linux设备驱动(23)网络设备驱动详解
1 概述
网卡的驱动其实很简单,它还是与硬件相关,主要是负责收发网络的数据包,它将上层协议传递下来的数据包以特定的媒介访问控制方式进行发送, 并将接收到的数据包传递给上层协议。
网卡设备与字符设备和块设备不同, 网络设备并不对应于/dev目录下的文件,不过会存放在/sys/class/net目录下。
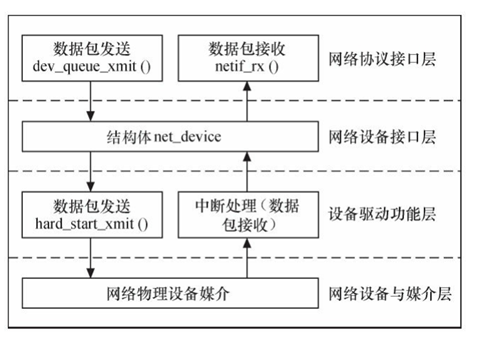
linux网络设备驱动分了四层:
(1)网络协议接口层:
实现统一的数据包收发的协议,该层主要负责调用dev_queue_xmit()函数发送数据, netif_rx()函数接收数据
(2)网络设备接口层:
通过net_device结构体来描述一个具体的网络设备的信息,实现不同的硬件的统一
(3)设备驱动功能层:
用来负责驱动网络设备硬件来完成各个功能, 它通过hard_start_xmit() 函数启动发送操作, 并通过网络设备上的中断触发接收操作,
(4)网络设备与媒介层:
用来负责完成数据包发送和接收的物理实体, 设备驱动功能层的函数都在这物理上驱动的
层次结构如下图所示:
2 数据结构体
2.1 网络设备结构体net_device
定义位于:linux-3.10.73\include\linux\netdevice.h
1 struct net_device { 2 3 /* 4 * This is the first field of the "visible" part of this structure 5 * (i.e. as seen by users in the "Space.c" file). It is the name 6 * of the interface. 7 */ 8 char name[IFNAMSIZ];//网卡设备名称 9 10 /* device name hash chain, please keep it close to name[] */ 11 struct hlist_node name_hlist; 12 13 /* snmp alias */ 14 char *ifalias; 15 16 /* 17 * I/O specific fields 18 * FIXME: Merge these and struct ifmap into one 19 */ 20 unsigned long mem_end; /* 该设备的内存结束地址*/ 21 unsigned long mem_start; /* 该设备的内存起始地址*/ 22 unsigned long base_addr; /* 该设备的内存I/O基地址*/ 23 unsigned int irq; /* 该设备的中断号*/ 24 25 /* 26 * Some hardware also needs these fields, but they are not 27 * part of the usual set specified in Space.c. 28 */ 29 30 unsigned long state;//网络设备和网络适配器的状态信息 31 32 struct list_head dev_list; 33 struct list_head napi_list; 34 struct list_head unreg_list; 35 struct list_head upper_dev_list; /* List of upper devices */ 36 37 38 /* currently active device features */ 39 netdev_features_t features; 40 /* user-changeable features */ 41 netdev_features_t hw_features; 42 /* user-requested features */ 43 netdev_features_t wanted_features; 44 /* mask of features inheritable by VLAN devices */ 45 netdev_features_t vlan_features; 46 /* mask of features inherited by encapsulating devices 47 * This field indicates what encapsulation offloads 48 * the hardware is capable of doing, and drivers will 49 * need to set them appropriately. 50 */ 51 netdev_features_t hw_enc_features; 52 53 /* Interface index. Unique device identifier */ 54 int ifindex; 55 int iflink; 56 57 struct net_device_stats stats; 58 atomic_long_t rx_dropped; /* dropped packets by core network 59 * Do not use this in drivers. 60 */ 61 62 #ifdef CONFIG_WIRELESS_EXT 63 /* List of functions to handle Wireless Extensions (instead of ioctl). 64 * See <net/iw_handler.h> for details. Jean II */ 65 const struct iw_handler_def * wireless_handlers; 66 /* Instance data managed by the core of Wireless Extensions. */ 67 struct iw_public_data * wireless_data; 68 #endif 69 /* Management operations */ 70 const struct net_device_ops *netdev_ops; 71 const struct ethtool_ops *ethtool_ops; 72 73 /* Hardware header description */ 74 const struct header_ops *header_ops; 75 76 unsigned int flags; /* interface flags (a la BSD) */ 77 unsigned int priv_flags; /* Like 'flags' but invisible to userspace. 78 * See if.h for definitions. */ 79 unsigned short gflags; 80 unsigned short padded; /* How much padding added by alloc_netdev() */ 81 82 unsigned char operstate; /* RFC2863 operstate */ 83 unsigned char link_mode; /* mapping policy to operstate */ 84 85 unsigned char if_port; /* Selectable AUI, TP,..*/ 86 unsigned char dma; /* DMA channel */ 87 88 unsigned int mtu; /* interface MTU value */ 89 unsigned short type; /* interface hardware type */ 90 unsigned short hard_header_len; /* hardware hdr length */ 91 92 /* extra head- and tailroom the hardware may need, but not in all cases 93 * can this be guaranteed, especially tailroom. Some cases also use 94 * LL_MAX_HEADER instead to allocate the skb. 95 */ 96 unsigned short needed_headroom; 97 unsigned short needed_tailroom; 98 99 /* Interface address info. */ 100 unsigned char perm_addr[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* permanent hw address */ 101 unsigned char addr_assign_type; /* hw address assignment type */ 102 unsigned char addr_len; /* hardware address length */ 103 unsigned char neigh_priv_len; 104 unsigned short dev_id; /* for shared network