linux-alsa详解2 pcm设备
1 pcm设备介绍
PCM是英文Pulse-code modulation的缩写,中文译名是脉冲编码调制.我们知道在现实生活中,人耳听到的声音是模拟信号,PCM就是要把声音从模拟转换成数字信号的一种技术,他的原理简单地说就是利用一个固定的频率对模拟信号进行采样,采样后的信号在波形上看就像一串连续的幅值不一的脉冲,把这些脉冲的幅值按一定的精度进行量化,这些量化后的数值被连续地输出、传输、处理或记录到存储介质中,所有这些组成了数字音频的产生过程。
PCM信号的两个重要指标是采样频率和量化精度,目前,CD音频的采样频率通常为44100Hz,量化精度是16bit.通常,播放音乐时,应用程序从存储介质中读取音频数据(MP3、WMA、AAC......),经过解码后,最终送到音频驱动程序中的就是PCM数据,反过来,在录音时,音频驱动不停地把采样所得的PCM数据送回给应用程序,由应用程序完成压缩、存储等任务.所以,音频驱动的两大核心任务就是:
playback 如何把用户空间的应用程序发过来的PCM数据,转化为人耳可以辨别的模拟音频
capture 把mic拾取到得模拟信号,经过采样、量化,转换为PCM信号送回给用户空间的应用程序
2 alsa drive中的pcm中间层
ALSA已经为我们实现了功能强劲的PCM中间层,自己的驱动中只要实现一些底层的需要访问硬件的函数即可。要访问PCM的中间层代码,你首先要包含头文件<sound/pcm.h>,另外,如果需要访问一些与 hw_param相关的函数,可能也要包含<sound/pcm_params.h>。
每个声卡最多可以包含4个pcm的实例,每个pcm实例对应一个pcm设备文件.pcm实例数量的这种限制源于linux设备号所占用的位大小,如果以后使用64位的设备号,我们将可以创建更多的pcm实例.不过大多数情况下,在嵌入式设备中,一个pcm实例已经足够了。一个pcm实例由一个playback stream和一个capture stream组成,这两个stream又分别有一个或多个substreams组成。
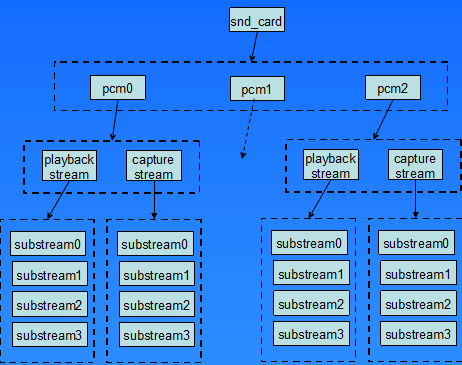
但是在嵌入式系统中,通常不会像上图2中这么复杂,大多数情况下是一个声卡,一个pcm实例,pcm下面有一个playback和capture stream,playback和capture下面各自有一个substream.
3 pcm的数据结构
定义位于:include\sound\pcm.h
3.1 struct snd_pcm
是挂在snd_card下面的一个snd_device。
1 struct snd_pcm { 2 struct snd_card *card; 3 struct list_head list; 4 int device; /* device number */ 5 unsigned int info_flags; 6 unsigned short dev_class; 7 unsigned short dev_subclass; 8 char id[64]; 9 char name[80]; 10 struct snd_pcm_str streams[2];//该数组中的两个元素指向两个snd_pcm_str结构,分别代表playback stream和capture stream 11 struct mutex open_mutex; 12 wait_queue_head_t open_wait; 13 void *private_data; 14 void (*private_free) (struct snd_pcm *pcm); 15 struct device *dev; /* actual hw device this belongs to */ 16 bool internal; /* pcm is for internal use only */ 17 #if defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS) || defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS_MODULE) 18 struct snd_pcm_oss oss; 19 #endif 20 }
3.2 struct snd_pcm_str
1 struct snd_pcm_str { 2 int stream; /* stream (direction) */ 3 struct snd_pcm *pcm; 4 /* -- substreams -- */ 5 unsigned int substream_count; 6 unsigned int substream_opened; 7 struct snd_pcm_substream *substream;//指向snd_pcm_substream结构 8 #if defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS) || defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS_MODULE) 9 /* -- OSS things -- */ 10 struct snd_pcm_oss_stream oss; 11 #endif 12 #ifdef CONFIG_SND_VERBOSE_PROCFS 13 struct snd_info_entry *proc_root; 14 struct snd_info_entry *proc_info_entry; 15 #ifdef CONFIG_SND_PCM_XRUN_DEBUG 16 unsigned int xrun_debug; /* 0 = disabled, 1 = verbose, 2 = stacktrace */ 17 struct snd_info_entry *proc_xrun_debug_entry; 18 #endif 19 #endif 20 struct snd_kcontrol *chmap_kctl; /* channel-mapping controls */ 21 }
3.3 struct snd_pcm_substream
是pcm中间层的核心,绝大部分任务都是在substream中处理,尤其是他的ops(snd_pcm_ops)字段,许多user空间的应用程序通过alsa-lib对驱动程序的请求都是由该结构中的函数处理.它的runtime字段则指向snd_pcm_runtime结构,snd_pcm_runtime记录这substream的一些重要的软件和硬件运行环境和参数。
