信号处理——EMD、VMD的一点小思考
作者:桂。
时间:2017-03-06 20:57:22
链接:http://www.cnblogs.com/xingshansi/p/6511916.html

前言
本文为Hilbert变换一篇的内容补充,主要内容为:
1)EMD原理介绍
2)代码分析
3)一种权衡的小trick
4)问题补充
内容主要为自己的学习总结,并多有借鉴他人,最后一并给出链接。
一、EMD原理介绍
A-EMD的意义
很多人都知道EMD(Empirical Mode Decomposition)可以将信号分解不同频率特性,并且结合Hilbert求解包络以及瞬时频率。EMD、Hilbert、瞬时频率三者有无内在联系?答案是:有。
按照Hilbert变换一篇的介绍,
然而,这样求解瞬时频率在某些情况下有问题,可能出现为负的情况:我1秒手指动5下,频率是5Hz;反过来,频率为8Hz时,手指1秒动8下,可如果频率为-5Hz呢?负频率没有意义。
考虑信号
为了简单起见,假设和恒定,且和是正的。信号的频谱应由两个在和的函数组成,即
因为假设和是正的,所以该信号解析。求得相位
分别取两组参数,对求导,得到对应参数下的瞬时频率:
参数:
和.
- 组1:{};
- 组2:{}
对于组2,瞬时频率出现了负值。
可见:
对任意信号进行Hilbert变换,可能出现无法解释、缺乏实际意义的频率分量。Norden E. Hung等人对瞬时频率进行研究后发现,只有满足特定条件的信号,其瞬时频率才具有物理意义,并将此类信号成为:IMF/基本模式分量。
B-EMD基本原理
此处给一个原理图:

C-基本模式分量(IMF)
EMD分解的IMF其瞬时频率具有实际物理意义,原因有两点:
- 限定1:
- 在整个数据序列中,极值点的数量(包括极大值、极小值点)与过零点的数量必须相等,或最多相差1个,即.
- 限定2:
- 在任意时间点上,信号局部极大值确定的上包络线和局部极小值确定的下包络线的均值为0.
限定1即要求信号具有类似传统平稳高斯过程的分布;限定2要求局部均值为0,同时用局部最大、最小值的包络作为近似,从而信号局部对称,避免了不对称带来的瞬时频率波动。
D-VMD
关于VMD(Variational Mode Decomposition),具体原理可以参考其论文,这里我们只要记住一点:其分解的各个基本分量——即各解析信号的瞬时频率具有实际的物理意义。
二、代码分析
首先给出信号分别用VMD、EMD的分解结果:

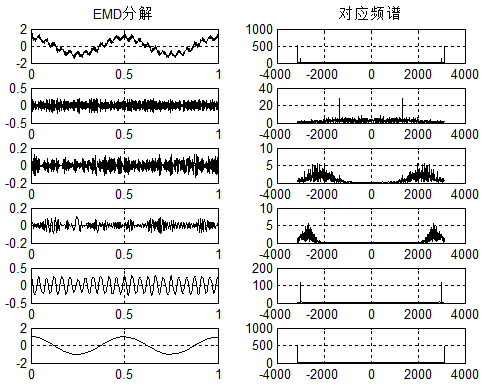
给出对应的代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 | %--------------- Preparationclear all;close all;clc;% Time Domain 0 to TT = 1000;fs = 1/T;t = (1:T)/T;freqs = 2*pi*(t-0.5-1/T)/(fs);% center frequencies of componentsf_1 = 2;f_2 = 24;f_3 = 288;% modesv_1 = (cos(2*pi*f_1*t));v_2 = 1/4*(cos(2*pi*f_2*t));v_3 = 1/16*(cos(2*pi*f_3*t));% for visualization purposeswsub{1} = 2*pi*f_1;wsub{2} = 2*pi*f_2;wsub{3} = 2*pi*f_3;% composite signal, including noisef = v_1 + v_2 + v_3 + 0.1*randn(size(v_1));% some sample parameters for VMDalpha = 2000; % moderate bandwidth constrainttau = 0; % noise-tolerance (no strict fidelity enforcement)K = 4; % 4 modesDC = 0; % no DC part imposedinit = 1; % initialize omegas uniformlytol = 1e-7;%--------------- Run actual VMD code[u, u_hat, omega] = VMD(f, alpha, tau, K, DC, init, tol);subplot(size(u,1)+1,2,1);plot(t,f,'k');grid on;title('VMD分解');subplot(size(u,1)+1,2,2);plot(freqs,abs(fft(f)),'k');grid on;title('对应频谱');for i = 2:size(u,1)+1 subplot(size(u,1)+1,2,i*2-1); plot(t,u(i-1,:),'k');grid on; subplot(size(u,1)+1,2,i*2); plot(freqs,abs(fft(u(i-1,:))),'k');grid on;end%---------------run EMD codeimf = emd(f);figure;subplot(size(imf,1)+1,2,1);plot(t,f,'k');grid on;title('EMD分解');subplot(size(imf,1)+1,2,2);plot(freqs,abs(fft(f)),'k');grid on;title('对应频谱');for i = 2:size(imf,1)+1 subplot(size(imf,1)+1,2,i*2-1); plot(t,imf(i-1,:),'k');grid on; subplot(size(imf,1)+1,2,i*2); plot(freqs,abs(fft(imf(i-1,:))),'k');grid on;end |
附上两个子程序的code.