cards */ 105 106 spinlock_t addr_list_lock; 107 struct netdev_hw_addr_list uc; /* Unicast mac addresses */ 108 struct netdev_hw_addr_list mc; /* Multicast mac addresses */ 109 struct netdev_hw_addr_list dev_addrs; /* list of device 110 * hw addresses 111 */ 112 #ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS 113 struct kset *queues_kset; 114 #endif 115 116 bool uc_promisc; 117 unsigned int promiscuity; 118 unsigned int allmulti; 119 120 121 /* Protocol specific pointers */ 122 123 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_VLAN_8021Q) 124 struct vlan_info __rcu *vlan_info; /* VLAN info */ 125 #endif 126 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_NET_DSA) 127 struct dsa_switch_tree *dsa_ptr; /* dsa specific data */ 128 #endif 129 void *atalk_ptr; /* AppleTalk link */ 130 struct in_device __rcu *ip_ptr; /* IPv4 specific data */ 131 struct dn_dev __rcu *dn_ptr; /* DECnet specific data */ 132 struct inet6_dev __rcu *ip6_ptr; /* IPv6 specific data */ 133 void *ax25_ptr; /* AX.25 specific data */ 134 struct wireless_dev *ieee80211_ptr; /* IEEE 802.11 specific data, 135 assign before registering */ 136 137 /* 138 * Cache lines mostly used on receive path (including eth_type_trans()) 139 */ 140 unsigned long last_rx; /* Time of last Rx 141 * This should not be set in 142 * drivers, unless really needed, 143 * because network stack (bonding) 144 * use it if/when necessary, to 145 * avoid dirtying this cache line. 146 */ 147 148 /* Interface address info used in eth_type_trans() */ 149 unsigned char *dev_addr; /* hw address, (before bcast 150 because most packets are 151 unicast) */ 152 153 154 #ifdef CONFIG_RPS 155 struct netdev_rx_queue *_rx; 156 157 /* Number of RX queues allocated at register_netdev() time */ 158 unsigned int num_rx_queues; 159 160 /* Number of RX queues currently active in device */ 161 unsigned int real_num_rx_queues; 162 163 #endif 164 165 rx_handler_func_t __rcu *rx_handler; 166 void __rcu *rx_handler_data; 167 168 struct netdev_queue __rcu *ingress_queue; 169 unsigned char broadcast[MAX_ADDR_LEN]; /* hw bcast add */ 170 171 172 /* 173 * Cache lines mostly used on transmit path 174 */ 175 struct netdev_queue *_tx ____cacheline_aligned_in_smp; 176 177 /* Number of TX queues allocated at alloc_netdev_mq() time */ 178 unsigned int num_tx_queues; 179 180 /* Number of TX queues currently active in device */ 181 unsigned int real_num_tx_queues; 182 183 /* root qdisc from userspace point of view */ 184 struct Qdisc *qdisc; 185 186 unsigned long tx_queue_len; /* Max frames per queue allowed */ 187 spinlock_t tx_global_lock; 188 189 #ifdef CONFIG_XPS 190 struct xps_dev_maps __rcu *xps_maps; 191 #endif 192 #ifdef CONFIG_RFS_ACCEL 193 /* CPU reverse-mapping for RX completion interrupts, indexed 194 * by RX queue number. Assigned by driver. This must only be 195 * set if the ndo_rx_flow_steer operation is defined. */ 196 struct cpu_rmap *rx_cpu_rmap; 197 #endif 198 199 /* These may be needed for future network-power-down code. */ 200 201 /* 202 * trans_start here is expensive for high speed devices on SMP, 203 * please use netdev_queue->trans_start instead. 204 */ 205 unsigned long trans_start; /* Time (in jiffies) of last Tx */ 206 207 int watchdog_timeo; /* used by dev_watchdog() */ 208 struct timer_list watchdog_timer; 209 210 /* Number of references to this device */ 211 int __percpu *pcpu_refcnt; 212 213 /* delayed register/unregister */ 214 struct list_head todo_list; 215 /* device index hash chain */ 216 struct hlist_node index_hlist; 217 218 struct list_head link_watch_list; 219 220 /* register/unregister state machine */ 221 enum { NETREG_UNINITIALIZED=0, 222 NETREG_REGISTERED, /* completed register_netdevice */ 223 NETREG_UNREGISTERING, /* called unregister_netdevice */ 224 NETREG_UNREGISTERED, /* completed unregister todo */ 225 NETREG_RELEASED, /* called free_netdev */ 226 NETREG_DUMMY, /* dummy device for NAPI poll */ 227 } reg_state:8; 228 229 bool dismantle; /* device is going do be freed */ 230 231 enum { 232 RTNL_LINK_INITIALIZED, 233 RTNL_LINK_INITIALIZING, 234 } rtnl_link_state:16; 