1 struct snd_pcm_substream { 2 struct snd_pcm *pcm; 3 struct snd_pcm_str *pstr; 4 void *private_data; /* copied from pcm->private_data */ 5 int number; 6 char name[32]; /* substream name */ 7 int stream; /* stream (direction) */ 8 struct pm_qos_request latency_pm_qos_req; /* pm_qos request */ 9 size_t buffer_bytes_max; /* limit ring buffer size */ 10 struct snd_dma_buffer dma_buffer; 11 unsigned int dma_buf_id; 12 size_t dma_max; 13 /* -- hardware operations -- */ 14 struct snd_pcm_ops *ops;//user空间的应用程序通过alsa-lib对驱动程序的请求都是由该结构中的函数处理 15 /* -- runtime information -- */ 16 struct snd_pcm_runtime *runtime;//记录这substream的一些重要的软件和硬件运行环境和参数 17 /* -- timer section -- */ 18 struct snd_timer *timer; /* timer */ 19 unsigned timer_running: 1; /* time is running */ 20 /* -- next substream -- */ 21 struct snd_pcm_substream *next; 22 /* -- linked substreams -- */ 23 struct list_head link_list; /* linked list member */ 24 struct snd_pcm_group self_group; /* fake group for non linked substream (with substream lock inside) */ 25 struct snd_pcm_group *group; /* pointer to current group */ 26 /* -- assigned files -- */ 27 void *file; 28 int ref_count; 29 atomic_t mmap_count; 30 unsigned int f_flags; 31 void (*pcm_release)(struct snd_pcm_substream *); 32 struct pid *pid; 33 #if defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS) || defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS_MODULE) 34 /* -- OSS things -- */ 35 struct snd_pcm_oss_substream oss; 36 #endif 37 #ifdef CONFIG_SND_VERBOSE_PROCFS 38 struct snd_info_entry *proc_root; 39 struct snd_info_entry *proc_info_entry; 40 struct snd_info_entry *proc_hw_params_entry; 41 struct snd_info_entry *proc_sw_params_entry; 42 struct snd_info_entry *proc_status_entry; 43 struct snd_info_entry *proc_prealloc_entry; 44 struct snd_info_entry *proc_prealloc_max_entry; 45 #endif 46 /* misc flags */ 47 unsigned int hw_opened: 1; 48 }
3.4 struct snd_pcm_ops
pcm设备的设备操作结构体
1 struct snd_pcm_ops { 2 int (*open)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream); 3 int (*close)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream); 4 int (*ioctl)(struct snd_pcm_substream * substream, 5 unsigned int cmd, void *arg); 6 int (*hw_params)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, 7 struct snd_pcm_hw_params *params); 8 int (*hw_free)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream); 9 int (*prepare)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream); 10 int (*trigger)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, int cmd); 11 snd_pcm_uframes_t (*pointer)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream); 12 int (*wall_clock)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, 13 struct timespec *audio_ts); 14 int (*copy)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, int channel, 15 snd_pcm_uframes_t pos, 16 void __user *buf, snd_pcm_uframes_t count); 17 int (*silence)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, int channel, 18 snd_pcm_uframes_t pos, snd_pcm_uframes_t count); 19 struct page *(*page)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, 20 unsigned long offset); 21 int (*mmap)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream, struct vm_area_struct *vma); 22 int (*ack)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream); 23 }
3.5 struct snd_pcm_file
1 struct snd_pcm_file { 2 struct snd_pcm_substream *substream; 3 int no_compat_mmap; 4 };
3.6 struct snd_pcm_runtime
记录这substream的一些重要的软件和硬件运行环境和参数