VMD:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 | function [u, u_hat, omega] = VMD(signal, alpha, tau, K, DC, init, tol)% Variational Mode Decomposition% Authors: Konstantin Dragomiretskiy and Dominique Zosso% zosso@math.ucla.edu --- http://www.math.ucla.edu/~zosso% Initial release 2013-12-12 (c) 2013%% Input and Parameters:% ---------------------% signal - the time domain signal (1D) to be decomposed% alpha - the balancing parameter of the data-fidelity constraint% tau - time-step of the dual ascent ( pick 0 for noise-slack )% K - the number of modes to be recovered% DC - true if the first mode is put and kept at DC (0-freq)% init - 0 = all omegas start at 0% 1 = all omegas start uniformly distributed% 2 = all omegas initialized randomly% tol - tolerance of convergence criterion; typically around 1e-6%% Output:% -------% u - the collection of decomposed modes% u_hat - spectra of the modes% omega - estimated mode center-frequencies%% When using this code, please do cite our paper:% -----------------------------------------------% K. Dragomiretskiy, D. Zosso, Variational Mode Decomposition, IEEE Trans.% on Signal Processing (in press)% please check here for update reference: % http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/TSP.2013.2288675%---------- Preparations% Period and sampling frequency of input signalsave_T = length(signal);fs = 1/save_T;% extend the signal by mirroringT = save_T;f_mirror(1:T/2) = signal(T/2:-1:1);f_mirror(T/2+1:3*T/2) = signal;f_mirror(3*T/2+1:2*T) = signal(T:-1:T/2+1);f = f_mirror;% Time Domain 0 to T (of mirrored signal)T = length(f);t = (1:T)/T;% Spectral Domain discretizationfreqs = t-0.5-1/T;% Maximum number of iterations (if not converged yet, then it won't anyway)N = 500;% For future generalizations: individual alpha for each modeAlpha = alpha*ones(1,K);% Construct and center f_hatf_hat = fftshift((fft(f)));f_hat_plus = f_hat;f_hat_plus(1:T/2) = 0;% matrix keeping track of every iterant // could be discarded for memu_hat_plus = zeros(N, length(freqs), K);% Initialization of omega_komega_plus = zeros(N, K);switch init case 1 for i = 1:K omega_plus(1,i) = (0.5/K)*(i-1); end case 2 omega_plus(1,:) = sort(exp(log(fs) + (log(0.5)-log(fs))*rand(1,K))); otherwise omega_plus(1,:) = 0;end% if DC mode imposed, set its omega to 0if DC omega_plus(1,1) = 0;end% start with empty dual variableslambda_hat = zeros(N, length(freqs));% other initsuDiff = tol+eps; % update stepn = 1; % loop countersum_uk = 0; % accumulator% ----------- Main loop for iterative updateswhile ( uDiff > tol && n < N ) % not converged and below iterations limit % update first mode accumulator k = 1; sum_uk = u_hat_plus(n,:,K) + sum_uk - u_hat_plus(n,:,1); % update spectrum of first mode through Wiener filter of residuals u_hat_plus(n+1,:,k) = (f_hat_plus - sum_uk - lambda_hat(n,:)/2)./(1+Alpha(1,k)*(freqs - omega_plus(n,k)).^2); % update first omega if not held at 0 if ~DC omega_plus(n+1,k) = (freqs(T/2+1:T)*(abs(u_hat_plus(n+1, T/2+1:T, k)).^2)')/sum(abs(u_hat_plus(n+1,T/2+1:T,k)).^2); end % update of any other mode for k=2:K % accumulator sum_uk = u_hat_plus(n+1,:,k-1) + sum_uk - u_hat_plus(n,:,k); % mode spectrum u_hat_plus(n+1,:,k) = (f_hat_plus - sum_uk - lambda_hat(n,:)/2)./(1+Alpha(1,k)*(freqs - omega_plus(n,k)).^2); % center frequencies omega_plus(n+1,k) = (freqs(T/2+1:T)*(abs(u_hat_plus(n+1, T/2+1:T, k)).^2)')/sum(abs(u_hat_plus(n+1,T/2+1:T,k)).^2); end % Dual ascent lambda_hat(n+1,:) = lambda_hat(n,:) + tau*(sum(u_hat_plus(n+1,:,:),3) - f_hat_plus); % loop counter n = n+1; % converged yet? uDiff = eps; for i=1:K uDiff = uDiff + 1/T*(u_hat_plus(n,:,i)-u_hat_plus(n-1,:,i))*conj((u_hat_plus(n,:,i)-u_hat_plus(n-1,:,i)))'; end uDiff = abs(uDiff); end%------ Postprocessing and cleanup% discard empty space if converged earlyN = min(N,n);omega = omega_plus(1:N,:);% Signal reconstructionu_hat = zeros(T, K);u_hat((T/2+1):T,:) = squeeze(u_hat_plus(N,(T/2+1):T,:));u_hat((T/2+1):-1:2,:) = squeeze(conj(u_hat_plus(N,(T/2+1):T,:)));u_hat(1,:) = conj(u_hat(end,:));u = zeros(K,length(t));for k = 1:K u(k,:)=real(ifft(ifftshift(u_hat(:,k))));end% remove mirror partu = u(:,T/4+1:3*T/4);% recompute spectrumclear u_hat;for k = 1:K u_hat(:,k)=fftshift(fft(u(k,:)))';endend |