235 236 /* Called from unregister, can be used to call free_netdev */ 237 void (*destructor)(struct net_device *dev); 238 239 #ifdef CONFIG_NETPOLL 240 struct netpoll_info __rcu *npinfo; 241 #endif 242 243 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_NS 244 /* Network namespace this network device is inside */ 245 struct net *nd_net; 246 #endif 247 248 /* mid-layer private */ 249 union { 250 void *ml_priv; 251 struct pcpu_lstats __percpu *lstats; /* loopback stats */ 252 struct pcpu_tstats __percpu *tstats; /* tunnel stats */ 253 struct pcpu_dstats __percpu *dstats; /* dummy stats */ 254 struct pcpu_vstats __percpu *vstats; /* veth stats */ 255 }; 256 /* GARP */ 257 struct garp_port __rcu *garp_port; 258 /* MRP */ 259 struct mrp_port __rcu *mrp_port; 260 261 /* class/net/name entry */ 262 struct device dev; 263 /* space for optional device, statistics, and wireless sysfs groups */ 264 const struct attribute_group *sysfs_groups[4]; 265 266 /* rtnetlink link ops */ 267 const struct rtnl_link_ops *rtnl_link_ops; 268 269 /* for setting kernel sock attribute on TCP connection setup */ 270 #define GSO_MAX_SIZE 65536 271 unsigned int gso_max_size; 272 #define GSO_MAX_SEGS 65535 273 u16 gso_max_segs; 274 275 #ifdef CONFIG_DCB 276 /* Data Center Bridging netlink ops */ 277 const struct dcbnl_rtnl_ops *dcbnl_ops; 278 #endif 279 u8 num_tc; 280 struct netdev_tc_txq tc_to_txq[TC_MAX_QUEUE]; 281 u8 prio_tc_map[TC_BITMASK + 1]; 282 283 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_FCOE) 284 /* max exchange id for FCoE LRO by ddp */ 285 unsigned int fcoe_ddp_xid; 286 #endif 287 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_NETPRIO_CGROUP) 288 struct netprio_map __rcu *priomap; 289 #endif 290 /* phy device may attach itself for hardware timestamping */ 291 struct phy_device *phydev; 292 293 struct lock_class_key *qdisc_tx_busylock; 294 295 /* group the device belongs to */ 296 int group; 297 298 struct pm_qos_request pm_qos_req; 299 }
2.2 net_device_stats结构体
1 struct net_device_stats { 2 unsigned long rx_packets;/*收到的数据包数*/ 3 unsigned long tx_packets;/*发送的数据包数*/ 4 unsigned long rx_bytes;/*收到的字节数,可以通过sk_buff结构体的成员len来获取*/ 5 unsigned long tx_bytes;/*发送的字节数,可以通过sk_buff结构体的成员len来获取*/ 6 unsigned long rx_errors;/*收到的错误数据包数*/ 7 unsigned long tx_errors;/*发送的错误数据包数*/ 8 unsigned long rx_dropped; 9 unsigned long tx_dropped; 10 unsigned long multicast; 11 unsigned long collisions; 12 unsigned long rx_length_errors; 13 unsigned long rx_over_errors; 14 unsigned long rx_crc_errors; 15 unsigned long rx_frame_errors; 16 unsigned long rx_fifo_errors; 17 unsigned long rx_missed_errors; 18 unsigned long tx_aborted_errors; 19 unsigned long tx_carrier_errors; 20 unsigned long tx_fifo_errors; 21 unsigned long tx_heartbeat_errors; 22 unsigned long tx_window_errors; 23 unsigned long rx_compressed; 24 unsigned long tx_compressed; 25 }
2.3 结构体sk_buff
1 struct sk_buff { 2 /* These two members must be first. */ 3 struct sk_buff *next;//指向下一个sk_buff结构体 4 struct sk_buff *prev;//指向前一个sk_buff结构体 5 6 ktime_t tstamp; 7 8 struct sock *sk; 9 struct net_device *dev; 10 11 /* 12 * This is the control buffer. It is free to use for every 13 * layer. Please put your private variables there. If you 14 * want to keep them across layers you have to do a skb_clone() 15 * first. This is owned by whoever has the skb queued ATM. 16 */ 17 char cb[48] __aligned(8); 18 19 unsigned long _skb_refdst; 20 #ifdef CONFIG_XFRM 21 struct sec_path *sp; 22 #endif 23 unsigned int len,//数据包的总长度,包括线性数据和非线性数据 24 data_len;//非线性的数据长度 25 __u16 mac_len, //mac包头长度 26 hdr_len; 27 union { 28 __wsum csum; 29 struct { 30 __u16 csum_start; 31 __u16 csum_offset; 32 }; 33 }; 34 __u32 priority;//该sk_buff结构体的优先级 35 kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags1); 36 __u8 local_df:1, 37 cloned:1, 38 ip_summed:2, 39 nohdr:1, 40 nfctinfo:3; 41 __u8 pkt_type:3, 42 fclone:2, 43 ipvs_property:1, 44 peeked:1, 45 nf_trace:1; 46 kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags1); 47 __be16 protocol;//存放上层的协议类型,可以通过eth_type_trans()来获取 48 49 void (*destructor)(struct sk_buff *skb); 50 #if defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK) || defined(CONFIG_NF_CONNTRACK_MODULE) 51 struct nf_conntrack *nfct; 52 #endif 53 #ifdef CONFIG_BRIDGE_NETFILTER 54 struct nf_bridge_info *nf_bridge; 55 #endif 56 57 int skb_iif; 58 59 __u32 rxhash; 60 61 __be16 vlan_proto; 62 __u16 vlan_tci; 63 64 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_SCHED 65 __u16 tc_index; /* traffic control index */ 66 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_CLS_ACT 67 __u16 tc_verd; /* traffic control verdict */ 68 #endif 69 #endif 70 71 __u16 queue_mapping; 72 kmemcheck_bitfield_begin(flags2); 73 #ifdef CONFIG_IPV6_NDISC_NODETYPE 74 __u8 ndisc_nodetype:2; 75 #endif 76 __u8 pfmemalloc:1; 77 __u8 ooo_okay:1; 78 __u8 l4_rxhash:1; 79 __u8 wifi_acked_valid:1; 80 __u8 wifi_acked:1; 81 __u8 no_fcs:1; 82 __u8 head_frag:1; 83 /* Encapsulation protocol and NIC drivers should use 84 * this flag to indicate to each other if the skb contains 85 * encapsulated packet or not and maybe use the inner packet 86 * headers if needed 87 */ 88 __u8 encapsulation:1; 89 /* 7/9 bit hole (depending on ndisc_nodetype presence) */ 90 kmemcheck_bitfield_end(flags2); 91 92 #ifdef CONFIG_NET_DMA 93 dma_cookie_t dma_cookie; 94 #endif 95 #ifdef CONFIG_NETWORK_SECMARK 96 __u32 secmark; 97 #endif 98 union { 99 __u32 mark; 100 __u32 dropcount; 101 __u32 reserved_tailroom; 102 }; 103 104 sk_buff_data_t inner_transport_header; 105 sk_buff_data_t inner_network_header; 106 sk_buff_data_t inner_mac_header; 107 sk_buff_data_t transport_header;//传输层头部的偏移值 108 sk_buff_data_t network_header;//网络层头部的偏移值 109 sk_buff_data_t mac_header;//MAC数据链路层头部的偏移值 110 /* These elements must be at the end, see alloc_skb() for details. */ 111 sk_buff_data_t tail;//指向缓冲区的数据包末尾 112 sk_buff_data_t end;//指向缓冲区的末尾 113 unsigned char *head,//指向缓冲区的协议头开始位置 114 *data;//指向缓冲区的数据包开始位置 115 unsigned int truesize; 116 atomic_t users; 117 }
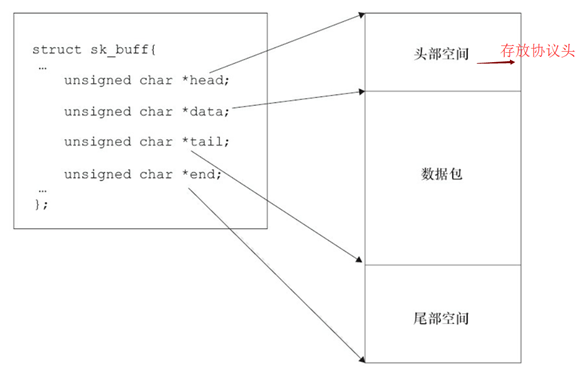
sk_buff结构体的空间,如下图所示:
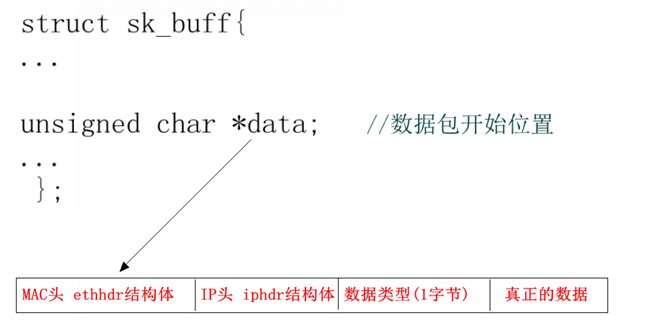
其中sk_buff-> data数据包格式如下图所示:
3 网络设备驱动初始化阶段api
3.1 函数alloc_netdev
分配网络设备结构体,返回网络设备结构体。
定义位于:linux-3.10.73\net\core\dev.c
1 #define alloc_netdev(sizeof_priv, name, setup) \ 2 alloc_netdev_mqs(sizeof_priv, name, setup, 1, 1) 3 4 struct net_device *alloc_netdev_mqs(int sizeof_priv, const char *name, 5 void (*setup)(struct net_device *), 6 unsigned int txqs, unsigned int rxqs) 7 { 8 struct net_device *dev; 9 size_t alloc_size; 10 struct net_device *p; 11 12 BUG_ON(strlen(name) >= sizeof(dev->name)); 13 14 if (txqs < 1) { 15 pr_err("alloc_netdev: Unable to allocate device with zero queues\n"); 16 return NULL; 17 } 18 19 #ifdef CONFIG_RPS 20 if (rxqs < 1) { 21 pr_err("alloc_netdev: Unable to allocate device with zero RX queues\n"); 22 return NULL; 23 } 24 #endif 25 26 alloc_size = sizeof(struct net_device); 27 if (sizeof_priv) { 28 /* ensure 32-byte alignment of private area */ 29 alloc_size = ALIGN(alloc_size, NETDEV_ALIGN); 30 alloc_size += sizeof_priv; 31 } 32 /* ensure 32-byte alignment of whole construct */ 33 alloc_size += NETDEV_ALIGN - 1; 34 35 p = kzalloc(alloc_size, GFP_KERNEL); 36 if (!p) 37 return NULL; 38 39 dev = PTR_ALIGN(p, NETDEV_ALIGN); 40 dev->padded = (char *)dev - (char *)p; 41 42 dev->pcpu_refcnt = alloc_percpu(int); 43 if (!dev->pcpu_refcnt) 44 goto free_p; 45 46 if (dev_addr_init(dev)) 47 goto free_pcpu; 48 49 dev_mc_init(dev); 50 dev_uc_init(dev); 51 52 dev_net_set(dev, &init_net); 53 54 dev->gso_max_size = GSO_MAX_SIZE; 55 dev->gso_max_segs = GSO_MAX_SEGS; 56 57 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->napi_list); 58 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->unreg_list); 59 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->link_watch_list); 60 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->upper_dev_list); 61 dev->priv_flags = IFF_XMIT_DST_RELEASE; 62 setup(dev); 63 64 dev->num_tx_queues = txqs; 65 dev->real_num_tx_queues = txqs; 66 if (netif_alloc_netdev_queues(dev)) 67 goto free_all; 68 69 #ifdef CONFIG_RPS 70 dev->num_rx_queues = rxqs; 71 dev->real_num_rx_queues = rxqs; 72 if (netif_alloc_rx_queues(dev)) 73 goto free_all; 74 #endif 75 76 strcpy(dev->name, name); 77 dev->group = INIT_NETDEV_GROUP; 78 if (!dev->ethtool_ops) 79 dev->ethtool_ops = &default_ethtool_ops; 80 return dev; 81 82 free_all: 83 free_netdev(dev); 84 return NULL; 85 86 free_pcpu: 87 free_percpu(dev->pcpu_refcnt); 88 kfree(dev->_tx); 89 #ifdef CONFIG_RPS 90 kfree(dev->_rx); 91 #endif 92 93 free_p: 94 kfree(p); 95 return NULL; 96 }