1 struct snd_pcm_runtime { 2 /* -- Status -- */ 3 struct snd_pcm_substream *trigger_master; 4 struct timespec trigger_tstamp; /* trigger timestamp */ 5 int overrange; 6 snd_pcm_uframes_t avail_max; 7 snd_pcm_uframes_t hw_ptr_base; /* Position at buffer restart */ 8 snd_pcm_uframes_t hw_ptr_interrupt; /* Position at interrupt time */ 9 unsigned long hw_ptr_jiffies; /* Time when hw_ptr is updated */ 10 unsigned long hw_ptr_buffer_jiffies; /* buffer time in jiffies */ 11 snd_pcm_sframes_t delay; /* extra delay; typically FIFO size */ 12 u64 hw_ptr_wrap; /* offset for hw_ptr due to boundary wrap-around */ 13 14 /* -- HW params -- */ 15 snd_pcm_access_t access; /* access mode */ 16 snd_pcm_format_t format; /* SNDRV_PCM_FORMAT_* */ 17 snd_pcm_subformat_t subformat; /* subformat */ 18 unsigned int rate; /* rate in Hz */ 19 unsigned int channels; /* channels */ 20 snd_pcm_uframes_t period_size; /* period size */ 21 unsigned int periods; /* periods */ 22 snd_pcm_uframes_t buffer_size; /* buffer size */ 23 snd_pcm_uframes_t min_align; /* Min alignment for the format */ 24 size_t byte_align; 25 unsigned int frame_bits; 26 unsigned int sample_bits; 27 unsigned int info; 28 unsigned int rate_num; 29 unsigned int rate_den; 30 unsigned int no_period_wakeup: 1; 31 32 /* -- SW params -- */ 33 int tstamp_mode; /* mmap timestamp is updated */ 34 unsigned int period_step; 35 snd_pcm_uframes_t start_threshold; 36 snd_pcm_uframes_t stop_threshold; 37 snd_pcm_uframes_t silence_threshold; /* Silence filling happens when 38 noise is nearest than this */ 39 snd_pcm_uframes_t silence_size; /* Silence filling size */ 40 snd_pcm_uframes_t boundary; /* pointers wrap point */ 41 42 snd_pcm_uframes_t silence_start; /* starting pointer to silence area */ 43 snd_pcm_uframes_t silence_filled; /* size filled with silence */ 44 45 union snd_pcm_sync_id sync; /* hardware synchronization ID */ 46 47 /* -- mmap -- */ 48 struct snd_pcm_mmap_status *status; 49 struct snd_pcm_mmap_control *control; 50 51 /* -- locking / scheduling -- */ 52 snd_pcm_uframes_t twake; /* do transfer (!poll) wakeup if non-zero */ 53 wait_queue_head_t sleep; /* poll sleep */ 54 wait_queue_head_t tsleep; /* transfer sleep */ 55 struct fasync_struct *fasync; 56 57 /* -- private section -- */ 58 void *private_data; 59 void (*private_free)(struct snd_pcm_runtime *runtime); 60 61 /* -- hardware description -- */ 62 struct snd_pcm_hardware hw; 63 struct snd_pcm_hw_constraints hw_constraints; 64 65 /* -- interrupt callbacks -- */ 66 void (*transfer_ack_begin)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream); 67 void (*transfer_ack_end)(struct snd_pcm_substream *substream); 68 69 /* -- timer -- */ 70 unsigned int timer_resolution; /* timer resolution */ 71 int tstamp_type; /* timestamp type */ 72 73 /* -- DMA -- */ 74 unsigned char *dma_area; /* DMA area */ 75 dma_addr_t dma_addr; /* physical bus address (not accessible from main CPU) */ 76 size_t dma_bytes; /* size of DMA area */ 77 78 struct snd_dma_buffer *dma_buffer_p; /* allocated buffer */ 79 80 #if defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS) || defined(CONFIG_SND_PCM_OSS_MODULE) 81 /* -- OSS things -- */ 82 struct snd_pcm_oss_runtime oss; 83 #endif 84 85 #ifdef CONFIG_SND_PCM_XRUN_DEBUG 86 struct snd_pcm_hwptr_log *hwptr_log; 87 #endif 88 }
3.7 struct snd_pcm_hardware