EMD:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 218 219 220 221 222 223 224 225 226 227 228 229 230 231 232 233 234 235 236 237 238 239 240 241 242 243 244 245 246 247 248 249 250 251 252 253 254 255 256 257 258 259 260 261 262 263 264 265 266 267 268 269 270 271 272 273 274 275 276 277 278 279 280 281 282 283 284 285 286 287 288 289 290 291 292 293 294 295 296 297 298 299 300 301 302 303 304 305 306 307 308 309 310 311 312 313 314 315 316 317 318 319 320 321 322 323 324 325 326 327 328 329 330 331 332 333 334 335 336 337 338 339 340 341 342 343 344 345 346 347 348 349 350 351 352 353 354 355 356 357 358 359 360 361 362 363 364 365 366 367 368 369 370 371 372 373 374 375 376 377 378 379 380 381 382 383 384 385 386 387 388 389 390 391 392 393 394 395 396 397 398 399 400 401 402 403 404 405 406 407 408 409 410 411 412 413 414 415 416 417 418 419 420 421 422 423 424 425 426 427 428 429 430 431 432 433 434 435 436 437 438 439 440 441 442 443 444 445 446 447 448 449 450 451 452 453 454 455 456 457 458 459 460 461 462 463 464 465 466 467 468 469 470 471 472 473 474 475 476 477 478 479 480 481 482 483 484 485 486 487 488 489 490 491 492 493 494 495 496 497 498 499 500 501 502 503 504 505 506 507 508 509 510 511 512 513 514 515 516 517 518 519 520 521 522 523 524 525 526 527 528 529 530 531 532 533 534 535 536 537 538 539 540 541 542 543 544 545 546 547 548 549 550 551 552 553 554 555 556 557 558 559 560 561 562 563 564 565 566 567 568 569 570 571 572 573 574 575 576 577 578 579 580 581 582 583 584 585 586 587 588 589 590 591 592 593 594 595 596 597 598 599 600 601 602 603 604 605 606 607 608 609 610 611 612 613 614 615 616 617 618 619 620 621 622 623 624 625 626 627 628 629 630 631 632 633 634 635 636 637 638 639 640 641 642 643 644 645 646 647 648 649 650 651 652 653 654 655 656 657 658 659 660 661 662 663 664 665 666 667 668 669 670 671 672 673 674 675 676 677 678 679 680 681 682 683 684 685 686 687 688 689 690 691 692 693 694 695 696 697 698 699 700 701 702 703 704 705 706 707 708 709 710 711 712 713 714 715 716 717 718 719 720 721 722 723 724 725 726 727 728 729 730 731 732 733 734 735 736 737 738 739 740 741 742 743 744 745 746 747 748 749 750 751 752 753 754 755 756 757 758 759 760 761 762 763 764 765 766 767 768 769 770 771 772 773 774 775 776 777 778 779 780 781 782 783 784 785 786 787 788 789 790 791 792 793 794 795 796 797 798 799 800 801 802 803 804 805 806 807 808 809 810 811 812 813 814 815 816 817 818 819 820 821 822 823 824 825 826 827 828 829 830 831 832 833 834 835 836 837 838 839 840 841 842 843 844 845 846 847 848 849 850 851 852 853 854 855 856 857 858 859 860 861 862 | %EMD computes Empirical Mode Decomposition%%% Syntax%%% IMF = EMD(X)% IMF = EMD(X,...,'Option_name',Option_value,...)% IMF = EMD(X,OPTS)% [IMF,ORT,NB_ITERATIONS] = EMD(...)%%% Description%%% IMF = EMD(X) where X is a real vector computes the Empirical Mode% Decomposition [1] of X, resulting in a matrix IMF containing 1 IMF per row, the% last one being the residue. The default stopping criterion is the one proposed% in [2]:%% at each point, mean_amplitude < THRESHOLD2*envelope_amplitude% &% mean of boolean array {(mean_amplitude)/(envelope_amplitude) > THRESHOLD} < TOLERANCE% &% |#zeros-#extrema|<=1%% where mean_amplitude = abs(envelope_max+envelope_min)/2% and envelope_amplitude = abs(envelope_max-envelope_min)/2% % IMF = EMD(X) where X is a complex vector computes Bivariate Empirical Mode% Decomposition [3] of X, resulting in a matrix IMF containing 1 IMF per row, the% last one being the residue. The default stopping criterion is similar to the% one proposed in [2]:%% at each point, mean_amplitude < THRESHOLD2*envelope_amplitude% &% mean of boolean array {(mean_amplitude)/(envelope_amplitude) > THRESHOLD} < TOLERANCE%% where mean_amplitude and envelope_amplitude have definitions similar to the% real case%% IMF = EMD(X,...,'Option_name',Option_value,...) sets options Option_name to% the specified Option_value (see Options)%% IMF = EMD(X,OPTS) is equivalent to the above syntax provided OPTS is a struct % object with field names corresponding to option names and field values being the % associated values %% [IMF,ORT,NB_ITERATIONS] = EMD(...) returns an index of orthogonality% ________% _ |IMF(i,:).*IMF(j,:)|% ORT = \ _____________________% /% ? || X ||?% i~=j%% and the number of iterations to extract each mode in NB_ITERATIONS%%% Options%%% stopping criterion options:%% STOP: vector of stopping parameters [THRESHOLD,THRESHOLD2,TOLERANCE]% if the input vector's length is less than 3, only the first parameters are% set, the remaining ones taking default values.