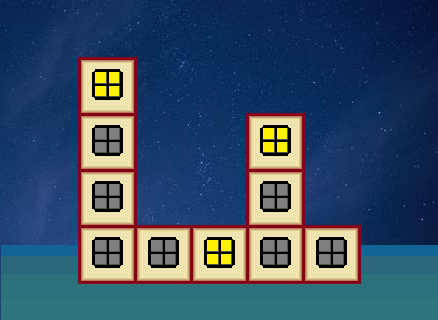
微软大楼的设计方案(解题报告)
近日,微软新大楼的设计方案正在广泛征集中,其中一种方案格外引人注目。在这个方案中,大楼由 n 栋楼组成,这些楼从左至右连成一排,编号依次为 1 到 n,其中第 i 栋楼有 h_i 层。每栋楼的每一层为一个独立的 办公区域,可以步行 直达同层相邻楼栋的办公区域,以及 直达同楼栋相邻楼层的办公区域。
由于方案设计巧妙,上一层楼、下一层楼、向左右移动到相邻楼栋同层的办公区域均刚好需要 111 分钟。在这些办公区域中,有一些被 核心部门 占用了(一个办公区域内最多只有一个核心部门),出于工作效率的考虑,微软希望核心部门之间的移动时间越短越好。对于一个给定的 最大移动时间 kkk,大楼的 协同值 定义为:有多少个 核心部门对 之间的移动时间不超过 kkk。由于大楼门禁的限制,不可以走出整个大楼,也不可以登上天台思考人生。你可以认为在办公区域内的移动时间忽略不计,并且在大楼内总是按照最优方案进行移动。
对于一个给定的新大楼设计方案,你能算出方案的协同值么?
输入格式
第一行包含两个正整数 n,k(1≤k≤200020)n,k(1\leq k\leq 200020)n,k(1≤k≤200020),分别表示大楼的栋数以及最大移动时间。
第二行包含 nnn 个正整数 h1,h2,...,hn(1≤hi≤20)h_1,h_2,...,h_n(1\leq h_i\leq 20)h1,h2,...,hn(1≤hi≤20),分别表示每栋楼的层数。
接下来一行包含一个正整数 mmm,表示 核心部门 个数。
接下来 mmm 行,每行两个正整数 xi,yi(1≤xi≤n,1≤yi≤hxi)x_i,y_i(1\leq x_i\leq n,1\leq y_i\leq h_{x_i})xi,yi(1≤xi≤n,1≤yi≤hxi),表示该核心部门位于第 xix_ixi 栋楼的第 yiy_iyi 层。
输入数据保证 mmm 个核心部门的位置不会重复。
对于简单版本:1≤n,m≤501\leq n,m\leq 501≤n,m≤50;
对于中等版本:1≤n≤200000,1≤m≤20001\leq n\leq 200000,1\leq m\leq 20001≤n≤200000,1≤m≤2000;
对于困难版本:1≤n,m≤2000001\leq n,m\leq 2000001≤n,m≤200000。
输出格式
输出一个整数,即整个大楼的 协同值。
样例解释
样例对应题目描述中的图,核心部门 111 和核心部门 333 之间的距离为 8>78>78>7,因此不能计入答案。
样例输入
5 7 4 1 1 3 1 3 1 4 3 1 4 3
样例输出
2
比赛时只做出简单的,好辣鸡!!!
1 #include <bits/stdc++.h> 2 using namespace std; 3 typedef pair<int,int> P; 4 const int N = 55; 5 int n, k, m, x1, x2, yy, y2; 6 int a[N]; 7 int dist[N][N]; 8 int qx[N],qy[N]; 9 int dx[] = {1, 0, -1, 0}, dy[] = {0, -1, 0, 1}; 10 int d[N][N]; 11 void init(){ 12 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){ 13 int j; 14 for(j = 1; j <= a[i]; j ++){ 15 dist[i][j] = 1; 16 } 17 for(;j <= n; j ++){ 18 dist[i][j] = 0; 19 } 20 } 21 } 22 int solve(){ 23 memset(d,-1,sizeof(d)); 24 queue<P> que; 25 que.push(P(x1,yy)); 26 d[x1][yy] = 0; 27 while(que.size()){ 28 P p = que.front(); 29 que.pop(); 30 if(p.first == x2 && p.second == y2) break; 31 for(int i = 0; i < 4; i ++){ 32 int nx = p.first + dx[i], ny = p.second + dy[i]; 33 if(0 < nx && nx <= n && 0 < ny && ny <= n && dist[nx][ny] == 1 && d[nx][ny] == -1){ 34 que.push(P(nx,ny)); 35 d[nx][ny] = d[p.first][p.second] + 1; 36 } 37 } 38 } 39 return d[x2][y2]; 40 } 41 int main(){ 42 cin >> n >> k; 43 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){ 44 cin >> a[i]; 45 } 46 init(); 47 cin >> m; 48 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++){ 49 cin >> qx[i] >> qy[i]; 50 } 51 int ans = 0; 52 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++){ 53 x1 = qx[i]; yy = qy[i]; 54 for(int j = i+1; j <= m; j ++){ 55 if(i == j) continue; 56 x2 = qx[j]; y2 = qy[j]; 57 int cnt = solve(); 58 //printf(" %d %d : %d\n",i,j,cnt); 59 if(cnt <= k) ans++; 60 } 61 } 62 cout << ans << endl; 63 return 0; 64 }
中等的看下题解才会的。
对于两个核心部门A,B。假设XA < XB ,那么A与B之间的距离就是XB-XA+YA+YB-2*[XA,XB],[XA,XB]表示从XA到XB之间楼层最低的楼。
设S[i][j]表示前i个位置中有多少h为j,从小到大枚举下就可以得到最小值,每次查询时间为O(h),时间复杂度为O(nh+mmh)
代码如下:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <queue> 3 #include <algorithm> 4 #include <string.h> 5 #define ll long long 6 using namespace std; 7 const int N = 2e5+10; 8 const int M = 2e3+10; 9 struct Nod{ 10 int x, y; 11 }nod[M]; 12 bool cmp(Nod a, Nod b){ 13 if(a.x != b.x) return a.x < b.x; 14 else return a.y < b.y; 15 } 16 int s[N][22], h[N], n, k, m; 17 int minCheck(int l, int r){ 18 for(int i = 1; i <= 20; i ++){ 19 if(s[l-1][i] != s[r][i]){ 20 return i; 21 } 22 } 23 } 24 int main(){ 25 scanf("%d %d",&n,&k); 26 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){ 27 scanf("%d",&h[i]); 28 for(int j = 0; j <= 20; j ++){ 29 s[i][j] = s[i-1][j]; 30 } 31 s[i][h[i]]++; 32 } 33 scanf("%d",&m); 34 //cout << "----" << endl; 35 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++){ 36 scanf("%d %d",&nod[i].x,&nod[i].y); 37 } 38 sort(nod+1,nod+1+m,cmp); 39 int ans = 0; 40 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++){ 41 for(int j = i + 1; j <= m; j ++){ 42 int x1 = nod[i].x, y1 = nod[i].y; 43 int x2 = nod[j].x, y2 = nod[j].y; 44 int cnt; 45 if(x1 == x2){ 46 if(abs(y1-y2) <= k) ans++; 47 }else{ 48 cnt = x2 - x1 + y1 + y2 - 2*minCheck(x1,x2); 49 if(cnt <= k) ans ++; 50 } 51 } 52 } 53 printf("%d\n",ans); 54 55 return 0; 56 }
由于是区间求最小值,可以用线段树来做:
1 #include <iostream> 2 #include <algorithm> 3 #define lson l,mid,rt<<1 4 #define rson mid+1,r,rt<<1|1 5 using namespace std; 6 const int N = 2e5+10; 7 const int M = 2e3+10; 8 int n, m, k, h[N], tree[N<<2]; 9 pair<int,int> room[M]; 10 void Push_up(int rt){ 11 tree[rt] = min(tree[rt<<1],tree[rt<<1|1]); 12 } 13 void build(int l, int r, int rt){ 14 if(l == r){ 15 tree[rt] = h[l]; 16 return; 17 } 18 int mid = (l+r)>>1; 19 build(lson); 20 build(rson); 21 Push_up(rt); 22 } 23 int query(int l, int r, int rt,int LL, int RR){ 24 if(LL <= l && r <= RR){ 25 return tree[rt]; 26 } 27 int cnt = 22; 28 int mid = (l+r)>>1; 29 if(mid >= LL) cnt = min(cnt,query(lson,LL,RR)); 30 if(mid < RR) cnt = min(cnt,query(rson,LL,RR)); 31 return cnt; 32 } 33 int main(){ 34 scanf("%d %d",&n,&k); 35 for(int i = 1; i <= n; i ++){ 36 scanf("%d",&h[i]); 37 } 38 build(1,n,1); 39 scanf("%d",&m); 40 int a,b; 41 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++){ 42 scanf("%d %d",&a,&b); 43 room[i] = make_pair(a,b); 44 } 45 sort(room+1,room+1+m); 46 int ans = 0; 47 for(int i = 1; i <= m; i ++){ 48 for(int j = i+1; j <= m; j ++){ 49 int x1 = room[i].first, y1 = room[i].second; 50 int x2 = room[j].first, y2 = room[j].second; 51 if(x1 == x2){ 52 if((y2-y1) <= k) ans++; 53 }else{ 54 int cnt = x2-x1+y1+y2-2*query(1,n,1,x1,x2); 55 if(cnt <= k)ans++; 56 } 57 } 58 } 59 printf("%d\n",ans); 60 return 0; 61 }
困难的话就无从下手了,题解也看不懂。