ManualResetEvent类的使用
线程可以通过调用ManualResetEvent对象的WaitOne方法进入等待或阻塞状态。当控制线程调用Set()方法,所有等待线程将恢复并继续执行。
ManualResetEvent是如何工作的
在内存中保持着一个bool值,如果bool值为False,则使所有线程阻塞,反之,如果bool值为True,则使所有线程退出阻塞。当我们创建ManualResetEvent对象的实例时,我们在函数构造中传递默认的bool值,以下是实例化ManualResetEvent的例子。
2、阻塞
mre.WaitOne(); //该方法用于给所有等待线程发送信号。 Set() 方法的调用使得ManualResetEvent对象的bool变量值为True,所有线程被释放并继续执行
3、解除阻塞
mre.Set(); //当你想要的状态达到了,就接触阻塞,继续执行线程后面的代码,一旦我们调用了ManualResetEvent对象的Set()方法,它的bool值就变为true,我们可以调用Reset()方法来重置该值,Reset()方法重置该值为False。
备注: Set()后,如果再调用WaitOne()是无效的,线程不会被阻塞,必须调用Reset()才行
4、重置
mre.Reset(); //重置,只有这样,当再次执行WaitOne()的时候才会再次被阻塞
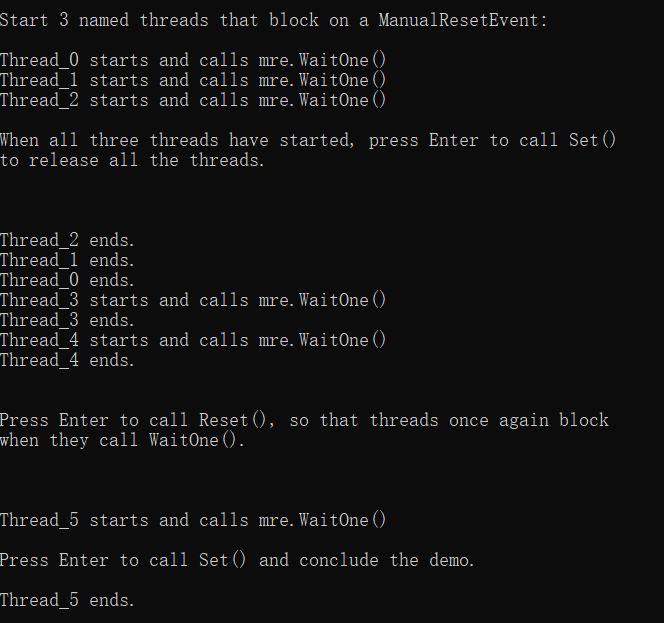
1 Console.WriteLine("\nStart 3 named threads that block on a ManualResetEvent:\n"); 2 for (int i = 0; i < 3; i++) 3 { 4 Thread t = new Thread(ThreadProc); 5 t.Name = "Thread_" + i.ToString(); 6 t.Start(); 7 } 8 Thread.Sleep(500); 9 Console.WriteLine("\nWhen all three threads have started, press Enter to call Set()" + 10 "\nto release all the threads.\n\n\n"); 11 manualResetEvent.Set(); 12 //中文注释3:继续再开两个线程,仍然调用WaitOne(),但是不会阻塞,会继续执行 13 for (int i = 3; i <= 4; i++) 14 { 15 Thread t = new Thread(ThreadProc); 16 t.Name = "Thread_" + i; 17 t.Start(); 18 } 19 20 Thread.Sleep(500); 21 Console.WriteLine("\n\nPress Enter to call Reset(), so that threads once again block" + 22 "\nwhen they call WaitOne().\n\n\n"); 23 24 //中文注释4:只有Reset()后,下面再开线程就会继续被阻塞 25 manualResetEvent.Reset(); 26 27 // Start a thread that waits on the ManualResetEvent. 28 Thread t5 = new Thread(ThreadProc); 29 t5.Name = "Thread_5"; 30 t5.Start(); 31 32 Thread.Sleep(500); 33 Console.WriteLine("\nPress Enter to call Set() and conclude the demo."); 34 Console.ReadLine(); 35 //中文注释5:再次Set(),就可以了 36 manualResetEvent.Set(); 37 38 Console.ReadLine();
执行结果: