内存分析,类加载
查询 垃圾收集器 java -XX:+PrintCommandLineFlags -version
GC 日志:启用 GC 日志,这样就能分析垃圾回收的活动情况。比如可以用以下 JVM 参数:“-XX:+HeapDumpOnOutOfMemoryError -XX:HeapDumpPath=/path/to/dump -xlog:gc*:file=gc.log:time”。 让程序在出现 OOM 错误的时候自动生成堆转储文件 用 MAT 打开生成的堆转储文件 https://mp.weixin.qq.com/s/5eKnk3CdWT2EmwgayAq_8w
jstat分析
netstat -ano|findstr :8801 查看进程id jstat -gc 25028 jstat -gc 25028 1000 对象优先在 Eden 区分配,Eden区 没有足够空间分配的时候,会发起 Minor GC Minor GC 处理 Eden 区时,如果发现 Survivor区 不够放,就会根据 分配担保机制 将新生代的数据提前转移到老年代中。 https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/708402035 如下图: 方法中的局部变量赋值了大对象,模拟了一次YGC
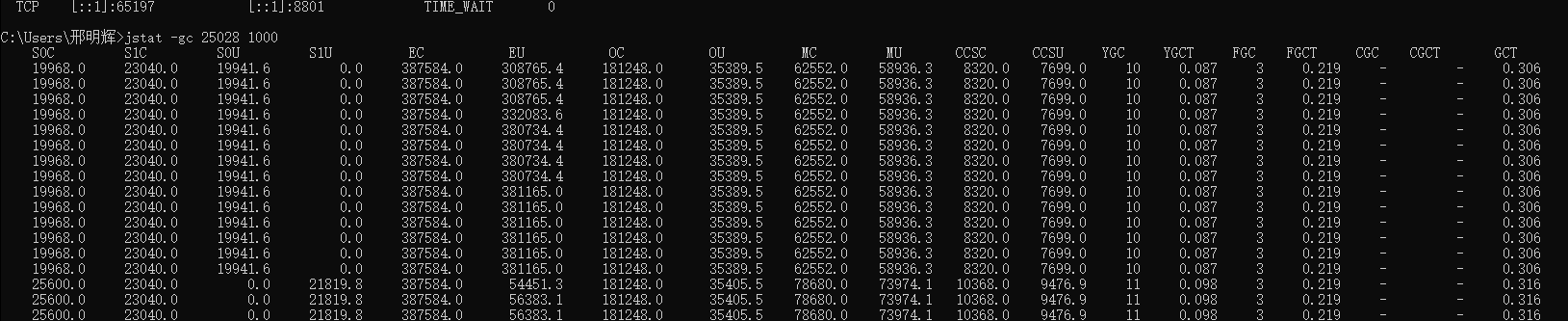
字段 说明 S0C 年轻代第一个Survivor区的大小(单位:KB) S1C 年轻代第二个Survivor区的大小(单位:KB) S0U 年轻代第一个Survivor区的使用大小(单位:KB) S1U 年轻代第二个Survivor区的使用大小(单位:KB) EC 年轻代中Eden区的大小(单位:KB) EU 年轻代中Eden区的使用大小(单位:KB) OC 老年代大小(单位:KB) OU 