1 /* 2 * Hardware (lowlevel) section 3 */ 4 5 struct snd_pcm_hardware { 6 unsigned int info; /* SNDRV_PCM_INFO_* */ 7 u64 formats; /* SNDRV_PCM_FMTBIT_* */ 8 unsigned int rates; /* SNDRV_PCM_RATE_* */ 9 unsigned int rate_min; /* min rate */ 10 unsigned int rate_max; /* max rate */ 11 unsigned int channels_min; /* min channels */ 12 unsigned int channels_max; /* max channels */ 13 size_t buffer_bytes_max; /* max buffer size */ 14 size_t period_bytes_min; /* min period size */ 15 size_t period_bytes_max; /* max period size */ 16 unsigned int periods_min; /* min # of periods */ 17 unsigned int periods_max; /* max # of periods */ 18 size_t fifo_size; /* fifo size in bytes */ 19 }
3.8 以上pcm各数据结构的关系如下:

4 创建pcm设备
4.1 创建pcm
函数snd_pcm_new,定义位于:sound\core\pcm.c
1 /** 2 * snd_pcm_new - create a new PCM instance 3 * @card: the card instance 4 * @id: the id string 5 * @device: the device index (zero based) 参数device 表示目前创建的是该声卡下的第几个pcm,第一个pcm设备从0开始. 6 * @playback_count: the number of substreams for playback 参数playback_count 表示该pcm将会有几个playback substream. 7 * @capture_count: the number of substreams for capture 参数capture_count 表示该pcm将会有几个capture substream. 8 * @rpcm: the pointer to store the new pcm instance 9 * 10 * Creates a new PCM instance. 11 * 12 * The pcm operators have to be set afterwards to the new instance 13 * via snd_pcm_set_ops(). 14 * 15 * Return: Zero if successful, or a negative error code on failure. 16 */ 17 int snd_pcm_new(struct snd_card *card, const char *id, int device, 18 int playback_count, int capture_count, struct snd_pcm **rpcm) 19 { 20 return _snd_pcm_new(card, id, device, playback_count, capture_count, 21 false, rpcm); 22 }
调用函数 _snd_pcm_new
调用该api创建一个pcm,然后会做以下事情:
(1)如果有,建立playback stream,相应的substream也同时建立
(2)如果有,建立capture stream,相应的substream也同时建立
(3)调用snd_device_new()把该pcm挂到声卡中,参数ops中的dev_register字段指向了函数snd_pcm_dev_register,这个回调函数会在声卡的注册阶段被调用.
1 static int _snd_pcm_new(struct snd_card *card, const char *id, int device, 2 int playback_count, int capture_count, bool internal, 3 struct snd_pcm **rpcm) 4 { 5 struct snd_pcm *pcm;//创建一个pcm 6 int err; 7 static struct snd_device_ops ops = { 8 .dev_free = snd_pcm_dev_free, 9 .dev_register = snd_pcm_dev_register, 10 .dev_disconnect = snd_pcm_dev_disconnect, 11 }; 12 13 if (snd_BUG_ON(!card)) 14 return -ENXIO; 15 if (rpcm) 16 *rpcm = NULL; 17 pcm = kzalloc(sizeof(*pcm), GFP_KERNEL); 18 if (pcm == NULL) { 19 snd_printk(KERN_ERR "Cannot allocate PCM\n"); 20 return -ENOMEM; 21 } 22 pcm->card = card; 23 pcm->device = device; 24 pcm->internal = internal; 25 if (id) 26 strlcpy(pcm->id, id, sizeof(pcm->id)); 27 if ((err = snd_pcm_new_stream(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK, playback_count)) < 0) {//创建playback stream 播放 28 snd_pcm_free(pcm); 29 return err; 30 } 31 if ((err = snd_pcm_new_stream(pcm, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE, capture_count)) < 0) {//创建capture stream 录音 32 snd_pcm_free(pcm); 33 return err; 34 } 35 mutex_init(&pcm->open_mutex); 36 init_waitqueue_head(&pcm->open_wait); 37 if ((err = snd_device_new(card, SNDRV_DEV_PCM, pcm, &ops)) < 0) {//把该pcm挂到声卡中,参数ops中的dev_register字段指向了函数snd_pcm_dev_register,这个回调函数会在声卡的注册阶段被调用 38 snd_pcm_free(pcm); 39 return err; 40 } 41 if (rpcm) 42 *rpcm = pcm; 43 return 0; 44 }
4.2 snd_device_new函数
定义位于:linux-4.9.73\sound\core\device.c
作用:(1)拿到声卡逻辑设备的设备操作结构体
(2)将该设备逻辑设备加入声卡结构体devices链表中(该声卡下逻辑设备比如control、pcm等),dev->list加入card->devies,在注册时根据此链表找到对应逻辑设备,调用其注册函数。
