linux设备驱动(16)platfrom详解
1 platfrom的概括
platform总线是区别于实体总线USB、 I2C、SPI 、PIC总线的虚拟总线,一些usb设备选址的话需要通过USB总线来进行寻址,而有些类似于SoC内部外设如led 看门狗 定时器是直接通过内存的寻址空间来进行寻址的,cpu与这些设备通信是不需要总线的,2.6内核以后要对所有设备进行统一管理,通过kset、kobject来建立层次关系,对这些直接通过内存寻址的设备虚拟了一种总线即platform总线,在硬件上实际是没有这个总线;platform内核纯软件的总线,所有的直接通过内存寻址的设备都映射到这条总线上。设备用platform_device表示,驱动用platform_driver进行注册。platform由内核进行统一管理,在驱动中使用资源,提高了代码的安全性和可移植性。更换硬件时只需要修改硬件部分的代码,其中还一部分代码是属于内核中稳定的部分,通用的接口,不用修改。
相对输入input子系统,platform是对驱动的模型的分离的思想,而input子系统测试分层的思想。
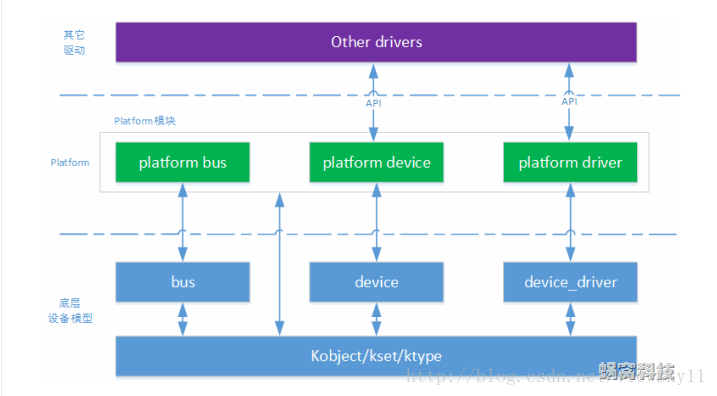
2 平台总线优点:
(1)可以通过platform总线,可以遍历所有的platform总线设备;platform本质其实也是kset、kobject,具有kobject的特性
(2)实现设备与驱动的分离,通过platform总线,设备与驱动是分开注册的,通过platform总线的probe来随时检测与设备匹配的驱动,如匹配上即进行这个设备的驱动注册;
(3)由于上面这个优势,一个驱动可以供同类的几个设备使用;
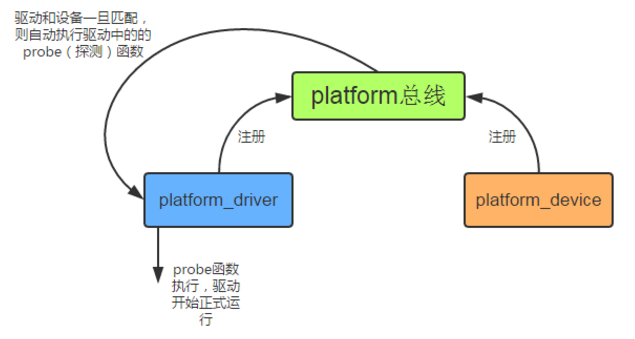
3 platform总线以及platform总线设备驱动的实现流程
platform总线注册 -->> platform_device注册 -->> platform_driver注册 -->> 设备与驱动的匹配 -->> 驱动的注册
platform总线的工作流程如下图:
代码分析
定义位于:drivers\base\platform.c
platform总线的注册:platform的注册是linux内核工程师已经设注册好的;重点是.match = platform_match函数;platform_driver和platform_device就是通过这个函数来匹配的
4 platform_bus
platform是bus的一种,是一种虚拟总线。
1 struct bus_type platform_bus_type = { 2 .name = "platform", 3 .dev_attrs = platform_dev_attrs, 4 .match = platform_match, 5 .uevent = platform_uevent, 6 .pm = &platform_dev_pm_ops, 7 };
4.1platform_bus_init
1 int __init platform_bus_init(void) 2 { 3 int error; 4 /*清除早期的platform数据和信息(早期的platform建立时sysfs等都没建立,不完善,所以要这里清掉之前的建立),重新注册platform*/ 5 early_platform_cleanup(); 6 7 error = device_register(&platform_bus);//设备的注册,在sysfs的device下注册一个位platform的空文件夹 8 if (error) 9 return error; 10 error = bus_register(&platform_bus_type);//bus的注册,在sysfs的bus下注册一个platform的文件夹 ,同时使用platform总线注册的设备的bus都会被赋值为platform_bus_type,即将来所有设备会在bus下的platform里出现 11 if (error) 12 device_unregister(&platform_bus); 13 return error; 14 }
platform_bus的device,定义如下:
struct device platform_bus = { .init_name = "platform", };
4.2 platform_match
platform总线上设备和驱动的匹配规则
1 /** 2 * platform_match - bind platform device to platform driver. 3 * @dev: device. 4 * @drv: driver. 5 * 6 * Platform device IDs are assumed to be encoded like this: 7 * "<name><instance>", where <name> is a short description of the type of 8 * device, like "pci" or "floppy", and <instance> is the enumerated 9 * instance of the device, like '0' or '42'. Driver IDs are simply 10 * "<name>". So, extract the <name> from the platform_device structure, 11 * and compare it against the name of the driver. Return whether they match 12 * or not. 13 */ 14 static int platform_match(struct device *dev, struct device_driver *drv) 15 { 16 struct platform_device *pdev = to_platform_device(dev); 17 struct platform_driver *pdrv = to_platform_driver(drv); 18 19 /* Attempt an OF style match first */ 20 if (of_driver_match_device(dev, drv)) 21 return 1; 22 23 /* Then try ACPI style match */ 24 if (acpi_driver_match_device(dev, drv)) 25 return 1; 26 27 /* Then try to match against the id table */ 28 if (pdrv->id_table)//如果driver的id_table存在,则只匹配id_table 29 return platform_match_id(pdrv->id_table, pdev) != NULL; 30 31 /* fall-back to driver name match */ 32 return (strcmp(pdev->name, drv->name) == 0);//如果drv的id_table不存在,则比较name是否相等 33 }
