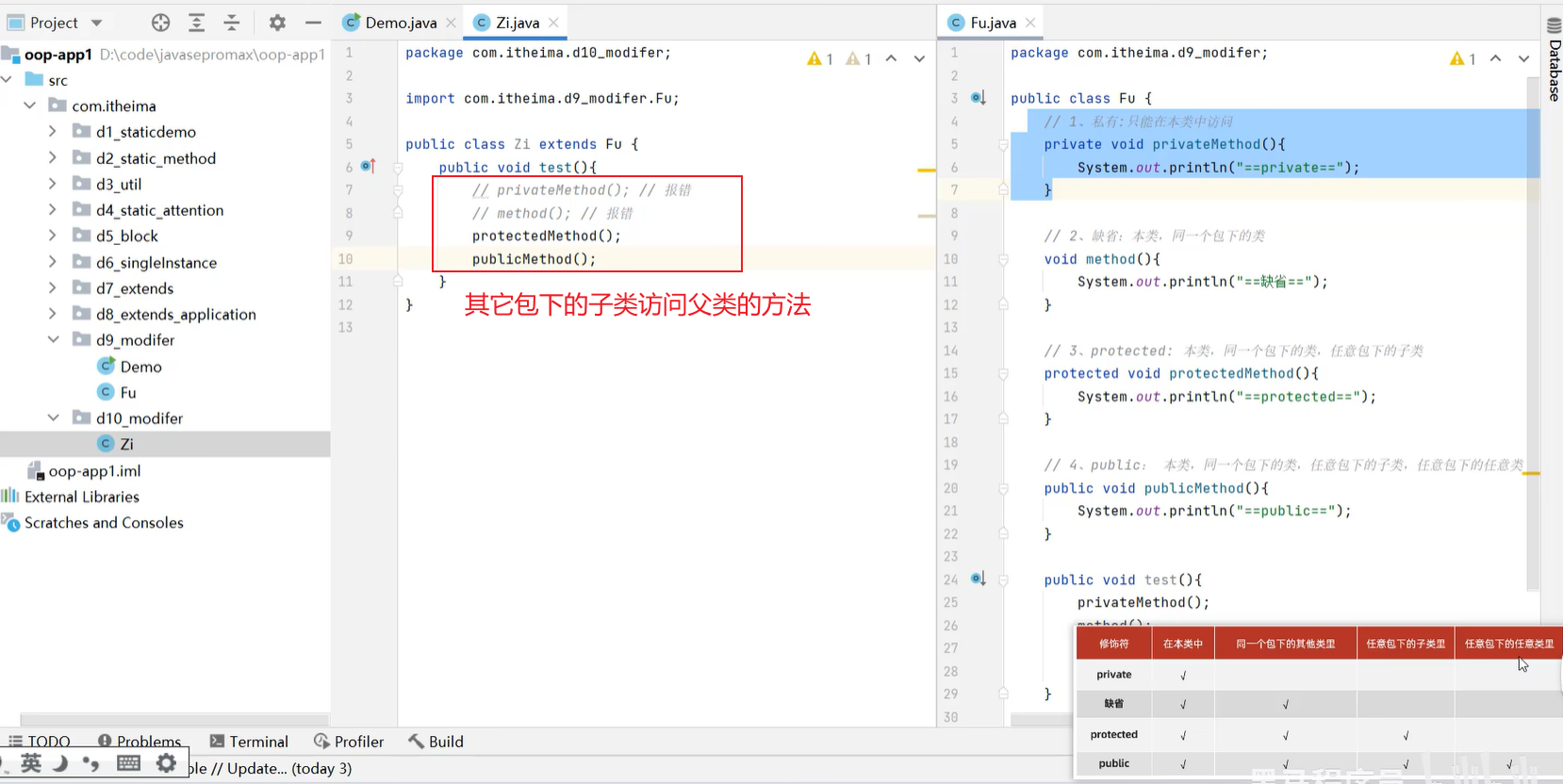
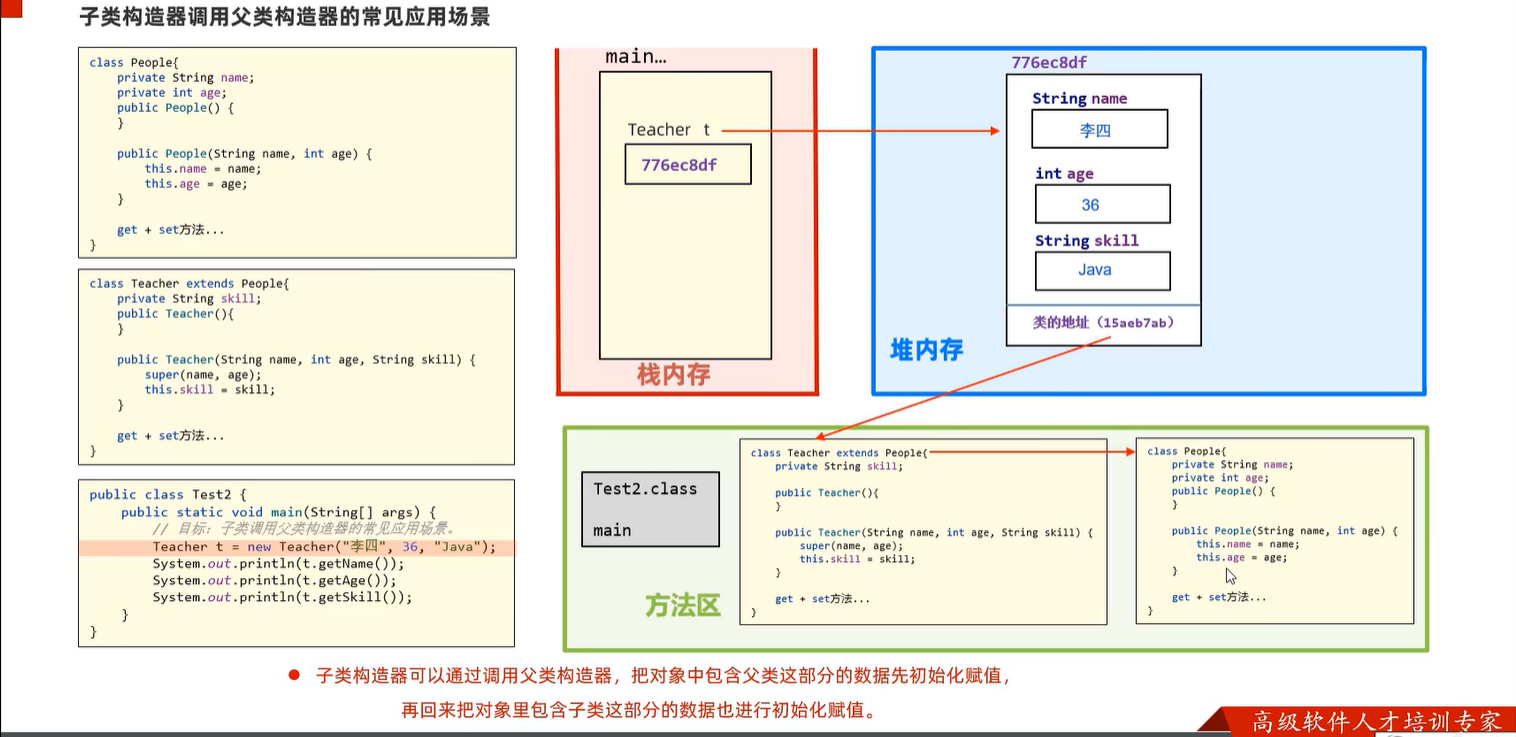
7.3 子类构造器

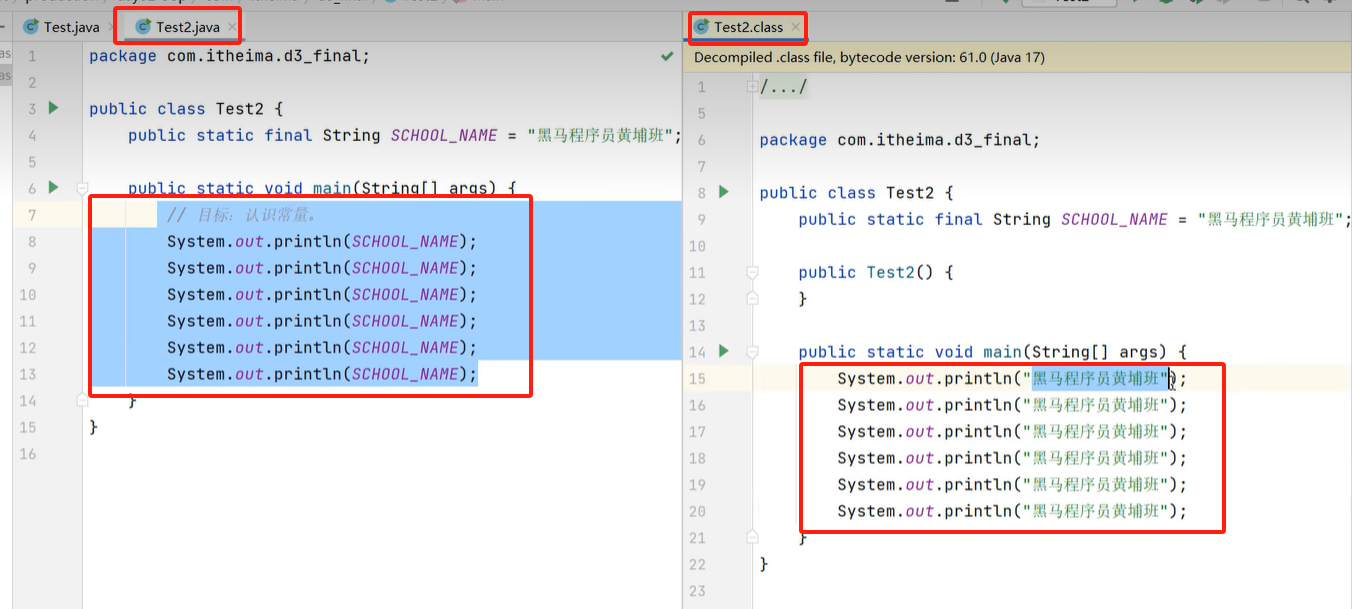
7.4 final

package com.itheima.d3_final;
public class Test {
/**
* 常量: public static final修饰的成员变量,建议名称全部大写,多个单词下划线连接
*/
public static final String SCHOOL_NAME = "黑马";
private final String name = "猪八戒"; // 这种用法没有意义,知道就行
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:认识final的作用。
// 3、final可以修饰变量总规则:有且仅能赋值一次
/* 变量:
一,局部变量
二,成员变量
1、静态成员变量
2、实例成员变量
*/
final int a;
a = 12;
// a = 13; // 第二次赋值,出错了
final double r = 3.14;
// r = 0.1; // 第二次赋值,出错了
final int[] arr = {11, 22, 33};
// arr = null; // 第二次赋值,出错了
arr[1] = 222;
// schoolName = "白马"; // 第二次赋值,出错了
Test t = new Test();
// t.name = "孙悟空";// 第二次赋值,出错了
}
public static void buy(final double z){
// z = 0.1;// 第二次赋值,出错了
}
}
// 1、final修饰类,类不能被继承了
final class A{}
//class B extends A{}
// 2、final修饰方法,方法不能被重写了
class C{
public final void test(){
}
}
class D extends C{
// @Override
// public void test() {
//
// }
}

final int[] arr = {11, 22, 33};
// arr = null; // 第二次赋值,出错了,final修饰地址不能改变
arr[1] = 222; //值是可以改变的

8. 抽象类

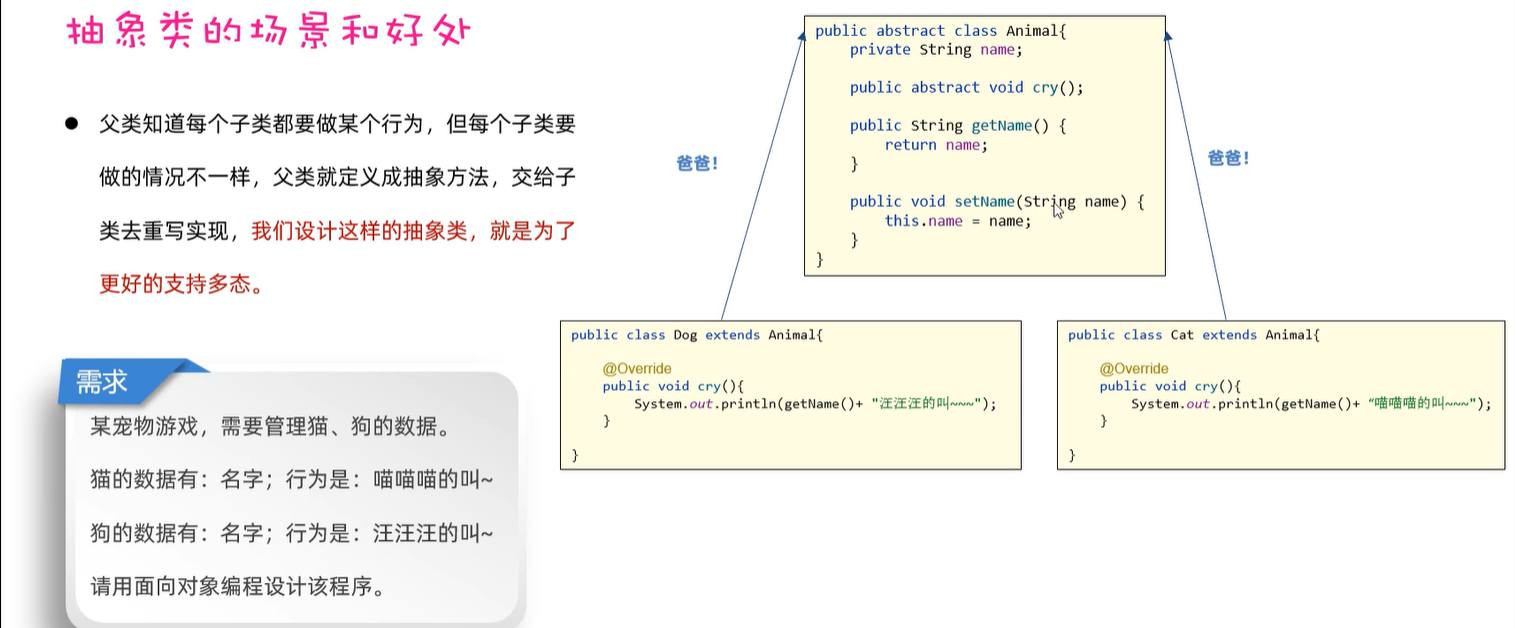
8.1 模板方法设计模式
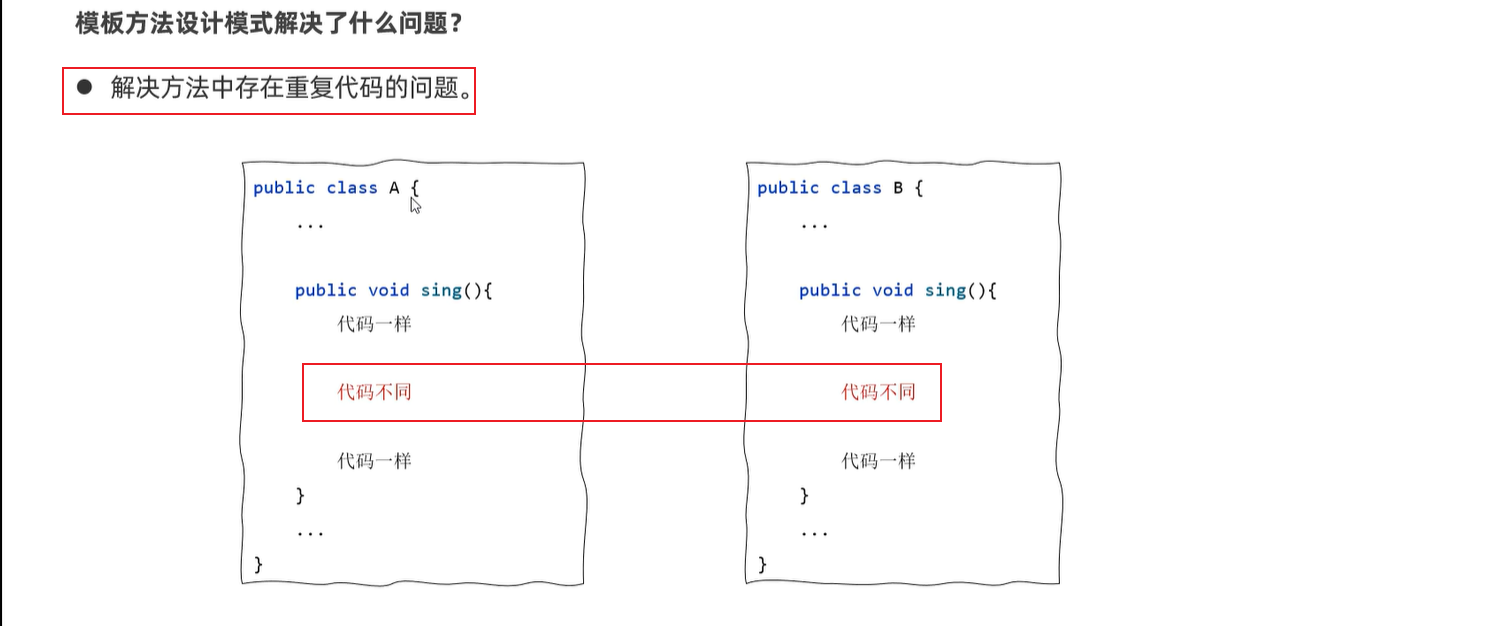


9. 接口

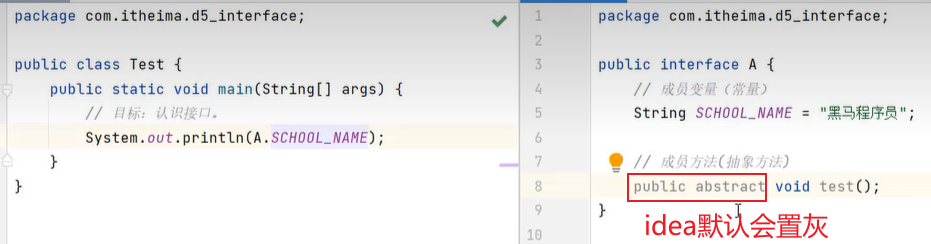
jdk 8 之后接口新增了三种方法

package com.itheima.d10_interface_jdk8;
public interface A {
/**
* 1、默认方法:必须使用default修饰,默认会被public修饰
* 实例方法:对象的方法,必须使用实现类的对象来访问。
*/
default void test1(){
System.out.println("===默认方法==");
test2();
}
/**
* 2、私有方法:必须使用private修饰。(JDK 9开始才支持的)
* 实例方法:对象的方法。
*/
private void test2(){
System.out.println("===私有方法==");
}
/**
* 3、静态方法:必须使用static修饰,默认会被public修饰
*/
static void test3(){
System.out.println("==静态方法==");
}
void test4();
void test5();
default void test6(){
}
}
10. 内部类


10.1 成员内部类


package com.itheima.d1_inner_class1;
public class Outer {
private int age = 99;
public static String a;
// 成员内部类
public class Inner{
private String name;
public static String schoolName; // JDK 16开始才支持定义静态成员的
private int age = 88;
public void test(){
System.out.println(age); //内部类可以访问外部类的成员变量
System.out.println(a);
int age = 66; //内部类、外部类变量名相同,如何访问
System.out.println(age);// 66
System.out.println(this.age);// 88
System.out.println(Outer.this.age);// 99
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public void test2(){
System.out.println(age);
System.out.println(a);
}
}
package com.itheima.d1_inner_class1;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:了解成员内部类和其特点。
Outer.Inner in = new Outer().new Inner();
in.test();
}
}
10.2 静态内部类

package com.itheima.d2_inner_class2;
public class Outer {
private int age = 99;
public static String schoolName;
// 静态内部类
public static class Inner{
private String name;
public static int a;
private int age = 88;
public void test(){
System.out.println(schoolName);
// System.out.println(age); //静态内部类与静态方法类似,只能访问外部类的静态成员变量, //不能访问实例变量
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
public static void test2(){
System.out.println(schoolName); //静态方法只能访问静态成员变量
// System.out.println(age); //静态方法不能访问实例变量
}
}
package com.itheima.d2_inner_class2;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:了解静态内部类。
Outer.Inner in = new Outer.Inner();
in.test();
}
}
10.3 局部内部类

10.4 匿名内部类

利用之前的子类去实现功能
package com.itheima.d3_inner_class3;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:认识匿名内部类,并掌握其作用。
Animal a = new Cat();
a.cry();
}
}
class Cat extends Animal{
@Override
public void cry() {
System.out.println("猫喵喵喵的叫~~~");
}
}
abstract class Animal{
public abstract void cry();
}
利用匿名内部类实现该功能
package com.itheima.d3_inner_class3;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:认识匿名内部类,并掌握其作用。
// 1、把这个匿名内部类编译成一个子类,然后会立即创建一个子类对象出来。
Animal a = new Animal(){
@Override
public void cry() {
System.out.println("猫喵喵喵的叫~~~");
}
};
a.cry();
}
}
abstract class Animal{
public abstract void cry();
}
10.5 匿名内部类的使用场景

package com.itheima.d3_inner_class3;
public class Test2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:掌握匿名的常见使用场景。
// Swimming s1 = new Swimming(){
// @Override
// public void swim() {
// System.out.println("狗🏊飞快~~~~");
// }
// };
// go(s1);
go(new Swimming(){
@Override
public void swim() {
System.out.println("狗🏊飞快~~~~");
}
});
}
// 设计一个方法,可以接收swimming接口的一切实现类对象进来参加游泳比赛。
public static void go(Swimming s){
System.out.println("开始-----------------------");
s.swim();
}
}
// 猫和狗都要参加游泳比赛
interface Swimming{
void swim();
}
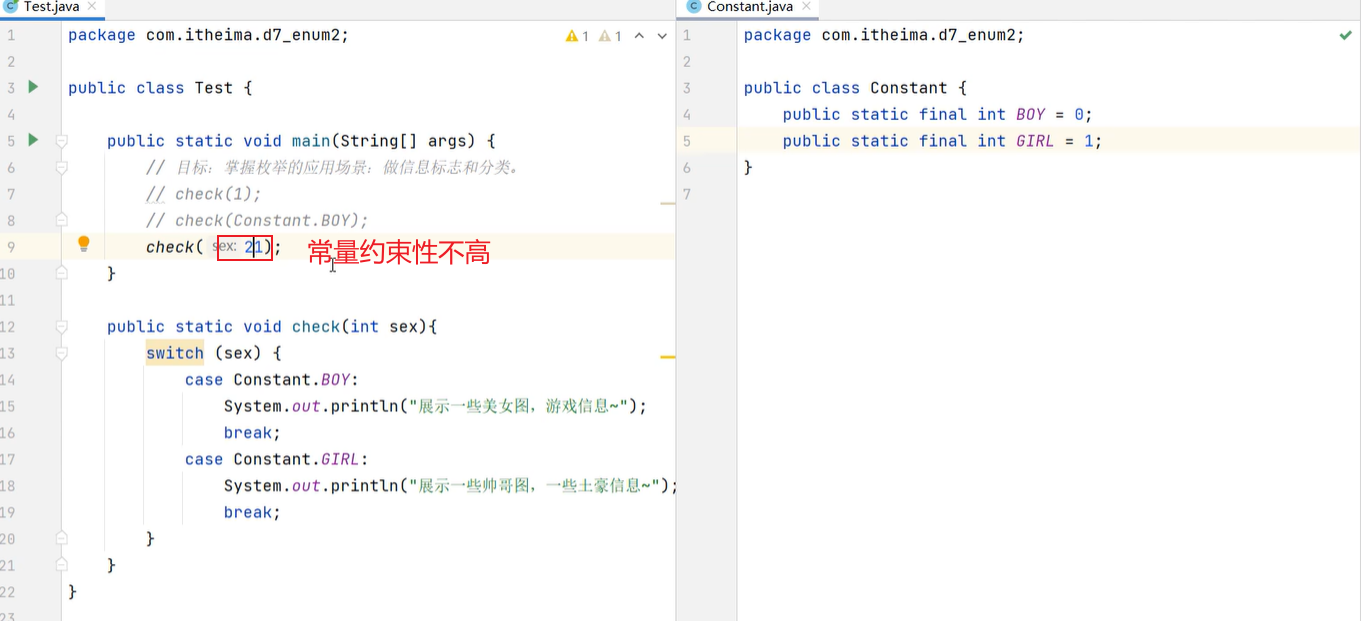
11. 枚举类

package com.itheima.d4_enum;
// 枚举类
public enum A {
// 常量,每个常量都是记住枚举类的一个对象的。
X, Y, Z;
A(){
}
A(String name){ //枚举类中的默认有参和无参构造方法都是私有的
}
private String name;
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
}
package com.itheima.d4_enum;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:认识枚举类。
// A.X = null;
A a1 = A.X;
A a2 = A.Y;
A a3 = A.Z;
System.out.println(a2.ordinal());
}
}
应用
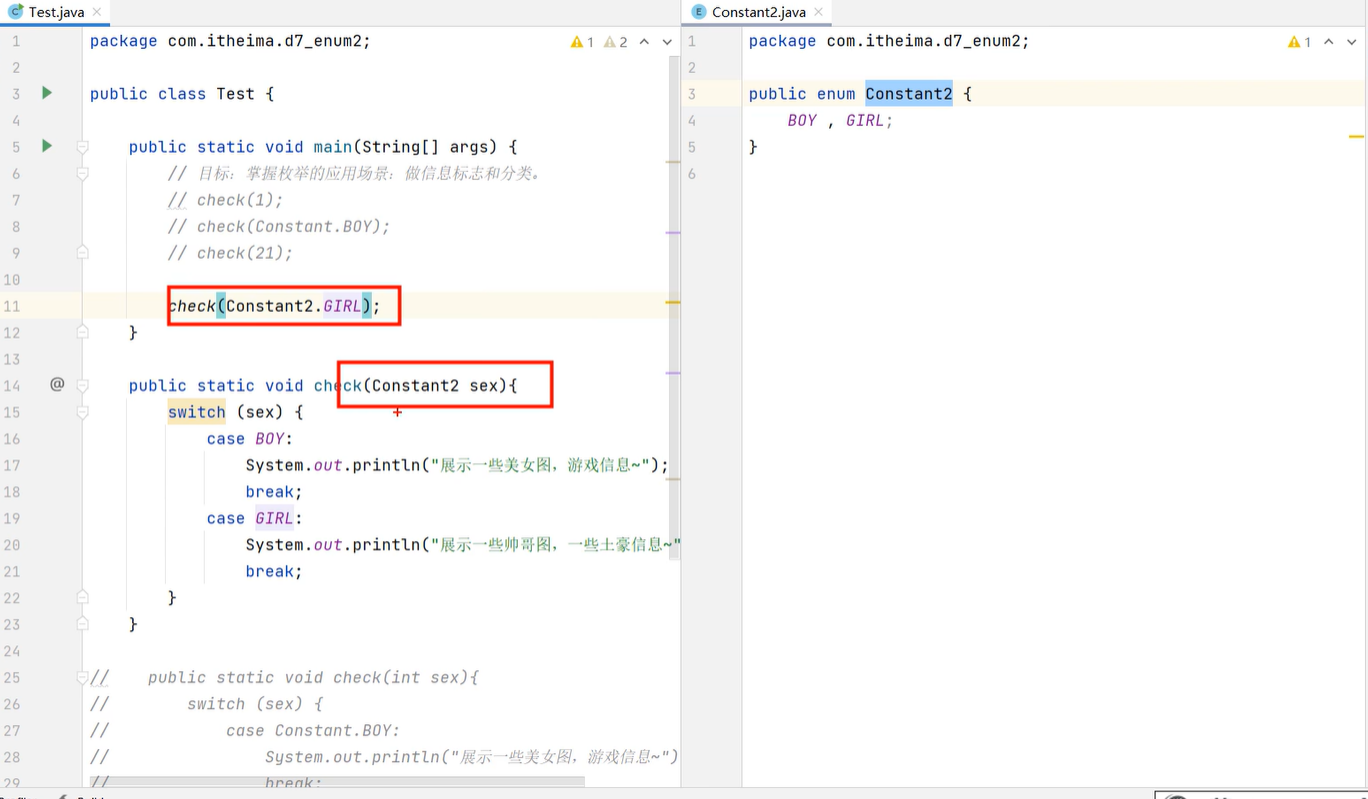
使用了枚举之后比较严谨,且代码可读性更高
12. 泛型

12.1 泛型类
package com.itheima.d6_generics_class;
// 泛型类
public class MyArrayList<E> { //此处的E也可以是其它字母,只是习惯于用E来表示泛型
private Object[] arr = new Object[10];
private int size; // 记录当前位置的
public boolean add(E e){
arr[size++] = e;
return true;
}
public E get(int index){
return (E) arr[index];
}
}
package com.itheima.d6_generics_class;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:掌握泛型类的定义和使用。
MyArrayList<String> list = new MyArrayList<>();
list.add("java1");
list.add("java2");
String ele = list.get(1);
System.out.println(ele);
}
}
声明多个类型变量
package com.itheima.d6_generics_class;
public class MyClass2<E, T> {
public void put(E e, T t){
}
}
package com.itheima.d6_generics_class;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyClass2<Cat, String> c2 = new MyClass2<>();
}
}
限定类型变量
package com.itheima.d6_generics_class;
public class MyClass3<E extends Animal> { // 该泛型变量约束为Animal或者Animal的子类
}
package com.itheima.d6_generics_class;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// MyClass3<String> c3 = new MyClass3<>(); // 报错
MyClass3<Animal> c4 = new MyClass3<>();
MyClass3<Dog> c5 = new MyClass3<>();
}
}
12.2 泛型接口

package com.itheima.d7_generics_interface;
import java.util.ArrayList;
// 泛型接口
public interface Data<T> {
void add(T t);
ArrayList<T> getByName(String name);
}
package com.itheima.d7_generics_interface;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class StudentData implements Data<Student>{
@Override
public void add(Student student) {
}
@Override
public ArrayList<Student> getByName(String name) {
return null;
}
}
package com.itheima.d7_generics_interface;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class TeacherData implements Data<Teacher>{
@Override
public void add(Teacher teacher) {
}
@Override
public ArrayList<Teacher> getByName(String name) {
return null;
}
}
12.3 泛型方法

package com.itheima.d8_generics_method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 目标:掌握泛型方法的定义和使用。
String rs = test("java"); //方法的返回值类型为string
System.out.println(rs);
Dog d = test(new Dog()); //方法的返回值类型为狗
System.out.println(d);
// 泛型方法
public static <T> T test(T t){
return t;
}
}
泛型方法应用:
package com.itheima.d8_generics_method;
public class Car {
}
package com.itheima.d8_generics_method;
public class BENZ extends Car{
}
package com.itheima.d8_generics_method;
public class BMW extends Car{
}
/
public static void go(ArrayList<Car> cars){
}
package com.itheima.d8_generics_method;
import java.util.ArrayList;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:所有的汽车可以一起参加比赛。
ArrayList<Car> cars = new ArrayList<>();
cars.add(new BMW());
cars.add(new BENZ());
go(cars); // 此处运行正常
ArrayList<BMW> bmws = new ArrayList<>();
bmws.add(new BMW());
bmws.add(new BMW());
go(bmws); // 此处会报错,因为BMW虽然是Car的子类,但是ArrayList<BMW> 却和 // ArrayList<Car>没有关系
ArrayList<BENZ> benzs = new ArrayList<>();
benzs.add(new BENZ());
benzs.add(new BENZ());
go(benzs); // 同理此处会报错
}
public static void go(ArrayList<Car> cars){
}
}
为了解决上述报错问题,可以使用泛型方法
public static <T> void go(ArrayList<T> cars){
}
但是上述代码不严谨,非Car的子类的list也可以传入进来:
ArrayList<Dog> dogs = new ArrayList<>();
dogs.add(new Dog());
dogs.add(new Dog());
go(dogs); // 此处也不会报错
因而可以进一步限定类型
public static <T extends Car> void go(ArrayList<T> cars){
}
Array List本身就是一种泛型,上述方法也可以这样实现:
// ? 通配符,在使用泛型的时候可以代表一切类型
public static void go(ArrayList<?> cars){
}
// 进一步限定类型, ? extends Car(上限:上限最多为Car,即Car或Car的子类) ; ? super Car(下限:下限最低为Car,即Car或Car的父类)
public static void go(ArrayList<? extends Car> cars){
}
12.4 泛型擦除及注意事项