1 int snd_device_new(struct snd_card *card, enum snd_device_type type, 2 void *device_data, struct snd_device_ops *ops) 3 { 4 struct snd_device *dev; 5 struct list_head *p; 6 7 if (snd_BUG_ON(!card || !device_data || !ops)) 8 return -ENXIO; 9 dev = kzalloc(sizeof(*dev), GFP_KERNEL); 10 if (!dev) 11 return -ENOMEM; 12 INIT_LIST_HEAD(&dev->list); 13 dev->card = card; 14 dev->type = type; 15 dev->state = SNDRV_DEV_BUILD; 16 dev->device_data = device_data; 17 dev->ops = ops;//拿到声卡逻辑设备的设备操作结构体 18 19 /* insert the entry in an incrementally sorted list */ 20 list_for_each_prev(p, &card->devices) {//将该设备逻辑设备加入声卡结构体devices链表中(该声卡下逻辑设备比如control、pcm等),dev->list加入card->devies 21 struct snd_device *pdev = list_entry(p, struct snd_device, list);//获取声卡逻辑设备结构体 22 if ((unsigned int)pdev->type <= (unsigned int)type)//判断该逻辑设备的类型,常用的control或者pcm 23 break; 24 } 25 26 list_add(&dev->list, p);//在链表p的前面加入链表dev->list 27 return 0; 28 }
设备操作结构体定义,位于_snd_pcm_new函数中,最重要的是注册函数
static struct snd_device_ops ops = {
.dev_free = snd_pcm_dev_free,
.dev_register = snd_pcm_dev_register,
.dev_disconnect = snd_pcm_dev_disconnect,
}
4.3 函数snd_pcm_set_ops
定义位于:sound\core\pcm_lib.c
设置操作该pcm的控制/操作接口函数,参数中的snd_pcm_ops结构中的函数通常就是我们驱动要实现的函数。
1 /** 2 * snd_pcm_set_ops - set the PCM operators 3 * @pcm: the pcm instance 4 * @direction: stream direction, SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_XXX 5 * @ops: the operator table 6 * 7 * Sets the given PCM operators to the pcm instance. 8 */ 9 void snd_pcm_set_ops(struct snd_pcm *pcm, int direction, struct snd_pcm_ops *ops) 10 { 11 struct snd_pcm_str *stream = &pcm->streams[direction]; 12 struct snd_pcm_substream *substream; 13 14 for (substream = stream->substream; substream != NULL; substream = substream->next) 15 substream->ops = ops; 16 }
5 注册pcm设备
在上面创建的pcm设备信息基础上,注册pcm设备。
先调用函数snd_card_register注册声卡,然后该函数中会调用pcm注册函数snd_pcm_dev_register注册pcm设备。下面分别讲解,先看pcm注册函数。
5.1 pcm设备注册函数
snd_pcm_dev_register,定义位于sound\core\pcm.c。
1 static int snd_pcm_dev_register(struct snd_device *device) 2 { 3 int cidx, err; 4 struct snd_pcm_substream *substream; 5 struct snd_pcm_notify *notify; 6 struct snd_pcm *pcm; 7 8 if (snd_BUG_ON(!device || !device->device_data)) 9 return -ENXIO; 10 pcm = device->device_data; 11 if (pcm->internal) 12 return 0; 13 14 mutex_lock(®ister_mutex); 15 err = snd_pcm_add(pcm); 16 if (err) 17 goto unlock; 18 for (cidx = 0; cidx < 2; cidx++) { 19 int devtype = -1; 20 if (pcm->streams[cidx].substream == NULL) 21 continue; 22 switch (cidx) { 23 case SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_PLAYBACK: 24 devtype = SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_PLAYBACK; 25 break; 26 case SNDRV_PCM_STREAM_CAPTURE: 27 devtype = SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_PCM_CAPTURE; 28 break; 29 } 30 /* register pcm */ 31 err = snd_register_device(devtype, pcm->card, pcm->device, 32 &snd_pcm_f_ops[cidx], pcm,//指定pcm设备的文件操作结构体 33 &pcm->streams[cidx].dev); 34 if (err < 0) { 35 list_del_init(&pcm->list); 36 goto unlock; 37 } 38 39 for (substream = pcm->streams[cidx].substream; substream; substream = substream->next) 40 snd_pcm_timer_init(substream); 41 } 42 43 list_for_each_entry(notify, &snd_pcm_notify_list, list) 44 notify->n_register(pcm); 45 46 unlock: 47 mutex_unlock(®ister_mutex); 48 return err; 49 }
该pcm设备注册函数snd_pcm_dev_register会加入设备操作结构体snd_device_ops 作为回调函数。
然后调用函数snd_register_device完成最终的注册.