4.3 platform_match_id
1 static const struct platform_device_id *platform_match_id( 2 const struct platform_device_id *id, 3 struct platform_device *pdev) 4 {/*其实id也是匹配name,只不过可能driver要支持多个device,所以有多个名字,就做成一个id_table比较*/ 5 while (id->name[0]) { 6 if (strcmp(pdev->name, id->name) == 0) { 7 pdev->id_entry = id; 8 return id; 9 } 10 id++; 11 } 12 return NULL; 13 }
5 platform_device
5.1 platform_device结构体
1 struct platform_device { 2 const char *name; 3 int id;/*区分使用相同driver的同种设备,从0开始,-1为自动分配*/ 4 bool id_auto; 5 struct device dev;/*具体的设备,无论是何种总线里的设备,都是对dev再次增加信息封装*/ 6 u32 num_resources;/*多少个资源,为下面准备的*/ 7 struct resource *resource;/*存放资源的地址*/ 8 9 const struct platform_device_id *id_entry;/*区分统一厂家的不同版本设备*/ 10 11 /* MFD cell pointer */ 12 struct mfd_cell *mfd_cell; 13 14 /* arch specific additions */ 15 struct pdev_archdata archdata;/*特殊架构准备,基本不用*/ 16 }
5.2 platform_device_alloc
通常我们自定义一个静态的platform_device并填充。
当然内核为了绝对的可裁剪性,也提供了通过动态分配的方法。
1 /** 2 * platform_device_alloc - create a platform device 3 * @name: base name of the device we're adding 4 * @id: instance id 5 * 6 * Create a platform device object which can have other objects attached 7 * to it, and which will have attached objects freed when it is released. 8 */ 9 struct platform_device *platform_device_alloc(const char *name, int id) 10 { 11 struct platform_object *pa; 12 13 pa = kzalloc(sizeof(struct platform_object) + strlen(name), GFP_KERNEL); 14 if (pa) { 15 strcpy(pa->name, name); 16 pa->pdev.name = pa->name; 17 pa->pdev.id = id; 18 device_initialize(&pa->pdev.dev); 19 pa->pdev.dev.release = platform_device_release;/*release放在dev里面unregister的时候只要device_del(dev)就可以*/ 20 arch_setup_pdev_archdata(&pa->pdev); 21 } 22 23 return pa ? &pa->pdev : NULL; 24 }
struct platform_object { struct platform_device pdev; char name[1]; };
5.2.1 platform_device_release
1 static void platform_device_release(struct device *dev) 2 { 3 struct platform_object *pa = container_of(dev, struct platform_object, 4 pdev.dev); 5 6 of_device_node_put(&pa->pdev.dev); 7 kfree(pa->pdev.dev.platform_data);//这部分由自己具体的设备实现具体的数据结构 8 kfree(pa->pdev.mfd_cell); 9 kfree(pa->pdev.resource);//释放存放resource的内存 10 kfree(pa);//释放platform_device_alloc中申请的obj 11 }
5.2.2 platform_device_register
无论是静态还是2.2中的动态定义的platform_device,都需要platform_device添加进platform_bus。
即使用下面platform_device_register函数就可以了。
1 /** 2 * platform_device_register - add a platform-level device 3 * @pdev: platform device we're adding 4 */ 5 int platform_device_register(struct platform_device *pdev) 6 { 7 device_initialize(&pdev->dev); 8 arch_setup_pdev_archdata(pdev); 9 return platform_device_add(pdev); 10 }