% default: [0.05,0.5,0.05]%% FIX (int): disable the default stopping criterion and do exactly <FIX> % number of sifting iterations for each mode%% FIX_H (int): disable the default stopping criterion and do <FIX_H> sifting % iterations with |#zeros-#extrema|<=1 to stop [4]%% bivariate/complex EMD options:%% COMPLEX_VERSION: selects the algorithm used for complex EMD ([3])% COMPLEX_VERSION = 1: "algorithm 1"% COMPLEX_VERSION = 2: "algorithm 2" (default)% % NDIRS: number of directions in which envelopes are computed (default 4)% rem: the actual number of directions (according to [3]) is 2*NDIRS% % other options:%% T: sampling times (line vector) (default: 1:length(x))%% MAXITERATIONS: maximum number of sifting iterations for the computation of each% mode (default: 2000)%% MAXMODES: maximum number of imfs extracted (default: Inf)%% DISPLAY: if equals to 1 shows sifting steps with pause% if equals to 2 shows sifting steps without pause (movie style)% rem: display is disabled when the input is complex%% INTERP: interpolation scheme: 'linear', 'cubic', 'pchip' or 'spline' (default)% see interp1 documentation for details%% MASK: masking signal used to improve the decomposition according to [5]%%% Examples%%%X = rand(1,512);%%IMF = emd(X);%%IMF = emd(X,'STOP',[0.1,0.5,0.05],'MAXITERATIONS',100);%%T=linspace(0,20,1e3);%X = 2*exp(i*T)+exp(3*i*T)+.5*T;%IMF = emd(X,'T',T);%%OPTIONS.DISLPAY = 1;%OPTIONS.FIX = 10;%OPTIONS.MAXMODES = 3;%[IMF,ORT,NBITS] = emd(X,OPTIONS);%%% References%%% [1] N. E. Huang et al., "The empirical mode decomposition and the% Hilbert spectrum for non-linear and non stationary time series analysis",% Proc. Royal Soc. London A, Vol. 454, pp. 903-995, 1998%% [2] G. Rilling, P. Flandrin and P. Gon鏰lves% "On Empirical Mode Decomposition and its algorithms",% IEEE-EURASIP Workshop on Nonlinear Signal and Image Processing% NSIP-03, Grado (I), June 2003%% [3] G. Rilling, P. Flandrin, P. Gon鏰lves and J. M. Lilly.,% "Bivariate Empirical Mode Decomposition",% Signal Processing Letters (submitted)%% [4] N. E. Huang et al., "A confidence limit for the Empirical Mode% Decomposition and Hilbert spectral analysis",% Proc. Royal Soc. London A, Vol. 459, pp. 2317-2345, 2003%% [5] R. Deering and J. F. Kaiser, "The use of a masking signal to improve % empirical mode decomposition", ICASSP 2005%%% See also% emd_visu (visualization),% emdc, emdc_fix (fast implementations of EMD),% cemdc, cemdc_fix, cemdc2, cemdc2_fix (fast implementations of bivariate EMD),% hhspectrum (Hilbert-Huang spectrum)%%% G. Rilling, last modification: 3.2007% gabriel.rilling@ens-lyon.frfunction [imf,ort,nbits] = emd(varargin)[x,t,sd,sd2,tol,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs,display_sifting,sdt,sd2t,r,imf,k,nbit,NbIt,MAXITERATIONS,FIXE,FIXE_H,MAXMODES,INTERP,mask] = init(varargin{:});if display_sifting fig_h = figure;end%main loop : requires at least 3 extrema to proceedwhile ~stop_EMD(r,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs) && (k < MAXMODES+1 || MAXMODES == 0) && ~any(mask) % current mode m = r; % mode at previous iteration mp = m; %computation of mean and stopping criterion if FIXE [stop_sift,moyenne] = stop_sifting_fixe(t,m,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs); elseif FIXE_H stop_count = 0; [stop_sift,moyenne] = stop_sifting_fixe_h(t,m,INTERP,stop_count,FIXE_H,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs); else [stop_sift,moyenne] = stop_sifting(m,t,sd,sd2,tol,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs); end % in case the current mode is so small that machine precision can cause % spurious extrema to appear if (max(abs(m))) < (1e-10)*(max(abs(x))) if ~stop_sift warning('emd:warning','forced stop of EMD : too small amplitude') else disp('forced stop of EMD : too small amplitude') end break end % sifting loop while ~stop_sift && nbit<MAXITERATIONS if(~MODE_COMPLEX && nbit>MAXITERATIONS/5 && mod(nbit,floor(MAXITERATIONS/10))==0 && ~FIXE && nbit > 100) disp(['mode ',int2str(k),', iteration ',int2str(nbit)]) if exist('s','var') disp(['stop parameter mean value : ',num2str(s)]) end [im,iM] = extr(m); disp([int2str(sum(m(im) > 0)),' minima > 0; ',int2str(sum(m(iM) < 0)),' maxima < 0.']) end %sifting m = m - moyenne; %computation of mean and stopping criterion if FIXE [stop_sift,moyenne] = stop_sifting_fixe(t,m,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs); elseif FIXE_H [stop_sift,moyenne,stop_count] = stop_sifting_fixe_h(t,m,INTERP,stop_count,FIXE_H,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs); else [stop_sift,moyenne,s] = stop_sifting(m,t,sd,sd2,tol,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs); end % display if display_sifting && ~MODE_COMPLEX NBSYM = 2; [indmin,indmax] = extr(mp); [tmin,tmax,mmin,mmax] = boundary_conditions(indmin,indmax,t,mp,mp,NBSYM); envminp = interp1(tmin,mmin,t,INTERP); envmaxp = interp1(tmax,mmax,t,INTERP); envmoyp = (envminp+envmaxp)/2; if FIXE || FIXE_H display_emd_fixe(t,m,mp,r,envminp,envmaxp,envmoyp,nbit,k,display_sifting) else