5.1.1 函数snd_register_device
1 /**
2 * snd_register_device - Register the ALSA device file for the card
3 * @type: the device type, SNDRV_DEVICE_TYPE_XXX
4 * @card: the card instance
5 * @dev: the device index
6 * @f_ops: the file operations
7 * @private_data: user pointer for f_ops->open()
8 * @device: the device to register
9 *
10 * Registers an ALSA device file for the given card.
11 * The operators have to be set in reg parameter.
12 *
13 * Return: Zero if successful, or a negative error code on failure.
14 */
15 int snd_register_device(int type, struct snd_card *card, int dev,
16 const struct file_operations *f_ops,
17 void *private_data, struct device *device)
18 {
19 int minor;
20 int err = 0;
21 struct snd_minor *preg;//建立次设备
22
23 if (snd_BUG_ON(!device))
24 return -EINVAL;
25 /*给次设备赋值*/
26 preg = kmalloc(sizeof *preg, GFP_KERNEL);
27 if (preg == NULL)
28 return -ENOMEM;
29 preg->type = type;
30 preg->card = card ? card->number : -1;
31 preg->device = dev;
32 preg->f_ops = f_ops;//获取文件操作结构体
33 preg->private_data = private_data;
34 preg->card_ptr = card;
35 mutex_lock(&sound_mutex);
36 minor = snd_find_free_minor(type, card, dev);
37 if (minor < 0) {
38 err = minor;
39 goto error;
40 }
41
42 preg->dev = device;
43 device->devt = MKDEV(major, minor);
44 err = device_add(device);//创建设备节点
45 if (err < 0)
46 goto error;
47
48 snd_minors[minor] = preg;//赋值给全局的次设备信息结构体
49 error:
50 mutex_unlock(&sound_mutex);
51 if (err < 0)
52 kfree(preg);
53 return err;
54 }
主要作用:
(1)获取声卡次设备snd_minor ,并将其赋值给全局声卡次设备变量snd_minor中
(2)获取次设备pcm的文件操作结构体,供用户层使用的api回调函数。snd_pcm_f_ops作为snd_register_device的参数被传入,并被记录在snd_minors[minor]中的字段f_ops中.最后创建设备节点。创建节点之后我们就能在/dev目录下查看到相应的设备文件。
5.1.2 pcm设备的文件操作结构体
回调函数,供用户层使用的api。分为playback和capature,即播放设备和录音设备。
1 /* 2 * Register section 3 */ 4 5 const struct file_operations snd_pcm_f_ops[2] = { 6 { 7 .owner = THIS_MODULE, 8 .write = snd_pcm_write, 9 .write_iter = snd_pcm_writev, 10 .open = snd_pcm_playback_open, 11 .release = snd_pcm_release, 12 .llseek = no_llseek, 13 .poll = snd_pcm_playback_poll, 14 .unlocked_ioctl = snd_pcm_playback_ioctl, 15 .compat_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl_compat, 16 .mmap = snd_pcm_mmap, 