5.2.3 platform_add_devices
系统也提供了可以同时注册多个device的API,起始就是多次调用上面的。
1 /** 2 * platform_add_devices - add a numbers of platform devices 3 * @devs: array of platform devices to add 4 * @num: number of platform devices in array 5 */ 6 int platform_add_devices(struct platform_device **devs, int num) 7 { 8 int i, ret = 0; 9 10 for (i = 0; i < num; i++) { 11 ret = platform_device_register(devs[i]); 12 if (ret) { 13 while (--i >= 0) 14 platform_device_unregister(devs[i]); 15 break; 16 } 17 } 18 19 return ret; 20 }
5.2.4 platform_device_add
1 /** 2 * platform_device_add - add a platform device to device hierarchy 3 * @pdev: platform device we're adding 4 * 5 * This is part 2 of platform_device_register(), though may be called 6 * separately _iff_ pdev was allocated by platform_device_alloc(). 7 */ 8 int platform_device_add(struct platform_device *pdev) 9 { 10 int i, ret; 11 12 if (!pdev) 13 return -EINVAL; 14 15 if (!pdev->dev.parent)//如果设备没指定parent的话,默认就是platform(通常都是) 16 pdev->dev.parent = &platform_bus; 17 18 pdev->dev.bus = &platform_bus_type;//绑定总线类型,sysfs体现 19 20 switch (pdev->id) { 21 default: 22 dev_set_name(&pdev->dev, "%s.%d", pdev->name, pdev->id);//指定了具体id,-1,自动分配id 23 break; 24 case PLATFORM_DEVID_NONE: 25 dev_set_name(&pdev->dev, "%s", pdev->name); 26 break; 27 case PLATFORM_DEVID_AUTO: 28 /* 29 * Automatically allocated device ID. We mark it as such so 30 * that we remember it must be freed, and we append a suffix 31 * to avoid namespace collision with explicit IDs. 32 */ 33 ret = ida_simple_get(&platform_devid_ida, 0, 0, GFP_KERNEL); 34 if (ret < 0) 35 goto err_out; 36 pdev->id = ret; 37 pdev->id_auto = true; 38 dev_set_name(&pdev->dev, "%s.%d.auto", pdev->name, pdev->id); 39 break; 40 } 41 /*对资源进行处理和检查*/ 42 for (i = 0; i < pdev->num_resources; i++) { 43 struct resource *p, *r = &pdev->resource[i]; 44 45 if (r->name == NULL) 46 r->name = dev_name(&pdev->dev);//该resouce没name的话,则使用该dev的name 47 48 p = r->parent; 49 if (!p) { 50 if (resource_type(r) == IORESOURCE_MEM) 51 p = &iomem_resource;//没指定resouce的父项,则用系统默认的 PCI MEM 52 else if (resource_type(r) == IORESOURCE_IO) 53 p = &ioport_resource;//没指定resouce的父项,则用系统默认的 PCI IO 54 } 55 /*把该soucurce插入到source tree中*/ 56 if (p && insert_resource(p, r)) { 57 dev_err(&pdev->dev, "failed to claim resource %d\n", i); 58 ret = -EBUSY; 59 goto failed; 60 } 61 } 62 63 pr_debug("Registering platform device '%s'. Parent at %s\n", 64 dev_name(&pdev->dev), dev_name(pdev->dev.parent)); 65 /*把该设备增加到设备节点中去,对应的在sysfs的bus,platform下和sysfs的device,platform会出现响应设备*/ 66 ret = device_add(&pdev->dev); 67 if (ret == 0) 68 return ret; 69 70 failed: 71 if (pdev->id_auto) { 72 ida_simple_remove(&platform_devid_ida, pdev->id); 73 pdev->id = PLATFORM_DEVID_AUTO; 74 } 75 76 while (--i >= 0) { 77 struct resource *r = &pdev->resource[i]; 78 unsigned long type = resource_type(r); 79 80 if (type == IORESOURCE_MEM || type == IORESOURCE_IO) 81 release_resource(r); 82 } 83 84 err_out: 85 return ret; 86 }