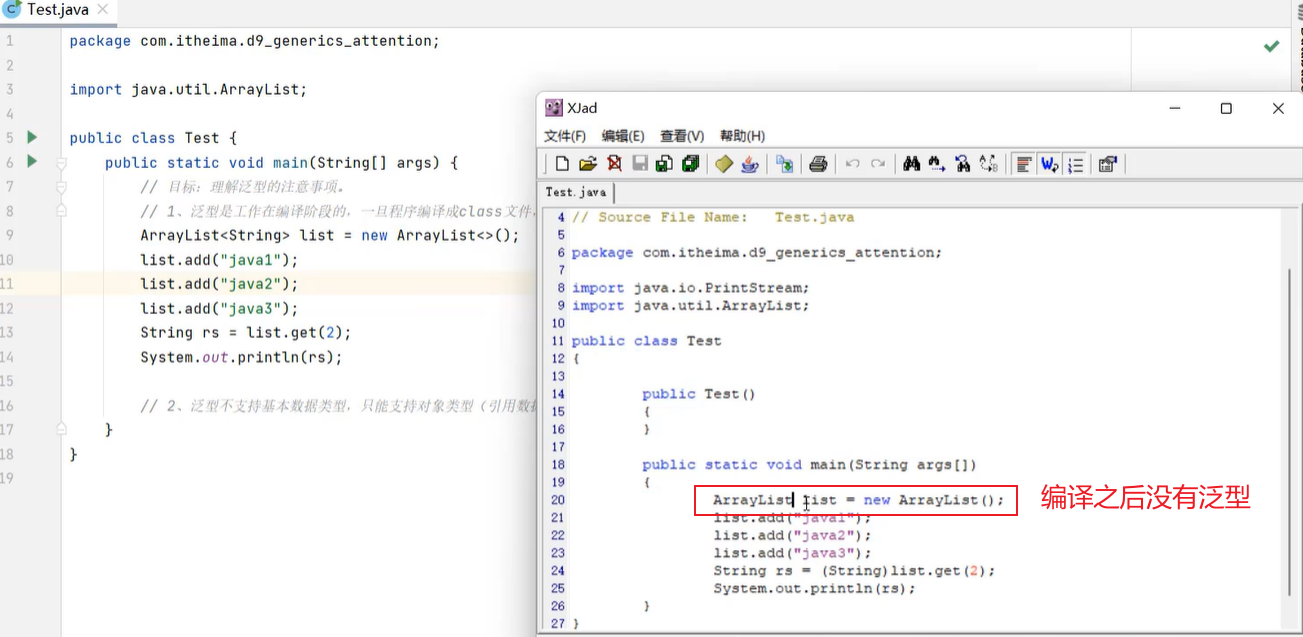
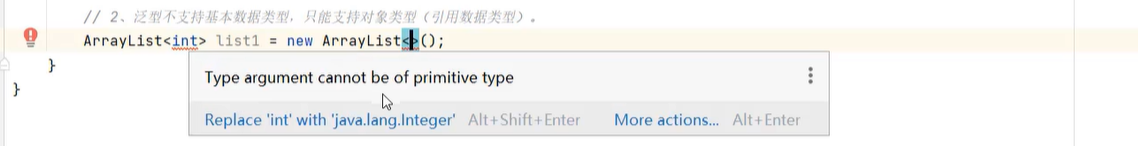
13. lambda表达式

匿名类常规写法
public class Main {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new Animal(){
@Override
public void run() {
System.out.println("狗跑的贼快~~");
}
}.run();
}
}
abstract class Animal{
public abstract void run();
}
// 注意:Lambda表达式并不是说能简化全部匿名内部类的写法,只能简化**函数式接口**的匿名内部类。错误的代码!
// Animal a = () -> {
// System.out.println("狗跑的贼快~~");
// };
// a.run();
看如下示例:
interface Swimming{
void swim();
}
Swimming s = new Swimming(){
@Override
public void swim() {
System.out.println("学生快乐的游泳~~~~");
}
};
s.swim();
使用lambda表达式进行简化写法:
Swimming s = () -> {
System.out.println("学生快乐的游泳~~~~");
};
s.swim();
注意:使用了lambda表达式,必须要使用 变量类型接收,不能链式直接调用,否则会报错
() -> {
System.out.println("学生快乐的游泳~~~~");
}.swim();
)
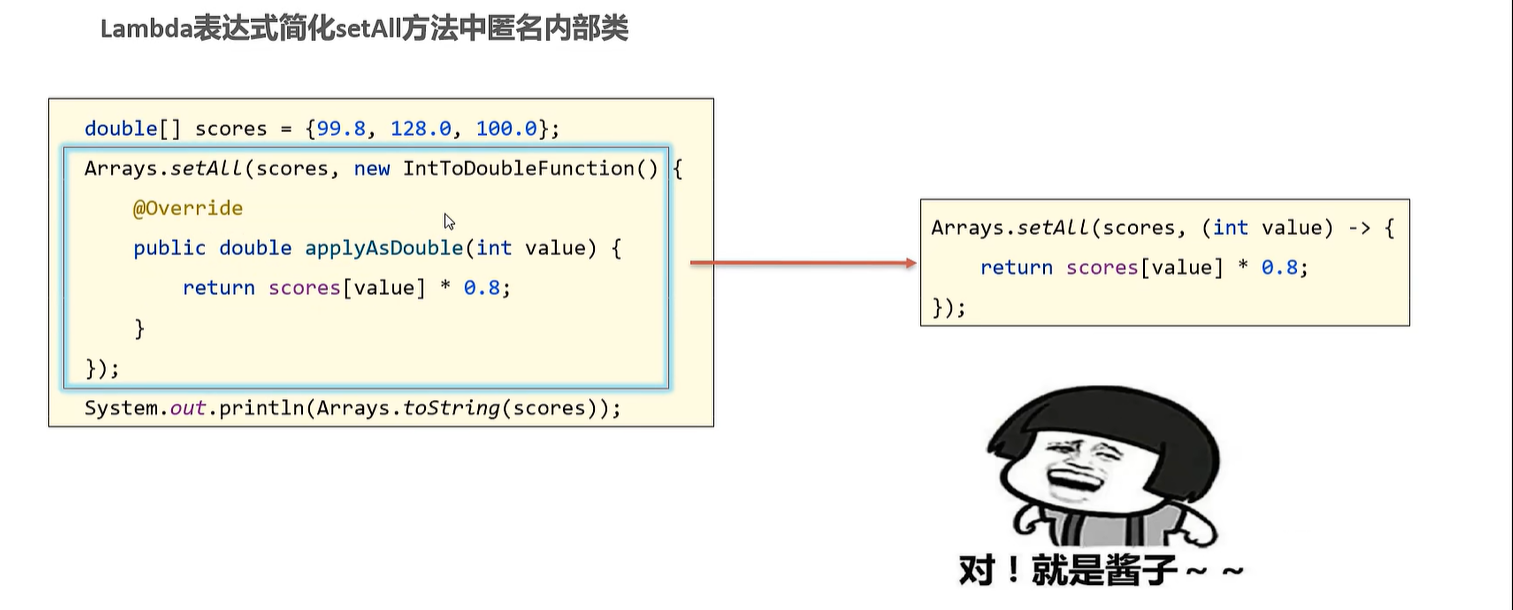
13.1 lambda表达式的省略规则
Arrays.setAll(prices, new IntToDoubleFunction() {
@Override
public double applyAsDouble(int value) {
// value = 0 1 2
return prices[value] * 0.8;
}
});
Arrays.setAll(prices, (int value) -> {
return prices[value] * 0.8;
});
//参数类型可以省略不写
Arrays.setAll(prices, (value) -> {
return prices[value] * 0.8;
});
//参数只有一个,参数类型可以不写,括号也可以省略
Arrays.setAll(prices, value -> {
return prices[value] * 0.8;
});
//方法体代码只有一行,可以省略大括号,同时省略分号;
Arrays.setAll(prices, value -> prices[value] * 0.8 );
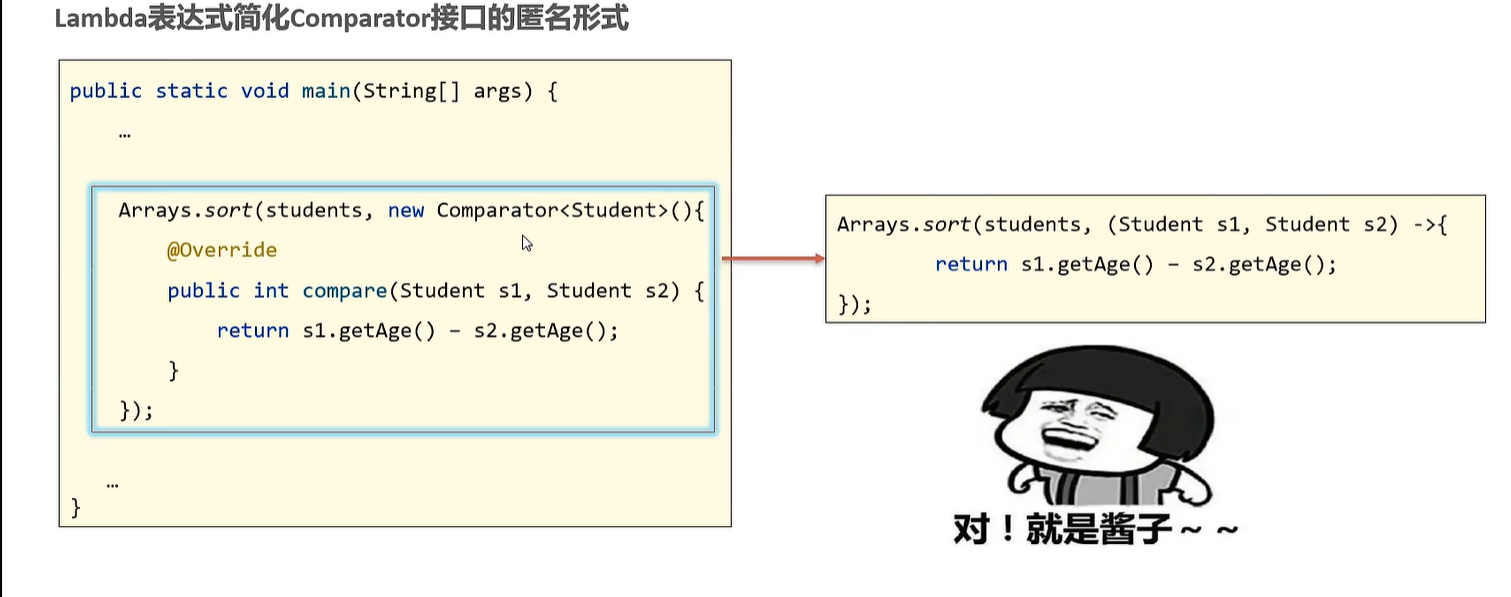
两个参数
Arrays.sort(students, new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return Double.compare(o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight()); // 升序
}
});
Arrays.sort(students, (Student o1, Student o2) -> {
return Double.compare(o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight()); // 升序
});
//参数类型可以省略不写
Arrays.sort(students, ( o1, o2) -> {
return Double.compare(o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight()); // 升序
});
//方法体代码只有一行,可以省略大括号,同时省略分号;
Arrays.sort(students, ( o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight()));
13.2 lambda表达式遍历 collection集合
Collection<String> c = new ArrayList<>();
c.add("赵敏");
c.add("小昭");
c.add("殷素素");
c.add("周芷若");
System.out.println(c); // [赵敏, 小昭, 殷素素, 周芷若]
// default void forEach(Consumer<? super T> action): 结合Lambda表达式遍历集合:
c.forEach(new Consumer<String>() {
@Override
public void accept(String s) {
System.out.println(s);
}
});
c.forEach((String s) -> {
System.out.println(s);
});
c.forEach(s -> {
System.out.println(s);
});
c.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s) );
c.forEach(System.out::println );
14. 方法引用
14.1 静态方法引用

public class CompareByData {
public static int compareByAge(Student o1, Student o2){
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge(); // 升序排序的规则
}
public int compareByAgeDesc(Student o1, Student o2){
return o2.getAge() - o1.getAge(); // 降序排序的规则
}
}
Student[] students = new Student[4];
students[0] = new Student("蜘蛛精", 169.5, 23);
students[1] = new Student("紫霞", 163.8, 26);
students[2] = new Student("紫霞", 163.8, 26);
students[3] = new Student("至尊宝", 167.5, 24);
// 原始写法:对数组中的学生对象,按照年龄升序排序
Arrays.sort(students, new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
return o1.getAge() - o2.getAge(); // 按照年龄升序排序
}
});
// 使用Lambda简化后的形式
Arrays.sort(students, (o1, o2) -> o1.getAge() - o2.getAge());
//封装成方法后,等价于
Arrays.sort(students, (o1, o2) -> CompareByData.compareByAge(o1, o2));
// 静态方法引用
Arrays.sort(students, CompareByData::compareByAge);
14.2 实例方法引用

Arrays.sort(students, (o1, o2) -> o2.getAge() - o1.getAge()); // 降序
CompareByData compare = new CompareByData();
Arrays.sort(students, (o1, o2) -> compare.compareByAgeDesc(o1, o2)); // 降序
// 实例方法引用
Arrays.sort(students, compare::compareByAgeDesc); // 降序
14.3 特定类型的方法引用

String[] names = {"boby", "angela", "Andy" ,"dlei", "caocao", "Babo", "jack", "Cici"};
// 进行排序(默认是按照字符串的首字符编号进行升序排序的)
// Arrays.sort(names);
// 要求忽略首字符大小写进行排序。
Arrays.sort(names, new Comparator<String>() {
@Override
public int compare(String o1, String o2) {
// 制定比较规则。o1 = "Andy" o2 = "angela"
return o1.compareToIgnoreCase(o2);
}
});
// Arrays.sort(names, ( o1, o2) -> o1.compareToIgnoreCase(o2) ); // o1为方法的主调
// 特定类型的方法引用!
Arrays.sort(names, String::compareToIgnoreCase);
14.4 构造器引用

public class Car {
private String name;
private double price;
public Car() {
}
public Car(String name, double price) {
this.name = name;
this.price = price;
}
//get set方法
}
// 1、创建这个接口的匿名内部类对象。
CreateCar cc = new CreateCar(){
@Override
public Car create(String name, double price) {
return new Car(name, price);
}
};
CreateCar cc = ( name, price) -> new Car(name, price);
// 构造器引用
CreateCar cc = Car::new;
Car c = cc.create("奔驰", 49.9);
15. Collection集合
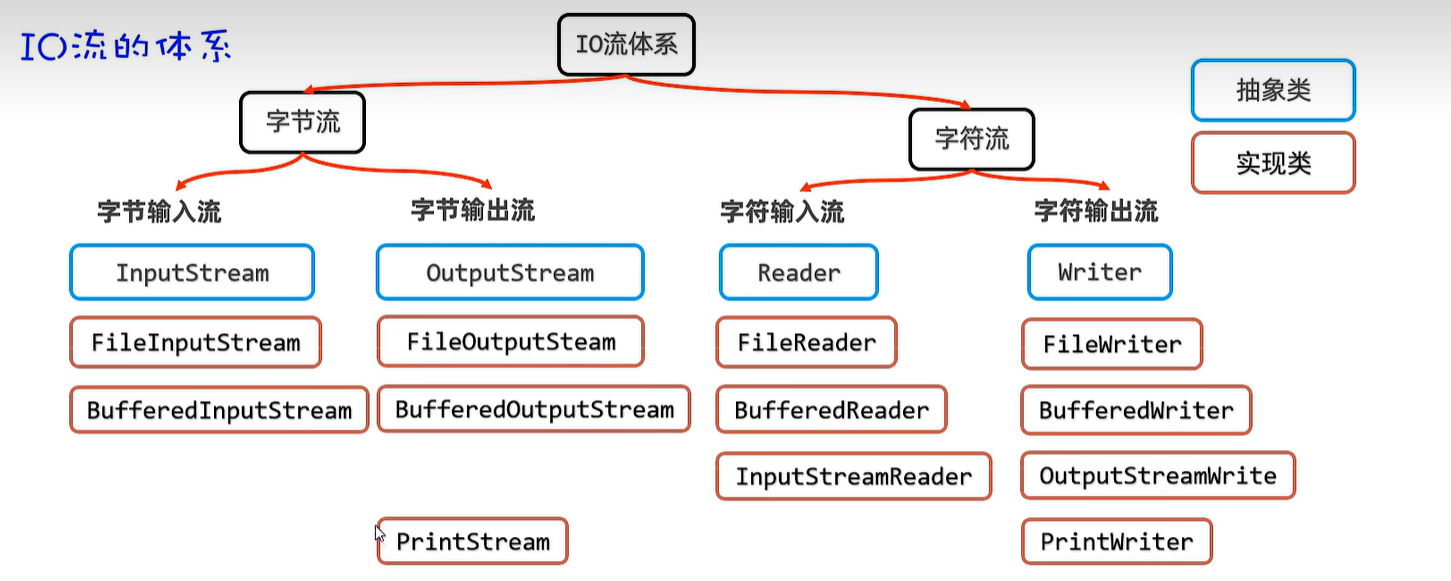
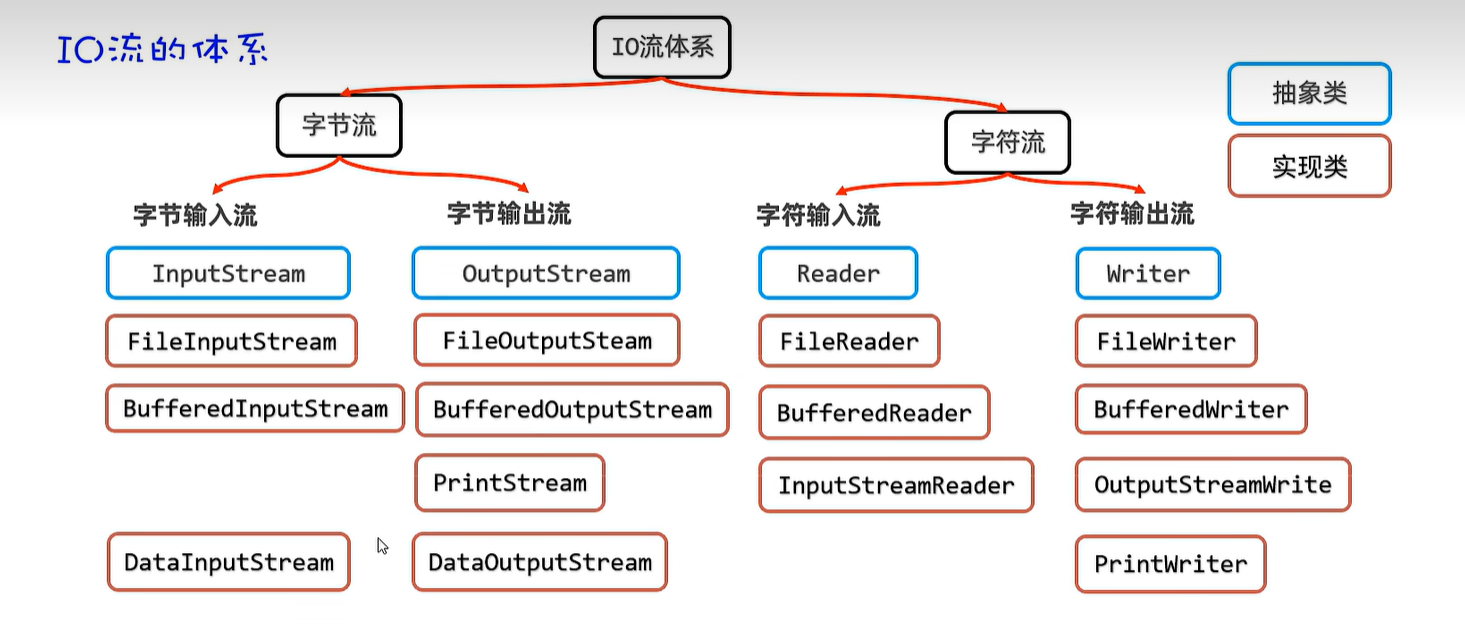
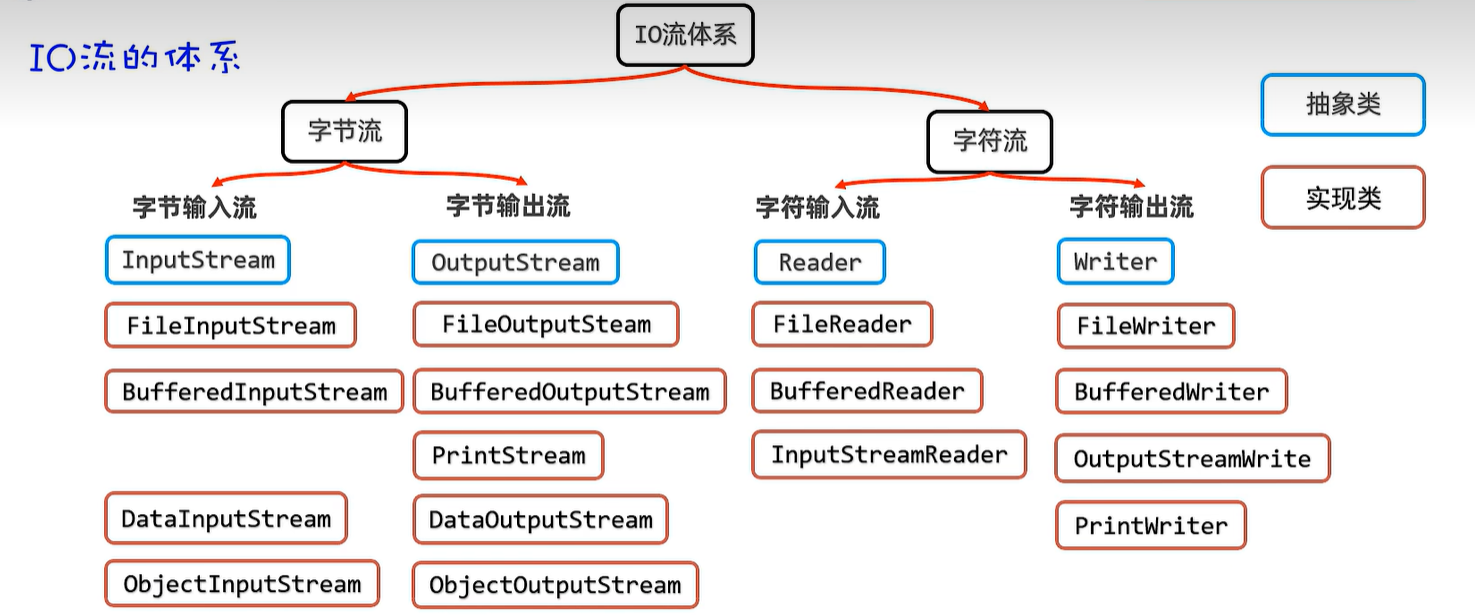
15.1 体系
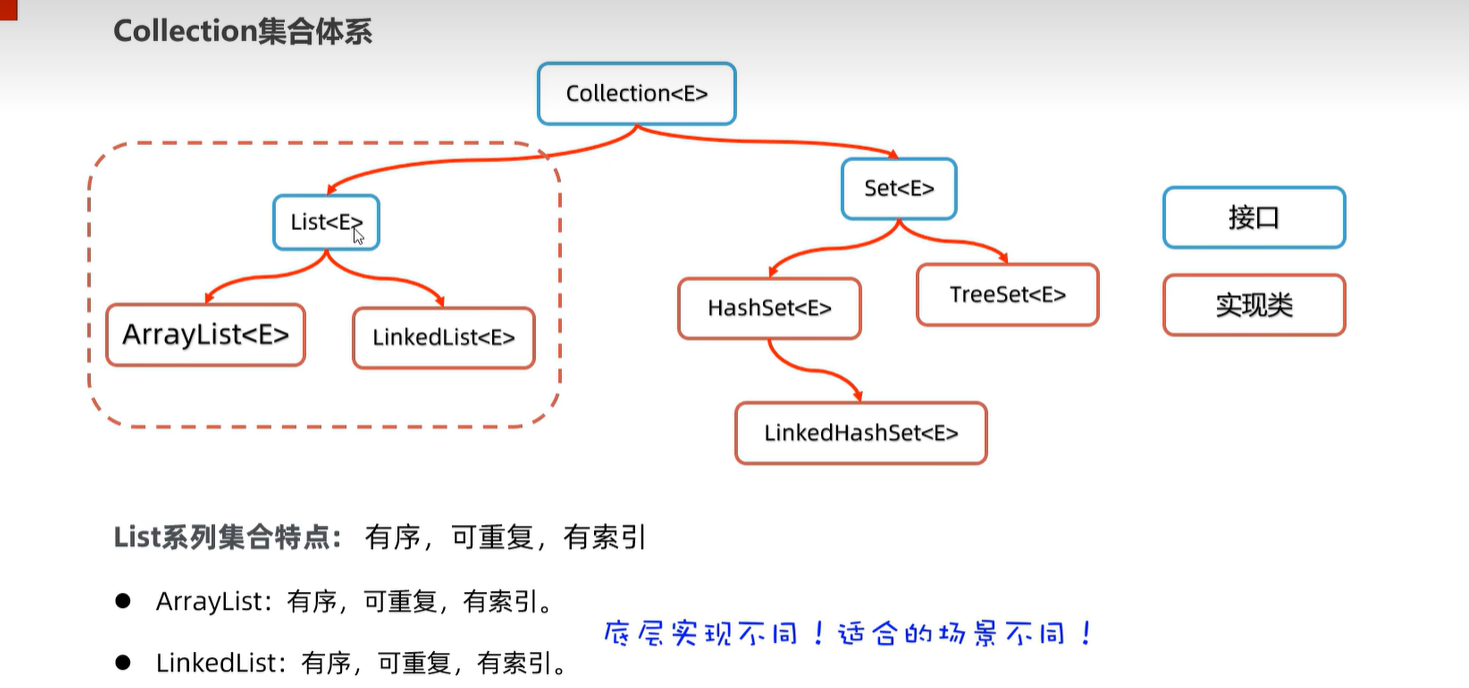
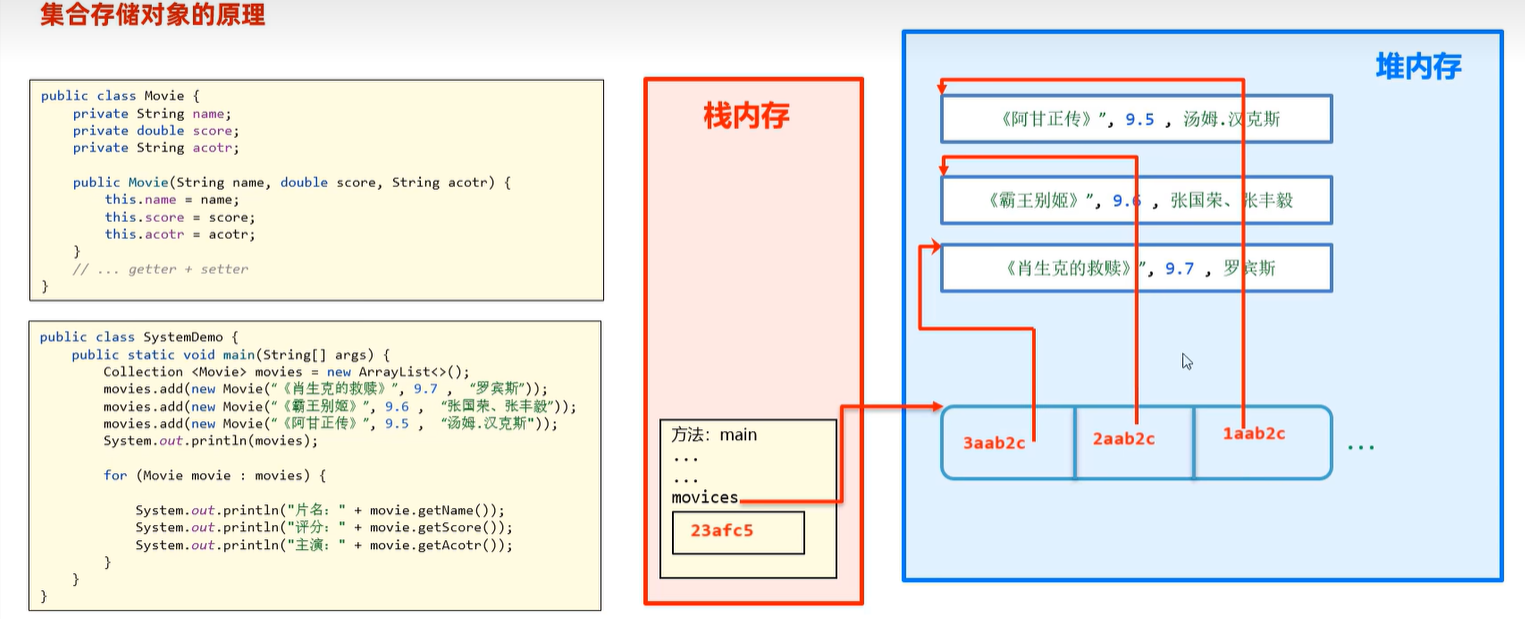
15.2 集合对象的存储原理
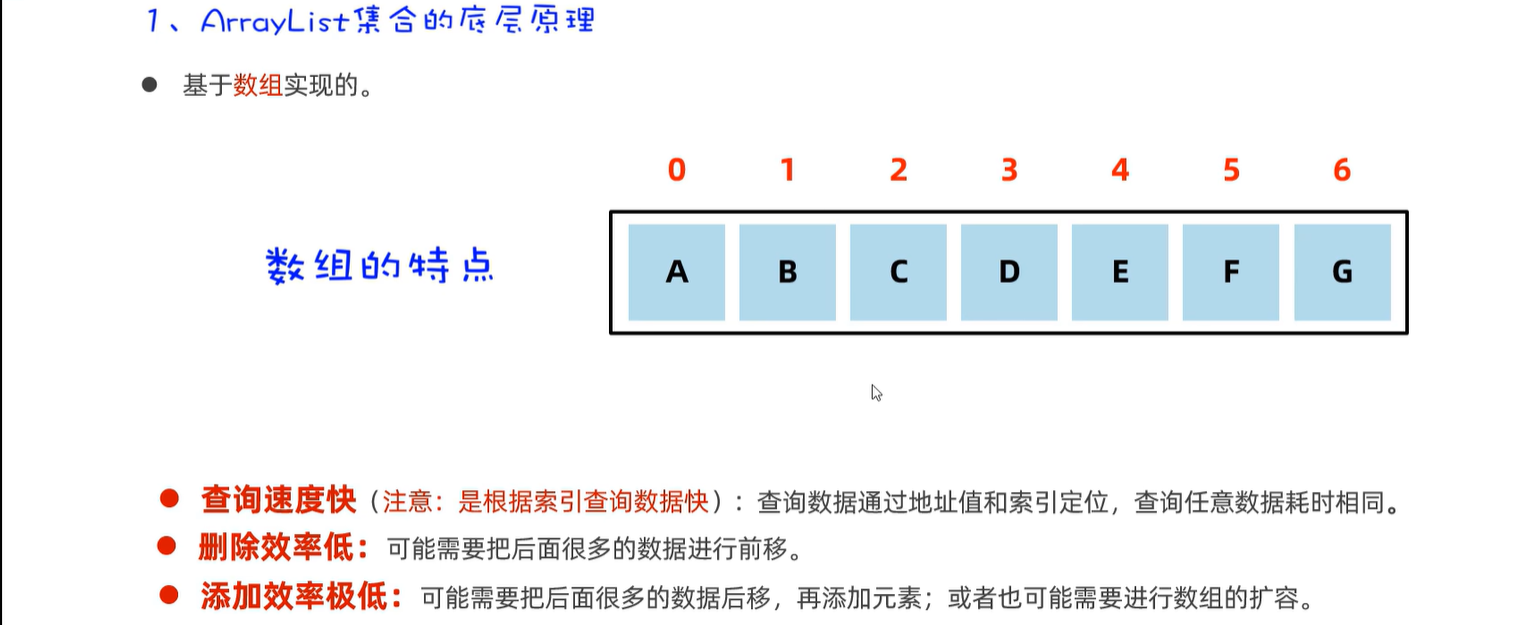
15.3 ArrayList
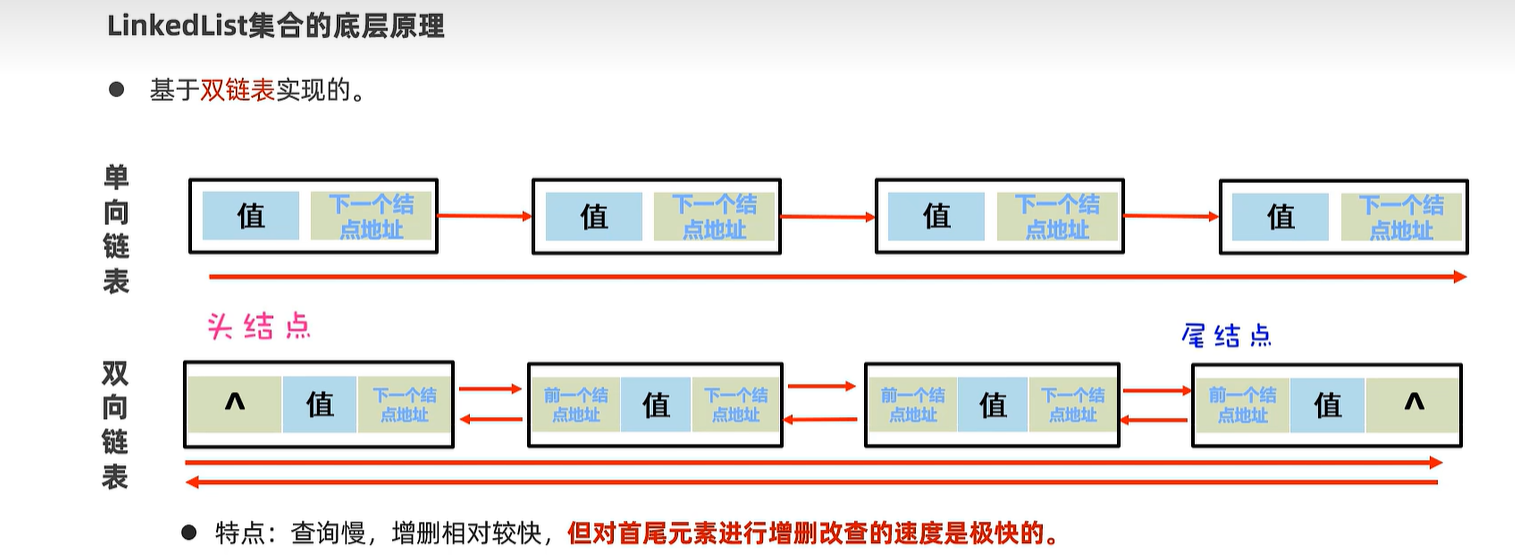
15.4 LinkedList