17 .fasync = snd_pcm_fasync, 18 .get_unmapped_area = snd_pcm_get_unmapped_area, 19 }, 20 { 21 .owner = THIS_MODULE, 22 .read = snd_pcm_read, 23 .read_iter = snd_pcm_readv, 24 .open = snd_pcm_capture_open, 25 .release = snd_pcm_release, 26 .llseek = no_llseek, 27 .poll = snd_pcm_capture_poll, 28 .unlocked_ioctl = snd_pcm_capture_ioctl, 29 .compat_ioctl = snd_pcm_ioctl_compat, 30 .mmap = snd_pcm_mmap, 31 .fasync = snd_pcm_fasync, 32 .get_unmapped_area = snd_pcm_get_unmapped_area, 33 } 34 }
然后看声卡注册函数。
5.2 声卡注册函数
snd_card_register 详见:linux - alsa详解1概括。dev/snd/pcmCxxDxxp、pcmCxxDxxc,设备文件节点的建立。注意和上面pcm设备注册函数的区别,声卡注册函数最终会调用pcm注册函数注册pcm设备,或者调用control设备注册函数注册控制设备。
snd_card_register 函数调用函数snd_device_register_all
5.3 snd_device_register_all
1 /* 2 * register all the devices on the card. 3 * called from init.c 4 */ 5 int snd_device_register_all(struct snd_card *card) 6 { 7 struct snd_device *dev; 8 int err; 9 10 if (snd_BUG_ON(!card)) 11 return -ENXIO; 12 list_for_each_entry(dev, &card->devices, list) {//遍历声卡结构体中的设备链表,逐个注册声卡下挂载的逻辑设备 13 err = __snd_device_register(dev); 14 if (err < 0) 15 return err; 16 } 17 return 0; 18 }
5.4 函数__snd_device_register
1 static int __snd_device_register(struct snd_device *dev) 2 { 3 if (dev->state == SNDRV_DEV_BUILD) { 4 if (dev->ops->dev_register) { 5 int err = dev->ops->dev_register(dev);//调用声卡逻辑设备的注册函数,即5.1中pcm设备注册函数snd_pcm_dev_register 6 if (err < 0) 7 return err; 8 } 9 dev->state = SNDRV_DEV_REGISTERED; 10 } 11 return 0; 12 }
注册声卡,在这个阶段会遍历声卡下的所有逻辑设备,并且调用各设备的注册回调函数,对于pcm,就是第二步提到的snd_pcm_dev_register函数,该回调函数建立了和用户空间应用程序(alsa-lib)通信所用的设备文件节点:/dev/snd/pcmCxxDxxp和/dev/snd/pcmCxxDxxc
注:一共有两个关键的结构体:
(1)设备操作结构体snd_device_ops ,在声卡创建时注册回调函数,主要是设备注册回调函数snd_pcm_dev_register,在声卡注册时会调用其注册pcm设备
(2)文件操作结构体struct file_operations snd_pcm_f_ops,在pcm设备注册函数snd_pcm_dev_register中,加入全局变量snd_minors数组中,就是告诉声卡,供用户调用的接口。用户层操作时会获取到数组snd_minors的下标,就可以找到相应的次设备是control或者pcm,操作对用文件操作结构体中的函数。
以上api的调用关系:
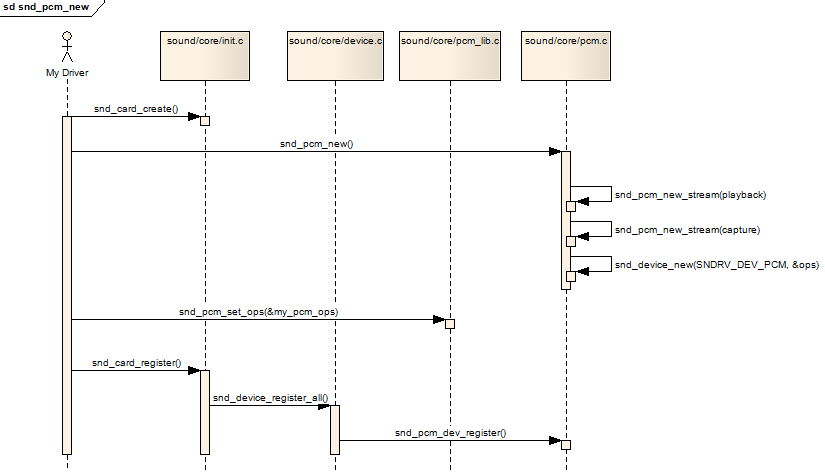
以上代码我们可以看出,对于一个pcm设备,可以生成两个设备文件,一个用于playback,一个用于capture,代码中也确定了他们的命名规则:
(1)playback -- pcmCxDxp,通常系统中只有一各声卡和一个pcm,它就是pcmC0D0p
(2)capture -- pcmCxDxc,通常系统中只有一各声卡和一个pcm,它就是pcmC0D0c
6 pcm设备的open
以从应用程序到驱动层pcm为例一步一步讲解。
6.1 声卡字符设备的注册