5.2.5 platform_device_del
删除和注册刚好相反
1 /** 2 * platform_device_del - remove a platform-level device 3 * @pdev: platform device we're removing 4 * 5 * Note that this function will also release all memory- and port-based 6 * resources owned by the device (@dev->resource). This function must 7 * _only_ be externally called in error cases. All other usage is a bug. 8 */ 9 void platform_device_del(struct platform_device *pdev) 10 { 11 int i; 12 13 if (pdev) { 14 device_del(&pdev->dev); 15 16 if (pdev->id_auto) { 17 ida_simple_remove(&platform_devid_ida, pdev->id); 18 pdev->id = PLATFORM_DEVID_AUTO; 19 } 20 21 for (i = 0; i < pdev->num_resources; i++) { 22 struct resource *r = &pdev->resource[i]; 23 unsigned long type = resource_type(r); 24 25 if (type == IORESOURCE_MEM || type == IORESOURCE_IO) 26 release_resource(r); 27 } 28 } 29 }
5.3 platfrom_device注册
以三星s3c2440为例,在arch/arm/mach-s3c2440/mach-mini2440.c文件中。
这里注意.name、.dev.platform_data 这两个变量。
(1)platform_driver和platform_device就是通过name来匹配的。name一致则匹配上;
(2).dev.platform_data这个元素是中的内容是name、gpio flag def_trigger四个元素。
定义s3c24xx_led_platdata数据:
1 static struct s3c24xx_led_platdata mini2440_led1_pdata = { 2 .name = "led1", 3 .gpio = S3C2410_GPB(5), 4 .flags = S3C24XX_LEDF_ACTLOW | S3C24XX_LEDF_TRISTATE, 5 .def_trigger = "heartbeat", 6 }; 7 8 static struct s3c24xx_led_platdata mini2440_led2_pdata = { 9 .name = "led2", 10 .gpio = S3C2410_GPB(6), 11 .flags = S3C24XX_LEDF_ACTLOW | S3C24XX_LEDF_TRISTATE, 12 .def_trigger = "nand-disk", 13 };
将上述数据赋值给platfrom_device->dev->platfrom_data
1 static struct platform_device mini2440_led1 = { 2 .name = "s3c24xx_led", 3 .id = 1, 4 .dev = { 5 .platform_data = &mini2440_led1_pdata, 6 }, 7 }; 8 9 static struct platform_device mini2440_led2 = { 10 .name = "s3c24xx_led", 11 .id = 2, 12 .dev = { 13 .platform_data = &mini2440_led2_pdata, 14 }, 15 };
设置好platform_device 结构体以后就可以注册platform_device设备了,把我们设置好的platform_device结构体放到mini2440这个结构体数组指针中;
1 static struct platform_device *mini2440_devices[] __initdata = { 2 &s3c_device_ohci, 3 &s3c_device_wdt, 4 &s3c_device_i2c0, 5 &s3c_device_rtc, 6 &s3c_device_usbgadget, 7 &mini2440_device_eth, 8 &mini2440_led1, 9 &mini2440_led2, 10 &mini2440_led3, 11 &mini2440_led4, 12 &mini2440_button_device, 13 &s3c_device_nand, 14 &s3c_device_sdi, 15 &s3c_device_iis, 16 &uda1340_codec, 17 &mini2440_audio, 18 };
在arch/arm/mach-s3c2440/mach-mini2440.c
mini2440_init 函数下
1 static void __init mini2440_init(void) 2 { 3 struct mini2440_features_t features = { 0 }; 4 int i; 5 6 printk(KERN_INFO "MINI2440: Option string mini2440=%s\n", 7 mini2440_features_str); 8 9 /* Parse the feature string */ 10 mini2440_parse_features(&features, mini2440_features_str); 11 12 /* turn LCD on */ 13 s3c_gpio_cfgpin(S3C2410_GPC(0), S3C2410_GPC0_LEND); 14 15 /* Turn the backlight early on */ 16 WARN_ON(gpio_request_one(S3C2410_GPG(4), GPIOF_OUT_INIT_HIGH, NULL)); 