15.5 HashSet

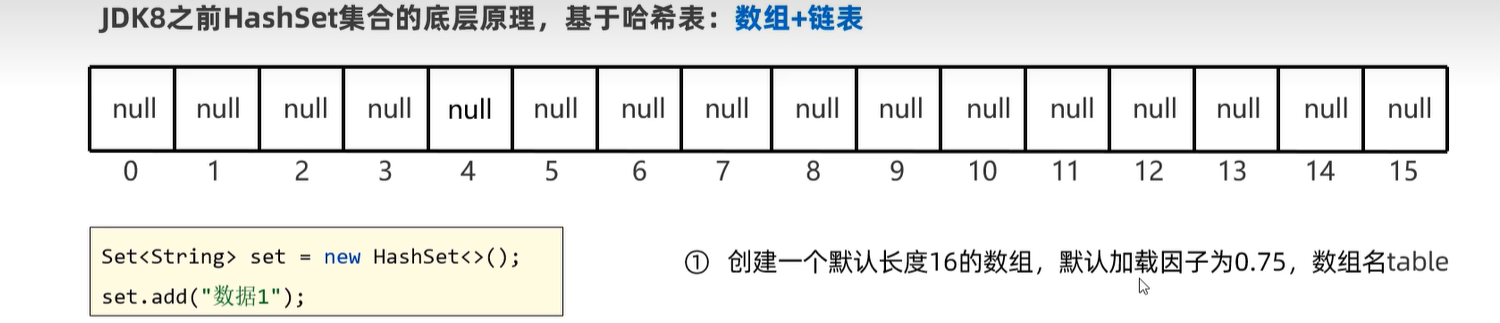
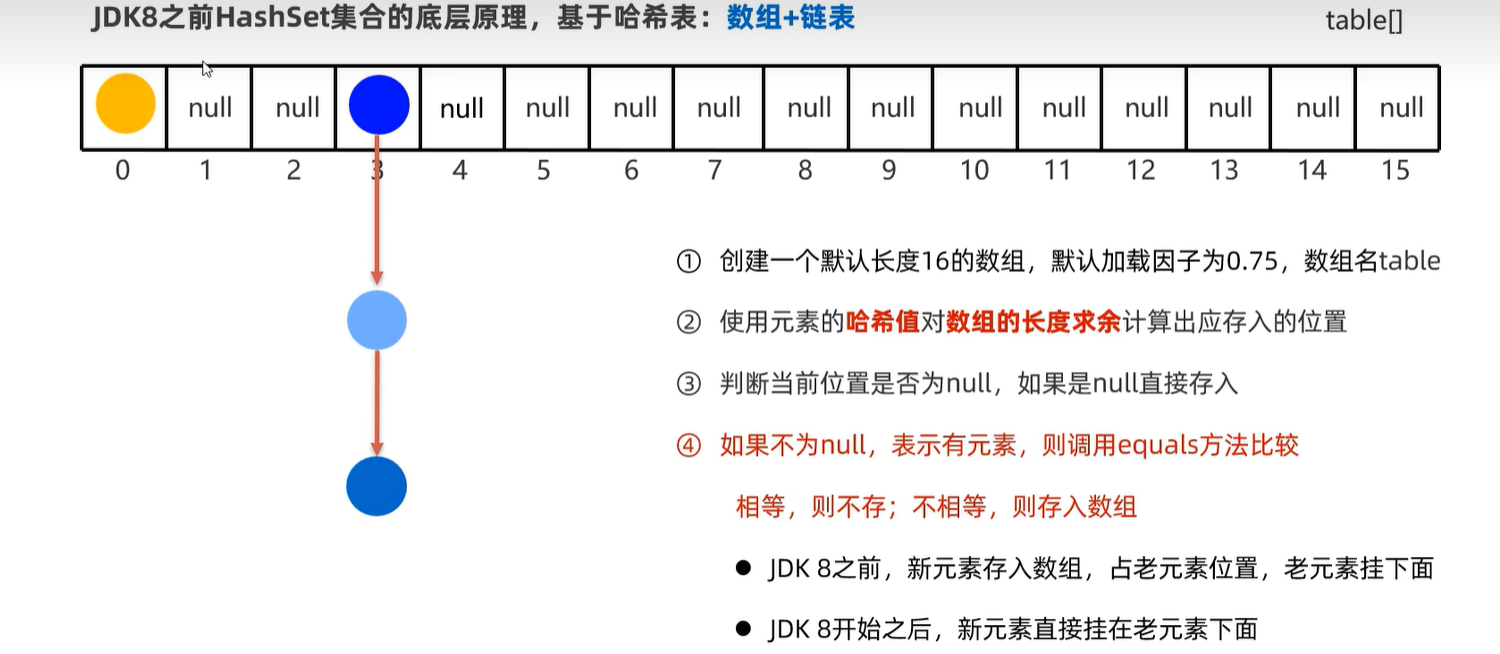
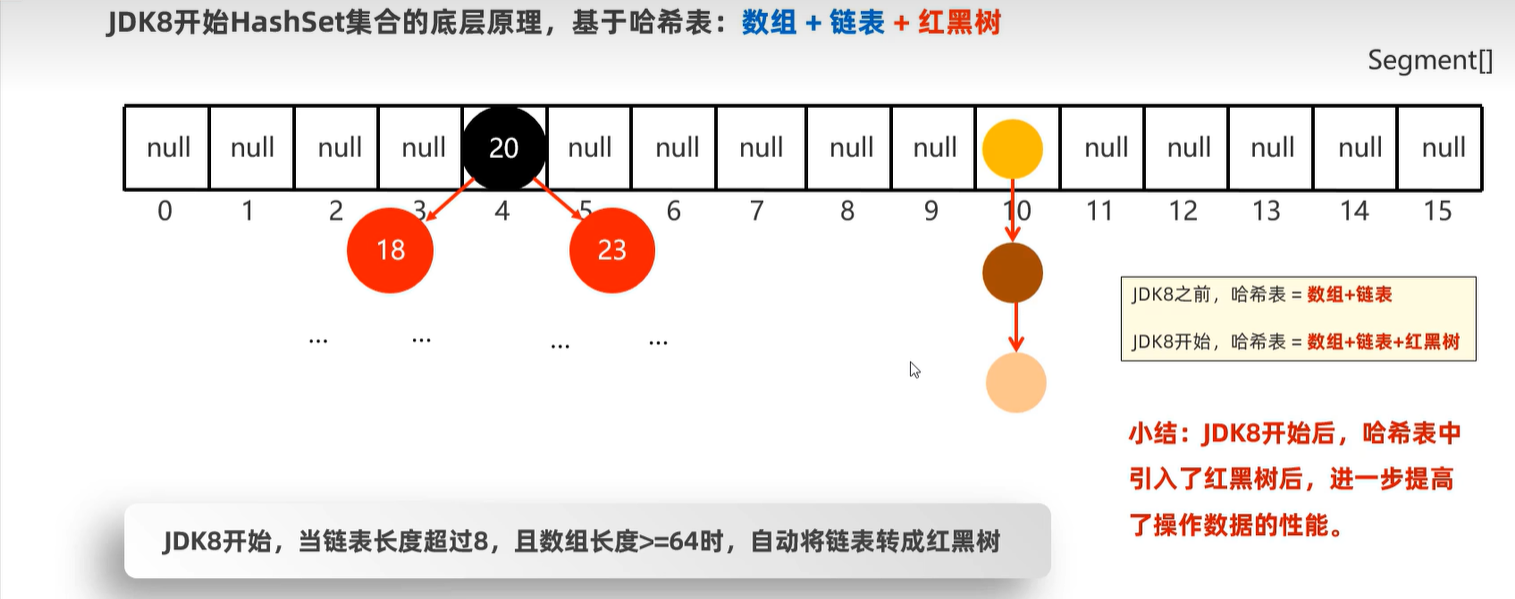
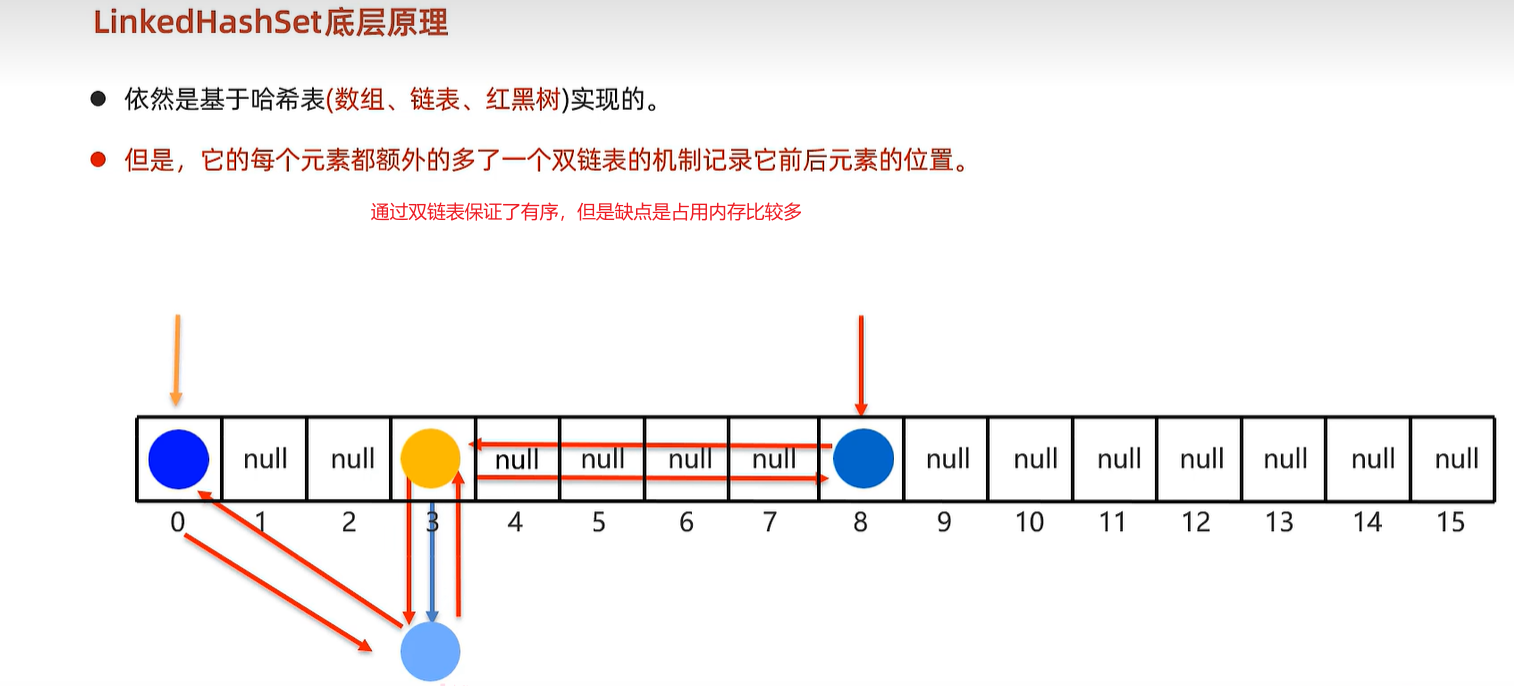
15.6 LinkedHashSet
15.7 TreeSet

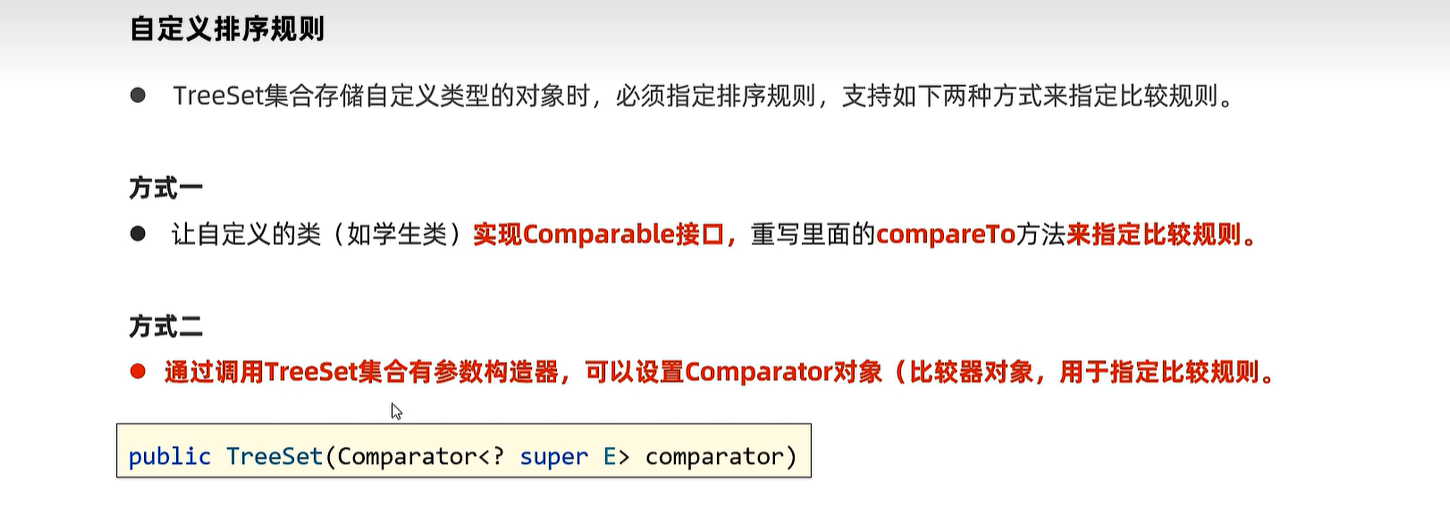
public class Student implements Comparable<Student>{
private String name;
private int age;
private double height;
// this o
@Override
public int compareTo(Student o) {
// 如果认为左边对象大于右边对象返回正整数
// 如果认为左边对象小于右边对象返回负整数
// 如果认为左边对象等于右边对象返回0
// 需求:按照年龄升序排序、
return this.age - o.age;
}
}
Set<Integer> set1 = new TreeSet<>();
set1.add(6);
set1.add(5);
set1.add(5);
set1.add(7);
System.out.println(set1);
public class Student {
private String name;
private int age;
private double height;
}
// 如果student类本身已经实现了比较接口, TreeSet就近选择自己自带的比较器对象进行排序
Set<Student> students = new TreeSet<>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student o1, Student o2) {
// 需求:按照身高升序排序
return Double.compare(o1.getHeight() , o2.getHeight());
}
});
Set<Student> students = new TreeSet<>(( o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o1.getHeight() , o2.getHeight()));
students.add(new Student("蜘蛛精",23, 169.7));
students.add(new Student("紫霞",22, 169.8));
students.add(new Student("至尊宝",26, 165.5));
students.add(new Student("牛魔王",22, 183.5));
System.out.println(students);
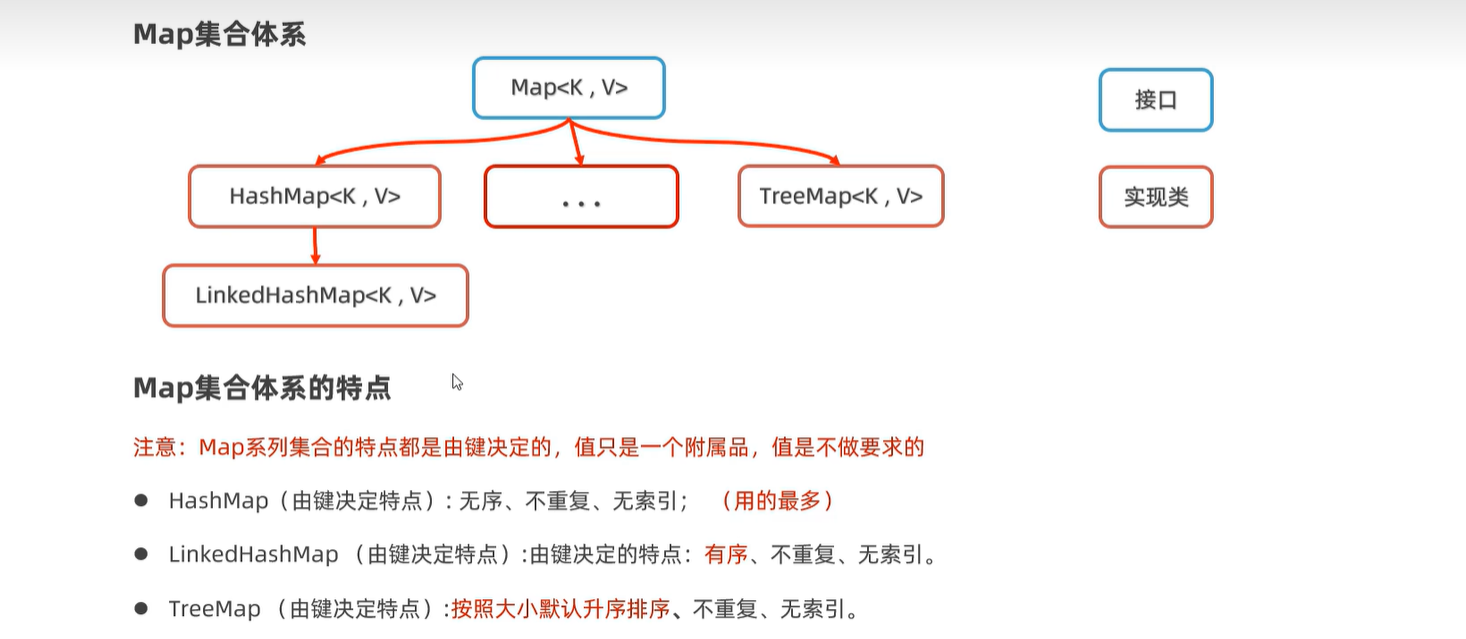
16. Map集合
16.1 体系
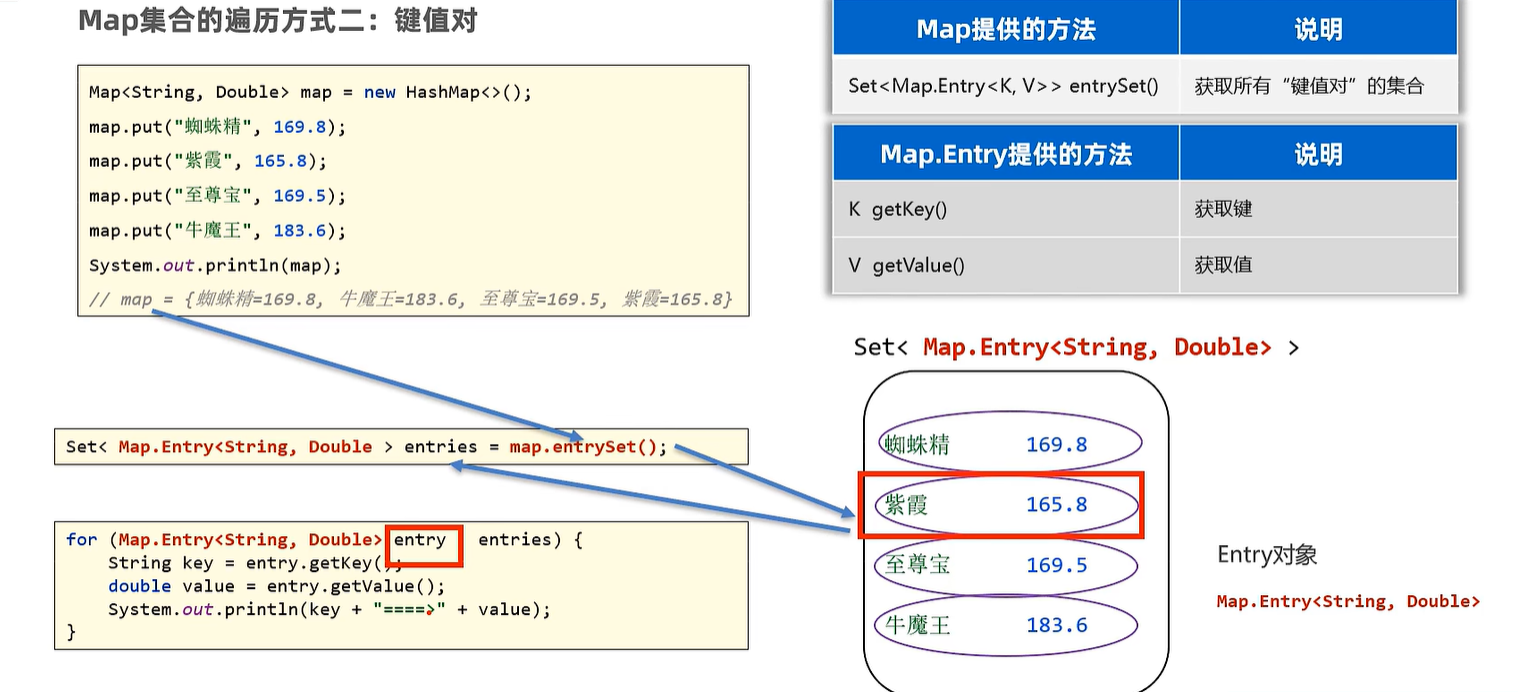
16.2 遍历方法

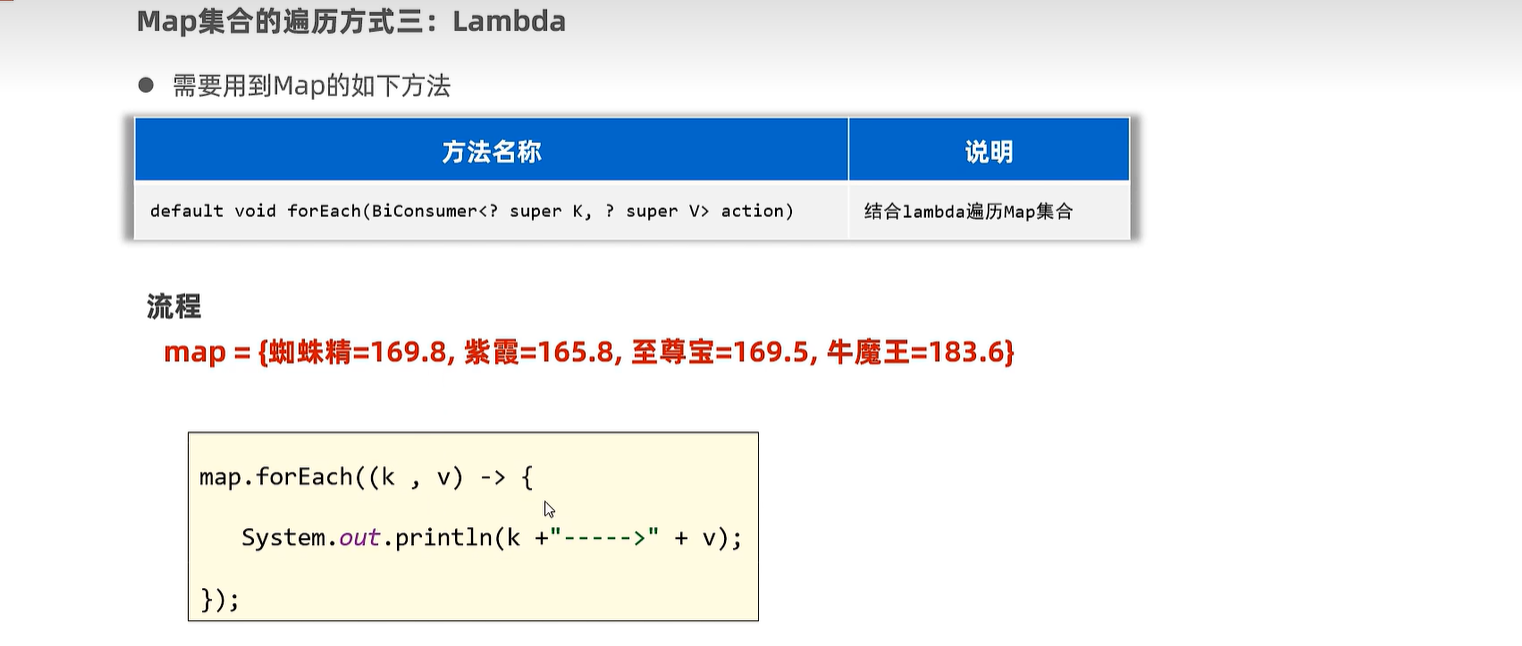
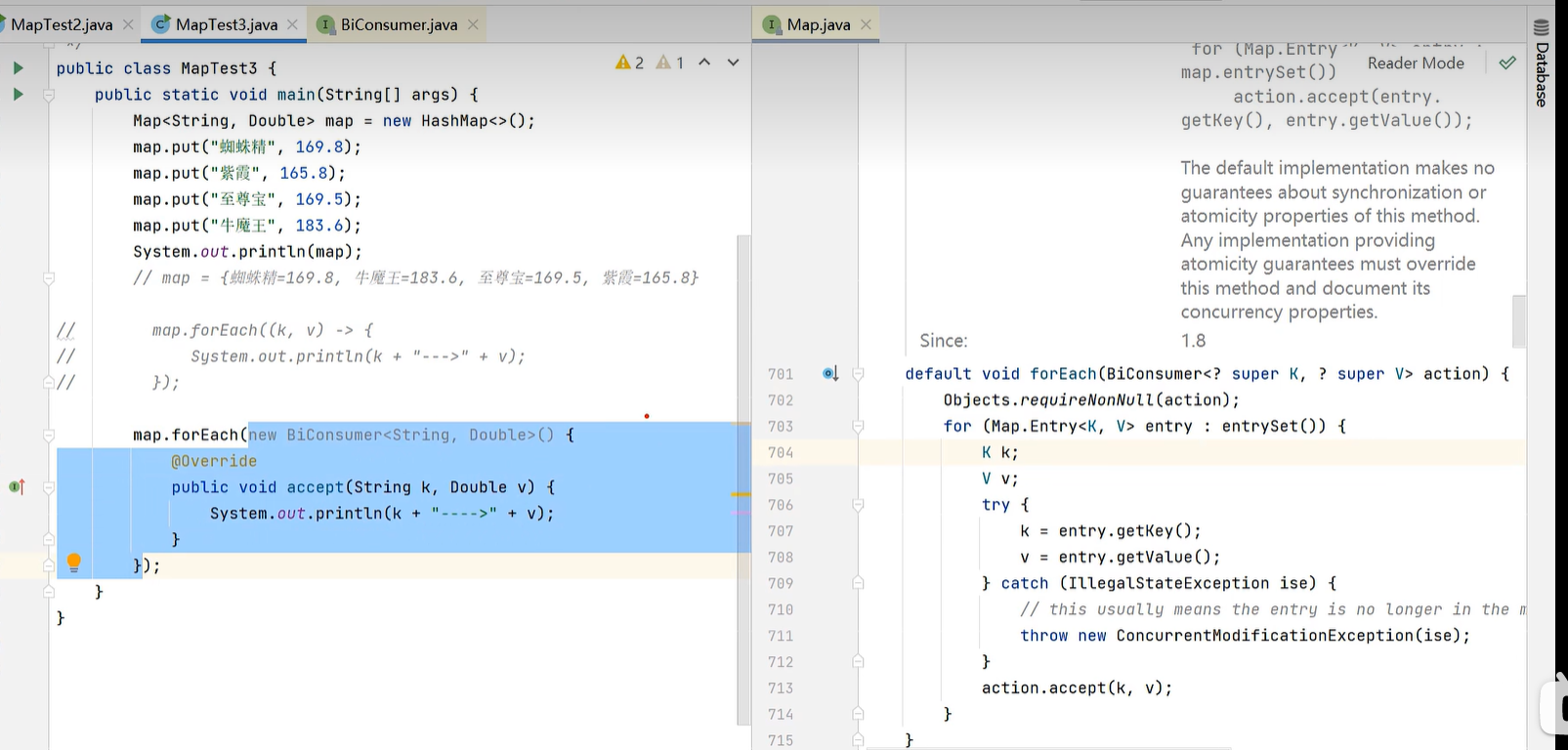
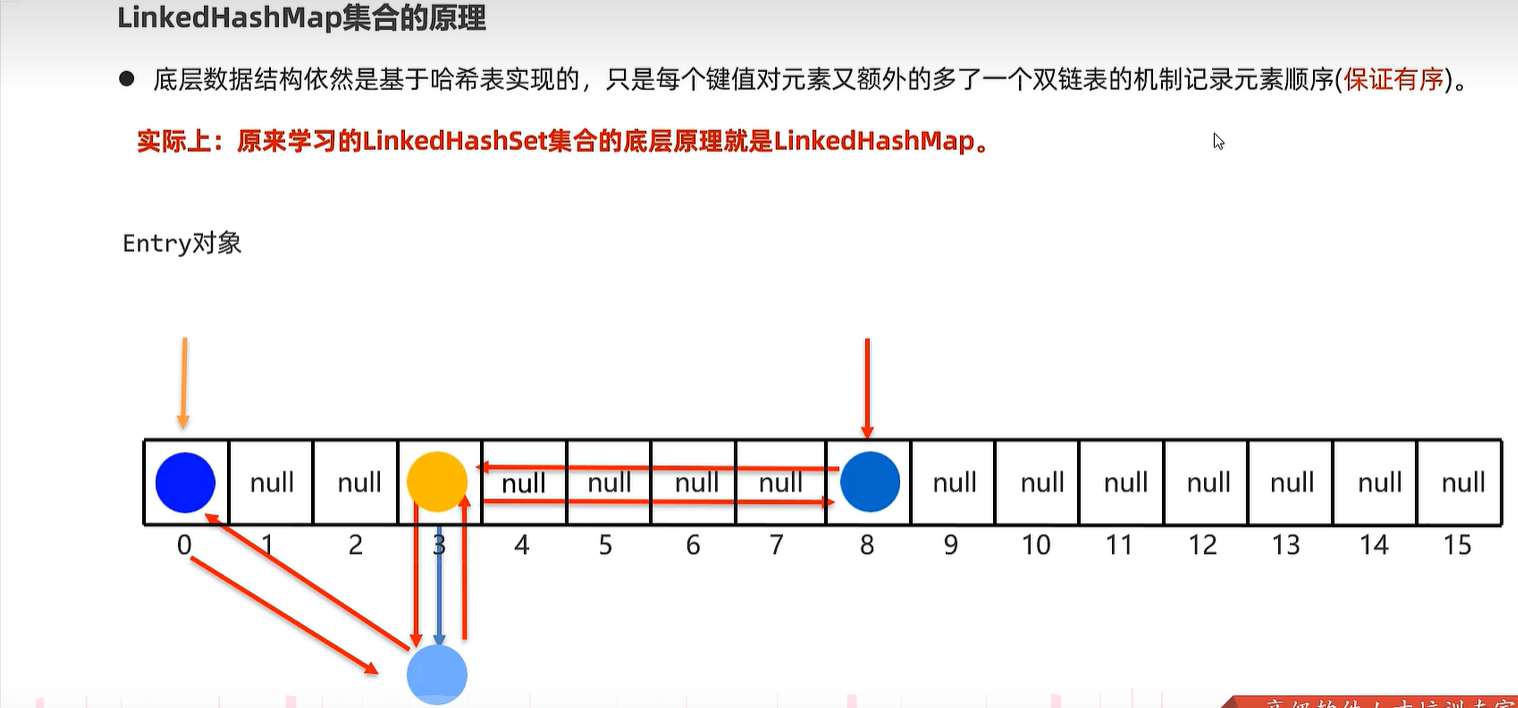
16.3 底层原理



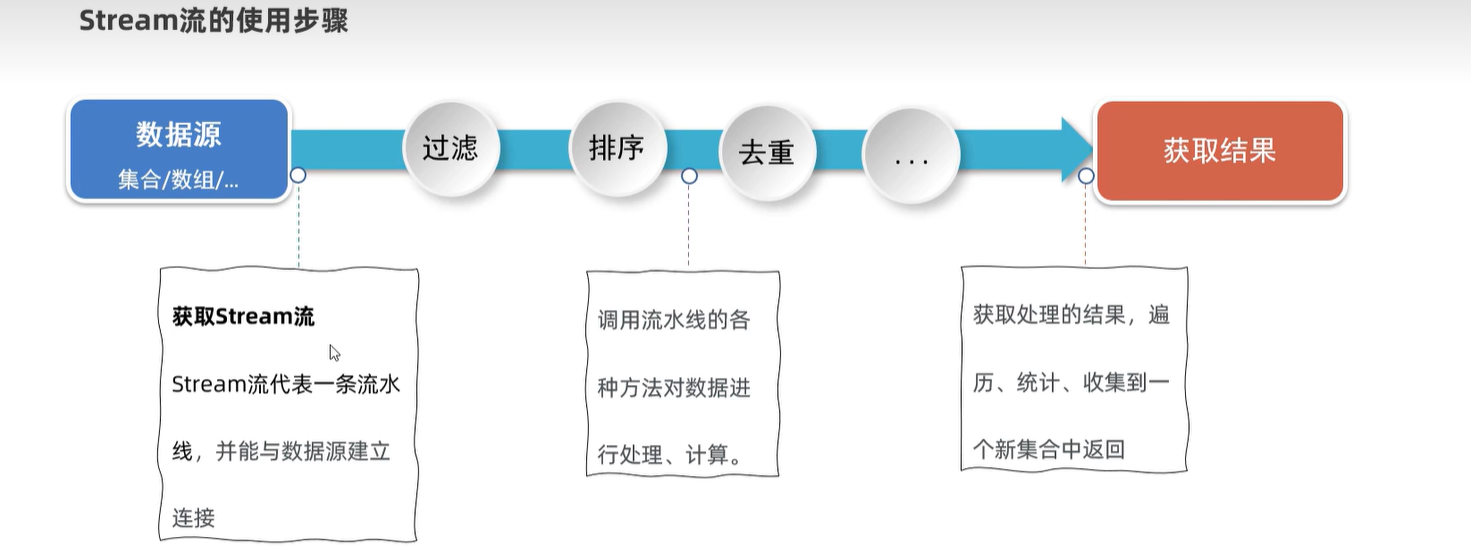
17. Stream

public static void main(String[] args) {
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(names, "张三丰","张无忌","周芷若","赵敏","张强");
System.out.println(names);
// names = [张三丰, 张无忌, 周芷若, 赵敏, 张强]
// 找出姓张,且是3个字的名字,存入到一个新集合中去。
List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
for (String name : names) {
if(name.startsWith("张") && name.length() == 3){
list.add(name);
}
}
System.out.println(list);
// 开始使用Stream流来解决这个需求。
List<String> list2 = names.stream().filter(s -> s.startsWith("张"))
.filter(a -> a.length()==3).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(list2);
}
17.1 获取stream流

public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、如何获取List集合的Stream流?
List<String> names = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(names, "张三丰","张无忌","周芷若","赵敏","张强");
Stream<String> stream = names.stream();
// 2、如何获取Set集合的Stream流?
Set<String> set = new HashSet<>();
Collections.addAll(set, "刘德华","张曼玉","蜘蛛精","马德","德玛西亚");
Stream<String> stream1 = set.stream();
stream1.filter(s -> s.contains("德")).forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
// 3、如何获取Map集合的Stream流?
Map<String, Double> map = new HashMap<>();
map.put("古力娜扎", 172.3);
map.put("迪丽热巴", 168.3);
map.put("马尔扎哈", 166.3);
map.put("卡尔扎巴", 168.3);
// 3.1 获取键和值对
Set<String> keys = map.keySet();
Stream<String> ks = keys.stream();
Collection<Double> values = map.values();
Stream<Double> vs = values.stream();
// 3.2 转成entrySet
Set<Map.Entry<String, Double>> entries = map.entrySet();
Stream<Map.Entry<String, Double>> kvs = entries.stream();
kvs.filter(e -> e.getKey().contains("巴"))
.forEach(e -> System.out.println(e.getKey()+ "-->" + e.getValue()));
// 4、如何获取数组的Stream流?
String[] names2 = {"张翠山", "东方不败", "唐大山", "独孤求败"};
//4.1 Arrays.stream()
Stream<String> s1 = Arrays.stream(names2);
//4.2 Stream.of()
Stream<String> s2 = Stream.of(names2);
}
17.2 stream流常用的中间方法

public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Double> scores = new ArrayList<>();
Collections.addAll(scores, 88.5, 100.0, 60.0, 99.0, 9.5, 99.6, 25.0);
// 需求1:找出成绩大于等于60分的数据,并升序后,再输出。
scores.stream().filter(s -> s >= 60).sorted().forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
Student s1 = new Student("蜘蛛精", 26, 172.5);
Student s2 = new Student("蜘蛛精", 26, 172.5);
Student s3 = new Student("紫霞", 23, 167.6);
Student s4 = new Student("白晶晶", 25, 169.0);
Student s5 = new Student("牛魔王", 35, 183.3);
Student s6 = new Student("牛夫人", 34, 168.5);
Collections.addAll(students, s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6);
// 需求2:找出年龄大于等于23,且年龄小于等于30岁的学生,并按照年龄降序输出.
students.stream().filter(s -> s.getAge() >= 23 && s.getAge() <= 30)
.sorted((o1, o2) -> o2.getAge() - o1.getAge())
.forEach(s -> System.out.println(s));
// 需求3:取出身高最高的前3名学生,并输出。
students.stream().sorted((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o2.getHeight(), o1.getHeight()))
.limit(3).forEach(System.out::println);
System.out.println("----------------------------------------------------------------");
// 需求4:取出身高倒数的2名学生,并输出。 s1 s2 s3 s4 s5 s6
students.stream().sorted((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o2.getHeight(), o1.getHeight()))
.skip(students.size() - 2).forEach(System.out::println);
// 需求5:找出身高超过168的学生叫什么名字,要求去除重复的名字,再输出。
students.stream().filter(s -> s.getHeight() > 168).map(Student::getName)
.distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
// distinct去重复,自定义类型的对象(希望内容一样就认为重复,重写hashCode,equals)
students.stream().filter(s -> s.getHeight() > 168)
.distinct().forEach(System.out::println);
// 需求6:合并两个stream
Stream<String> st1 = Stream.of("张三", "李四");
Stream<String> st2 = Stream.of("张三2", "李四2", "王五");
Stream<String> allSt = Stream.concat(st1, st2);
allSt.forEach(System.out::println);
}
17.3 Stream流常用的终结方法


public static void main(String[] args) {
List<Student> students = new ArrayList<>();
Student s1 = new Student("蜘蛛精", 26, 172.5);
Student s2 = new Student("蜘蛛精", 26, 172.5);
Student s3 = new Student("紫霞", 23, 167.6);
Student s4 = new Student("白晶晶", 25, 169.0);
Student s5 = new Student("牛魔王", 35, 183.3);
Student s6 = new Student("牛夫人", 34, 168.5);
Collections.addAll(students, s1, s2, s3, s4, s5, s6);
// 需求1:请计算出身高超过168的学生有几人。
long size = students.stream().filter(s -> s.getHeight() > 168).count();
System.out.println(size);
// 需求2:请找出身高最高的学生对象,并输出。
Student s = students.stream().max((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight())).get();
System.out.println(s);
// 需求3:请找出身高最矮的学生对象,并输出。
Student ss = students.stream().min((o1, o2) -> Double.compare(o1.getHeight(), o2.getHeight())).get();
System.out.println(ss);
// 需求4:请找出身高超过170的学生对象,并放到一个新集合中去返回。
// 流只能收集一次。
List<Student> students1 = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170).collect(Collectors.toList());
System.out.println(students1);
Set<Student> students2 = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170).collect(Collectors.toSet());
System.out.println(students2);
// 需求5:请找出身高超过170的学生对象,并把学生对象的名字和身高,存入到一个Map集合返回。
Map<String, Double> map =
students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170)
.distinct().collect(Collectors.toMap(a -> a.getName(), a -> a.getHeight()));
System.out.println(map);
// 需求6: 收集到数组中
// Object[] arr = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170).toArray();
Student[] arr = students.stream().filter(a -> a.getHeight() > 170).toArray(len -> new Student[len]);
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(arr));
}
18. File



public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、创建一个File对象,指代某个具体的文件。
// 路径分隔符
// File f1 = new File("D:/resource/ab.txt");
// File f1 = new File("D:\\resource\\ab.txt");
File f1 = new File("D:" + File.separator +"resource" + File.separator + "ab.txt");
System.out.println(f1.length()); // 文件大小
File f2 = new File("D:/resource");
System.out.println(f2.length());
// 注意:File对象可以指代一个不存在的文件路径
File f3 = new File("D:/resource/aaaa.txt");
System.out.println(f3.length());
System.out.println(f3.exists()); // false
// 我现在要定位的文件是在模块中,应该怎么定位呢?
// 绝对路径:带盘符的
// File f4 = new File("D:\\code\\javasepromax\\file-io-app\\src\\itheima.txt");
// 相对路径(重点):不带盘符,默认是直接去工程下寻找文件的。
File f4 = new File("file-io-app\\src\\itheima.txt");
System.out.println(f4.length());
}
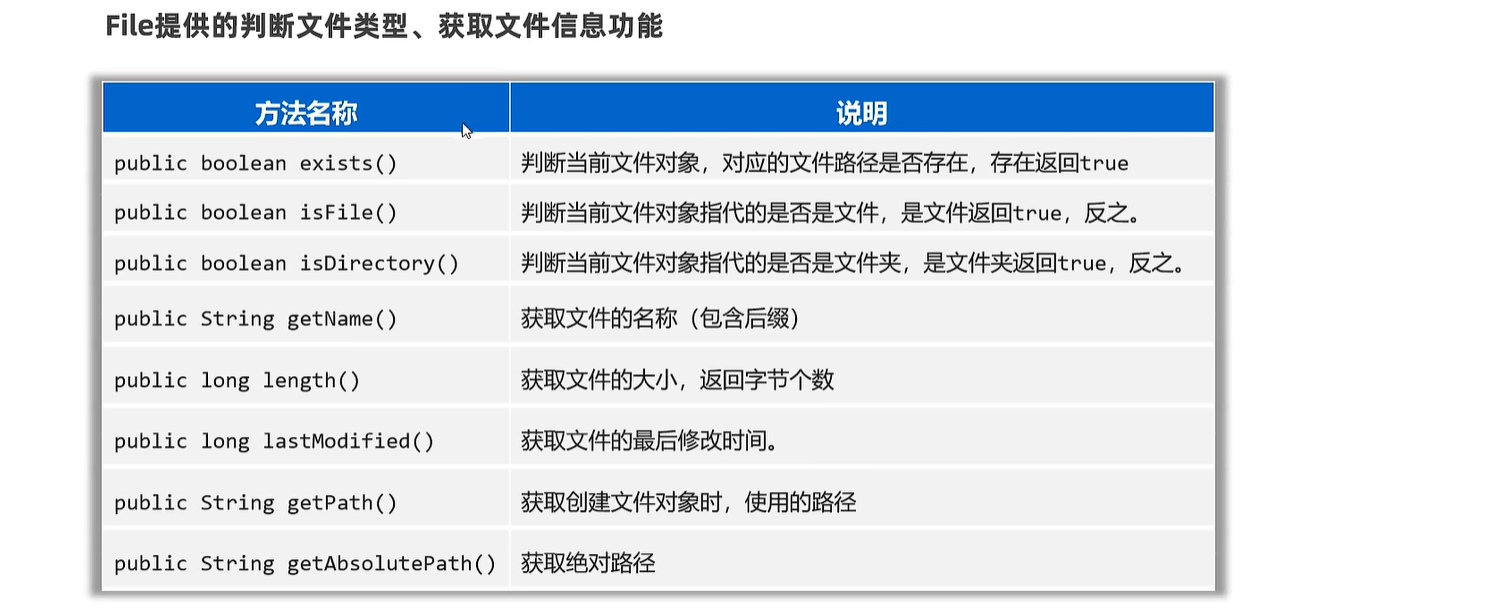
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
// 1.创建文件对象,指代某个文件
File f1 = new File("D:/resource/ab.txt");
//File f1 = new File("D:/resource/");
// 2、public boolean exists():判断当前文件对象,对应的文件路径是否存在,存在返回true.
System.out.println(f1.exists());
// 3、public boolean isFile() : 判断当前文件对象指代的是否是文件,是文件返回true,反之。
System.out.println(f1.isFile());
// 4、public boolean isDirectory() : 判断当前文件对象指代的是否是文件夹,是文件夹返回true,反之。
System.out.println(f1.isDirectory());
// 5.public String getName():获取文件的名称(包含后缀)
System.out.println(f1.getName());
// 6.public long length():获取文件的大小,返回字节个数
System.out.println(f1.length());
// 7.public long lastModified():获取文件的最后修改时间。
long time = f1.lastModified();
SimpleDateFormat sdf = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy/MM/dd HH:mm:ss");
System.out.println(sdf.format(time));
// 8.public String getPath():获取创建文件对象时,使用的路径
File f2 = new File("D:\\resource\\ab.txt");
File f3 = new File("file-io-app\\src\\itheima.txt");
System.out.println(f2.getPath());
System.out.println(f3.getPath());
// 9.public String getAbsolutePath():获取绝对路径
System.out.println(f2.getAbsolutePath());
System.out.println(f3.getAbsolutePath());
}

public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1、public boolean createNewFile():创建一个新文件(文件内容为空),创建成功返回true,反之。
File f1 = new File("D:/resource/itheima2.txt");
System.out.println(f1.createNewFile());
// 2、public boolean mkdir():用于创建文件夹,注意:只能创建一级文件夹
File f2 = new File("D:/resource/aaa");
System.out.println(f2.mkdir());
// 3、public boolean mkdirs():用于创建文件夹,注意:可以创建多级文件夹
File f3 = new File("D:/resource/bbb/ccc/ddd/eee/fff/ggg");
System.out.println(f3.mkdirs());
// 3、public boolean delete():删除文件,或者空文件,注意:不能删除非空文件夹。
System.out.println(f1.delete());
System.out.println(f2.delete());
File f4 = new File("D:/resource");
System.out.println(f4.delete());
}

public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、public String[] list():获取当前目录下所有的"一级文件名称"到一个字符串数组中去返回。
File f1 = new File("D:\\course\\待研发内容");
String[] names = f1.list();
for (String name : names) {
System.out.println(name);
}
// 2、public File[] listFiles():(重点)获取当前目录下所有的"一级文件对象"到一个文件对象数组中去返回(重点)
File[] files = f1.listFiles();
for (File file : files) {
System.out.println(file.getAbsolutePath());
}
File f = new File("D:/resource/aaa"); //若文件夹下没有东西
File[] files1 = f.listFiles();
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(files1)); //[]
}
19. 字符集



public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1、编码
String data = "a我b";
byte[] bytes = data.getBytes(); // 默认是按照平台字符集(UTF-8)进行编码的。
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes));
// 按照指定字符集进行编码。
byte[] bytes1 = data.getBytes("GBK");
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(bytes1));
// 2、解码
String s1 = new String(bytes); // 按照平台默认编码(UTF-8)解码
System.out.println(s1);
String s2 = new String(bytes1, "GBK");
System.out.println(s2);
}
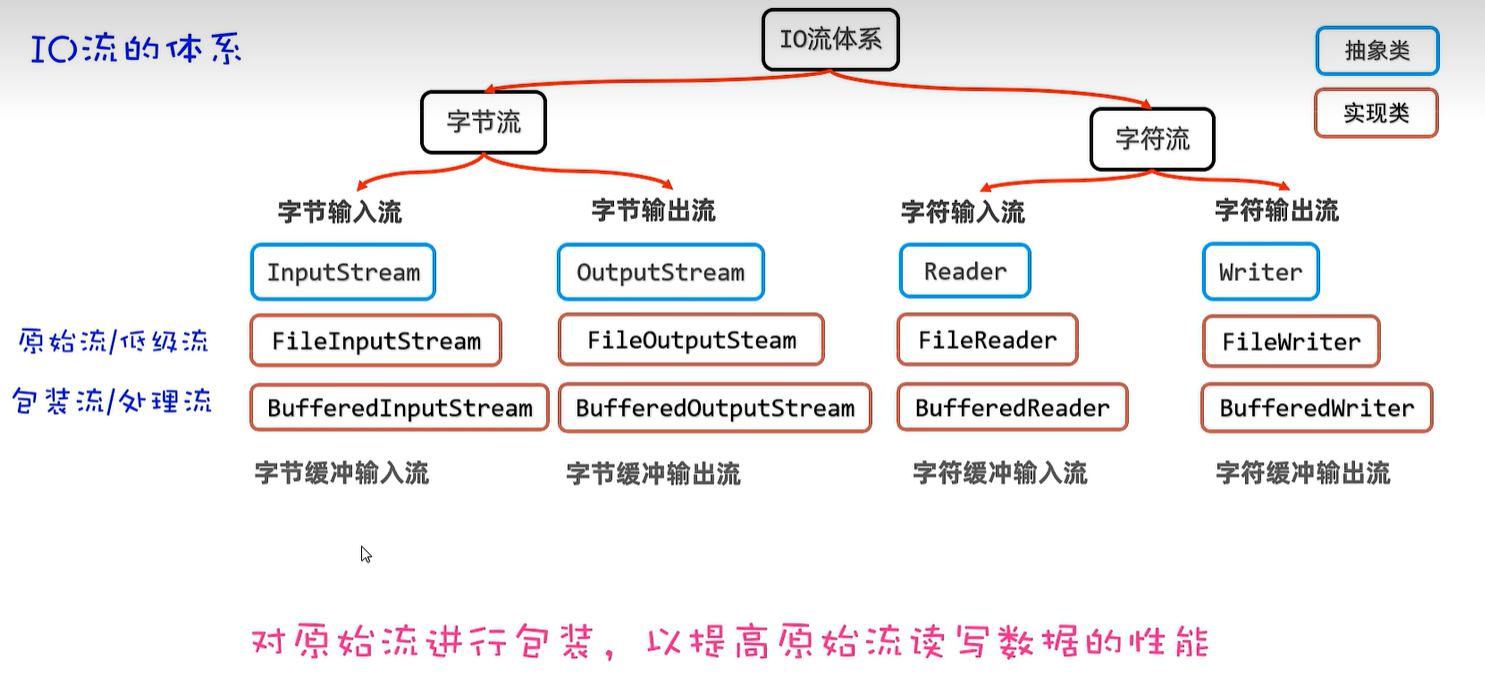
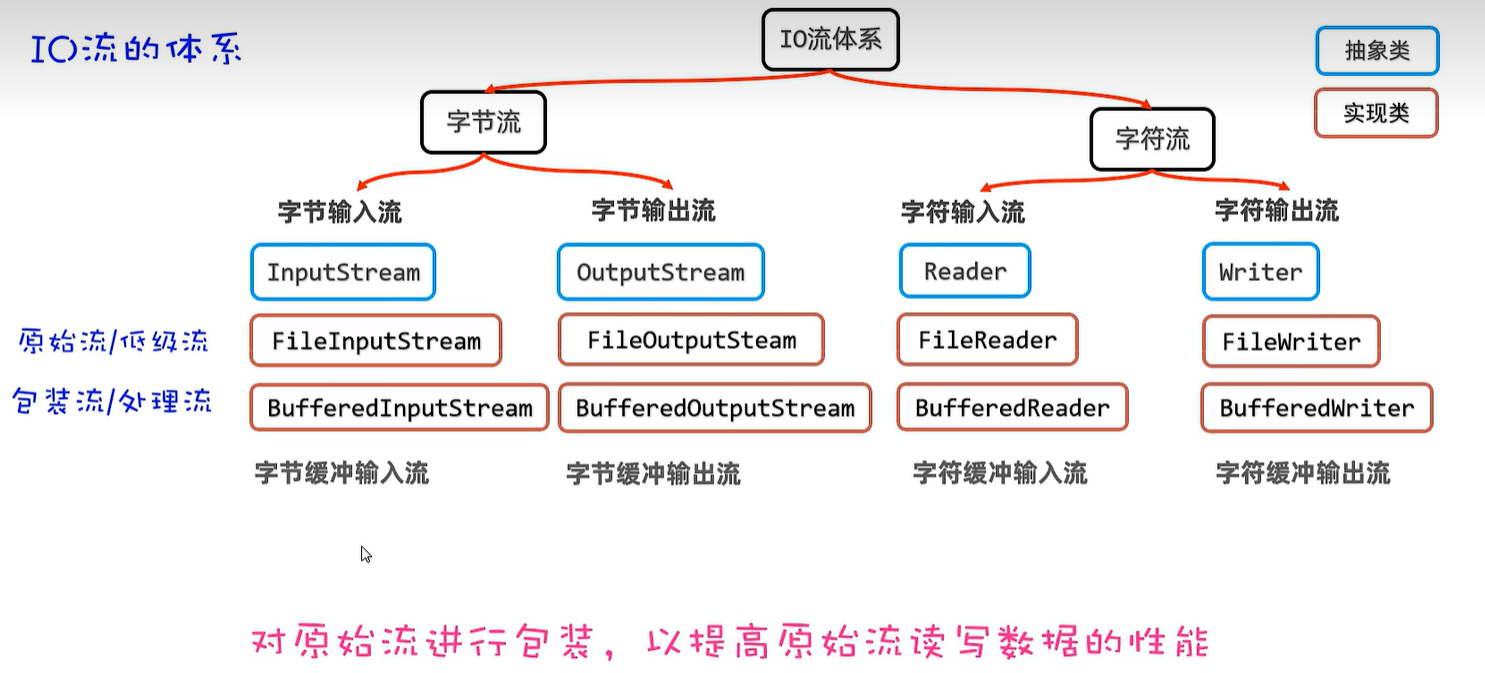
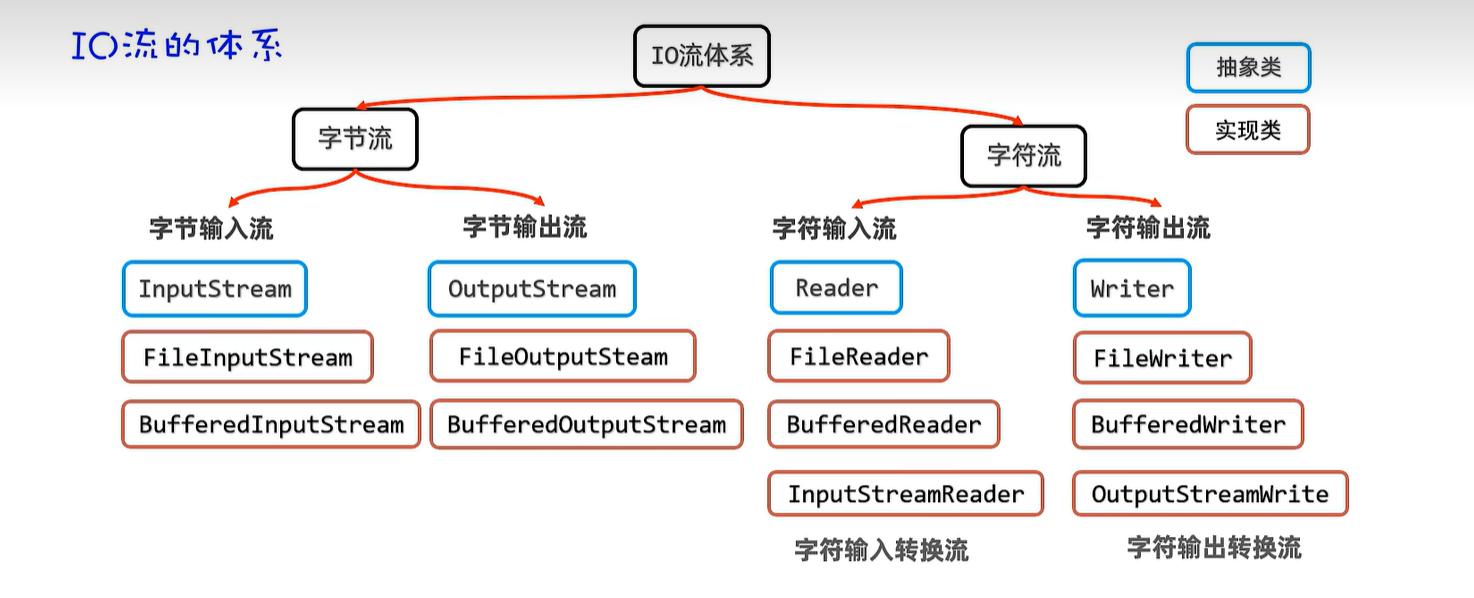
20. IO流
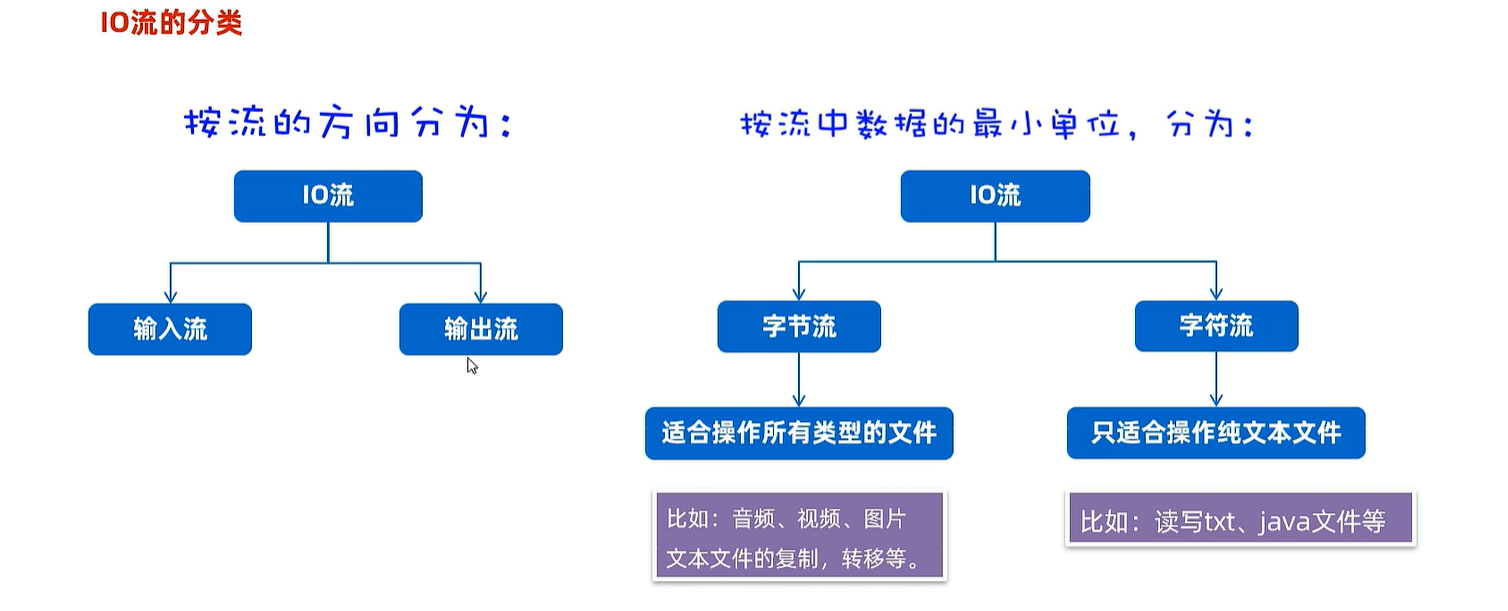
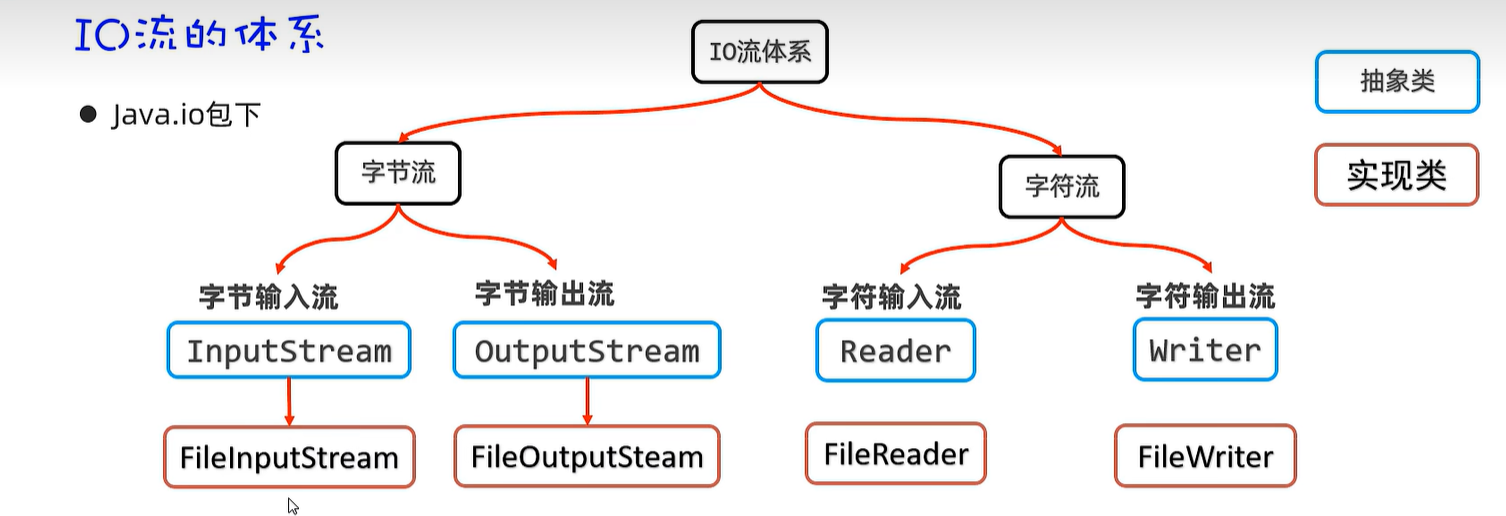
20.1 字节输入流