sxp=2*(abs(envmoyp))./(abs(envmaxp-envminp)); sp = mean(sxp); display_emd(t,m,mp,r,envminp,envmaxp,envmoyp,s,sp,sxp,sdt,sd2t,nbit,k,display_sifting,stop_sift) end end mp = m; nbit=nbit+1; NbIt=NbIt+1; if(nbit==(MAXITERATIONS-1) && ~FIXE && nbit > 100) if exist('s','var') warning('emd:warning',['forced stop of sifting : too many iterations... mode ',int2str(k),'. stop parameter mean value : ',num2str(s)]) else warning('emd:warning',['forced stop of sifting : too many iterations... mode ',int2str(k),'.']) end end end % sifting loop imf(k,:) = m; if display_sifting disp(['mode ',int2str(k),' stored']) end nbits(k) = nbit; k = k+1; r = r - m; nbit=0;end %main loopif any(r) && ~any(mask) imf(k,:) = r;endort = io(x,imf);if display_sifting closeendend%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------% tests if there are enough (3) extrema to continue the decompositionfunction stop = stop_EMD(r,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs)if MODE_COMPLEX for k = 1:ndirs phi = (k-1)*pi/ndirs; [indmin,indmax] = extr(real(exp(i*phi)*r)); ner(k) = length(indmin) + length(indmax); end stop = any(ner < 3);else [indmin,indmax] = extr(r); ner = length(indmin) + length(indmax); stop = ner < 3;endend%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------% computes the mean of the envelopes and the mode amplitude estimatefunction [envmoy,nem,nzm,amp] = mean_and_amplitude(m,t,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs)NBSYM = 2;if MODE_COMPLEX switch MODE_COMPLEX case 1 for k = 1:ndirs phi = (k-1)*pi/ndirs; y = real(exp(-i*phi)*m); [indmin,indmax,indzer] = extr(y); nem(k) = length(indmin)+length(indmax); nzm(k) = length(indzer); [tmin,tmax,zmin,zmax] = boundary_conditions(indmin,indmax,t,y,m,NBSYM); envmin(k,:) = interp1(tmin,zmin,t,INTERP); envmax(k,:) = interp1(tmax,zmax,t,INTERP); end envmoy = mean((envmin+envmax)/2,1); if nargout > 3 amp = mean(abs(envmax-envmin),1)/2; end case 2 for k = 1:ndirs phi = (k-1)*pi/ndirs; y = real(exp(-i*phi)*m); [indmin,indmax,indzer] = extr(y); nem(k) = length(indmin)+length(indmax); nzm(k) = length(indzer); [tmin,tmax,zmin,zmax] = boundary_conditions(indmin,indmax,t,y,y,NBSYM); envmin(k,:) = exp(i*phi)*interp1(tmin,zmin,t,INTERP); envmax(k,:) = exp(i*phi)*interp1(tmax,zmax,t,INTERP); end envmoy = mean((envmin+envmax),1); if nargout > 3 amp = mean(abs(envmax-envmin),1)/2; end endelse [indmin,indmax,indzer] = extr(m); nem = length(indmin)+length(indmax); nzm = length(indzer); [tmin,tmax,mmin,mmax] = boundary_conditions(indmin,indmax,t,m,m,NBSYM); envmin = interp1(tmin,mmin,t,INTERP); envmax = interp1(tmax,mmax,t,INTERP); envmoy = (envmin+envmax)/2; if nargout > 3 amp = mean(abs(envmax-envmin),1)/2; endendend%-------------------------------------------------------------------------------% default stopping criterionfunction [stop,envmoy,s] = stop_sifting(m,t,sd,sd2,tol,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs)try [envmoy,nem,nzm,amp] = mean_and_amplitude(m,t,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs); sx = abs(envmoy)./amp; s = mean(sx); stop = ~((mean(sx > sd) > tol | any(sx > sd2)) & (all(nem > 2))); if ~MODE_COMPLEX stop = stop && ~(abs(nzm-nem)>1); endcatch stop = 1; envmoy = zeros(1,length(m)); s = NaN;endend%-------------------------------------------------------------------------------% stopping criterion corresponding to option FIXfunction [stop,moyenne]= stop_sifting_fixe(t,m,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs)try moyenne = mean_and_amplitude(m,t,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs); stop = 0;catch moyenne = zeros(1,length(m)); stop = 1;endend%-------------------------------------------------------------------------------% stopping criterion corresponding to option FIX_Hfunction [stop,moyenne,stop_count]= stop_sifting_fixe_h(t,m,INTERP,stop_count,FIXE_H,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs)try [moyenne,nem,nzm] = mean_and_amplitude(m,t,INTERP,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs); if (all(abs(nzm-nem)>1)) stop = 0; stop_count = 0; else stop_count = stop_count+1; stop = (stop_count == FIXE_H); endcatch moyenne = zeros(1,length(m)); stop = 1;endend%-------------------------------------------------------------------------------% displays the progression of the decomposition with the default stopping criterionfunction display_emd(t,m,mp,r,envmin,envmax,envmoy,s,sb,sx,sdt,sd2t,nbit,k,display_sifting,stop_sift)subplot(4,1,1)plot(t,mp);hold on;plot(t,envmax,'--k');plot(t,envmin,'--k');plot(t,envmoy,'r');title(['IMF ',int2str(k),'; iteration ',int2str(nbit),' before sifting']);set(gca,'XTick',[])hold offsubplot(4,1,2)plot(t,sx)hold