老年代使用大小(单位:KB) MC 方法区大小(单位:KB) MU 方法区使用大小(单位:KB) CCSC 压缩类空间大小(单位:KB) CCSU 压缩类空间使用大小(单位:KB) YGC 年轻代垃圾回收次数 YGCT 年轻代垃圾回收消耗时间 FGC 老年代垃圾回收次数 FGCT 老年代垃圾回收消耗时间 GCT 垃圾回收消耗总时间
jmap分析
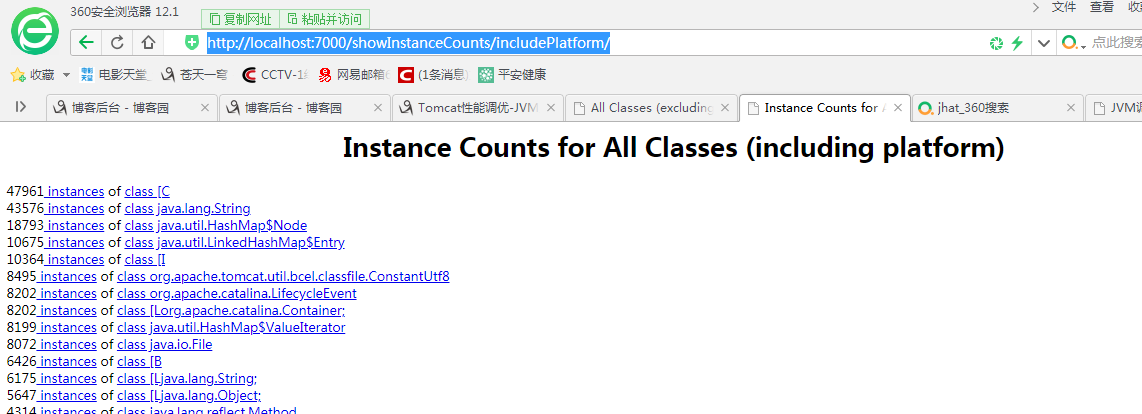
1,获取hprof命令 jmap -dump:format=b,file=/path/file.hprof pid 2,window获取进程命令 netstat -ano | findstr 8081 jmap -dump:format=b,file=file.hprof 7528 C:\Users\xingminghui\file.hprof 3, jmap -dump:format=b,file=mem.dat 7528 #将内存使用的详细情况输出到mem.dat 文件 通过 jhat -port 7000 C:\Users\xingminghui\mem.dat 可以将mem.dat的内容以web的方式暴露到网络,访问http://ip-server:7000查看。
当对象有被引用时,可达性存在,如图GCRoots ,hprof文件拖入idea中查看 Shallow:分配用于存储对象本身的内存大小
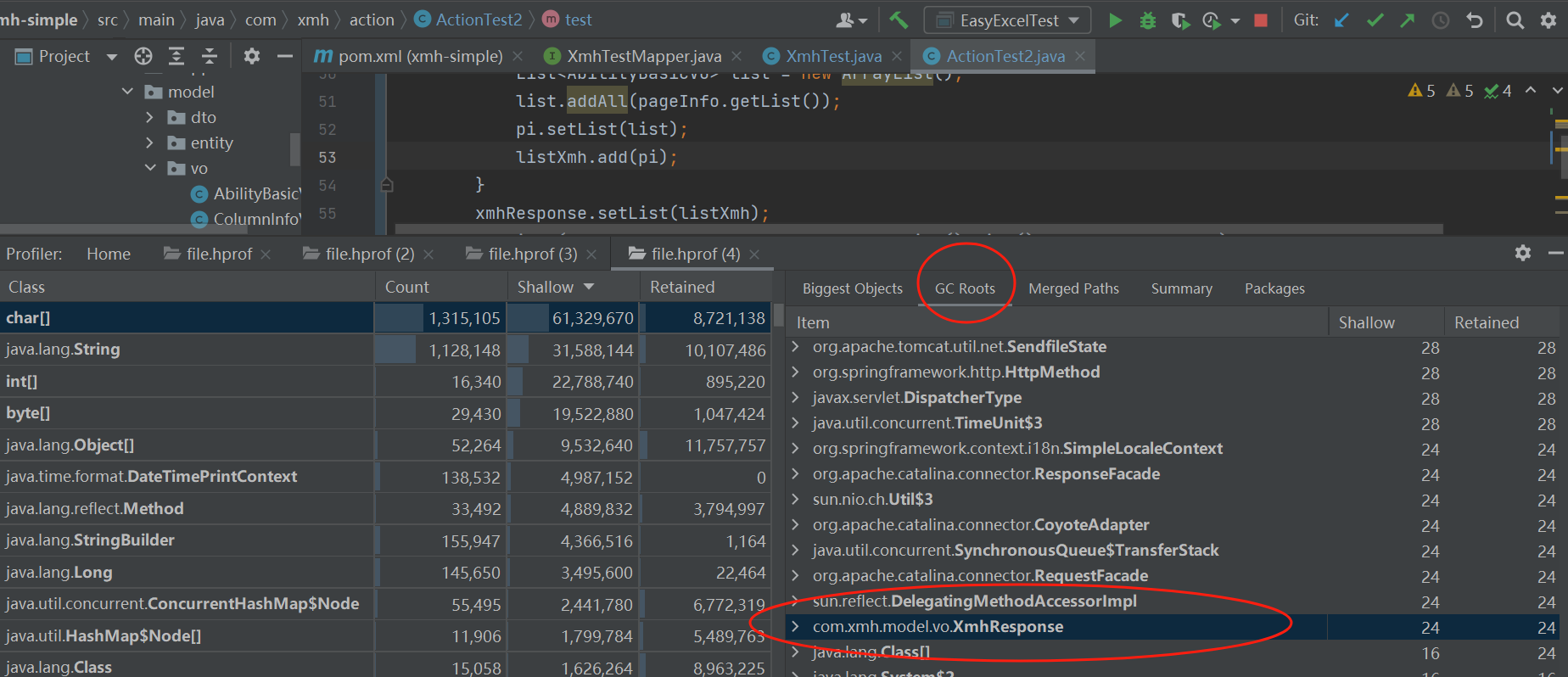
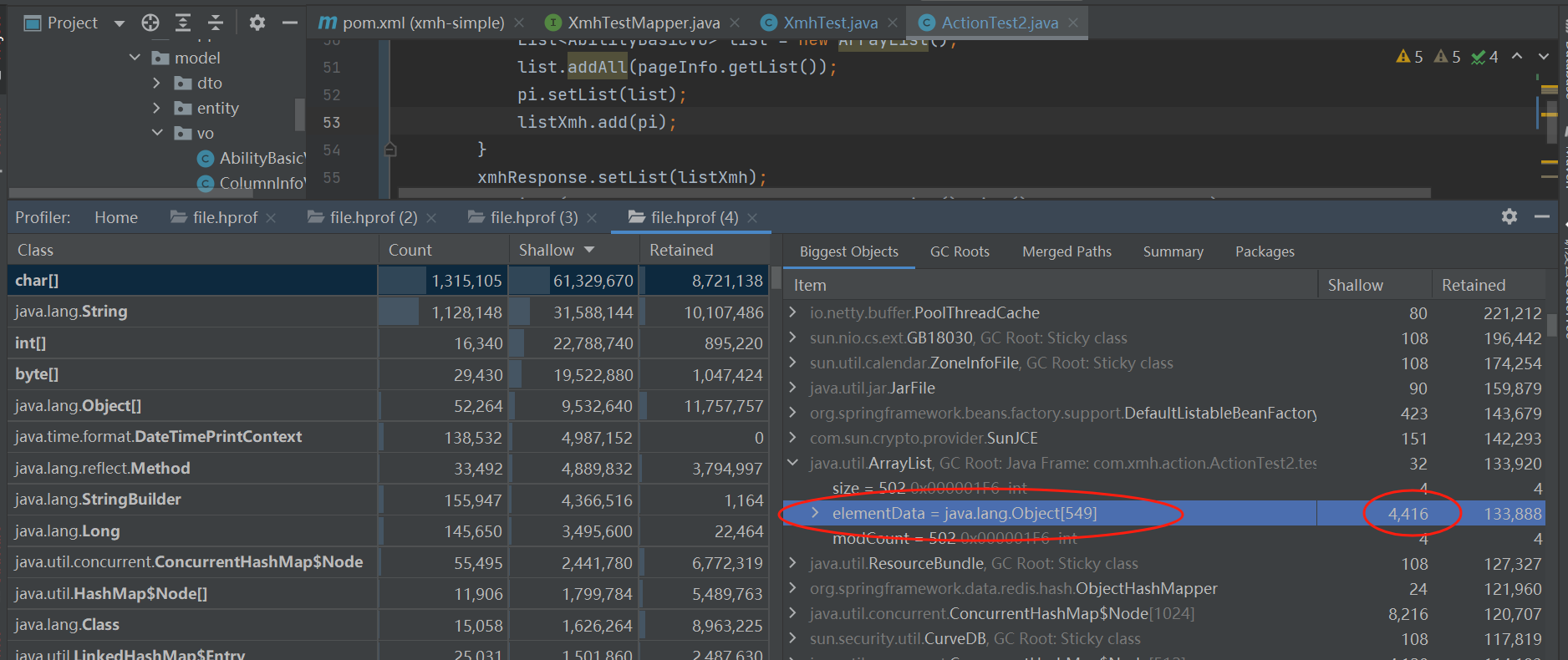
对象中的list属性存入大量数据,如下