17 gpio_free(S3C2410_GPG(4)); 18 19 /* remove pullup on optional PWM backlight -- unused on 3.5 and 7"s */ 20 gpio_request_one(S3C2410_GPB(1), GPIOF_IN, NULL); 21 s3c_gpio_setpull(S3C2410_GPB(1), S3C_GPIO_PULL_UP); 22 gpio_free(S3C2410_GPB(1)); 23 24 /* mark the key as input, without pullups (there is one on the board) */ 25 for (i = 0; i < ARRAY_SIZE(mini2440_buttons); i++) { 26 s3c_gpio_setpull(mini2440_buttons[i].gpio, S3C_GPIO_PULL_UP); 27 s3c_gpio_cfgpin(mini2440_buttons[i].gpio, S3C2410_GPIO_INPUT); 28 } 29 if (features.lcd_index != -1) { 30 int li; 31 32 mini2440_fb_info.displays = 33 &mini2440_lcd_cfg[features.lcd_index]; 34 35 printk(KERN_INFO "MINI2440: LCD"); 36 for (li = 0; li < ARRAY_SIZE(mini2440_lcd_cfg); li++) 37 if (li == features.lcd_index) 38 printk(" [%d:%dx%d]", li, 39 mini2440_lcd_cfg[li].width, 40 mini2440_lcd_cfg[li].height); 41 else 42 printk(" %d:%dx%d", li, 43 mini2440_lcd_cfg[li].width, 44 mini2440_lcd_cfg[li].height); 45 printk("\n"); 46 s3c24xx_fb_set_platdata(&mini2440_fb_info); 47 } 48 49 s3c24xx_udc_set_platdata(&mini2440_udc_cfg); 50 s3c24xx_mci_set_platdata(&mini2440_mmc_cfg); 51 s3c_nand_set_platdata(&mini2440_nand_info); 52 s3c_i2c0_set_platdata(NULL); 53 54 i2c_register_board_info(0, mini2440_i2c_devs, 55 ARRAY_SIZE(mini2440_i2c_devs)); 56 57 platform_add_devices(mini2440_devices, ARRAY_SIZE(mini2440_devices));//把所有platfrom_device注册到内核中 58 59 if (features.count) /* the optional features */ 60 platform_add_devices(features.optional, features.count); 61 62 }
使用的platform_add_devices这个函数把mini2440的所有设备注册到内核中;内核会自动查找platform_device链表以及platform_driver链表,当match以后字自动执行platform_driver的probe函数。
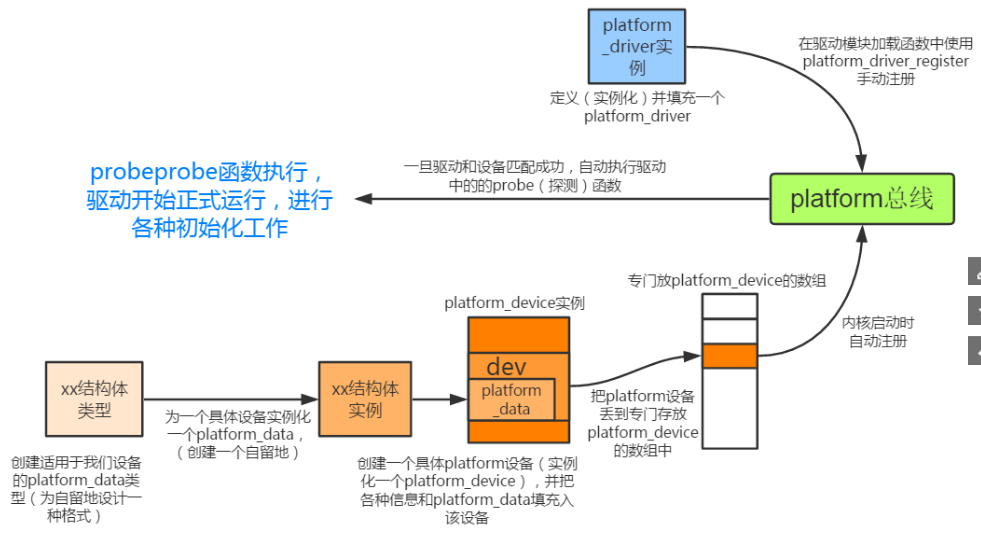
总结platform_device的注册过程:
(1)设置好platform_device结构体(对于led驱动来说关键是name、dev->platform_data两个元素)
(2)初始化好dev->platform_data结构体,这里主要涉及到led驱动所要用到的gpio,
这里我们可以看到linux内核platform驱动框架的设计思想:首先设备和驱动是分开的,同类设备有共性的部分,不同的部分,不同的部分在初始化的即被设置好;共性的部分内核工程师以及设置好;然后在通过一个匹配函数如果内核链表的设备与驱动链表的驱动匹配,则会自动安装驱动,否则不会安装驱动;
(3)把设置好的platform_device设备加入到mini2440_devices中
(4)在mini2440_device初始化的时候通过platform_add_devices函数把platform设备注册上去;注册以后再/sys/bus/platform/devices目录下会看到dev.name的文件夹
6 platform_driver
6.1 struct platform_driver
1 struct platform_driver { 2 int (*probe)(struct platform_device *); /* 负责使用device传递过来的platform_data初始化具体的device */ 3 int (*remove)(struct platform_device *); 4 void (*shutdown)(struct platform_device *); 5 int (*suspend)(struct platform_device *, pm_message_t state); 6 int (*resume)(struct platform_device *); 7 struct device_driver driver; /* 驱动程序共有接口,也是实现在sysfs接口的核心 */ 8 const struct platform_device_id *id_table; 9 };
6.2 platform_driver_register
platform_driver 的注册很简单,主要是调用系统提供的driver_regiser接口。