3.2 函数 register_netdev
注册一个网络设备
1 int register_netdev(struct net_device *dev) 2 { 3 int err; 4 5 rtnl_lock(); 6 err = register_netdevice(dev); 7 rtnl_unlock(); 8 return err; 9 } 10 11 int register_netdevice(struct net_device *dev) 12 { 13 int ret; 14 struct net *net = dev_net(dev); 15 16 BUG_ON(dev_boot_phase); 17 ASSERT_RTNL(); 18 19 might_sleep(); 20 21 /* When net_device's are persistent, this will be fatal. */ 22 BUG_ON(dev->reg_state != NETREG_UNINITIALIZED); 23 BUG_ON(!net); 24 25 spin_lock_init(&dev->addr_list_lock); 26 netdev_set_addr_lockdep_class(dev); 27 28 dev->iflink = -1; 29 30 ret = dev_get_valid_name(net, dev, dev->name); 31 if (ret < 0) 32 goto out; 33 34 /* Init, if this function is available */ 35 if (dev->netdev_ops->ndo_init) { 36 ret = dev->netdev_ops->ndo_init(dev); 37 if (ret) { 38 if (ret > 0) 39 ret = -EIO; 40 goto out; 41 } 42 } 43 44 if (((dev->hw_features | dev->features) & 45 NETIF_F_HW_VLAN_CTAG_FILTER) && 46 (!dev->netdev_ops->ndo_vlan_rx_add_vid || 47 !dev->netdev_ops->ndo_vlan_rx_kill_vid)) { 48 netdev_WARN(dev, "Buggy VLAN acceleration in driver!\n"); 49 ret = -EINVAL; 50 goto err_uninit; 51 } 52 53 ret = -EBUSY; 54 if (!dev->ifindex) 55 dev->ifindex = dev_new_index(net); 56 else if (__dev_get_by_index(net, dev->ifindex)) 57 goto err_uninit; 58 59 if (dev->iflink == -1) 60 dev->iflink = dev->ifindex; 61 62 /* Transfer changeable features to wanted_features and enable 63 * software offloads (GSO and GRO). 64 */ 65 dev->hw_features |= NETIF_F_SOFT_FEATURES; 66 dev->features |= NETIF_F_SOFT_FEATURES; 67 dev->wanted_features = dev->features & dev->hw_features; 68 69 /* Turn on no cache copy if HW is doing checksum */ 70 if (!(dev->flags & IFF_LOOPBACK)) { 71 dev->hw_features |= NETIF_F_NOCACHE_COPY; 72 if (dev->features & NETIF_F_ALL_CSUM) { 73 dev->wanted_features |= NETIF_F_NOCACHE_COPY; 74 dev->features |= NETIF_F_NOCACHE_COPY; 75 } 76 } 77 78 /* Make NETIF_F_HIGHDMA inheritable to VLAN devices. 79 */ 80 dev->vlan_features |= NETIF_F_HIGHDMA; 81 82 /* Make NETIF_F_SG inheritable to tunnel devices. 83 */ 84 dev->hw_enc_features |= NETIF_F_SG; 85 86 ret = call_netdevice_notifiers(NETDEV_POST_INIT, dev); 87 ret = notifier_to_errno(ret); 88 if (ret) 89 goto err_uninit; 90 91 ret = netdev_register_kobject(dev); 92 if (ret) 93 goto err_uninit; 94 dev->reg_state = NETREG_REGISTERED; 95 96 __netdev_update_features(dev); 97 98 /* 99 * Default initial state at registry is that the 100 * device is present. 101 */ 102 103 set_bit(__LINK_STATE_PRESENT, &dev->state); 104 105 linkwatch_init_dev(dev); 106 107 dev_init_scheduler(dev); 108 dev_hold(dev); 109 list_netdevice(dev); 110 add_device_randomness(dev->dev_addr, dev->addr_len); 111 112 /* If the device has permanent device address, driver should 113 * set dev_addr and also addr_assign_type should be set to 114 * NET_ADDR_PERM (default value). 115 */ 116 if (dev->addr_assign_type == NET_ADDR_PERM) 117 memcpy(dev->perm_addr, dev->dev_addr, dev->addr_len); 118 119 /* Notify protocols, that a new device appeared. */ 120 ret = call_netdevice_notifiers(NETDEV_REGISTER, dev); 121 ret = notifier_to_errno(ret); 122 if (ret) { 123 rollback_registered(dev); 124 dev->reg_state = NETREG_UNREGISTERED; 125 } 126 /* 127 * Prevent userspace races by waiting until the network 128 * device is fully setup before sending notifications. 129 */ 130 if (!dev->rtnl_link_ops || 131 dev->rtnl_link_state == RTNL_LINK_INITIALIZED) 132 rtmsg_ifinfo(RTM_NEWLINK, dev, ~0U); 133 134 out: 135 return ret; 136 137 err_uninit: 138 if (dev->netdev_ops->ndo_uninit) 139 dev->netdev_ops->ndo_uninit(dev); 140 goto out; 141 }
3.4 函数netdev_register_kobject
定义位于:net\core\net-sysfs.c
1 /* Create sysfs entries for network device. */ 2 int netdev_register_kobject(struct net_device *net) 3 { 4 struct device *dev = &(net->dev); 5 const struct attribute_group **groups = net->sysfs_groups; 6 int error = 0; 7 8 device_initialize(dev);//初始化驱动模型设备结构 9 dev->class = &net_class; 10 dev->platform_data = net; 11 dev->groups = groups; 12 13 dev_set_name(dev, "%s", net->name); 14 15 #ifdef CONFIG_SYSFS 16 /* Allow for a device specific group */ 17 if (*groups) 18 groups++; 19 20 *groups++ = &netstat_group; 21 22 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_WIRELESS_EXT) || IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_CFG80211) 23 if (net->ieee80211_ptr) 24 *groups++ = &wireless_group; 25 #if IS_ENABLED(CONFIG_WIRELESS_EXT) 26 else if (net->wireless_handlers) 27 *groups++ = &wireless_group; 28 #endif 29 #endif 30 #endif /* CONFIG_SYSFS */ 31 32 error = device_add(dev);//添加驱动模型设备,在sys创建设备目录文件 33 if (error) 34 return error; 35 36 error = register_queue_kobjects(net); 37 if (error) { 38 device_del(dev); 39 return error; 40 } 41 42 pm_runtime_set_memalloc_noio(dev, true); 43 44 return error; 45 }
4 网络设备发送数据阶段api
以linux-3.10.73\drivers\net\ethernet\cirrus\cs89x0.c为例来叙述。
4.1 函数netif_stop_queue
使用netif_stop_queue()来阻止上层向网络设备驱动层发送数据包,定义位于:include\linux\netdevice.h
1 /** 2 * netif_stop_queue - stop transmitted packets 3 * @dev: network device 4 * 5 * Stop upper layers calling the device hard_start_xmit routine. 6 * Used for flow control when transmit resources are unavailable. 7 */ 8 static inline void netif_stop_queue(struct net_device *dev) 9 { 10 netif_tx_stop_queue(netdev_get_tx_queue(dev, 0)); 11 } 12 13 static inline void netif_tx_stop_queue(struct netdev_queue *dev_queue) 14 { 15 if (WARN_ON(!dev_queue)) { 16 pr_info("netif_stop_queue() cannot be called before register_netdev()\n"); 17 return; 18 } 19 set_bit(__QUEUE_STATE_DRV_XOFF, &dev_queue->state); 20 }
4.2 函数 dev_kfree_skb
当数据包发出去后, 再调用dev_kfree_skb()函数来释放sk_buff
定义位于:include\linux\skbuff.h 和 linux-3.10.73\net\core\skbuff.c
1 #define dev_kfree_skb(a) consume_skb(a) 2 3 void consume_skb(struct sk_buff *skb) 4 { 5 if (unlikely(!skb)) 6 return; 7 if (likely(atomic_read(&skb->users) == 1)) 8 smp_rmb(); 9 else if (likely(!atomic_dec_and_test(&skb->users))) 10 return; 11 trace_consume_skb(skb); 12 __kfree_skb(skb); 13 }
4.3 函数netif_wake_queue
当数据包发出成功,就会进入TX中断函数,然后更新统计信息,调用netif_wake_queue()来唤醒,启动上层继续发包下来。
若数据包发出去超时,一直进不到TX中断函数,就会调用net_device结构体的(*tx_timeout)超时成员函数,在该函数中更新统计信息, 调用netif_wake_queue()来唤醒。
唤醒被阻塞的上层,启动继续向网络设备驱动层发送数据包。
1 /** 2 * netif_wake_queue - restart transmit 3 * @dev: network device 4 * 5 * Allow upper layers to call the device hard_start_xmit routine. 6 * Used for flow control when transmit resources are available. 7 */ 8 static inline void netif_wake_queue(struct net_device *dev) 9 { 10 netif_tx_wake_queue(netdev_get_tx_queue(dev, 0)); 11 } 12 13 static inline void netif_tx_wake_queue(struct netdev_queue *dev_queue) 14 { 15 #ifdef CONFIG_NETPOLL_TRAP 16 if (netpoll_trap()) { 17 netif_tx_start_queue(dev_queue); 18 return; 19 } 20 #endif 21 if (test_and_clear_bit(__QUEUE_STATE_DRV_XOFF, &dev_queue->state)) 22 __netif_schedule(dev_queue->qdisc); 23 }
4.4 cs89x0的实例发送函数
1 static netdev_tx_t net_send_packet(struct sk_buff *skb, struct net_device *dev) 2 { 3 struct net_local *lp = netdev_priv(dev); 4 unsigned long flags; 5 6 cs89_dbg(3, debug, "%s: sent %d byte packet of type %x\n", 7 dev->name, skb->len, 8 ((skb->data[ETH_ALEN + ETH_ALEN] << 8) | 9 skb->data[ETH_ALEN + ETH_ALEN + 1])); 10 11 /* keep the upload from being interrupted, since we 12 * ask the chip to start transmitting before the 13 * whole packet has been completely uploaded. 14 */ 15 16 spin_lock_irqsave(&lp->lock, flags); 17 netif_stop_queue(dev);//阻止上层向网络设备驱动层发送数据包 18 19 /* initiate a transmit sequence */ 20 iowrite16(lp->send_cmd, lp->virt_addr + TX_CMD_PORT); 21 iowrite16(skb->len, lp->virt_addr + TX_LEN_PORT); 22 23 /* Test to see if the chip has allocated memory for the packet */ 24 if ((readreg(dev, PP_BusST) & READY_FOR_TX_NOW) == 0) { 25 /* Gasp! It hasn't. But that shouldn't happen since 26 * we're waiting for TxOk, so return 1 and requeue this packet. 