onplot(t,sdt,'--r')plot(t,sd2t,':k')title('stop parameter')set(gca,'XTick',[])hold offsubplot(4,1,3)plot(t,m)title(['IMF ',int2str(k),'; iteration ',int2str(nbit),' after sifting']);set(gca,'XTick',[])subplot(4,1,4);plot(t,r-m)title('residue');disp(['stop parameter mean value : ',num2str(sb),' before sifting and ',num2str(s),' after'])if stop_sift disp('last iteration for this mode')endif display_sifting == 2 pause(0.01)else pauseendend%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------% displays the progression of the decomposition with the FIX and FIX_H stopping criteriafunction display_emd_fixe(t,m,mp,r,envmin,envmax,envmoy,nbit,k,display_sifting)subplot(3,1,1)plot(t,mp);hold on;plot(t,envmax,'--k');plot(t,envmin,'--k');plot(t,envmoy,'r');title(['IMF ',int2str(k),'; iteration ',int2str(nbit),' before sifting']);set(gca,'XTick',[])hold offsubplot(3,1,2)plot(t,m)title(['IMF ',int2str(k),'; iteration ',int2str(nbit),' after sifting']);set(gca,'XTick',[])subplot(3,1,3);plot(t,r-m)title('residue');if display_sifting == 2 pause(0.01)else pauseendend%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------% defines new extrema points to extend the interpolations at the edges of the% signal (mainly mirror symmetry)function [tmin,tmax,zmin,zmax] = boundary_conditions(indmin,indmax,t,x,z,nbsym) lx = length(x); if (length(indmin) + length(indmax) < 3) error('not enough extrema') end % boundary conditions for interpolations : if indmax(1) < indmin(1) if x(1) > x(indmin(1)) lmax = fliplr(indmax(2:min(end,nbsym+1))); lmin = fliplr(indmin(1:min(end,nbsym))); lsym = indmax(1); else lmax = fliplr(indmax(1:min(end,nbsym))); lmin = [fliplr(indmin(1:min(end,nbsym-1))),1]; lsym = 1; end else if x(1) < x(indmax(1)) lmax = fliplr(indmax(1:min(end,nbsym))); lmin = fliplr(indmin(2:min(end,nbsym+1))); lsym = indmin(1); else lmax = [fliplr(indmax(1:min(end,nbsym-1))),1]; lmin = fliplr(indmin(1:min(end,nbsym))); lsym = 1; end end if indmax(end) < indmin(end) if x(end) < x(indmax(end)) rmax = fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end)); rmin = fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym,1):end-1)); rsym = indmin(end); else rmax = [lx,fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym+2,1):end))]; rmin = fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end)); rsym = lx; end else if x(end) > x(indmin(end)) rmax = fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym,1):end-1)); rmin = fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end)); rsym = indmax(end); else rmax = fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end)); rmin = [lx,fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym+2,1):end))]; rsym = lx; end end tlmin = 2*t(lsym)-t(lmin); tlmax = 2*t(lsym)-t(lmax); trmin = 2*t(rsym)-t(rmin); trmax = 2*t(rsym)-t(rmax); % in case symmetrized parts do not extend enough if tlmin(1) > t(1) || tlmax(1) > t(1) if lsym == indmax(1) lmax = fliplr(indmax(1:min(end,nbsym))); else lmin = fliplr(indmin(1:min(end,nbsym))); end if lsym == 1 error('bug') end lsym = 1; tlmin = 2*t(lsym)-t(lmin); tlmax = 2*t(lsym)-t(lmax); end if trmin(end) < t(lx) || trmax(end) < t(lx) if rsym == indmax(end) rmax = fliplr(indmax(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end)); else rmin = fliplr(indmin(max(end-nbsym+1,1):end)); end if rsym == lx error('bug') end rsym = lx; trmin = 2*t(rsym)-t(rmin); trmax = 2*t(rsym)-t(rmax); end zlmax =z(lmax); zlmin =z(lmin); zrmax =z(rmax); zrmin =z(rmin); tmin = [tlmin t(indmin) trmin]; tmax = [tlmax t(indmax) trmax]; zmin = [zlmin z(indmin) zrmin]; zmax = [zlmax z(indmax) zrmax];end %---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------%extracts the indices of extremafunction [indmin, indmax, indzer] = extr(x,t)if(nargin==1) t=1:length(x);endm = length(x);if nargout > 2 x1=x(1:m-1); x2=x(2:m); indzer = find(x1.*x2<0); if any(x == 0) iz = find( x==0 ); indz = []; if any(diff(iz)==1) zer = x == 0; dz = diff([0 zer 0]); debz = find(dz == 1); finz = find(dz == -1)-1; indz = round((debz+finz)/2); else indz = iz; end indzer = sort([indzer indz]); endendd = diff(x);n = length(d);d1 = d(1:n-1);d2 = d(2:n);indmin = find(d1.*d2<0 & d1<0)+1;indmax = find(d1.