1 /** 2 * platform_driver_register - register a driver for platform-level devices 3 * @drv: platform driver structure 4 */ 5 int platform_driver_register(struct platform_driver *drv) 6 { 7 drv->driver.bus = &platform_bus_type;//总线类型定位platform_bus 8 if (drv->probe) 9 drv->driver.probe = platform_drv_probe; 10 if (drv->remove) 11 drv->driver.remove = platform_drv_remove; 12 if (drv->shutdown) 13 drv->driver.shutdown = platform_drv_shutdown; 14 15 return driver_register(&drv->driver); 16 }
其实platform总线的device和driver本身注册并没有做任何实质性的东西,真正实质性的注册为driver_register和device_add函数。这两个也是各种总线来实现驱动和设备注册的根本函数。
6.3 以led_driver为实例
1 static struct platform_driver s3c24xx_led_driver = { 2 .probe = s3c24xx_led_probe, 3 .remove = s3c24xx_led_remove, 4 .driver = { 5 .name = "s3c24xx_led", 6 .owner = THIS_MODULE, 7 }, 8 }; 9 10 static int __init s3c24xx_led_init(void) 11 { 12 return platform_driver_register(&s3c24xx_led_driver); 13 }
设置好platform_driver 结构体,使用platform_driver_register注册即可,这里关键的是probe、remove、driver.name 三个变量;
platform_driver_register 使用这个函数注册以后再 /sys/bus/platform/drivers目录下会看到 dev.name的文件夹,内核会自动检测匹配以后会自动执行probe函数;
led_driver.c的注册:
1 #include <linux/module.h> // module_init module_exit 2 #include <linux/init.h> // __init __exit 3 #include <linux/fs.h> 4 #include <asm/uaccess.h> 5 #include <plat/map-base.h> 6 #include <plat/map-s5p.h> 7 #include <mach/regs-gpio.h> 8 #include <mach/gpio-bank.h> 9 #include <linux/ioport.h> 10 #include <linux/string.h> 11 #include <asm/io.h> 12 #include <linux/cdev.h> 13 #include <linux/device.h> 14 #include <linux/leds.h> 15 #include <linux/gpio.h> 16 #include <linux/slab.h> 17 #include <linux/platform_device.h> 18 #include <mach/leds-gpio.h> 19 20 struct led_classdev *led_device; 21 struct s5pv210_led_platdata *pdata; 22 23 #define x210_led_on 0 24 #define x210_led_off 1 25 26 static void s5pv210_led_set(struct led_classdev *led_cdev, 27 enum led_brightness value) 28 { 29 30 //真正控制硬件的函数 31 if (value == LED_OFF) { 32 gpio_set_value(pdata->gpio, x210_led_off); 33 printk(KERN_INFO "LED1 OFF..."); 34 } 35 else { 36 37 gpio_set_value(pdata->gpio, x210_led_on); 38 printk(KERN_INFO "LED1 ON..."); 39 } 40 41 } 42 43 // 模块安装函数 44 static int s5pv210_led_probe(struct platform_device *dev) 45 { 46 int ret = -1; 47 printk(KERN_INFO "led_device init\n"); 48 49 led_device = kzalloc(sizeof(struct led_classdev), GFP_KERNEL); 50 if (led_device == NULL) 51 { 52 printk(KERN_ERR "No memory for led_device\n"); 53 return -ENOMEM; 54 } 55 pdata = dev->dev.platform_data; 56 57 led_device->name = pdata->name; 58 led_device->brightness_set = s5pv210_led_set; 59 60 //在这里进行注册驱动; 61 ret = led_classdev_register(NULL, led_device); 62 if (ret < 0) 63 { 64 printk(KERN_ERR "led_classdev_register failed\n"); 65 kfree(led_device); 66 return ret; 67 } 68 69 //初始化gpio 70 ret = gpio_request(pdata->gpio, pdata->name); 71 if (ret < 0) { 72 printk(KERN_ERR "couldn't claim card detect pin \n"); 73 return -1; 74 } 75 gpio_direction_output(pdata->gpio, 1); 76 77 return 0; 78 } 79 80 // 模块删除函数 81 static int s5pv210_led_remove(struct platform_device *dev) 82 { 