public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1、创建文件字节输入流管道,与源文件接通。
// InputStream is = new FileInputStream(new File("file-io-app\\src\\itheima01.txt"));
// 简化写法:推荐使用。
InputStream is = new FileInputStream(("file-io-app\\src\\itheima01.txt"));
// 2、开始读取文件的字节数据。
// public int read():每次读取一个字节返回,如果没有数据了,返回-1.
int b1 = is.read();
System.out.println((char)b1);
int b2 = is.read();
System.out.println((char) b2);
int b3 = is.read();
System.out.println(b3);
// 3、使用循环改造上述代码
int b; // 用于记住读取的字节。
while ((b = is.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char) b);
}
// 读取数据的性能很差!
// 读取汉字输出会乱码!!无法避免的!!
// 流使用完毕之后,必须关闭!释放系统资源!
is.close();
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1、创建一个字节输入流对象代表字节输入流管道与源文件接通。
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("file-io-app\\src\\itheima02.txt");
// 2、开始读取文件中的字节数据:每次读取多个字节。
// public int read(byte b[]) throws IOException
// 每次读取多个字节到字节数组中去,返回读取的字节数量,读取完毕会返回-1.
byte[] buffer = new byte[3];
int len = is.read(buffer);
String rs = new String(buffer);
System.out.println(rs);
System.out.println("当次读取的字节数量:" + len);
// buffer = [abc]
// buffer = [66c]
int len2 = is.read(buffer);
// 注意:读取多少,倒出多少。
String rs2 = new String(buffer, 0, len2);
System.out.println(rs2);
System.out.println("当次读取的字节数量:" + len2);
int len3 = is.read(buffer);
System.out.println(len3); // -1
// 3、使用循环改造。
byte[] buffer = new byte[3];
int len; // 记住每次读取了多少个字节。 abc 66
while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
// 注意:读取多少,倒出多少。
String rs = new String(buffer, 0 , len);
System.out.print(rs);
}
// 性能得到了明显的提升!!
// 这种方案也不能避免读取汉字输出乱码的问题!!
is.close(); // 关闭流
}

public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1、一次性读取完文件的全部字节到一个字节数组中去。
// 创建一个字节输入流管道与源文件接通
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("file-io-app\\src\\itheima03.txt");
// 2、准备一个字节数组,大小与文件的大小正好一样大。
File f = new File("file-io-app\\src\\itheima03.txt");
long size = f.length();
byte[] buffer = new byte[(int) size];
int len = is.read(buffer);
System.out.println(new String(buffer));
System.out.println(size);
System.out.println(len);
byte[] buffer = is.readAllBytes();
System.out.println(new String(buffer));
is.close(); // 关闭流
}
20.2 字节输出流
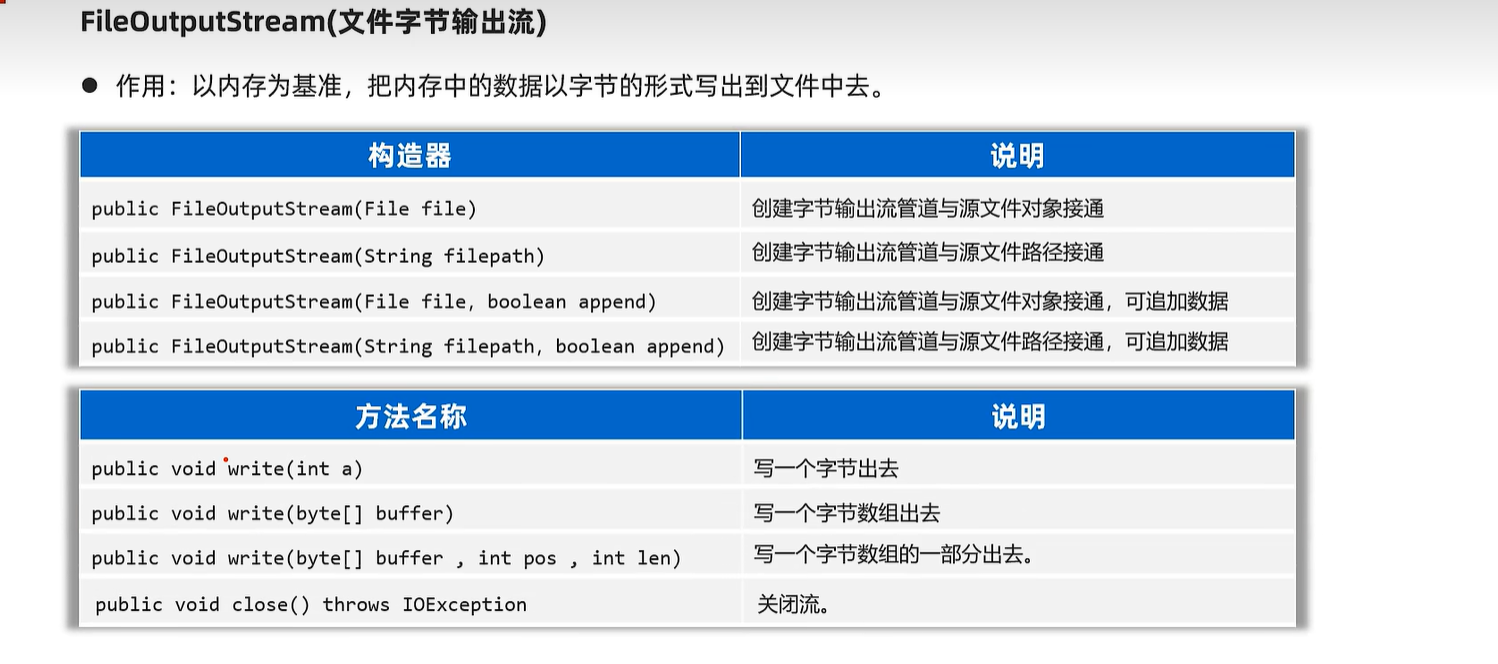
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1、创建一个字节输出流管道与目标文件接通。
// 覆盖管道:覆盖之前的数据
// OutputStream os =
// new FileOutputStream("file-io-app/src/itheima04out.txt");
// 追加数据的管道
OutputStream os =
new FileOutputStream("file-io-app/src/itheima04out.txt", true);
// 2、开始写字节数据出去了
os.write(97); // 97就是一个字节,代表a
os.write('b'); // 'b'也是一个字节
// os.write('磊'); // [ooo] 默认只能写出去一个字节
byte[] bytes = "我爱你中国abc".getBytes();
os.write(bytes);
os.write(bytes, 0, 15);
// 换行符
os.write("\r\n".getBytes());
os.close(); // 关闭流
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 需求:复制照片。
// 1、创建一个字节输入流管道与源文件接通
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("file-io-app\\src\\itheima03.txt");
// 2、创建一个字节输出流管道与目标文件接通。
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("file-io-app\\src\\itheima03copy.txt");
System.out.println(10 / 0);
// 3、创建一个字节数组,负责转移字节数据。
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; // 1KB.
// 4、从字节输入流中读取字节数据,写出去到字节输出流中。读多少写出去多少。
int len; // 记住每次读取了多少个字节。
while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
os.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
os.close();
is.close();
System.out.println("复制完成!!");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
InputStream is = null;
OutputStream os = null;
try {
System.out.println(10 / 0);
// 1、创建一个字节输入流管道与源文件接通
is = new FileInputStream("file-io-app\\src\\itheima03.txt");
// 2、创建一个字节输出流管道与目标文件接通。
os = new FileOutputStream("file-io-app\\src\\itheima03copy.txt");
System.out.println(10 / 0);
// 3、创建一个字节数组,负责转移字节数据。
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; // 1KB.
// 4、从字节输入流中读取字节数据,写出去到字节输出流中。读多少写出去多少。
int len; // 记住每次读取了多少个字节。
while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
os.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
System.out.println("复制完成!!");
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
// 释放资源的操作
try {
if(os != null) os.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
try {
if(is != null) is.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}

public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
// 1、创建一个字节输入流管道与源文件接通
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("file-io-app\\src\\itheima03.txt");
// 2、创建一个字节输出流管道与目标文件接通。
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("file-io-app\\src\\itheima03copy.txt");
// 注意:这里只能放置资源对象。(流对象)
// int age = 21;
// 什么是资源呢?资源都是会实现AutoCloseable接口。资源都会有一个close方法,并且资源放到这里后
// 用完之后,会被自动调用其close方法完成资源的释放操作。
MyConnection conn = new MyConnection();
){
// 3、创建一个字节数组,负责转移字节数据。
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024]; // 1KB.
// 4、从字节输入流中读取字节数据,写出去到字节输出流中。读多少写出去多少。
int len; // 记住每次读取了多少个字节。
while ((len = is.read(buffer)) != -1){
os.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
System.out.println(conn);
System.out.println("复制完成!!");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
20.3 字符输入流

public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
// 1、创建一个文件字符输入流管道与源文件接通
Reader fr = new FileReader("io-app2\\src\\itheima01.txt");
){
// 2、读取文本文件的内容了。
int c; // 记住每次读取的字符编号。
while ((c = fr.read()) != -1){
System.out.print((char) c);
}
// 每次读取一个字符的形式,性能肯定是比较差的。
// 3、每次读取多个字符。
char[] buffer = new char[3];
int len; // 记住每次读取了多少个字符。
while ((len = fr.read(buffer)) != -1){
// 读取多少倒出多少
System.out.print(new String(buffer, 0, len));
}
// 性能是比较不错的!
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
20.4 字符输出流
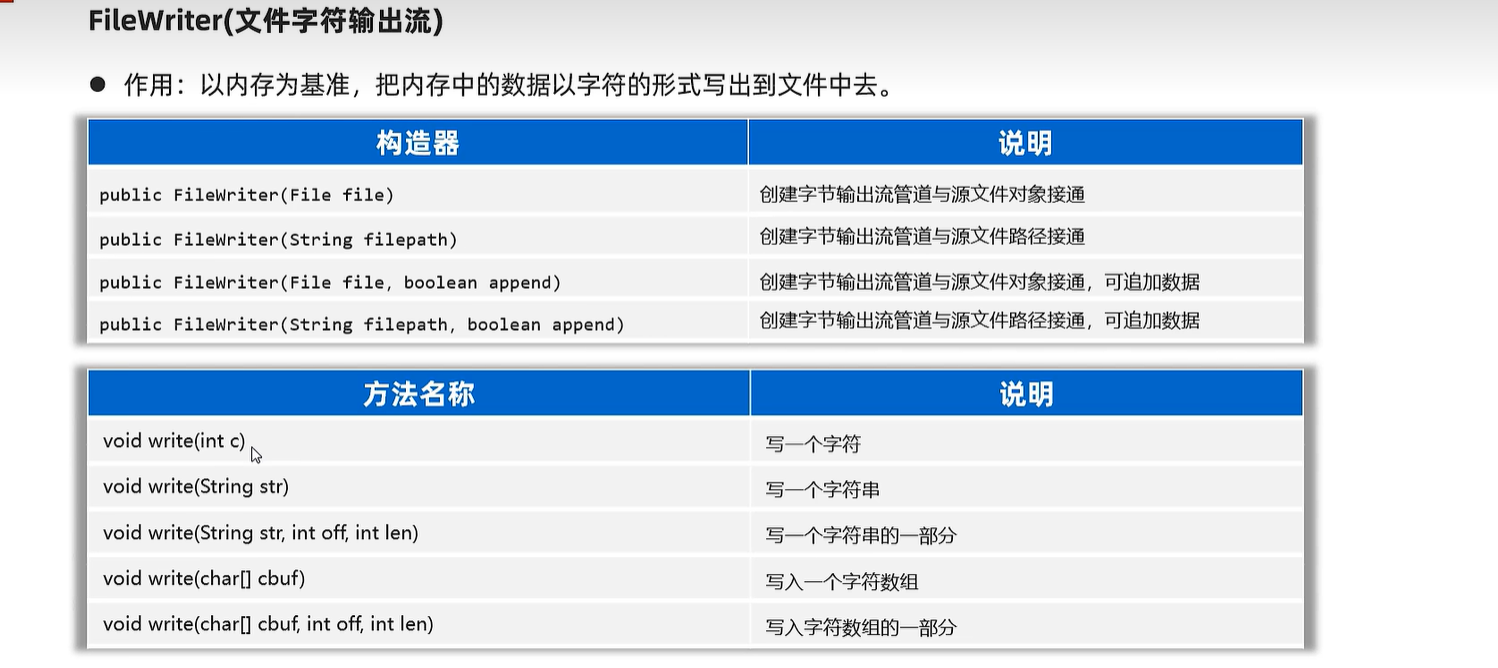

public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
// 0、创建一个文件字符输出流管道与目标文件接通。
// 覆盖管道
// Writer fw = new FileWriter("io-app2/src/itheima02out.txt");
// 追加数据的管道
Writer fw = new FileWriter("io-app2/src/itheima02out.txt", true);
){
// 1、public void write(int c):写一个字符出去
fw.write('a');
fw.write(97);
//fw.write('磊'); // 写一个字符出去
fw.write("\r\n"); // 换行
// 2、public void write(String c)写一个字符串出去
fw.write("我爱你中国abc");
fw.write("\r\n");
// 3、public void write(String c ,int pos ,int len):写字符串的一部分出去
fw.write("我爱你中国abc", 0, 5);
fw.write("\r\n");
// 4、public void write(char[] buffer):写一个字符数组出去
char[] buffer = {'黑', '马', 'a', 'b', 'c'};
fw.write(buffer);
fw.write("\r\n");
// 5、public void write(char[] buffer ,int pos ,int len):写字符数组的一部分出去
fw.write(buffer, 0, 2);
fw.write("\r\n");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
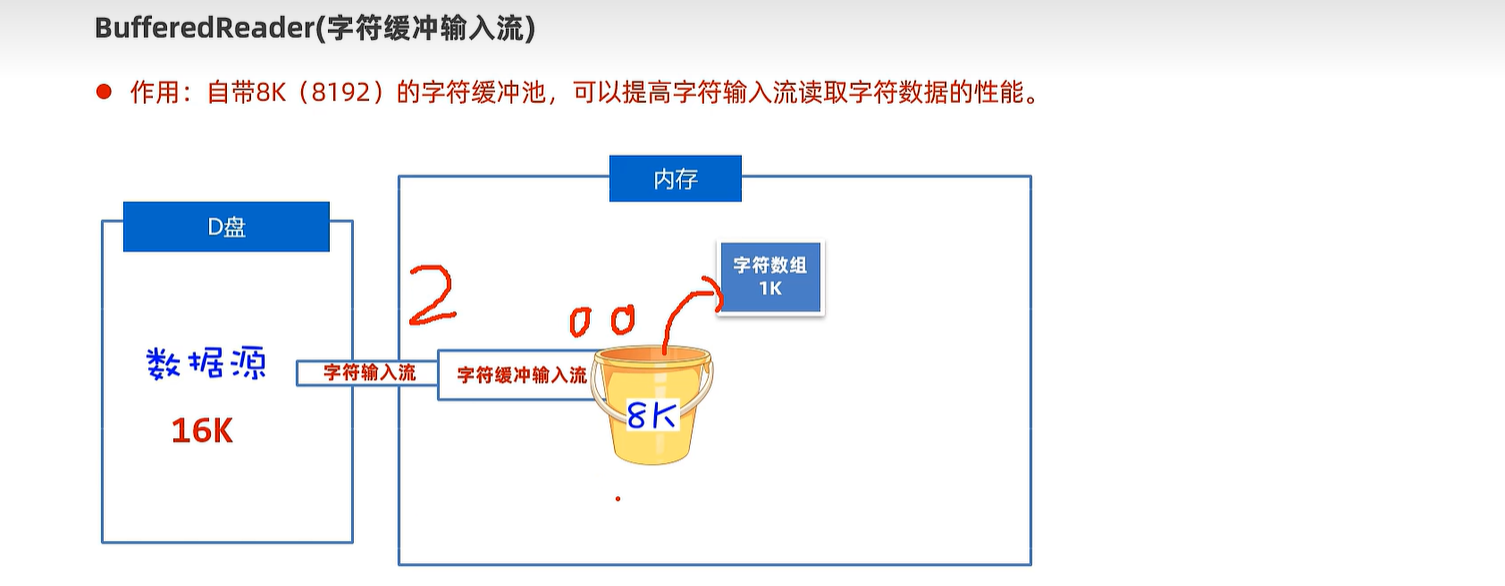
20.5 字节缓冲输入及输出流
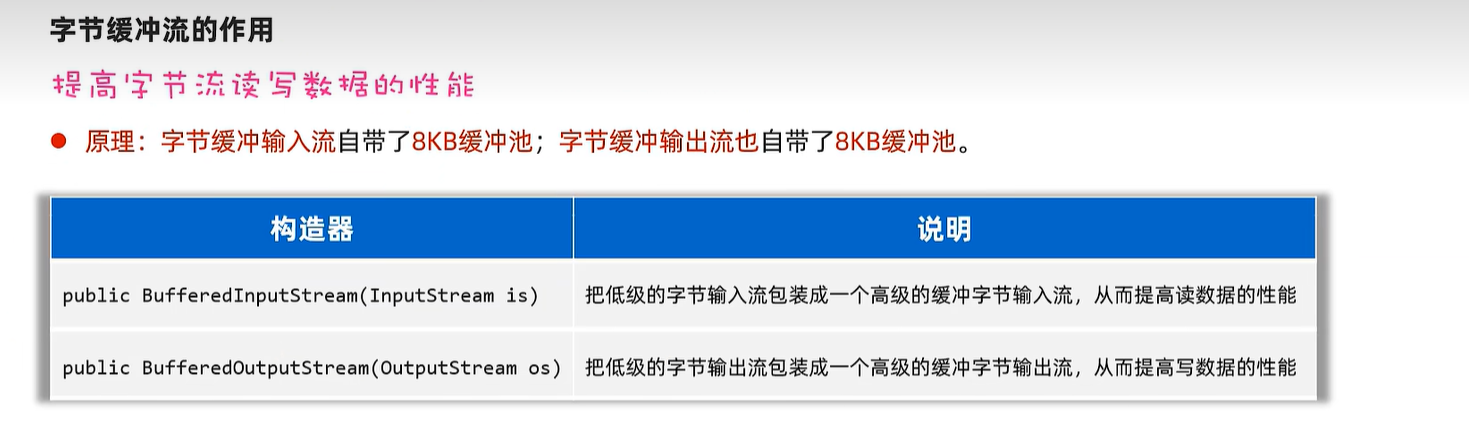
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("io-app2/src/itheima01.txt");
// 1、定义一个字节缓冲输入流包装原始的字节输入流
InputStream bis = new BufferedInputStream(is);
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("io-app2/src/itheima01_bak.txt");
// 2、定义一个字节缓冲输出流包装原始的字节输出流
OutputStream bos = new BufferedOutputStream(os);
){
byte[] buffer = new byte[1024];
int len;
while ((len = bis.read(buffer)) != -1){
bos.write(buffer, 0, len);
}
System.out.println("复制完成!!");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
20.6 字符缓冲输入及输出流

public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
Reader fr = new FileReader("io-app2\\src\\itheima04.txt");
// 创建一个字符缓冲输入流包装原始的字符输入流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
){
char[] buffer = new char[3];
int len;
while ((len = br.read(buffer)) != -1){
System.out.print(new String(buffer, 0, len));
}
System.out.println(br.readLine());
System.out.println(br.readLine());
System.out.println(br.readLine());
System.out.println(br.readLine());
String line; // 记住每次读取的一行数据
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
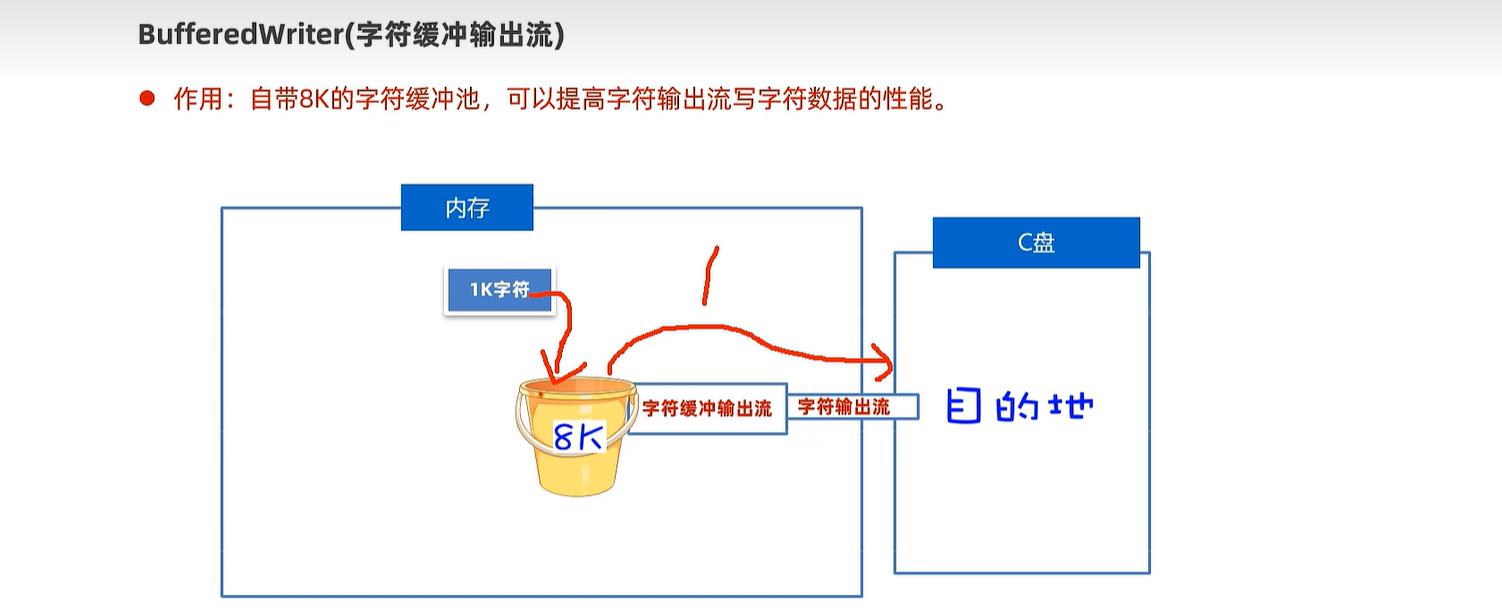
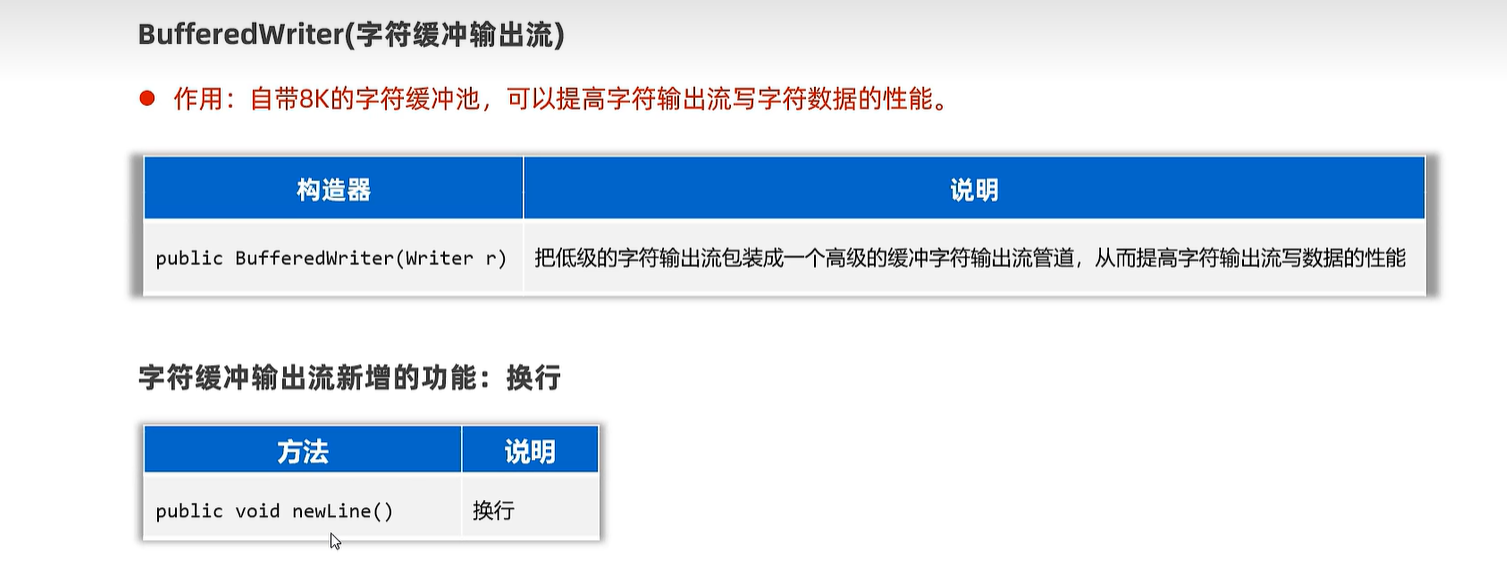
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
Writer fw = new FileWriter("io-app2/src/itheima05out.txt", true);
// 创建一个字符缓冲输出流管道包装原始的字符输出流
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(fw);
){
bw.write('a');
bw.write(97);
bw.write('磊');
bw.newLine();
bw.write("我爱你中国abc");
bw.newLine();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
20.7 字符转换输入及输出流

public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
// 1、得到文件的原始字节流(GBK的字节流形式)
InputStream is = new FileInputStream("io-app2/src/itheima06.txt");
// 2、把原始的字节输入流按照指定的字符集编码转换成字符输入流
Reader isr = new InputStreamReader(is, "GBK");
// 3、把字符输入流包装成缓冲字符输入流
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(isr);
){
String line;
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null){
System.out.println(line);
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 指定写出去的字符编码。
try (
// 1、创建一个文件字节输出流
OutputStream os = new FileOutputStream("io-app2/src/itheima07out.txt");
// 2、把原始的字节输出流,按照指定的字符集编码转换成字符输出转换流。
Writer osw = new OutputStreamWriter(os, "GBK");
// 3、把字符输出流包装成缓冲字符输出流
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(osw);
){
bw.write("我是中国人abc");
bw.write("我爱你中国123");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
20.8 打印流

try (
// 1、创建一个打印流管道
// PrintStream ps =
// new PrintStream("io-app2/src/itheima08.txt", Charset.forName("GBK"));
// PrintStream ps =
// new PrintStream("io-app2/src/itheima08.txt");
PrintWriter ps =
new PrintWriter(new FileOutputStream("io-app2/src/itheima08.txt", true));
){
ps.println(97);
ps.println('a');
ps.println("我爱你中国abc");
ps.println(true);
ps.println(99.5);
// ps.write(97); // 'a'
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}



public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("老骥伏枥");
System.out.println("志在千里");
try ( PrintStream ps = new PrintStream("io-app2/src/itheima09.txt"); ){
// 把系统默认的打印流对象改成自己设置的打印流
System.setOut(ps);
System.out.println("烈士暮年");
System.out.println("壮心不已");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
20.9 数据流
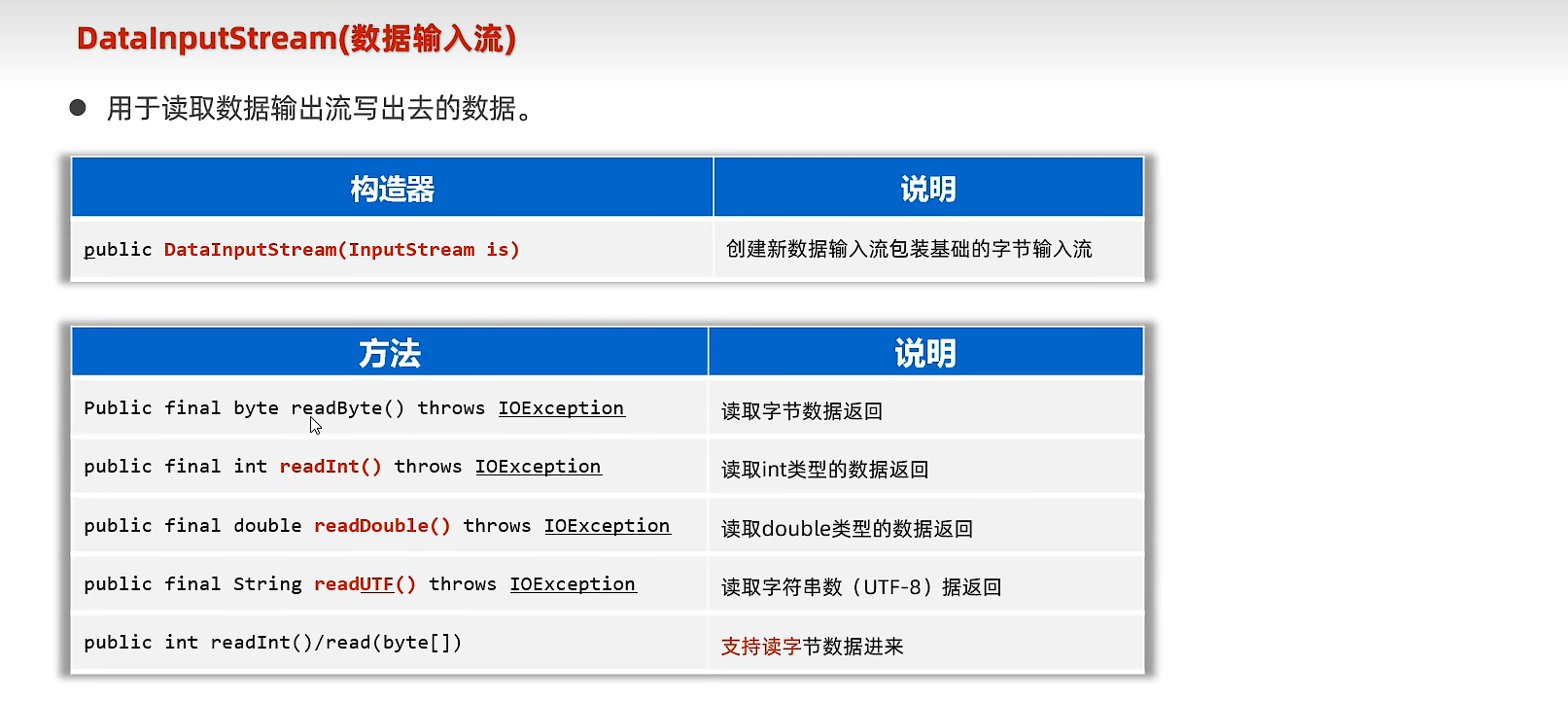
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
DataInputStream dis =
new DataInputStream(new FileInputStream("io-app2/src/itheima10out.txt"));
){
int i = dis.readInt();
System.out.println(i);
double d = dis.readDouble();
System.out.println(d);
boolean b = dis.readBoolean();
System.out.println(b);
String rs = dis.readUTF();
System.out.println(rs);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
// 1、创建一个数据输出流包装低级的字节输出流
DataOutputStream dos =
new DataOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("io-app2/src/itheima10out.txt"));
){
dos.writeInt(97);
dos.writeDouble(99.5);
dos.writeBoolean(true);
dos.writeUTF("黑马程序员666!");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
20.10 序列化流

// 注意:对象如果需要序列化,必须实现序列化接口。
public class User implements Serializable {
private String loginName;
private String userName;
private int age;
// transient 这个成员变量将不参与序列化。
private transient String passWord;
public User() {
}
public User(String loginName, String userName, int age, String passWord) {
this.loginName = loginName;
this.userName = userName;
this.age = age;
this.passWord = passWord;
}
//get set 方法
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
// 2、创建一个对象字节输出流包装原始的字节 输出流。
ObjectOutputStream oos =
new ObjectOutputStream(new FileOutputStream("io-app2/src/itheima11out.txt"));
){
// 1、创建一个Java对象。
User u = new User("admin", "张三", 32, "666888xyz");
// 3、序列化对象到文件中去
oos.writeObject(u);
System.out.println("序列化对象成功!!");
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}

public static void main(String[] args) {
try (
// 1、创建一个对象字节输入流管道,包装 低级的字节输入流与源文件接通
ObjectInputStream ois = new ObjectInputStream(new FileInputStream("io-app2/src/itheima11out.txt"));
){
User u = (User) ois.readObject();
System.out.println(u);
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
20.11 commons-io框架


public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
FileUtils.copyFile(new File("io-app2\\src\\itheima01.txt"), new File("io-app2/src/a.txt"));
FileUtils.copyDirectory(new File("D:\\resource\\私人珍藏"), new File("D:\\resource\\私人珍藏3"));
FileUtils.deleteDirectory(new File("D:\\resource\\私人珍藏3"));
// Java提供的原生的一行代码搞定很多事情
Files.copy(Path.of("io-app2\\src\\itheima01.txt"), Path.of("io-app2\\src\\b.txt"));
System.out.println(Files.readString(Path.of("io-app2\\src\\itheima01.txt")));
}
21. 常用特殊文件
21.1 properties
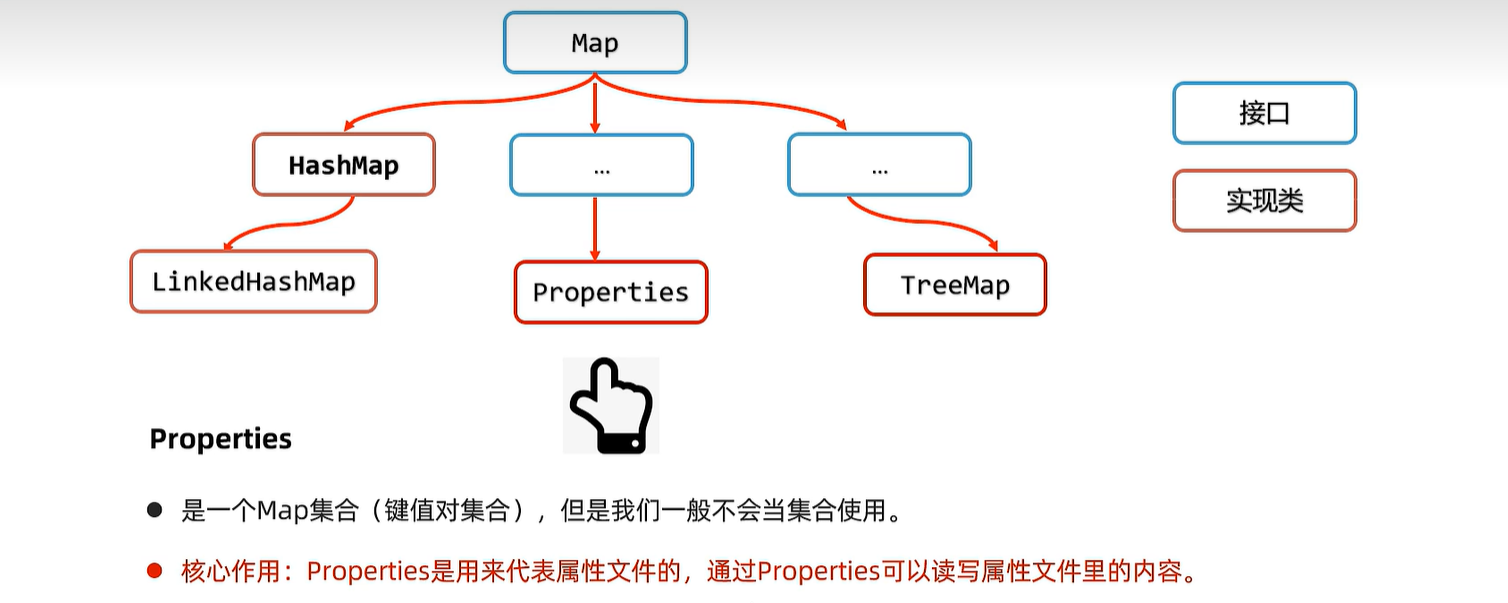

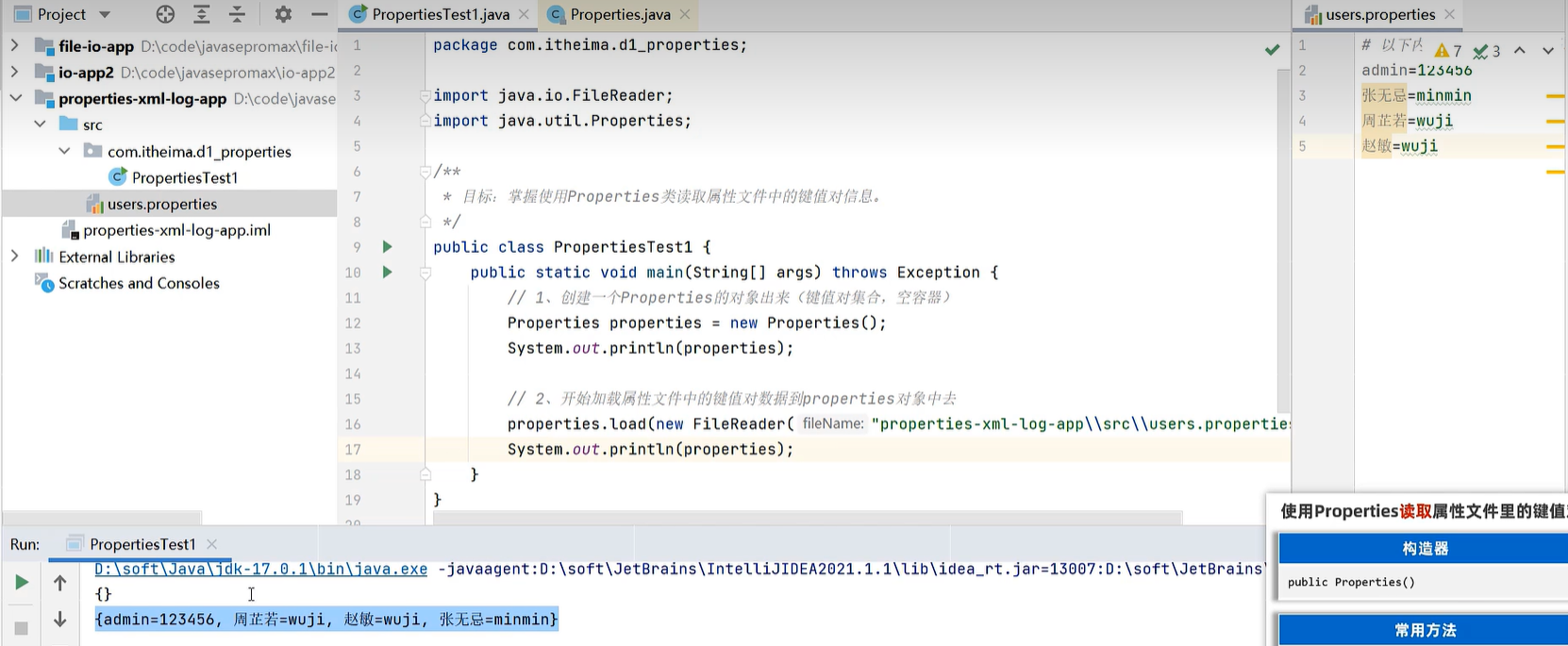
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1、创建一个Properties的对象出来(键值对集合,空容器)
Properties properties = new Properties();
System.out.println(properties);
// 2、开始加载属性文件中的键值对数据到properties对象中去
properties.load(new FileReader("properties-xml-log-app\\src\\users.properties"));
System.out.println(properties);
// 3、根据键取值
System.out.println(properties.getProperty("赵敏"));
System.out.println(properties.getProperty("张无忌"));
// 4、遍历全部的键和值。
Set<String> keys = properties.stringPropertyNames();
for (String key : keys) {
String value = properties.getProperty(key);
System.out.println(key + "---->" + value);
}
properties.forEach((k, v) -> {
System.out.println(k + "---->" + v);
});
}

public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1、创建Properties对象出来,先用它存储一些键值对数据
Properties properties = new Properties();
properties.setProperty("张无忌", "minmin");
properties.setProperty("殷素素", "cuishan");
properties.setProperty("张翠山", "susu");
// 2、把properties对象中的键值对数据存入到属性文件中去
properties.store(new FileWriter("properties-xml-log-app/src/users2.properties")
, "i saved many users!");
}
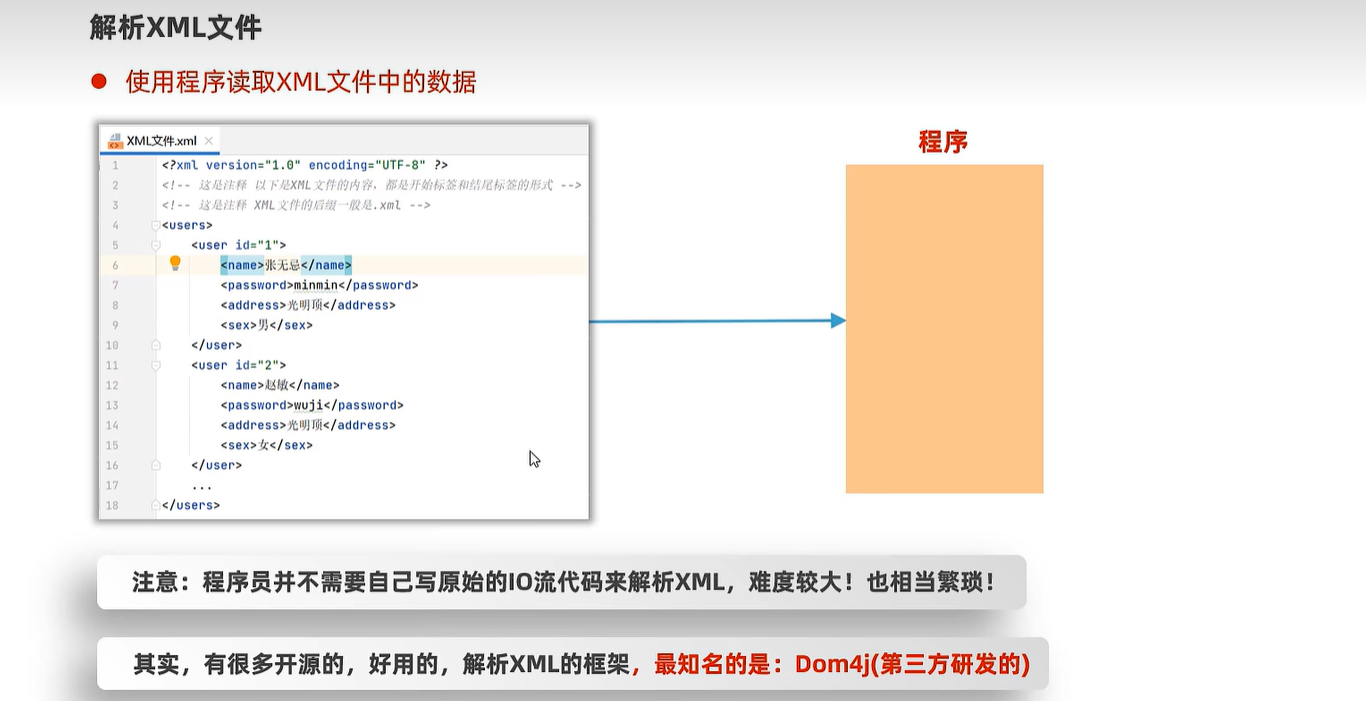
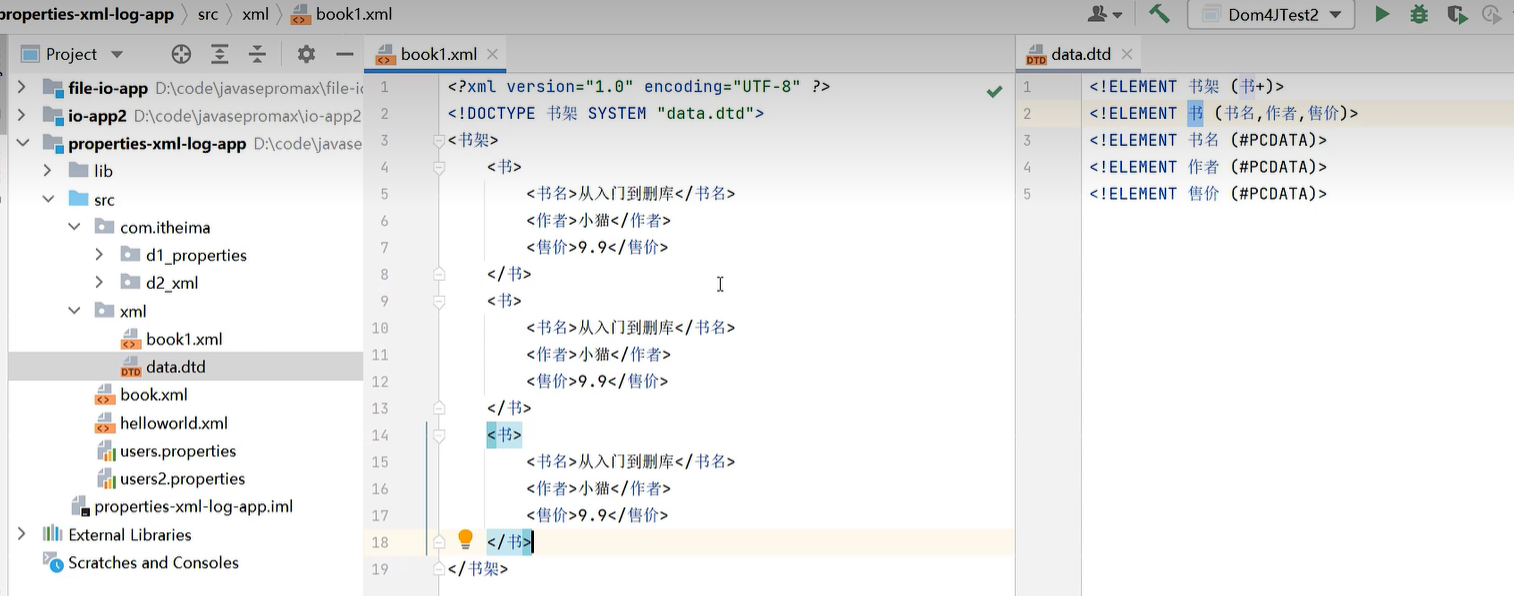
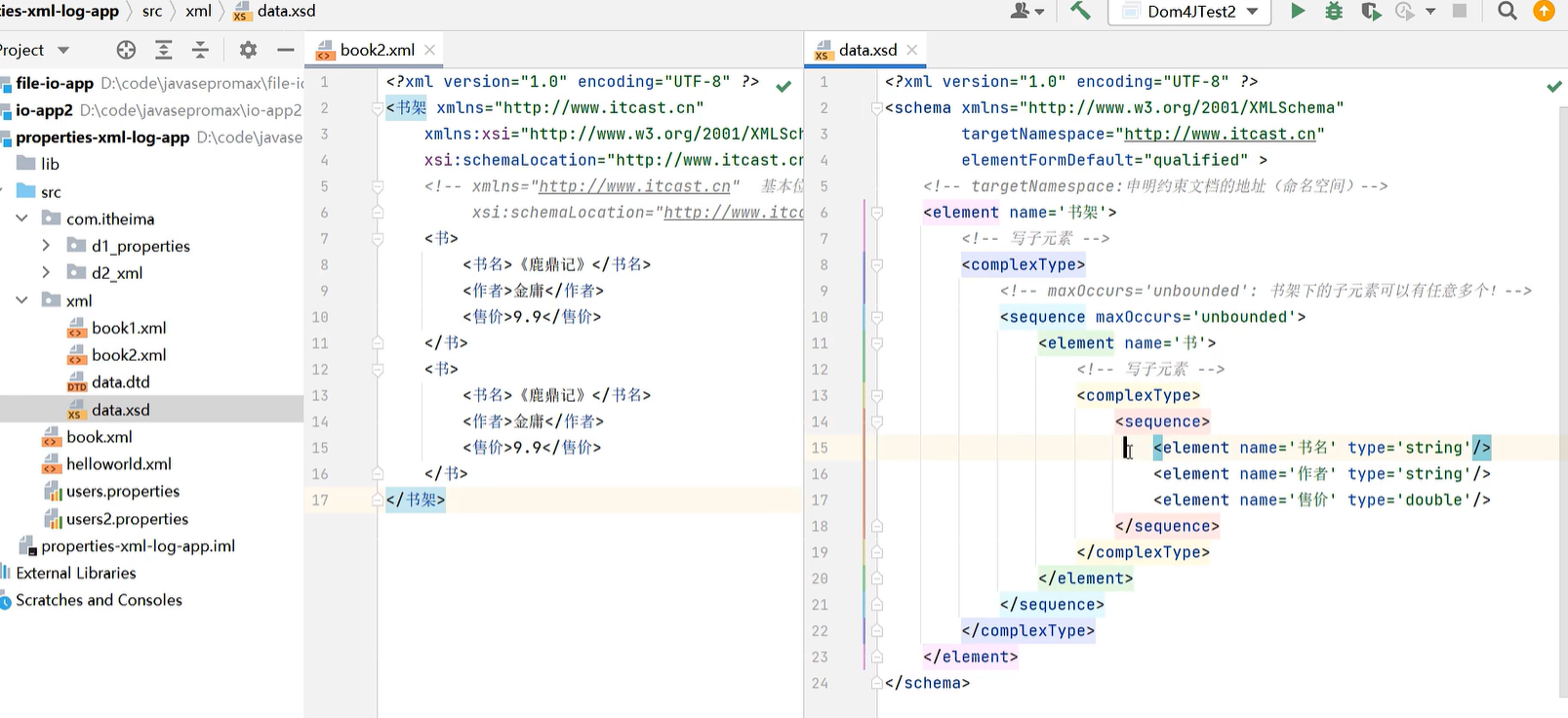
21.2 XML



public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1、创建一个Dom4J框架提供的解析器对象
SAXReader saxReader = new SAXReader();
// 2、使用saxReader对象把需要解析的XML文件读成一个Document对象。
Document document =
saxReader.read("properties-xml-log-app\\src\\helloworld.xml");
// 3、从文档对象中解析XML文件的全部数据了
Element root = document.getRootElement();
System.out.println(root.getName());
// 4、获取根元素下的全部一级子元素。
// List<Element> elements = root.elements();
List<Element> elements = root.elements("user");
for (Element element : elements) {
System.out.println(element.getName());
}
// 5、获取当前元素下的某个子元素。
Element people = root.element("people");
System.out.println(people.getText());
// 如果下面有很多子元素user,默认获取第一个。
Element user = root.element("user");
System.out.println(user.elementText("name"));
// 6、获取元素的属性信息呢?
System.out.println(user.attributeValue("id"));
Attribute id = user.attribute("id");
System.out.println(id.getName());
System.out.println(id.getValue());
List<Attribute> attributes = user.attributes();
for (Attribute attribute : attributes) {
System.out.println(attribute.getName() + "=" + attribute.getValue());
}
// 7、如何获取全部的文本内容:获取当前元素下的子元素文本值
System.out.println(user.elementText("name"));
System.out.println(user.elementText("地址"));
System.out.println(user.elementTextTrim("地址")); // 取出文本去除前后空格
System.out.println(user.elementText("password"));
Element data = user.element("data");
System.out.println(data.getText());
System.out.println(data.getTextTrim()); // 取出文本去除前后空格
}

public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、使用一个StringBuilder对象来拼接XML格式的数据。
StringBuilder sb = new StringBuilder();
sb.append("<?xml version=\"1.0\" encoding=\"UTF-8\" ?>\r\n");
sb.append("<book>\r\n");
sb.append("\t<name>").append("从入门到跑路").append("</name>\r\n");
sb.append("\t<author>").append("dlei").append("</author>\r\n");
sb.append("\t<price>").append(999.99).append("</price>\r\n");
sb.append("</book>");
try (
BufferedWriter bw = new BufferedWriter(new FileWriter("properties-xml-log-app/src/book.xml"));
){
bw.write(sb.toString());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}


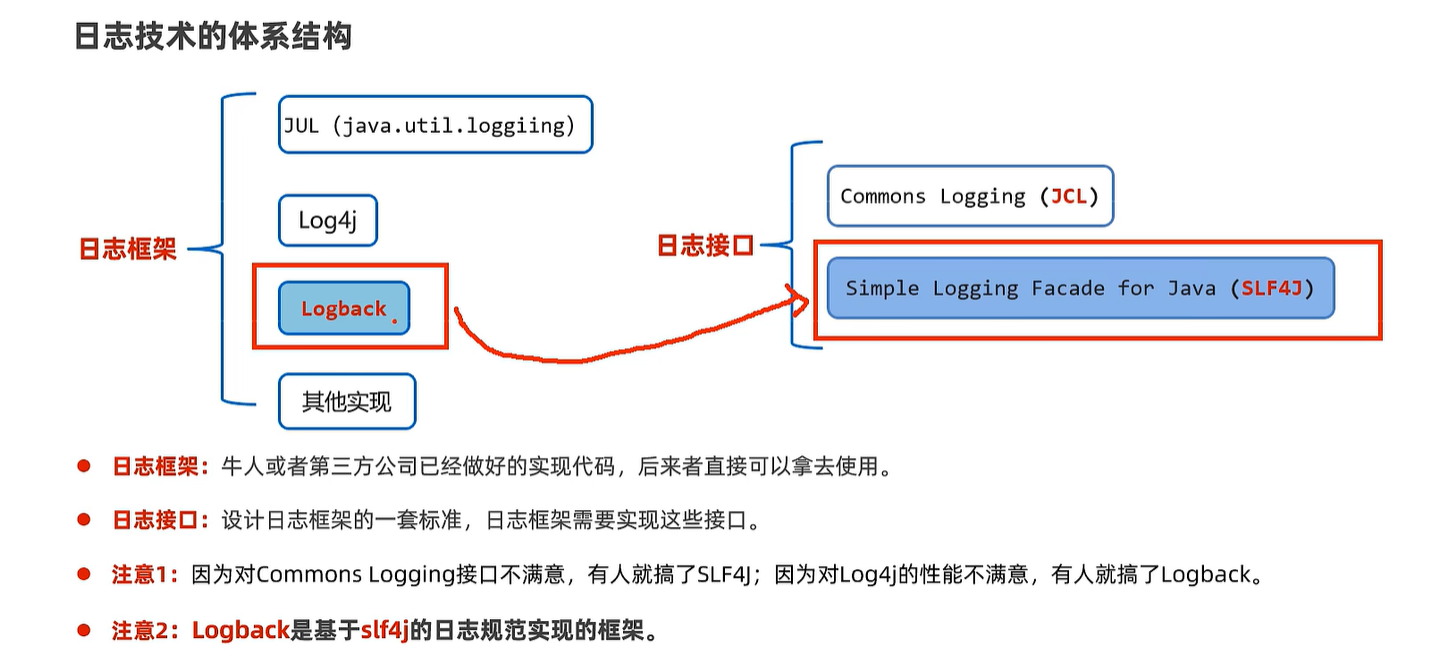
22. 日志框架
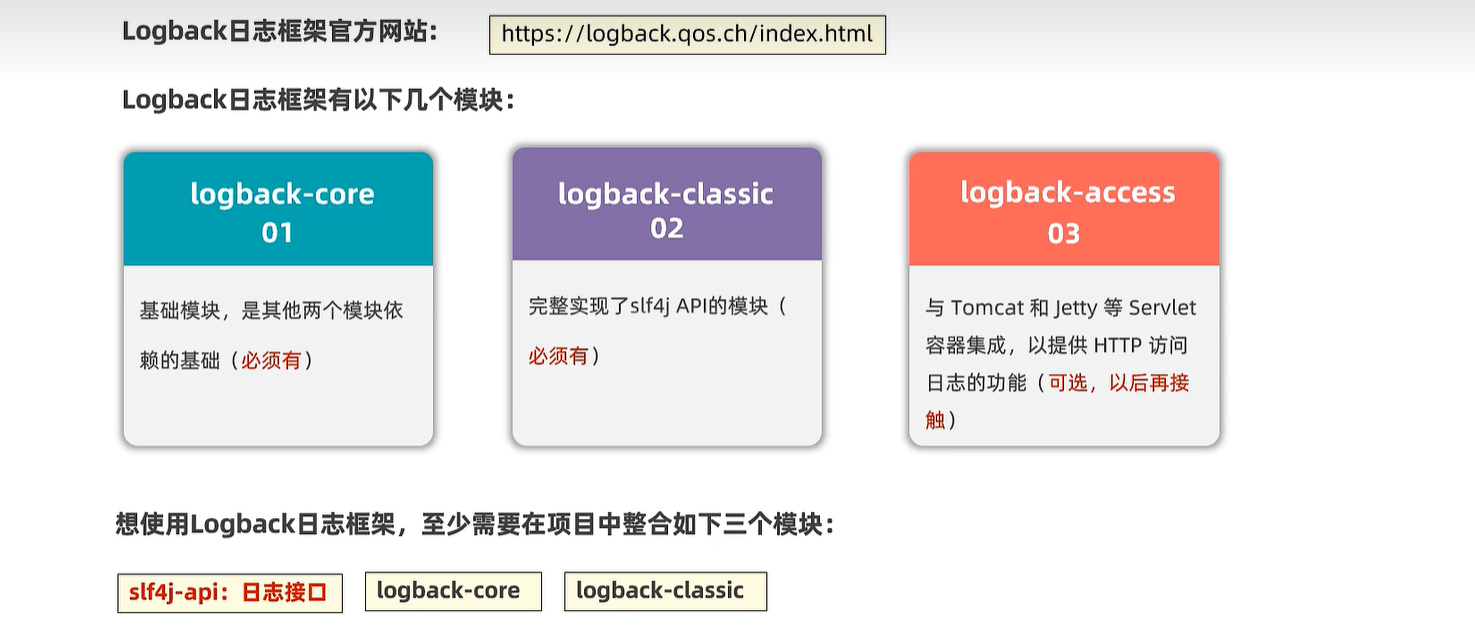
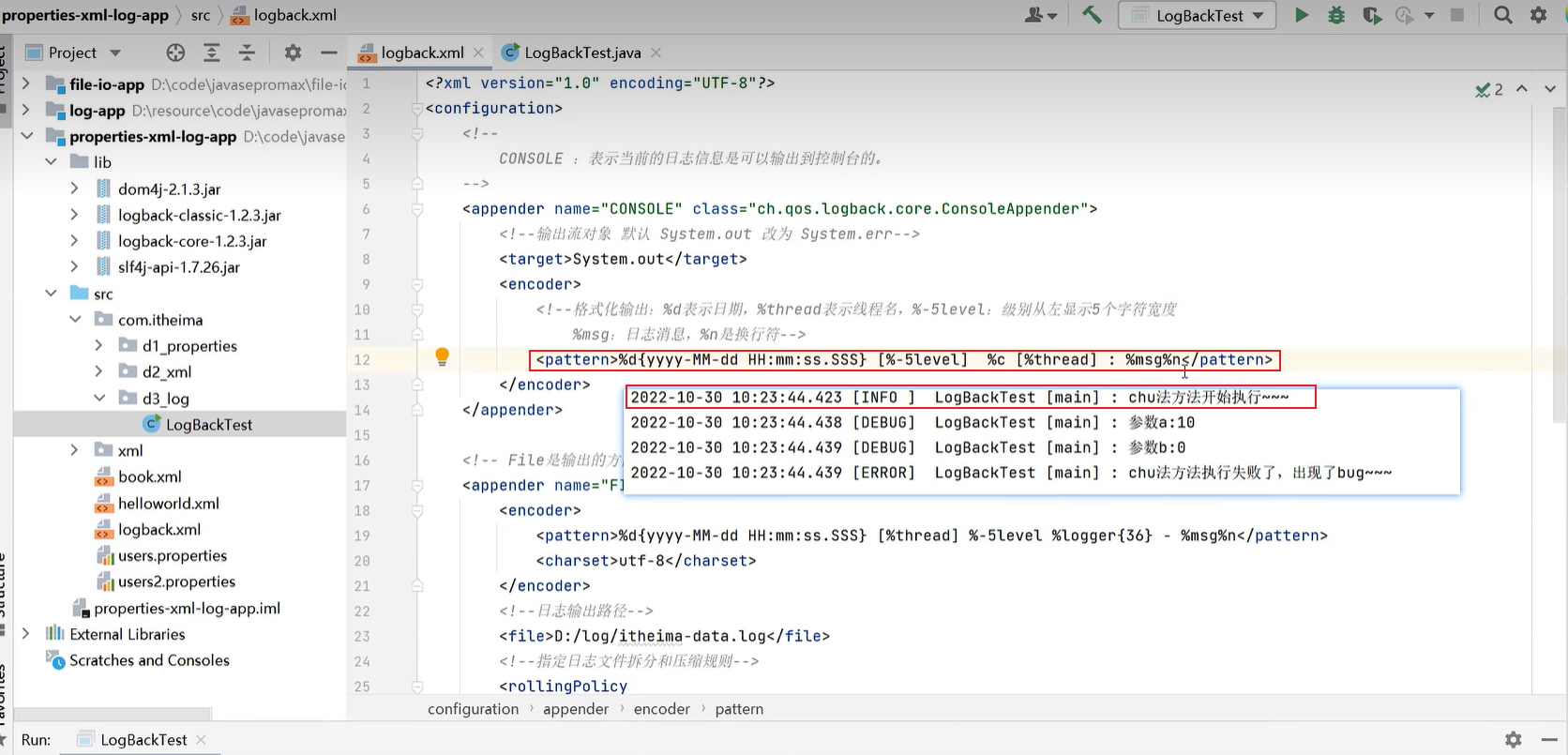
logback.xml
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<configuration>
<!--
CONSOLE :表示当前的日志信息是可以输出到控制台的。
-->
<appender name="CONSOLE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.ConsoleAppender">
<!--输出流对象 默认 System.out 改为 System.err-->
<target>System.out</target>
<encoder>
<!--格式化输出:%d表示日期,%thread表示线程名,%-5level:级别从左显示5个字符宽度
%msg:日志消息,%n是换行符-->
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%-5level] %c [%thread] : %msg%n</pattern>
</encoder>
</appender>
<!-- File是输出的方向通向文件的 -->
<appender name="FILE" class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.RollingFileAppender">
<encoder>
<pattern>%d{yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss.SSS} [%thread] %-5level %logger{36} - %msg%n</pattern>
<charset>utf-8</charset>
</encoder>
<!--日志输出路径-->
<file>D:/log/itheima-data.log</file>
<!--指定日志文件拆分和压缩规则-->
<rollingPolicy
class="ch.qos.logback.core.rolling.SizeAndTimeBasedRollingPolicy">
<!--通过指定压缩文件名称,来确定分割文件方式 -%i 序列号-->
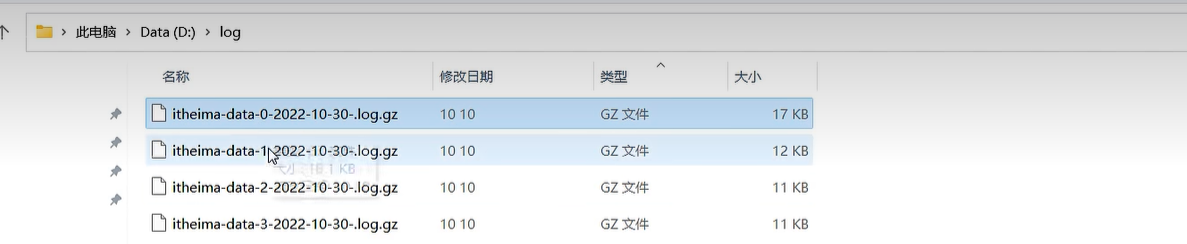
<fileNamePattern>D:/log/itheima-data-%i-%d{yyyy-MM-dd}-.log.gz</fileNamePattern>
<!--文件拆分大小-->
<maxFileSize>1MB</maxFileSize>
</rollingPolicy>
</appender>
<!--
1、控制日志的输出情况:如,开启日志,取消日志
-->
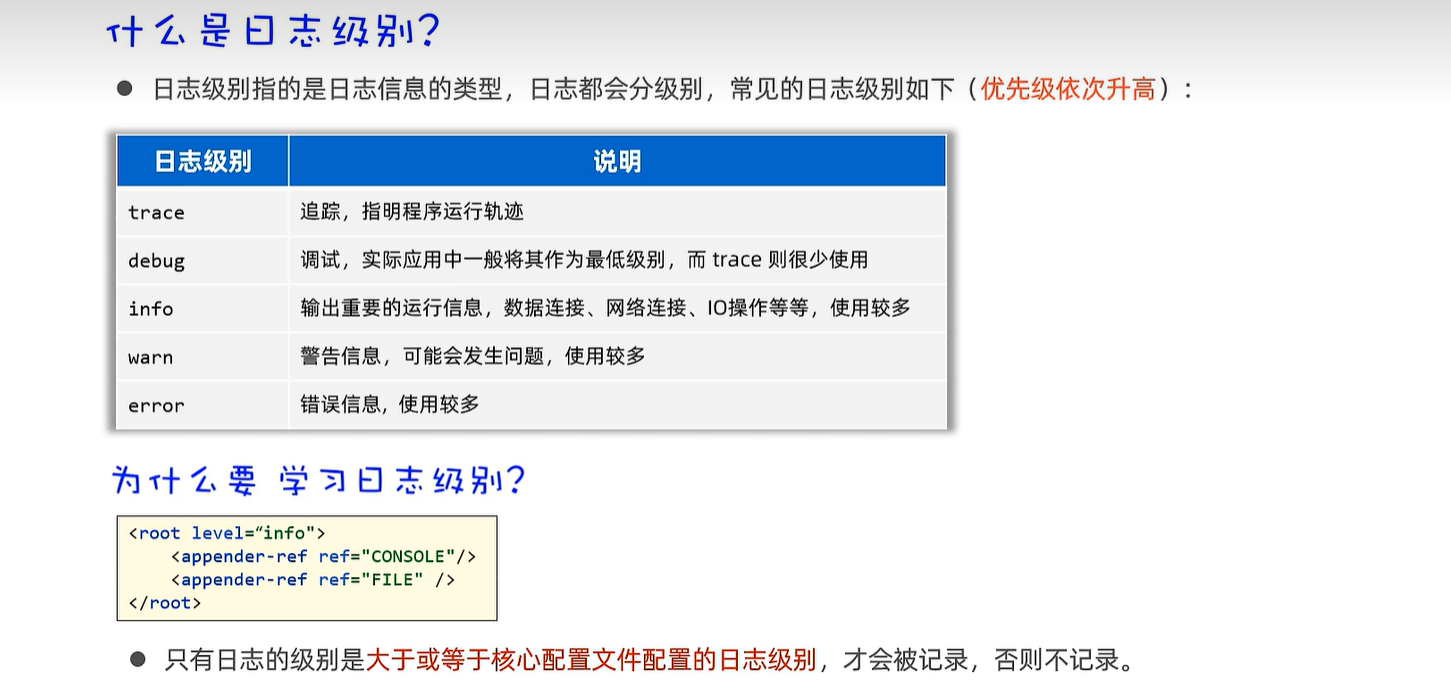
<root level="debug">
<appender-ref ref="CONSOLE"/>
<appender-ref ref="FILE" />
</root>
</configuration>
public class LogBackTest {
// 创建一个Logger日志对象
public static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger("LogBackTest");
public static void main(String[] args) {
//while (true) {
try {
LOGGER.info("chu法方法开始执行~~~");
chu(10, 0);
LOGGER.info("chu法方法执行成功~~~");
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("chu法方法执行失败了,出现了bug~~~");
}
//}
}
public static void chu(int a, int b){
LOGGER.debug("参数a:" + a);
LOGGER.debug("参数b:" + b);
int c = a / b;
LOGGER.info("结果是:" + c);
}
}
23. 线程
23.1 线程创建