*d2<0 & d1>0)+1;% when two or more successive points have the same value we consider only one extremum in the middle of the constant area% (only works if the signal is uniformly sampled)if any(d==0) imax = []; imin = []; bad = (d==0); dd = diff([0 bad 0]); debs = find(dd == 1); fins = find(dd == -1); if debs(1) == 1 if length(debs) > 1 debs = debs(2:end); fins = fins(2:end); else debs = []; fins = []; end end if length(debs) > 0 if fins(end) == m if length(debs) > 1 debs = debs(1:(end-1)); fins = fins(1:(end-1)); else debs = []; fins = []; end end end lc = length(debs); if lc > 0 for k = 1:lc if d(debs(k)-1) > 0 if d(fins(k)) < 0 imax = [imax round((fins(k)+debs(k))/2)]; end else if d(fins(k)) > 0 imin = [imin round((fins(k)+debs(k))/2)]; end end end end if length(imax) > 0 indmax = sort([indmax imax]); end if length(imin) > 0 indmin = sort([indmin imin]); endendend%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------function ort = io(x,imf)% ort = IO(x,imf) computes the index of orthogonality%% inputs : - x : analyzed signal% - imf : empirical mode decompositionn = size(imf,1);s = 0;for i = 1:n for j =1:n if i~=j s = s + abs(sum(imf(i,:).*conj(imf(j,:)))/sum(x.^2)); end endendort = 0.5*s;end%---------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------function [x,t,sd,sd2,tol,MODE_COMPLEX,ndirs,display_sifting,sdt,sd2t,r,imf,k,nbit,NbIt,MAXITERATIONS,FIXE,FIXE_H,MAXMODES,INTERP,mask] = init(varargin)x = varargin{1};if nargin == 2 if isstruct(varargin{2}) inopts = varargin{2}; else error('when using 2 arguments the first one is the analyzed signal X and the second one is a struct object describing the options') endelseif nargin > 2 try inopts = struct(varargin{2:end}); catch error('bad argument syntax') endend% default for stoppingdefstop = [0.05,0.5,0.05];opt_fields = {'t','stop','display','maxiterations','fix','maxmodes','interp','fix_h','mask','ndirs','complex_version'};defopts.stop = defstop;defopts.display = 0;defopts.t = 1:max(size(x));defopts.maxiterations = 2000;defopts.fix = 0;defopts.maxmodes = 0;defopts.interp = 'spline';defopts.fix_h = 0;defopts.mask = 0;defopts.ndirs = 4;defopts.complex_version = 2;opts = defopts;if(nargin==1) inopts = defopts;elseif nargin == 0 error('not enough arguments')endnames = fieldnames(inopts);for nom = names' if ~any(strcmpi(char(nom), opt_fields)) error(['bad option field name: ',char(nom)]) end if ~isempty(eval(['inopts.',char(nom)])) % empty values are discarded eval(['opts.',lower(char(nom)),' = inopts.',char(nom),';']) endendt = opts.t;stop = opts.stop;display_sifting = opts.display;MAXITERATIONS = opts.maxiterations;FIXE = opts.fix;MAXMODES = opts.maxmodes;INTERP = opts.interp;FIXE_H = opts.fix_h;mask = opts.mask;ndirs = opts.ndirs;complex_version = opts.complex_version;if ~isvector(x) error('X must have only one row or one column')endif size(x,1) > 1 x = x.';endif ~isvector(t) error('option field T must have only one row or one column')endif ~isreal(t) error('time instants T must be a real vector')endif size(t,1) > 1 t = t';endif (length(t)~=length(x)) error('X and option field T must have the same length')endif ~isvector(stop) || length(stop) > 3 error('option field STOP must have only one row or one column of max three elements')endif ~all(isfinite(x)) error('data elements must be finite')endif size(stop,1) > 1 stop = stop';endL = length(stop);if L < 3 stop(3)=defstop(3);endif L < 2 stop(2)=defstop(2);endif ~ischar(INTERP) || ~any(strcmpi(INTERP,{'linear','cubic','spline'})) error('INTERP field must be ''linear'', ''cubic'', ''pchip'' or ''spline''')end%special procedure when a masking signal is specifiedif any(mask) if ~isvector(mask) || length(mask) ~= length(x) error('masking signal must have the same dimension as the analyzed signal X') end if size(mask,1) > 1 mask = mask.'; end opts.mask = 0; imf1 = emd(x+mask,opts); imf2 = emd(x-mask,opts); if size(imf1,1) ~= size(imf2,1) warning('emd:warning',['the two sets of IMFs have different sizes: ',int2str(size(imf1,1)),' and ',int2str(size(imf2,1)),' IMFs.']) end S1 = size(imf1,1); S2 = size(imf2,1); if S1 ~= S2 if S1 < S2 tmp = imf1; imf1 = imf2; imf2 = tmp; end imf2(max(S1,S2),1) = 0; end imf = (imf1+imf2)/2;endsd = stop(1);sd2 = stop(2);tol = stop(3);lx = length(x);sdt = sd*ones(1,lx);sd2t = sd2*ones(1,lx);if FIXE MAXITERATIONS = FIXE; if FIXE_H error('cannot use both ''FIX'' and ''FIX_H'' modes') endendMODE_COMPLEX = ~isreal(x)*complex_version;if MODE_COMPLEX && complex_version ~= 1 && complex_version ~= 2 error('COMPLEX_VERSION parameter must equal 1 or 2')end% number of extrema and zero-crossings in residualner = lx;nzr = lx;r = x;if ~any(mask) % if a masking signal is specified "imf" already exists at this stage imf = [];endk = 1;% iterations counter for extraction of 1 modenbit=0;% total iterations counterNbIt=0;end%--------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- |
关于EMD,有对应的工具箱。VMD也有扩展的二维分解,此处不再展开。
三、一种权衡的小trick
关于瞬时频率的原理以及代码,参考另一篇博文。
比较来看:
- EMD分解的IMF分量个数不能人为设定,而VMD(Variational Mode Decomposition)则可以;
- 但VMD也有弊端:分解过多,则信号断断续续,没有多少规律可言。
能不能取长补短呢?