27 */ 28 29 spin_unlock_irqrestore(&lp->lock, flags); 30 cs89_dbg(0, err, "Tx buffer not free!\n"); 31 return NETDEV_TX_BUSY; 32 } 33 /* Write the contents of the packet */ 34 writewords(lp, TX_FRAME_PORT, skb->data, (skb->len + 1) >> 1); 35 spin_unlock_irqrestore(&lp->lock, flags); 36 dev->stats.tx_bytes += skb->len; 37 dev_kfree_skb(skb);//调用dev_kfree_skb()函数来释放sk_buff 38 39 /* We DO NOT call netif_wake_queue() here. 40 * We also DO NOT call netif_start_queue(). 41 * 42 * Either of these would cause another bottom half run through 43 * net_send_packet() before this packet has fully gone out. 44 * That causes us to hit the "Gasp!" above and the send is rescheduled. 45 * it runs like a dog. We just return and wait for the Tx completion 46 * interrupt handler to restart the netdevice layer 47 */ 48 49 return NETDEV_TX_OK; 50 }
5 网络设备接收数据阶段api
5.1 函数net_rx
而接收数据包主要是通过中断函数处理,来判断中断类型,如果等于ISQ_RECEIVER_EVENT,表示为接收中断,然后进入接收数据函数,通过netif_rx()将数据上交给上层。
定义位于:linux-3.10.73\drivers\net\ethernet\cirrus\cs89x0.c
1 /* We have a good packet(s), get it/them out of the buffers. */ 2 static void 3 net_rx(struct net_device *dev) 4 { 5 struct net_local *lp = netdev_priv(dev); 6 struct sk_buff *skb; 7 int status, length; 8 9 status = ioread16(lp->virt_addr + RX_FRAME_PORT); 10 length = ioread16(lp->virt_addr + RX_FRAME_PORT); 11 12 if ((status & RX_OK) == 0) { 13 count_rx_errors(status, dev); 14 return; 15 } 16 17 /* Malloc up new buffer. */ 18 skb = netdev_alloc_skb(dev, length + 2);//分配一个sk_buff结构体 19 if (skb == NULL) { 20 dev->stats.rx_dropped++; 21 return; 22 } 23 skb_reserve(skb, 2); /* longword align L3 header */将sk_buff缓冲区里的数据包先后位移2字节,来腾出sk_buff缓冲区里的头部空间 24 25 readwords(lp, RX_FRAME_PORT, skb_put(skb, length), length >> 1);//读取网络设备硬件上接收到的数据 26 if (length & 1) 27 skb->data[length-1] = ioread16(lp->virt_addr + RX_FRAME_PORT); 28 29 cs89_dbg(3, debug, "%s: received %d byte packet of type %x\n", 30 dev->name, length, 31 (skb->data[ETH_ALEN + ETH_ALEN] << 8) | 32 skb->data[ETH_ALEN + ETH_ALEN + 1]); 33 34 skb->protocol = eth_type_trans(skb, dev);//获取上层协议,将返回值赋给sk_buff的protocol成员里 35 netif_rx(skb);//使用netif_rx( )来将sk_fuffer传递给上层协议中 36 dev->stats.rx_packets++; 37 dev->stats.rx_bytes += length; 38 }
总结其作用如下:
(1)使用dev_alloc_skb()来构造一个新的sk_buff
(2)使用skb_reserve(rx_skb, 2); 将sk_buff缓冲区里的数据包先后位移2字节,来腾出sk_buff缓冲区里的头部空间
(3)读取网络设备硬件上接收到的数据
(4)使用memcpy()将数据复制到新的sk_buff里的data成员指向的地址处,可以使用skb_put()来动态扩大sk_buff结构体里中的数据区
(5)使用eth_type_trans()来获取上层协议,将返回值赋给sk_buff的protocol成员里
(6)然后更新统计信息,最后使用netif_rx( )来将sk_fuffer传递给上层协议中
5.2 函数netif_rx
使用netif_rx( )来将sk_fuffer传递给上层协议中。
定义位于:linux-3.10.73\net\core\dev.c
1 int netif_rx(struct sk_buff *skb) 2 { 3 int ret; 4 5 /* if netpoll wants it, pretend we never saw it */ 6 if (netpoll_rx(skb)) 7 return NET_RX_DROP; 8 9 net_timestamp_check(netdev_tstamp_prequeue, skb); 10 11 trace_netif_rx(skb); 12 #ifdef CONFIG_RPS 13 if (static_key_false(&rps_needed)) { 14 struct rps_dev_flow voidflow, *rflow = &voidflow; 15 int cpu; 16 17 preempt_disable(); 18 rcu_read_lock(); 19 20 cpu = get_rps_cpu(skb->dev, skb, &rflow); 21 if (cpu < 0) 22 cpu = smp_processor_id(); 23 24 ret = enqueue_to_backlog(skb, cpu, &rflow->last_qtail); 25 26 rcu_read_unlock(); 27 preempt_enable(); 28 } else 29 #endif 30 { 31 unsigned int qtail; 32 ret = enqueue_to_backlog(skb, get_cpu(), &qtail); 33 put_cpu(); 34 } 35 return ret; 36 }
5.3 函数skb_put
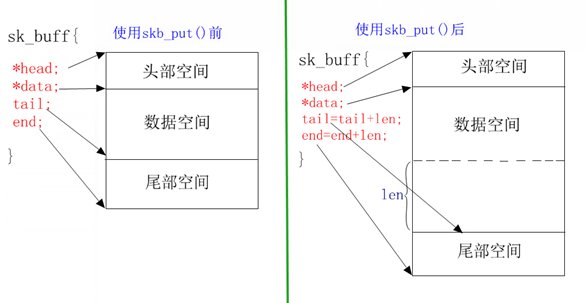
使用skb_put()来动态扩大sk_buff结构体里中的数据区,将数据区向下扩大len字节。
定义位于:linux-3.10.73\net\core\skbuff.c
1 unsigned char *skb_put(struct sk_buff *skb, unsigned int len) 2 { 3 unsigned char *tmp = skb_tail_pointer(skb); 4 SKB_LINEAR_ASSERT(skb); 5 skb->tail += len; 6 skb->len += len; 7 if (unlikely(skb->tail > skb->end)) 8 skb_over_panic(skb, len, __builtin_return_address(0)); 9 return tmp; 10 }
使用skb_put()函数后,其中sk_buff缓冲区变化如下图:
6 总结网络设备驱动的过程
6.1 数据发送过程总结
(1)把数据包发出去之前,需要使用netif_stop_queue()来停止上层传下来的数据包,
(2)设置寄存器,通过网络设备硬件,来发送数据
(3)当数据包发出去后, 再调用dev_kfree_skb()函数来释放sk_buff。
(4)当数据包发出成功,就会进入TX中断函数,然后更新统计信息,调用netif_wake_queue()来唤醒,启动上层继续发包下来.