83 printk(KERN_INFO "leddev_dev exit\n"); 84 85 //注销led设备驱动 86 led_classdev_unregister(led_device); 87 kfree(led_device); 88 89 //删除gpiolib库中引脚 90 gpio_free(pdata->gpio); 91 92 printk(KERN_INFO "leddev_dev unregist success\n"); 93 94 return 0; 95 } 96 97 static struct platform_driver s5pv210_led_driver = { 98 .probe = s5pv210_led_probe, 99 .remove = s5pv210_led_remove, 100 .driver = { 101 .name = "s5pv210_led", 102 .owner = THIS_MODULE, 103 }, 104 }; 105 106 static int __init s5pv210_led_init(void) 107 { 108 return platform_driver_register(&s5pv210_led_driver); 109 } 110 111 static void __exit s5pv210_led_exit(void) 112 { 113 platform_driver_unregister(&s5pv210_led_driver); 114 } 115 116 module_init(s5pv210_led_init); 117 module_exit(s5pv210_led_exit); 118 119 // MODULE_xxx这种宏作用是用来添加模块描述信息 120 MODULE_LICENSE("GPL"); // 描述模块的许可证 121 MODULE_AUTHOR("BHC <BHC>"); // 描述模块的作者 122 MODULE_DESCRIPTION("led test"); // 描述模块的介绍信息 123 MODULE_ALIAS("alias xxx"); // 描述模块的别名信息
device的注册:
1 static struct s5pv210_led_platdata s5pv210_led1_pdata = { 2 .name = "led0", 3 .gpio = S5PV210_GPJ0(3), 4 .flags = S3C24XX_LEDF_ACTLOW | S3C24XX_LEDF_TRISTATE, 5 .def_trigger = "", 6 }; 7 static struct s5pv210_led_platdata s5pv210_led2_pdata = { 8 .name = "led1", 9 .gpio = S5PV210_GPJ0(4), 10 .flags = S3C24XX_LEDF_ACTLOW | S3C24XX_LEDF_TRISTATE, 11 .def_trigger = "", 12 }; 13 static struct s5pv210_led_platdata s5pv210_led3_pdata = { 14 .name = "led2", 15 .gpio = S5PV210_GPJ0(5), 16 .flags = S3C24XX_LEDF_ACTLOW | S3C24XX_LEDF_TRISTATE, 17 .def_trigger = "", 18 }; 19 20 static struct platform_device s5pv210_led0 = { 21 .name = "s5pv210_led", 22 .id = 1, 23 .dev = { 24 .platform_data = &s5pv210_led1_pdata, 25 }, 26 }; 27 28 static struct platform_device s5pv210_led1 = { 29 .name = "s5pv210_led", 30 .id = 2, 31 .dev = { 32 .platform_data = &s5pv210_led2_pdata, 33 }, 34 }; 35 36 static struct platform_device s5pv210_led2 = { 37 .name = "s5pv210_led", 38 .id = 3, 39 .dev = { 40 .platform_data = &s5pv210_led3_pdata, 41 }, 42 };
把下面代码加入到static struct platform_device *smdkc110_devices[] __initdata 这个结构体中,即可注册设备和驱动了。
//led device &s5pv210_led1, &s5pv210_led2, &s5pv210_led0,
7 platform_get_resource()
C语言中的基本:
if语句中多条件判断顺序:
if ( conditionA && conditionB ) 和 if ( conditionA || conditionB ),
先判断conditionA再判断conditionB和编译器无关
不过对于&&只要conditionA为假conditionB就不判断了
对于||只要conditionA为真conditionB就不判断了
因为结果已经知道
7.1 struct resource
定义位于:include\linux\ioport.h
1 /* 2 * Resources are tree-like, allowing 3 * nesting etc.. 4 */ 5 struct resource { 6 resource_size_t start; 7 resource_size_t end; 8 const char *name; 9 unsigned long flags; 10 struct resource *parent, *sibling, *child; 11 };
7.2 platform_get_resource