在sound/core/sound.c中有alsa_sound_init()函数,定义如下:
1 static int __init alsa_sound_init(void) 2 { 3 snd_major = major; 4 snd_ecards_limit = cards_limit; 5 if (register_chrdev(major, "alsa", &snd_fops)) { 6 snd_printk(KERN_ERR "unable to register native major device number %d\n", major); 7 return -EIO; 8 } 9 if (snd_info_init() < 0) { 10 unregister_chrdev(major, "alsa"); 11 return -ENOMEM; 12 } 13 snd_info_minor_register(); 14 #ifndef MODULE 15 printk(KERN_INFO "Advanced Linux Sound Architecture Driver Initialized.\n"); 16 #endif 17 return 0; 18 }
register_chrdev中的参数major与之前创建pcm设备是device_create时的major是同一个,这样的结果是,当应用程序open设备文件/dev/snd/pcmCxDxp时,会进入snd_fops的open回调函数。
6.2 打开pcm设备
从上一节中我们得知,open一个pcm设备时,将会调用snd_fops的open回调函数,我们先看看snd_fops的定义:
位于:
1 static const struct file_operations snd_fops = 2 { 3 .owner = THIS_MODULE, 4 .open = snd_open, 5 .llseek = noop_llseek, 6 };
跟入snd_open函数,它首先从inode中取出此设备号,然后以次设备号为索引,从snd_minors全局数组中取出当初注册pcm设备时填充的snd_minor结构(参看linux-alsa详解1基本知识第4节的内容),然后从snd_minor结构中取出pcm设备的f_ops,并且把file->f_op替换为pcm设备的f_ops,紧接着直接调用pcm设备的f_ops->open(),然后返回.因为file->f_op已经被替换,以后,应用程序的所有read/write/ioctl调用都会进入pcm设备自己的回调函数中,也就是5.1.2节中提到的snd_pcm_f_ops结构中定义的回调。
1 static int snd_open(struct inode *inode, struct file *file) 2 { 3 unsigned int minor = iminor(inode); 4 struct snd_minor *mptr = NULL; 5 const struct file_operations *old_fops; 6 int err = 0; 7 8 if (minor >= ARRAY_SIZE(snd_minors)) 9 return -ENODEV; 10 mutex_lock(&sound_mutex); 11 mptr = snd_minors[minor]; 12 if (mptr == NULL) { 13 mptr = autoload_device(minor); 14 if (!mptr) { 15 mutex_unlock(&sound_mutex); 16 return -ENODEV; 17 } 18 } 19 old_fops = file->f_op; 20 file->f_op = fops_get(mptr->f_ops); 21 if (file->f_op == NULL) { 22 file->f_op = old_fops; 23 err = -ENODEV; 24 } 25 mutex_unlock(&sound_mutex); 26 if (err < 0) 27 return err; 28 29 if (file->f_op->open) { 30 err = file->f_op->open(inode, file); 31 if (err) { 32 fops_put(file->f_op); 33 file->f_op = fops_get(old_fops); 34 } 35 } 36 fops_put(old_fops); 37 return err; 38 }
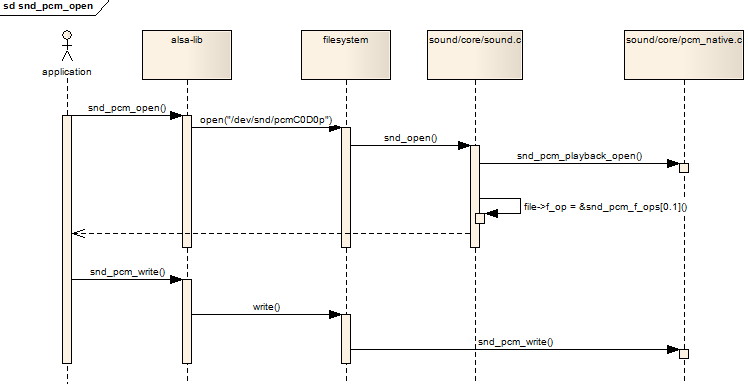
6.3 总结以上过程
下面的序列图表示了应用程序如何最终调用到snd_pcm_f_ops结构中的回调函数:
参考博文:
https://www.cnblogs.com/jason-lu/archive/2013/06/07/3123750.html