(5)若数据包发出去超时,一直进不到TX中断函数,就会调用net_device结构体的(*tx_timeout)超时成员函数,在该函数中更新统计信息, 调用netif_wake_queue()来唤醒
其中netif_wake_queue()和netif_stop_queue()函数原型如下所示:
void netif_wake_queue(struct net_device *dev); //唤醒被阻塞的上层,启动继续向网络设备驱动层发送数据包
void netif_stop_queue(struct net_device *dev); //阻止上层向网络设备驱动层发送数据包
6.2 数据接收过程总结
而接收数据包主要是通过中断函数处理,来判断中断类型,如果等于ISQ_RECEIVER_EVENT,表示为接收中断,然后进入接收数据函数,通过netif_rx()将数据上交给上层。
如网卡驱动:/drivers/net/cs89x0.c中断函数:
1 static irqreturn_t net_interrupt(int irq, void *dev_id) 2 { 3 struct net_device *dev = dev_id; 4 struct net_local *lp; 5 int status; 6 int handled = 0; 7 8 lp = netdev_priv(dev); 9 10 /* we MUST read all the events out of the ISQ, otherwise we'll never 11 * get interrupted again. As a consequence, we can't have any limit 12 * on the number of times we loop in the interrupt handler. The 13 * hardware guarantees that eventually we'll run out of events. Of 14 * course, if you're on a slow machine, and packets are arriving 15 * faster than you can read them off, you're screwed. Hasta la 16 * vista, baby! 17 */ 18 while ((status = ioread16(lp->virt_addr + ISQ_PORT))) {//通过获取的status标志来判断是什么中断 19 cs89_dbg(4, debug, "%s: event=%04x\n", dev->name, status); 20 handled = 1; 21 switch (status & ISQ_EVENT_MASK) { 22 case ISQ_RECEIVER_EVENT://接收中断,就进入net_rx() 23 /* Got a packet(s). */ 24 net_rx(dev); 25 break; 26 case ISQ_TRANSMITTER_EVENT: 27 dev->stats.tx_packets++; 28 netif_wake_queue(dev); /* Inform upper layers. */ 29 if ((status & (TX_OK | 30 TX_LOST_CRS | 31 TX_SQE_ERROR | 32 TX_LATE_COL | 33 TX_16_COL)) != TX_OK) { 34 if ((status & TX_OK) == 0) 35 dev->stats.tx_errors++; 36 if (status & TX_LOST_CRS) 37 dev->stats.tx_carrier_errors++; 38 if (status & TX_SQE_ERROR) 39 dev->stats.tx_heartbeat_errors++; 40 if (status & TX_LATE_COL) 41 dev->stats.tx_window_errors++; 42 if (status & TX_16_COL) 43 dev->stats.tx_aborted_errors++; 44 } 45 break; 46 case ISQ_BUFFER_EVENT: 47 if (status & READY_FOR_TX) { 48 /* we tried to transmit a packet earlier, 49 * but inexplicably ran out of buffers. 50 * That shouldn't happen since we only ever 51 * load one packet. Shrug. Do the right 52 * thing anyway. 53 */ 54 netif_wake_queue(dev); /* Inform upper layers. */ 55 } 56 if (status & TX_UNDERRUN) { 57 cs89_dbg(0, err, "%s: transmit underrun\n", 58 dev->name); 59 lp->send_underrun++; 60 if (lp->send_underrun == 3) 61 lp->send_cmd = TX_AFTER_381; 62 else if (lp->send_underrun == 6) 63 lp->send_cmd = TX_AFTER_ALL; 64 /* transmit cycle is done, although 65 * frame wasn't transmitted - this 66 * avoids having to wait for the upper 67 * layers to timeout on us, in the 68 * event of a tx underrun 69 */ 70 netif_wake_queue(dev); /* Inform upper layers. */ 71 } 72 #if ALLOW_DMA 73 if (lp->use_dma && (status & RX_DMA)) { 74 int count = readreg(dev, PP_DmaFrameCnt); 75 while (count) { 76 cs89_dbg(5, debug, 77 "%s: receiving %d DMA frames\n", 78 dev->name, count); 79 if (count > 1) 80 cs89_dbg(2, debug, 81 "%s: receiving %d DMA frames\n", 82 dev->name, count); 83 dma_rx(dev); 84 if (--count == 0) 85 count = readreg(dev, PP_DmaFrameCnt); 86 if (count > 0) 87 cs89_dbg(2, debug, 88 "%s: continuing with %d DMA frames\n", 89 dev->name, count); 90 } 91 } 92 #endif 93 break; 94 case ISQ_RX_MISS_EVENT: 95 dev->stats.rx_missed_errors += (status >> 6); 96 break; 97 case ISQ_TX_COL_EVENT: 98 dev->stats.collisions += (status >> 6); 99 break; 100 } 101 } 102 return IRQ_RETVAL(handled); 103 }
7 网卡设备驱动实例待续。。。