public class MyThread extends Thread{
// 2、必须重写Thread类的run方法
@Override
public void run() {
// 描述线程的执行任务。
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("子线程MyThread输出:" + i);
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest1 {
// main方法是由一条默认的主线程负责执行。
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 3、创建MyThread线程类的对象代表一个线程
Thread t = new MyThread();
// 4、启动线程(自动执行run方法的)
t.start(); // main线程 t线程
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("主线程main输出:" + i);
}
}
}
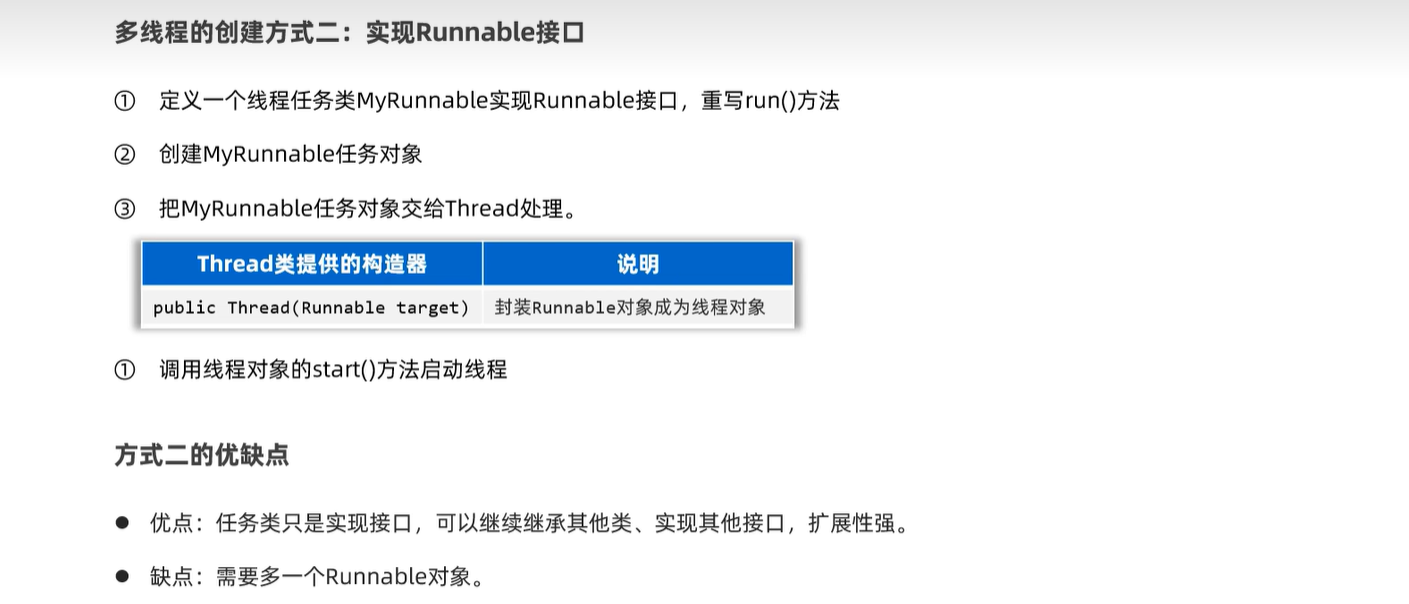
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
// 2、重写runnable的run方法
@Override
public void run() {
// 线程要执行的任务。
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("子线程输出 ===》" + i);
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 3、创建任务对象。
Runnable target = new MyRunnable();
// 4、把任务对象交给一个线程对象处理。
// public Thread(Runnable target)
new Thread(target).start();
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println("主线程main输出 ===》" + i);
}
}
}


public class MyCallable implements Callable<String> {
private int n;
public MyCallable(int n) {
this.n = n;
}
// 2、重写call方法
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
// 描述线程的任务,返回线程执行返回后的结果。
// 需求:求1-n的和返回。
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum += i;
}
return "线程求出了1-" + n + "的和是:" + sum;
}
}
public class ThreadTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 3、创建一个Callable的对象
Callable<String> call = new MyCallable(100);
// 4、把Callable的对象封装成一个FutureTask对象(任务对象)
// 未来任务对象的作用?
// 1、是一个任务对象,实现了Runnable对象.
// 2、可以在线程执行完毕之后,用未来任务对象调用get方法获取线程执行完毕后的结果。
FutureTask<String> f1 = new FutureTask<>(call);
// 5、把任务对象交给一个Thread对象
new Thread(f1).start();
Callable<String> call2 = new MyCallable(200);
FutureTask<String> f2 = new FutureTask<>(call2);
new Thread(f2).start();
// 6、获取线程执行完毕后返回的结果。
// 注意:如果执行到这儿,假如上面的线程还没有执行完毕
// 这里的代码会暂停,等待上面线程执行完毕后才会获取结果。
String rs = f1.get();
System.out.println(rs);
String rs2 = f2.get();
System.out.println(rs2);
}
}
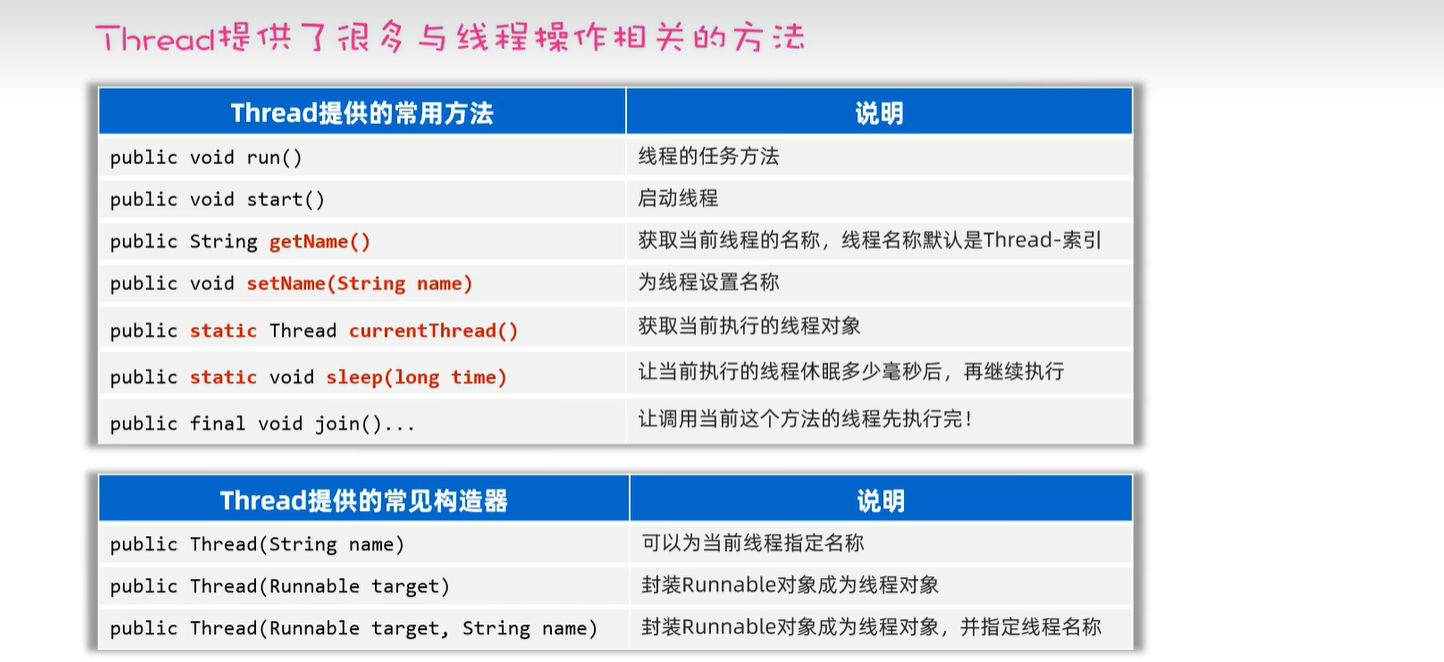
23.2 线程常用api
public class MyThread extends Thread{
public MyThread(String name){
super(name); // 为当前线程设置名字了
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 哪个线程执行它,它就会得到哪个线程对象。
Thread t = Thread.currentThread();
for (int i = 1; i <= 3; i++) {
System.out.println(t.getName() + "输出:" + i);
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Thread t1 = new MyThread("1号线程");
// t1.setName("1号线程");
t1.start();
System.out.println(t1.getName()); // Thread-0
Thread t2 = new MyThread("2号线程");
// t2.setName("2号线程");
t2.start();
System.out.println(t2.getName()); // Thread-1
// 主线程对象的名字
// 哪个线程执行它,它就会得到哪个线程对象。
Thread m = Thread.currentThread();
m.setName("最牛的线程");
System.out.println(m.getName()); // main
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(m.getName() + "线程输出:" + i);
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
System.out.println(Runtime.getRuntime().availableProcessors());
for (int i = 1; i <= 5; i++) {
System.out.println(i);
// 休眠5s
if(i == 3){
// 会让当前执行的线程暂停5秒,再继续执行
Thread.sleep(5000);
}
}
// join方法作用:让当前调用这个方法的线程先执行完。
Thread t1 = new MyThread("1号线程");
t1.start();
t1.join();
Thread t2 = new MyThread("2号线程");
t2.start();
t2.join();
Thread t3 = new MyThread("3号线程");
t3.start();
t3.join();
}
}
23.3 线程安全
23.3.1 同步代码块
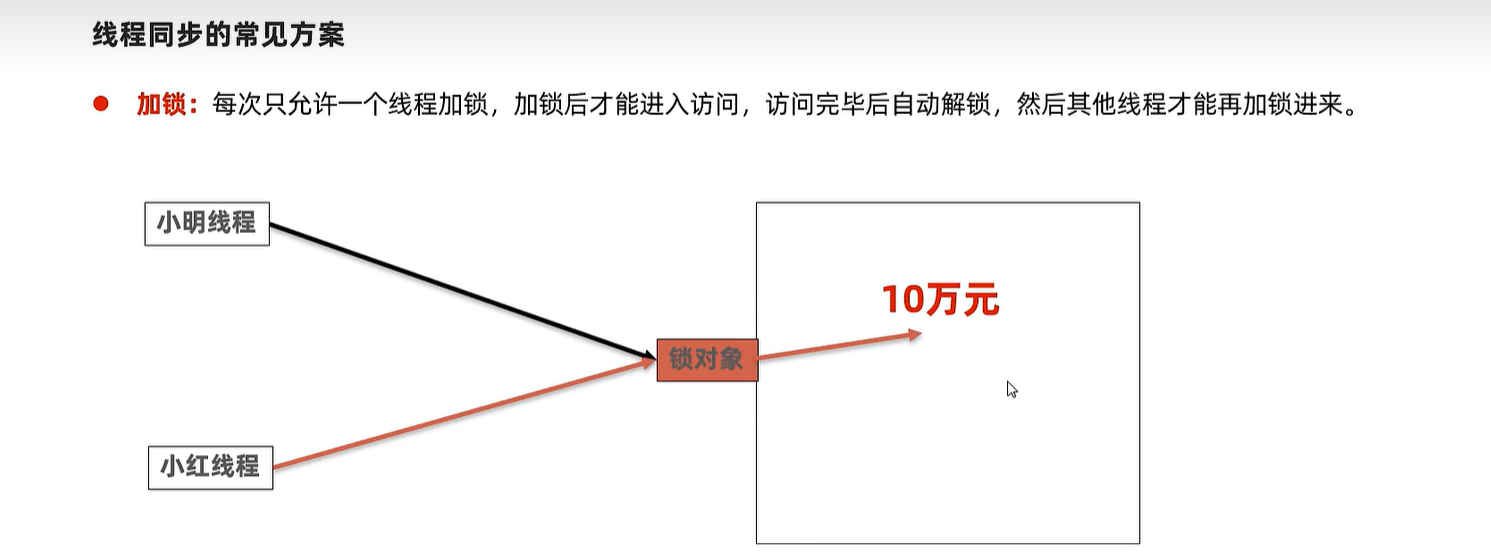

public class Account {
private String cardId; // 卡号
private double money; // 余额。
public Account() {
}
public Account(String cardId, double money) {
this.cardId = cardId;
this.money = money;
}
public static void test(){
// 静态方法建议使用类名.class
synchronized (Account.class){
}
}
// 小明 小红线程同时过来的
public void drawMoney(double money) {
// 先搞清楚是谁来取钱?
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
// 1、判断余额是否足够
// this正好代表共享资源!
synchronized (this) {
if(this.money >= money){
System.out.println(name + "来取钱" + money + "成功!");
this.money -= money;
System.out.println(name + "来取钱后,余额剩余:" + this.money);
}else {
System.out.println(name + "来取钱:余额不足~");
}
}
}
// get set 方法
}
public class DrawThread extends Thread{
private Account acc;
public DrawThread(Account acc, String name){
super(name);
this.acc = acc;
}
@Override
public void run() {
// 取钱(小明,小红)
acc.drawMoney(100000);
}
}
public class ThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Account acc = new Account("ICBC-110", 100000);
new DrawThread(acc, "小明").start(); // 小明
new DrawThread(acc, "小红").start(); // 小红
Account acc1 = new Account("ICBC-112", 100000);
new DrawThread(acc1, "小黑").start(); // 小黑
new DrawThread(acc1, "小白").start(); // 小白
}
}
23.2 同步方法

public class Account {
private String cardId; // 卡号
private double money; // 余额。
public Account() {
}
public Account(String cardId, double money) {
this.cardId = cardId;
this.money = money;
}
public static void test(){
synchronized (Account.class){
}
}
// 小明 小红线程同时过来的
// 同步方法
public synchronized void drawMoney(double money) {
// 先搞清楚是谁来取钱?
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
// 1、判断余额是否足够
if(this.money >= money){
System.out.println(name + "来取钱" + money + "成功!");
this.money -= money;
System.out.println(name + "来取钱后,余额剩余:" + this.money);
}else {
System.out.println(name + "来取钱:余额不足~");
}
}
}
23.3 Lock
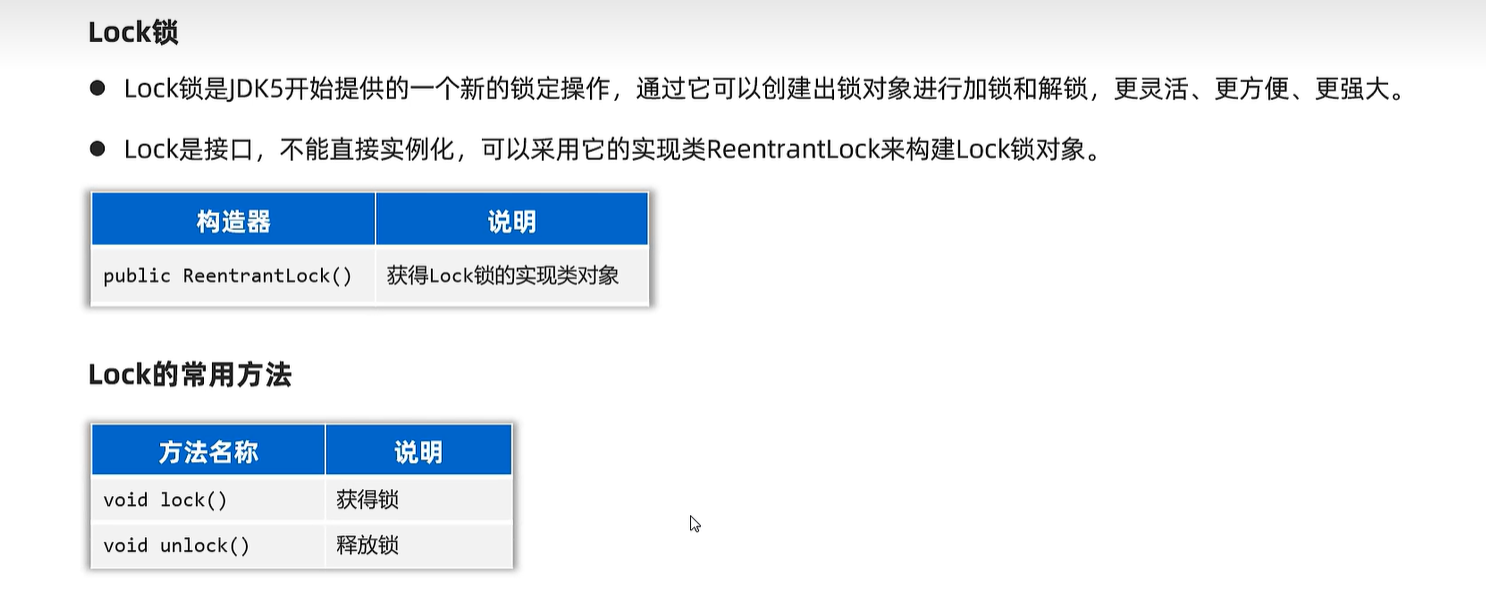
public class Account {
private String cardId; // 卡号
private double money; // 余额。
// 创建了一个锁对象
private final Lock lk = new ReentrantLock();
public Account() {
}
public Account(String cardId, double money) {
this.cardId = cardId;
this.money = money;
}
// 小明 小红线程同时过来的
public void drawMoney(double money) {
// 先搞清楚是谁来取钱?
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
try {
lk.lock(); // 加锁
// 1、判断余额是否足够
if(this.money >= money){
System.out.println(name + "来取钱" + money + "成功!");
this.money -= money;
System.out.println(name + "来取钱后,余额剩余:" + this.money);
}else {
System.out.println(name + "来取钱:余额不足~");
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
} finally {
lk.unlock(); // 解锁
}
}
}
23.4 线程通信



public class Desk {
private List<String> list = new ArrayList<>();
// 放1个包子的方法
// 厨师1 厨师2 厨师3
public synchronized void put() {
try {
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
// 判断是否有包子。
if(list.size() == 0){
list.add(name + "做的肉包子");
System.out.println(name + "做了一个肉包子~~");
Thread.sleep(2000);
// 唤醒别人, 等待自己
this.notifyAll();
this.wait();
}else {
// 有包子了,不做了。
// 唤醒别人, 等待自己
this.notifyAll();
this.wait();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
// 吃货1 吃货2
public synchronized void get() {
try {
String name = Thread.currentThread().getName();
if(list.size() == 1){
// 有包子,吃了
System.out.println(name + "吃了:" + list.get(0));
list.clear();
Thread.sleep(1000);
this.notifyAll();
this.wait();
}else {
// 没有包子
this.notifyAll();
this.wait();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class ThreadTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 需求:3个生产者线程,负责生产包子,每个线程每次只能生产1个包子放在桌子上
// 2个消费者线程负责吃包子,每人每次只能从桌子上拿1个包子吃。
Desk desk = new Desk();
// 创建3个生产者线程(3个厨师)
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
desk.put();
}
}, "厨师1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
desk.put();
}
}, "厨师2").start();
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
desk.put();
}
}, "厨师3").start();
// 创建2个消费者线程(2个吃货)
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
desk.get();
}
}, "吃货1").start();
new Thread(() -> {
while (true) {
desk.get();
}
}, "吃货2").start();
}
}
23.5 线程池



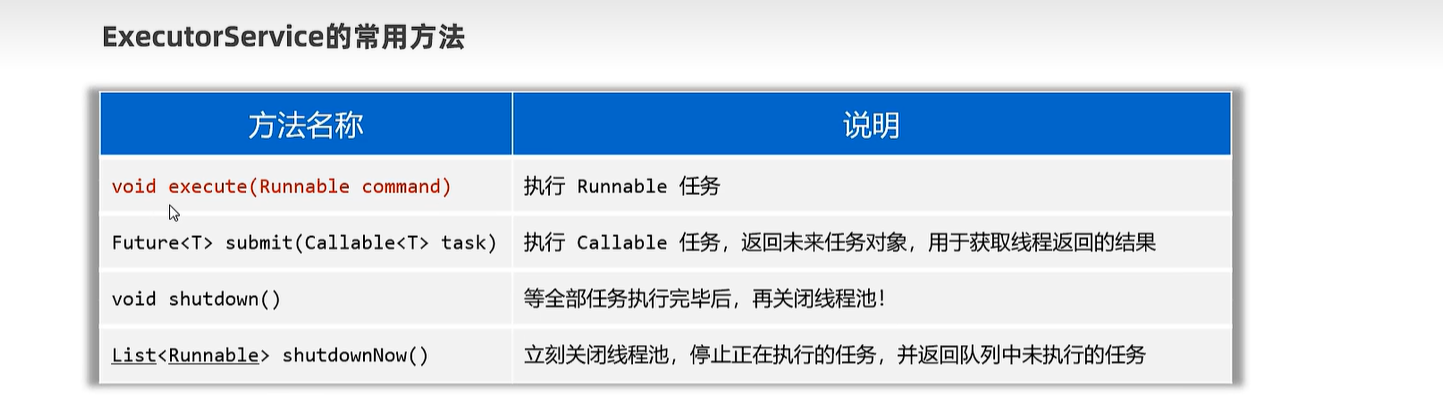
public class MyRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
// 任务是干啥的?
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + " ==> 输出666~~");
try {
Thread.sleep(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
public class ThreadPoolTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 1、通过ThreadPoolExecutor创建一个线程池对象。
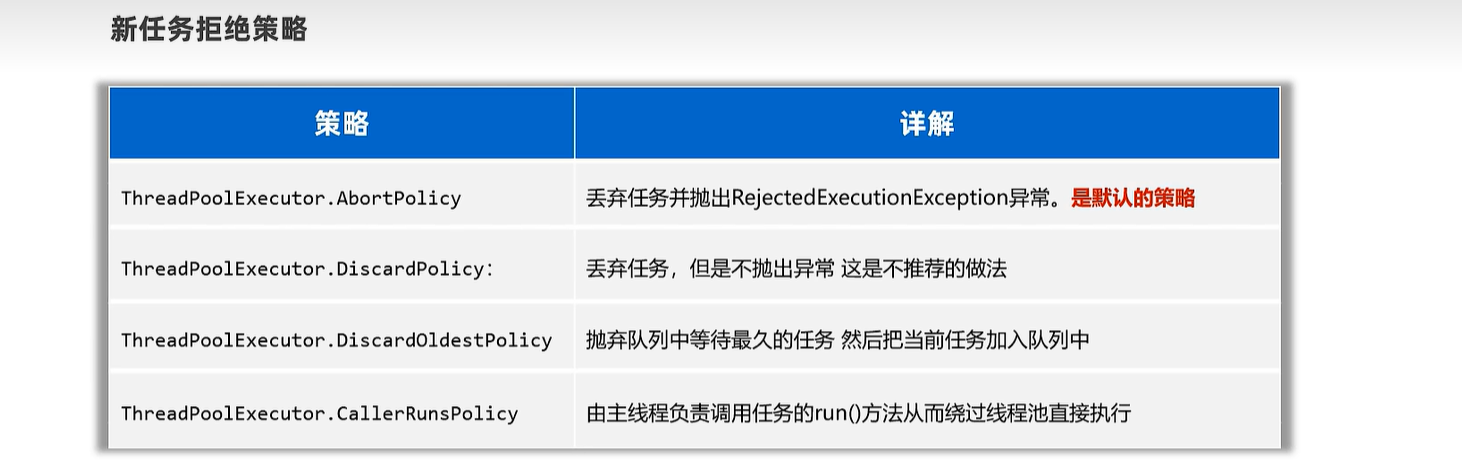
ExecutorService pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, 5, 8,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(4), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
Runnable target = new MyRunnable();
pool.execute(target); // 线程池会自动创建一个新线程,自动处理这个任务,自动执行的!
pool.execute(target); // 线程池会自动创建一个新线程,自动处理这个任务,自动执行的!
pool.execute(target); // 线程池会自动创建一个新线程,自动处理这个任务,自动执行的!
pool.execute(target);
pool.execute(target);
pool.execute(target);
pool.execute(target);
// 到了临时线程的创建时机了
pool.execute(target);
pool.execute(target);
// 到了新任务的拒绝时机了!
pool.execute(target);
// pool.shutdown(); // 等着线程池的任务全部执行完毕后,再关闭线程池
// pool.shutdownNow(); // 立即关闭线程池!不管任务是否执行完毕!
}
}
public class MyCallable implements Callable<String> {
private int n;
public MyCallable(int n) {
this.n = n;
}
// 2、重写call方法
@Override
public String call() throws Exception {
// 描述线程的任务,返回线程执行返回后的结果。
// 需求:求1-n的和返回。
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
sum += i;
}
return Thread.currentThread().getName() + "求出了1-" + n + "的和是:" + sum;
}
}
public class ThreadPoolTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1、通过ThreadPoolExecutor创建一个线程池对象。
ExecutorService pool = new ThreadPoolExecutor(3, 5, 8,
TimeUnit.SECONDS, new ArrayBlockingQueue<>(4), Executors.defaultThreadFactory(),
new ThreadPoolExecutor.CallerRunsPolicy());
// 2、使用线程处理Callable任务。
Future<String> f1 = pool.submit(new MyCallable(100));
Future<String> f2 = pool.submit(new MyCallable(200));
Future<String> f3 = pool.submit(new MyCallable(300));
Future<String> f4 = pool.submit(new MyCallable(400));
System.out.println(f1.get());
System.out.println(f2.get());
System.out.println(f3.get());
System.out.println(f4.get());
}
}

public class ThreadPoolTest3 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
// 1-2 通过Executors创建一个线程池对象。
ExecutorService pool = Executors.newFixedThreadPool(17);
// 老师:核心线程数量到底配置多少呢???
// 计算密集型的任务:核心线程数量 = CPU的核数 + 1
// IO密集型的任务:核心线程数量 = CPU核数 * 2
// 2、使用线程处理Callable任务。
Future<String> f1 = pool.submit(new MyCallable(100));
Future<String> f2 = pool.submit(new MyCallable(200));
Future<String> f3 = pool.submit(new MyCallable(300));
Future<String> f4 = pool.submit(new MyCallable(400));
System.out.println(f1.get());
System.out.println(f2.get());
System.out.println(f3.get());
System.out.println(f4.get());
}
}
大型系统开发规范