自己之前做了一个小code,放在这里,供大家交流使用(此理论为自己首创,版权所有,拿去也不介意!(●'◡'●))。
给定一个信号,下图是EMD分解结果,分解出了5个分量。
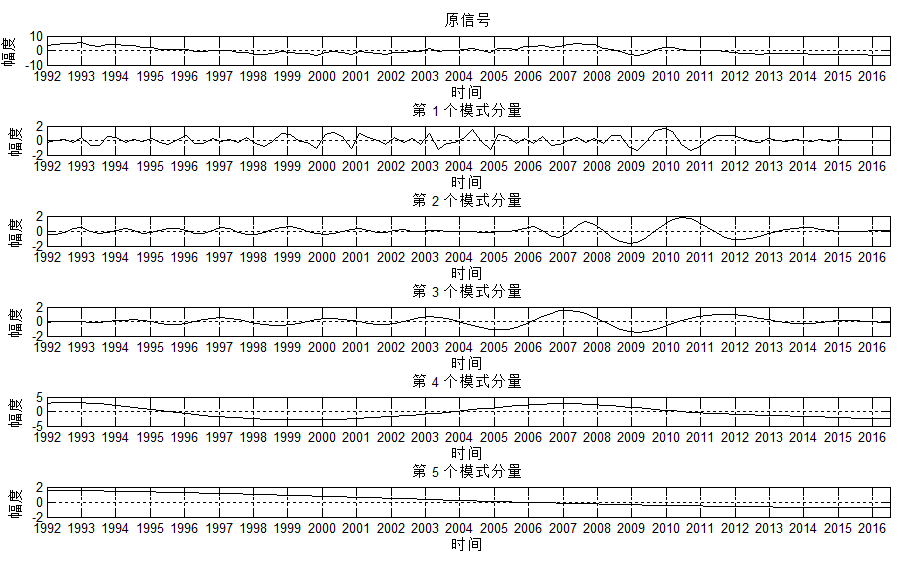
再来一个VMD(设定分量个数为3)的分解结果:

比较两个结果,可以发现:VMD的低频分量,更容易表达出经济波动的大趋势,而EMD则不易观察该特性。
或许有人会说:几个EMD分量叠加一下,也会有该效果,但如果不观察分解的数据,如何确定几个分量相加呢?更何况EMD总的IMF个数也是未知!
VMD的优势观察到了,但如何确定分量个数呢?
再来一个效果图:
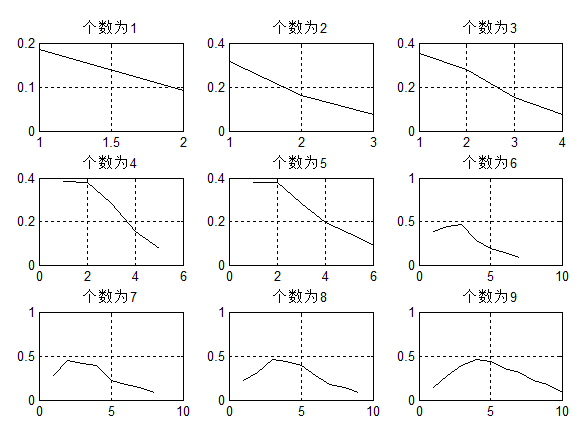
这里分析了VMD分量从1~9,9种情况下某特征的曲线,可以观察到:个数增加到一定数量,曲线有了明显的下弯曲现象(该特性容易借助曲率,进行量化分析,不再展开),这个临界的个数就是分解的合适数量,此处:K=3,因为到4就有了明显的下弯曲。
可见通过该特征,即可理论上得出最优K。下面讲一讲这个某特征为何物?
上一段代码:
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 | for st=1:9 K=st+1; [u, u_hat, omega] = VMD(data, length(data), 0, K, 0, 1, 1e-5); u=flipud(u); resf=zeros(1,K); for i=1:K testdata=u(i,:); hilbert(testdata'); z=hilbert(testdata'); % 希尔伯特变换 a=abs(z); % 包络线 fnor=instfreq(z); % 瞬时频率 resf(i)=mean(fnor); end subplot(3,3,st) plot(resf,'k');title(['个数为',num2str(st)]);grid on;end |
没错,该特征就是:分量瞬时频率的均值。如果分解个数过大,则分量会出现断断絮絮地现象,特别是在高频,这样一来,即使是高频,平均瞬时频率反而低一些,这也是下弯曲的根本原因。
这个小trick就介绍到这里。
四、问题补充
HHT算法中,有两处存在端点效应,VMD是否也有呢?这一点没有再去验证。另外,关于Hilbert的端点效应,在另一篇博文已经给出。
参考:
了凡春秋: http://blog.sina.com.cn/s/blog_6163bdeb0102e2cd.html
VMD-code:https://cn.mathworks.com/matlabcentral/fileexchange/44765-variational-mode-decomposition




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 字符编码:从基础到乱码解决