1 /** 2 * platform_get_resource - get a resource for a device 3 * @dev: platform device 4 * @type: resource type 5 * @num: resource index 6 */ 7 struct resource *platform_get_resource(struct platform_device *dev, 8 unsigned int type, unsigned int num) 9 { 10 int i; 11 12 for (i = 0; i < dev->num_resources; i++) { 13 struct resource *r = &dev->resource[i]; 14 15 if (type == resource_type(r) && num-- == 0) 16 return r; 17 } 18 return NULL; 19 }
struct resource *r = &dev->resource[i];
这行代码使得不管你是想获取哪一份资源都从第一份资源开始搜索。
if (type == resource_type(r) && num-- == 0)
这行代码首先通过type == resource_type(r)判断当前这份资源的类型是否匹配,如果匹配则再通过num-- == 0判断是否是你要的,如果不匹配重新提取下一份资源而不会执行num-- == 0这一句代码。
通过以上两步就能定位到你要找的资源了,接着把资源返回即可。如果都不匹配就返回NULL。
7.3 实例
下面通过一个例子来看看它是如何拿到设备资源的。
设备资源如下:
1 static struct resource s3c_buttons_resource[] = { 2 [0]={ 3 .start = S3C24XX_PA_GPIO, 4 .end = S3C24XX_PA_GPIO + S3C24XX_SZ_GPIO - 1, 5 .flags = IORESOURCE_MEM, 6 }, 7 [1]={ 8 .start = IRQ_EINT8, 9 .end = IRQ_EINT8, 10 .flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ, 11 }, 12 13 [2]={ 14 .start = IRQ_EINT11, 15 .end = IRQ_EINT11, 16 .flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ, 17 }, 18 [3]={ 19 .start = IRQ_EINT13, 20 .end = IRQ_EINT13, 21 .flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ, 22 }, 23 [4]={ 24 .start = IRQ_EINT14, 25 .end = IRQ_EINT14, 26 .flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ, 27 }, 28 29 [5]={ 30 .start = IRQ_EINT15, 31 .end = IRQ_EINT15, 32 .flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ, 33 }, 34 35 [6]={ 36 .start = IRQ_EINT19, 37 .end = IRQ_EINT19, 38 .flags = IORESOURCE_IRQ, 39 } 40 41 };
驱动中通过下面代码拿到第一份资源:
struct resource *res;
res = platform_get_resource(pdev, IORESOURCE_MEM, 0);
函数进入for里面,i=0,num_resources=7,拿出resource[0]资源。resource_type(r)提取出该份资源 的资源类型并与函数传递下来的资源类型进行比较,匹配。
Num=0(这里先判断是否等于0再自减1)符合要求,从而返回该资源。
获取剩下资源的代码如下:
1 for(i=0; i<6; i++){ 2 buttons_irq = platform_get_resource(pdev,IORESOURCE_IRQ,i); 3 if(buttons_irq == NULL){ 4 dev_err(dev,"no irq resource specified\n"); 5 ret = -ENOENT; 6 goto err_map; 7 } 8 button_irqs[i] = buttons_irq->start; 9 }
分析如下:
For第一次循环:
buttons_irq = platform_get_resource(pdev,IORESOURCE_IRQ,0);
在拿出第一份资源进行resource_type(r)判断资源类型时不符合(此时num-- == 0这句没有执行),进而拿出第二份资源,此时i=1,num_resources=7,num传递下来为0,资源类型判断时候匹配,num也等于0,从而确定资源并返回。
For第二次循环:
buttons_irq = platform_get_resource(pdev,IORESOURCE_IRQ,1);
拿出第二份资源的时候resource_type(r)资源类型匹配,但是num传递下来时候为1,执行num-- == 0时不符合(但num开始自减1,这导致拿出第三份资源时num==0),只好拿出第三份资源。剩下的以此类推。
总结:
struct resource *platform_get_resource(struct platform_device *dev,unsigned int type, unsigned int num)
unsigned int type决定资源的类型,unsigned int num决定type类型的第几份资源(从0开始)。即使同类型资源在资源数组中不是连续排放也可以定位得到该资源。
比如第一份IORESOURCE_IRQ类型资源在resource[2],而第二份在resource[5],那
platform_get_resource(pdev,IORESOURCE_IRQ,0);
可以定位第一份IORESOURCE_IRQ资源;
platform_get_resource(pdev,IORESOURCE_IRQ,1);
可以定位第二份IORESOURCE_IRQ资源。之所以能定位到资源,在于函数实现中的这一行代码:
if (type == resource_type(r) && num-- == 0)
该行代码,如果没有匹配资源类型,num-- == 0不会执行而重新提取下一份资源,只有资源匹配了才会寻找该类型的第几份资源,即使这些资源排放不连续。
参考博文:
https://blog.csdn.net/xiaodingqq/article/details/80537887