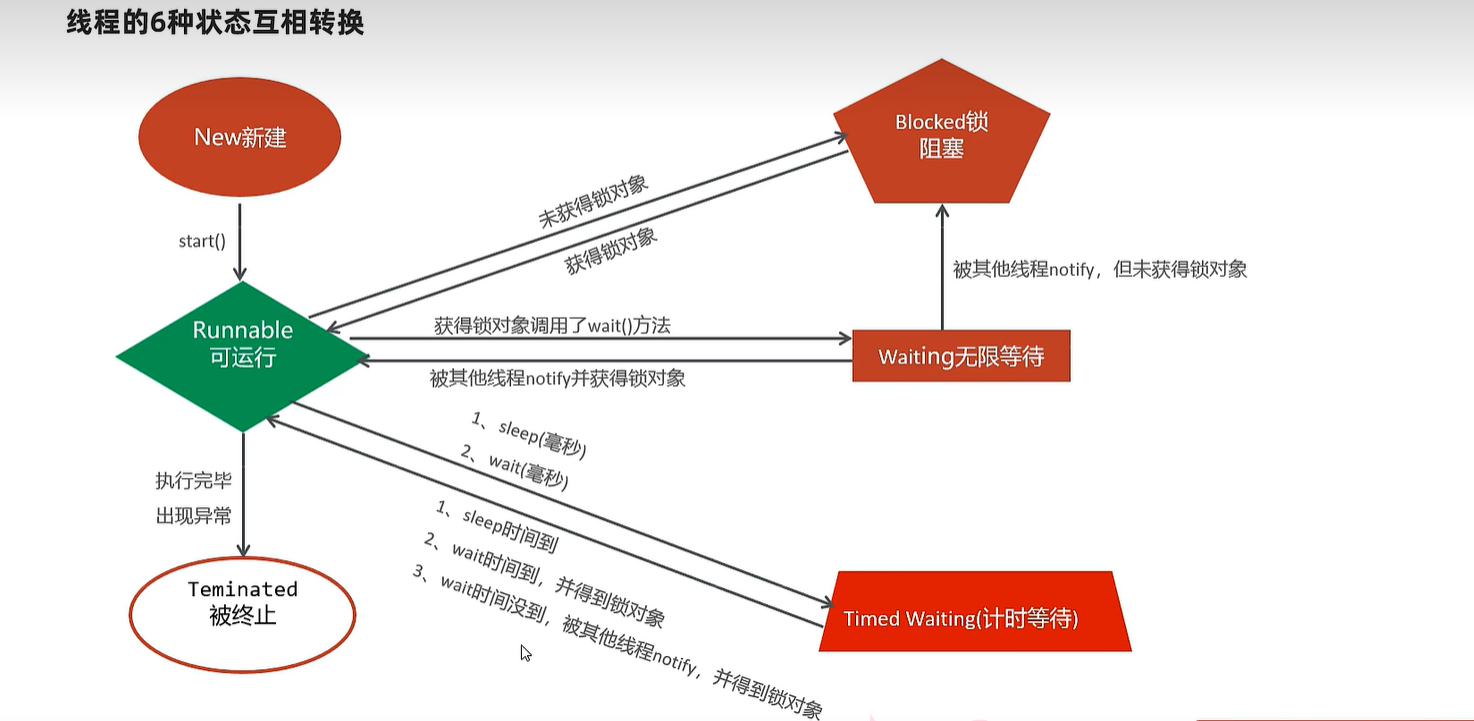
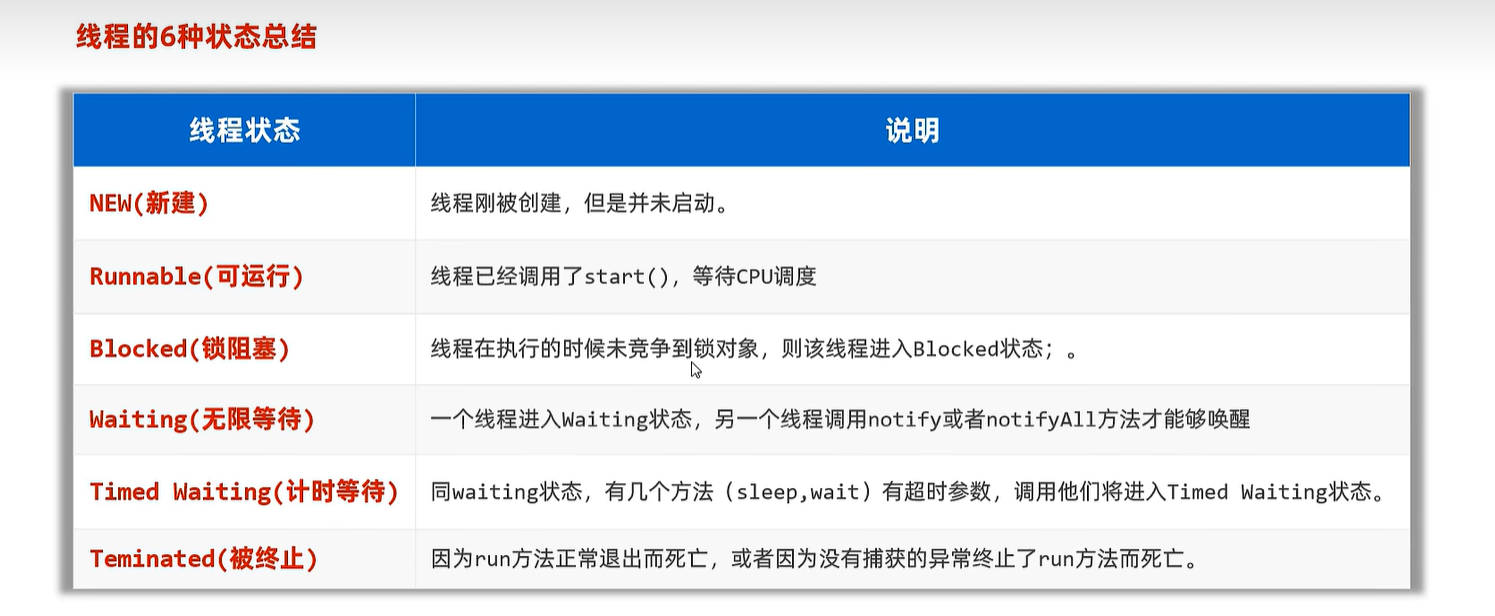
23.6 线程生命周期

24. junit

public class StringUtilTest {
@Before
public void test1(){
System.out.println("---> test1 Before 执行了---------");
}
@BeforeClass
public static void test11(){
System.out.println("---> test11 BeforeClass 执行了---------");
}
@After
public void test2(){
System.out.println("---> test2 After 执行了---------");
}
@AfterClass
public static void test22(){
System.out.println("---> test22 AfterClass 执行了---------");
}
@Test // 测试方法
public void testPrintNumber(){
StringUtil.printNumber("admin");
StringUtil.printNumber(null);
}
@Test // 测试方法
public void testGetMaxIndex(){
int index1 = StringUtil.getMaxIndex(null);
System.out.println(index1);
int index2 = StringUtil.getMaxIndex("admin");
System.out.println(index2);
// 断言机制:程序员可以通过预测业务方法的结果。
Assert.assertEquals("方法内部有bug!", 4, index2);
}
}
25. 反射

25.1 获取Class对象
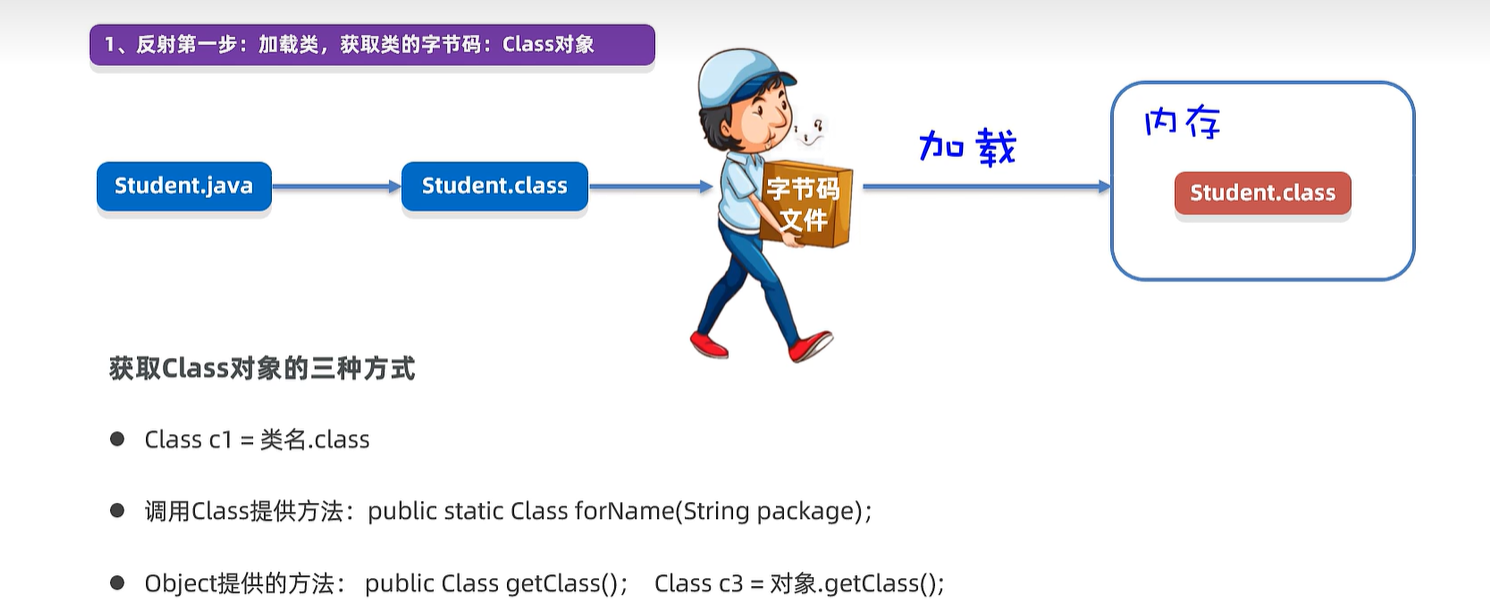
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
Class c1 = Student.class;
System.out.println(c1.getName()); // 全类名
System.out.println(c1.getSimpleName()); // 简名:Student
Class c2 = Class.forName("com.itheima.d2_reflect.Student");
System.out.println(c1 == c2);
Student s = new Student();
Class c3 = s.getClass();
System.out.println(c3 == c2);
}

25.2 获取类的构造方法
@Test
public void testGetConstructors(){
// 1、反射第一步:必须先得到这个类的Class对象
Class c = Cat.class;
// 2、获取类的全部构造器
// Constructor[] constructors = c.getConstructors();
Constructor[] constructors = c.getDeclaredConstructors();
// 3、遍历数组中的每个构造器对象
for (Constructor constructor : constructors) {
System.out.println(constructor.getName() + "--->"
+ constructor.getParameterCount());
}
}
@Test
public void testGetConstructor() throws Exception {
// 1、反射第一步:必须先得到这个类的Class对象
Class c = Cat.class;
// 2、获取类的某个构造器:无参数构造器
Constructor constructor1 = c.getDeclaredConstructor();
System.out.println(constructor1.getName() + "--->"
+ constructor1.getParameterCount());
constructor1.setAccessible(true); // 禁止检查访问权限
Cat cat = (Cat) constructor1.newInstance();
System.out.println(cat);
// 3、获取有参数构造器
Constructor constructor2 =
c.getDeclaredConstructor(String.class, int.class);
System.out.println(constructor2.getName() + "--->"
+ constructor2.getParameterCount());
constructor2.setAccessible(true); // 禁止检查访问权限
Cat cat2 = (Cat) constructor2.newInstance("叮当猫", 3);
System.out.println(cat2);
}
25.3 获取类的成员变量

@Test
public void testGetFields() throws Exception {
// 1、反射第一步:必须是先得到类的Class对象
Class c = Cat.class;
// 2、获取类的全部成员变量。
Field[] fields = c.getDeclaredFields();
// 3、遍历这个成员变量数组
for (Field field : fields) {
System.out.println(field.getName() + "---> "+ field.getType());
}
// 4、定位某个成员变量
Field fName = c.getDeclaredField("name");
System.out.println(fName.getName() + "--->" + fName.getType());
Field fAge = c.getDeclaredField("age");
System.out.println(fAge.getName() + "--->" + fAge.getType());
// 赋值
Cat cat = new Cat();
fName.setAccessible(true); // 禁止访问控制权限
fName.set(cat, "卡菲猫"); // 类的成员变量,注意赋值时要指定对象
System.out.println(cat);
// 取值
String name = (String) fName.get(cat);
System.out.println(name);
}
25.4 获取类的成员方法

@Test
public void testGetMethods() throws Exception {
// 1、反射第一步:先得到Class对象。
Class c = Cat.class;
// 2、获取类的全部成员方法。
Method[] methods = c.getDeclaredMethods();
// 3、遍历这个数组中的每个方法对象
for (Method method : methods) {
System.out.println(method.getName() + "--->"
+ method.getParameterCount() + "---->"
+ method.getReturnType());
}
// 4、获取某个方法对象
Method run = c.getDeclaredMethod("run"); // 拿run方法,无参数的
System.out.println(run.getName() + "--->"
+ run.getParameterCount() + "---->"
+ run.getReturnType());
Method eat = c.getDeclaredMethod("eat", String.class);
System.out.println(eat.getName() + "--->"
+ eat.getParameterCount() + "---->"
+ eat.getReturnType());
Cat cat = new Cat();
run.setAccessible(true); // 禁止检查访问权限
Object rs = run.invoke(cat); // 调用无参数的run方法,用cat对象触发调用的。
System.out.println(rs);
eat.setAccessible(true); // 禁止检查访问权限
String rs2 = (String) eat.invoke(cat, "鱼儿");
System.out.println(rs2);
}
26. 注解
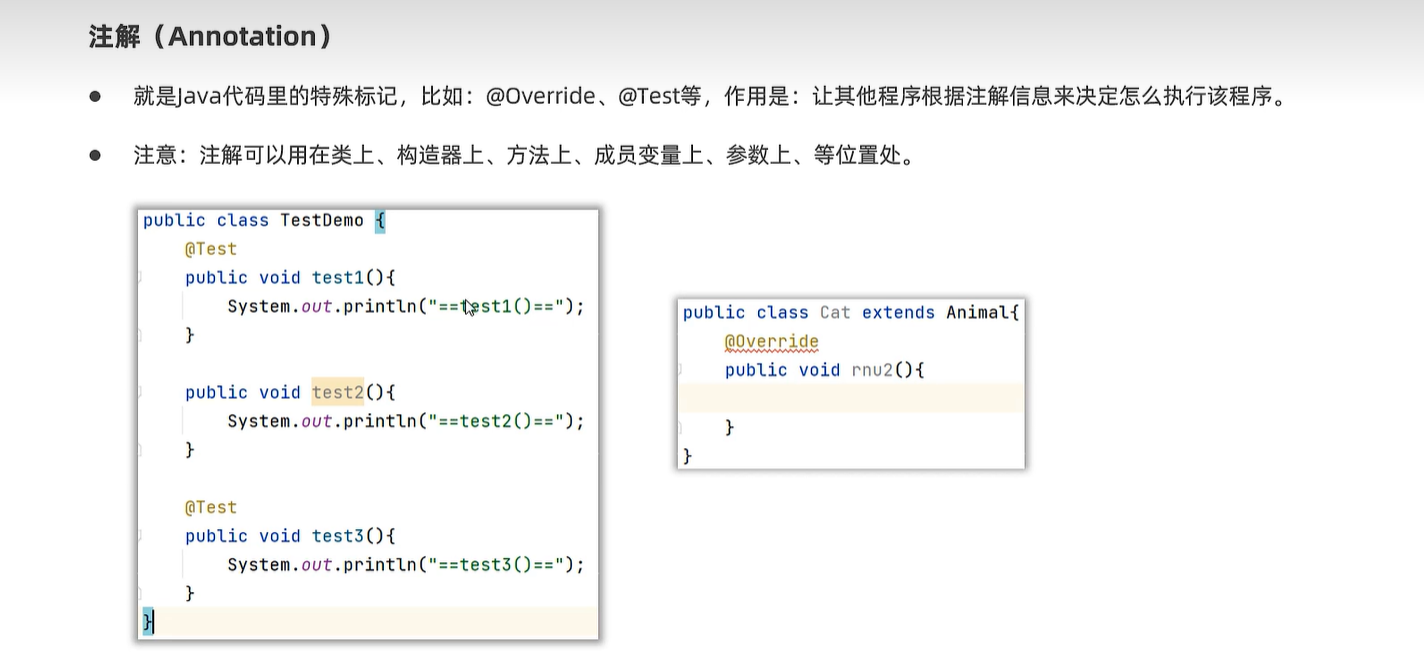
26.1 自定义注解

/**
* 自定义注解
*/
public @interface MyTest1 {
String aaa();
boolean bbb() default true;
String[] ccc();
}
public @interface MyTest2 {
String value(); // 特殊属性
int age() default 23;
}
@MyTest1(aaa="牛魔王", ccc={"HTML", "Java"})
// @MyTest2(value = "孙悟空")
//@MyTest2("孙悟空")
//@MyTest2(value = "孙悟空", age = 1000)
@MyTest2("孙悟空")
public class AnnotationTest1 {
@MyTest1(aaa="铁扇公主", bbb=false, ccc={"Python", "前端", "Java"})
public void test1(){
}
}
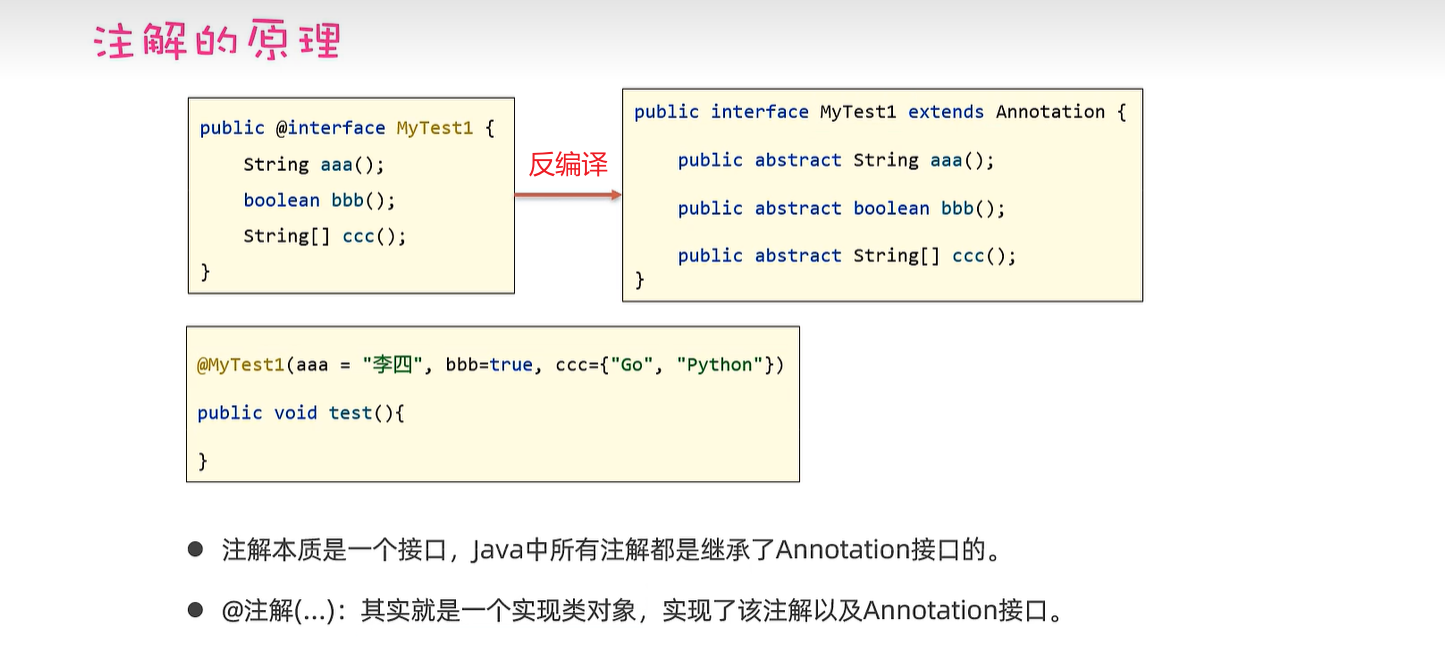
26.2 注解原理
26.3 元注解

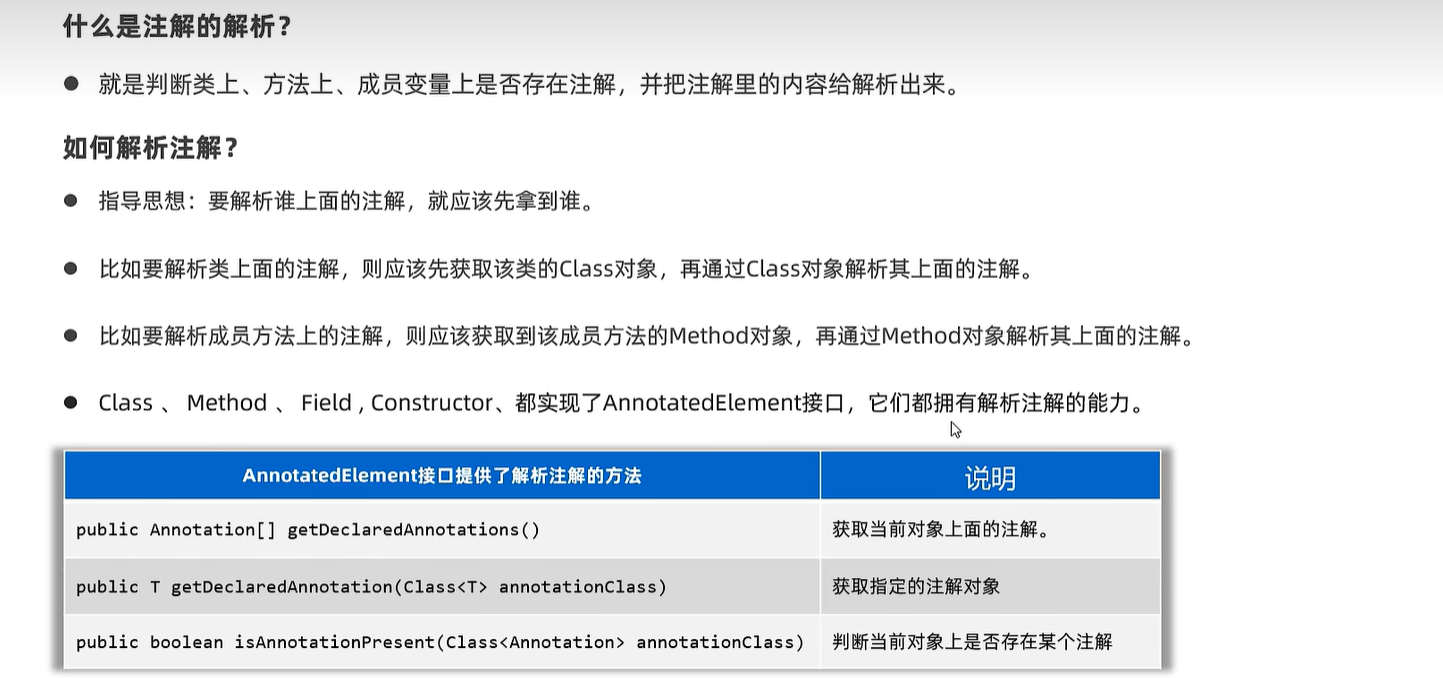
26.4 注解解析

@Target({ElementType.TYPE,ElementType.METHOD})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
public @interface MyTest4 {
String value();
double aaa() default 100;
String[] bbb();
}
@MyTest4(value = "蜘蛛精", aaa=99.5, bbb = {"至尊宝", "黑马"})
@MyTest3
public class Demo {
@MyTest4(value = "孙悟空", aaa=199.9, bbb = {"紫霞", "牛夫人"})
public void test1(){
}
}
public class AnnotationTest3 {
@Test
public void parseClass(){
// 1、先得到Class对象
Class c = Demo.class;
// 2、解析类上的注解
// 判断类上是否包含了某个注解
if(c.isAnnotationPresent(MyTest4.class)){
MyTest4 myTest4 =
(MyTest4) c.getDeclaredAnnotation(MyTest4.class);
System.out.println(myTest4.value());
System.out.println(myTest4.aaa());
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(myTest4.bbb()));
}
}
@Test
public void parseMethod() throws Exception {
// 1、先得到Class对象
Class c = Demo.class;
Method m = c.getDeclaredMethod("test1");
// 2、解析方法上的注解
// 判断方法对象上是否包含了某个注解
if(m.isAnnotationPresent(MyTest4.class)){
MyTest4 myTest4 =
(MyTest4) m.getDeclaredAnnotation(MyTest4.class);
System.out.println(myTest4.value());
System.out.println(myTest4.aaa());
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(myTest4.bbb()));
}
}
}

public class AnnotationTest4 {
// @MyTest
public void test1(){
System.out.println("===test1====");
}
@MyTest
public void test2(){
System.out.println("===test2====");
}
@MyTest
public void test3(){
System.out.println("===test3====");
}
@MyTest
public void test4(){
System.out.println("===test4====");
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
AnnotationTest4 a = new AnnotationTest4();
// 启动程序!
// 1、得到Class对象
Class c = AnnotationTest4.class;
// 2、提取这个类中的全部成员方法
Method[] methods = c.getDeclaredMethods();
// 3、遍历这个数组中的每个方法,看方法上是否存在@MyTest注解,存在
// 触发该方法执行。
for (Method method : methods) {
if(method.isAnnotationPresent(MyTest.class)){
// 说明当前方法上是存在@MyTest,触发当前方法执行。
method.invoke(a);
}
}
}
}
27. 动态代理
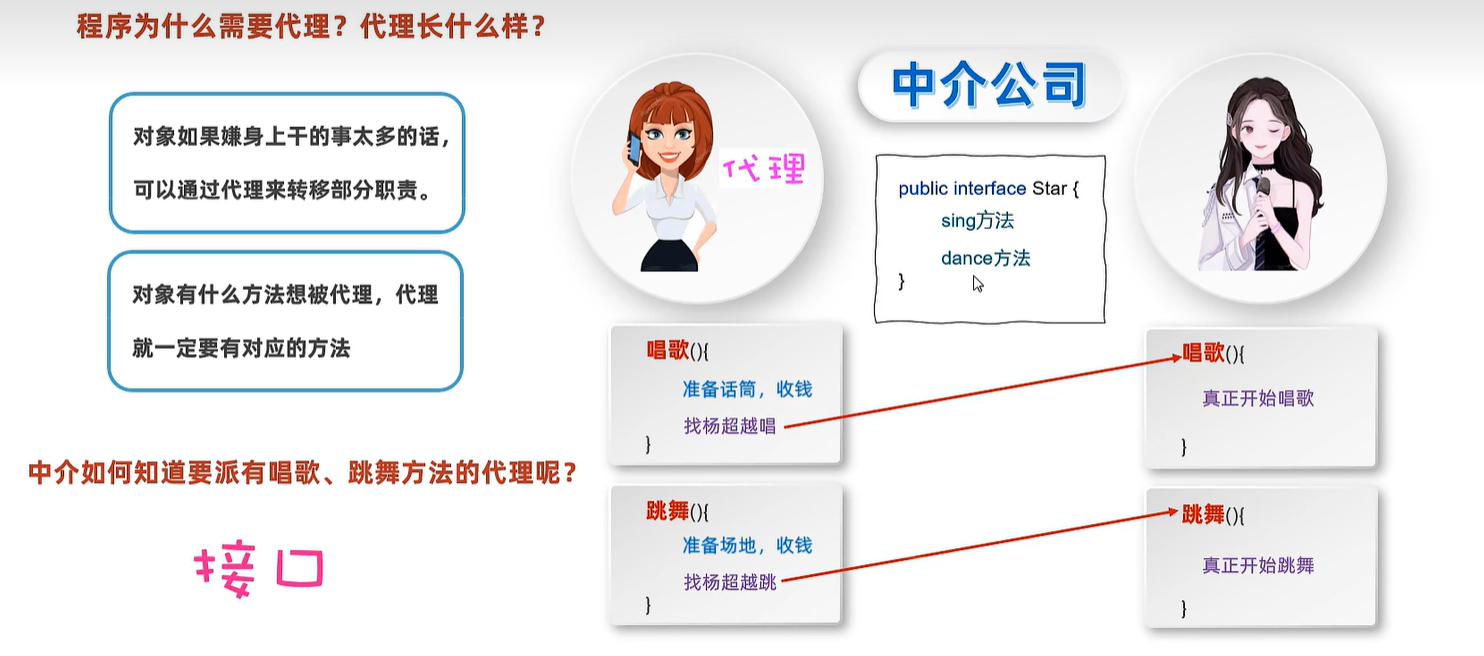
public interface Star {
String sing(String name);
void dance();
}
public class BigStar implements Star{
private String name;
public BigStar(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String sing(String name){
System.out.println(this.name + "正在唱:" + name);
return "谢谢!谢谢!";
}
public void dance(){
System.out.println(this.name + "正在优美的跳舞~~");
}
}
public class ProxyUtil {
public static Star createProxy(BigStar bigStar){
/* newProxyInstance(ClassLoader loader,
Class<?>[] interfaces,
InvocationHandler h)
参数1:用于指定一个类加载器
参数2:指定生成的代理长什么样子,也就是有哪些方法
参数3:用来指定生成的代理对象要干什么事情
*/
// Star starProxy = ProxyUtil.createProxy(s);
// starProxy.sing("好日子") starProxy.dance()
// 第一个参数固定,当前类的类加载器;第二个参数为接口的class数组(可能有多个接口);第三个参数固定,重现invoke方法
Star starProxy = (Star) Proxy.newProxyInstance(ProxyUtil.class.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{Star.class}, new InvocationHandler() {
@Override // 回调方法
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 代理对象要做的事情,会在这里写代码
if(method.getName().equals("sing")){
System.out.println("准备话筒,收钱20万");
}else if(method.getName().equals("dance")){
System.out.println("准备场地,收钱1000万");
}
return method.invoke(bigStar, args);
}
});
return starProxy;
}
}
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
BigStar s = new BigStar("杨超越");
Star starProxy = ProxyUtil.createProxy(s);
String rs = starProxy.sing("好日子");
System.out.println(rs);
starProxy.dance();
}
}