idea插件篇之java内存分析工具(JProfiler) jhat C:\Users\xingminghui\file.hprof -J -Xmx512m http://localhost:7000/ http://localhost:7000/showInstanceCounts/includePlatform/ https://www.cnblogs.com/KingIceMou/p/6967754.html 内存监控 使用sudo -u admin -H jmap -dump:format=b,file=文件名.hprof pid 来dump内存,生成dump文件 jvisualvm 工具里面有 Heap Dump的功能 Eclipse下的mat差距进行分析 http://www.eclipse.org/mat Eclipse Memory Analyzer,查看对象树和对象空间占用非常的方便 tomcat 查看内存占用量 https://blog.csdn.net/jkler_doyourself/article/details/6033500
http://localhost:7000/showInstanceCounts/includePlatform/
java内存分区
****方法区
主要用来存储已被虚拟机加载的类的信息、常量、静态变量和即时编译器编译后的代码等数据。
****堆
java堆是所有线程所共享的一块内存,在虚拟机启动时创建,几乎所有的对象实例都在这里创建,因此该区域经常发生垃圾回收操作。
****虚拟机栈
1. 虚拟机栈也就是我们平常所称的栈内存,它为java方法服务,每个方法在执行的时候都会创建一个栈帧,用于存储局部变量表、操作数栈、动态链接和方法出口等信息。
2. 虚拟机栈是线程私有的,它的生命周期与线程相同。
finalize() 对象释放会调用该方法
HashMap存进去的是t1跟t2指向的地址,t1=null,t2=null的时候,本来按照常理来说,Java回收机制会对那些没有引用的堆内存对象进行回收,但不幸的是,HashMap依旧会强引用着t1跟t2的堆内存对象,导致GC无法对其进行回收
public class TestMy {
public static void main(String[] args) {
TestE t2 = new TestE();
TestE t3 = null;
System.out.println(t2+","+t3);
System.gc();
System.out.println(t2+","+t3);
t2=null;
System.gc();
//System.out.println(t2+","+t3);
}
@org.junit.Test
private void test1(){
HashMap map = new HashMap();
TestE t1 = new TestE();
TestE t2 = new TestE();
map.put("1", t1);
map.put("2", t2);
t1 = null;
System.gc();
System.out.println("第1步" + map);
t2 = null;
System.gc();
System.out.println("第2步" + map);
map.clear();
System.gc();
System.out.println("第3步" + map);
}
}
public class TestE {
private String strTest = "该Test对象还存在";
@Override
public String toString() {
return strTest;
}
@Override
protected void finalize() throws Throwable {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
System.out.println("该Test对象被释放了");
}
}



