linux设备驱动(8)uevent 详解
1. Uevent的功能
Uevent是Kobject的一部分,用于在Kobject状态发生改变时,例如增加、移除等,通知用户空间程序。用户空间程序收到这样的事件后,会做相应的处理。
该机制通常是用来支持热拔插设备的,例如U盘插入后,USB相关的驱动软件会动态创建用于表示该U盘的device结构(相应的也包括其中的kobject),并告知用户空间程序,为该U盘动态的创建/dev/目录下的设备节点,更进一步,可以通知其它的应用程序,将该U盘设备mount到系统中,从而动态的支持该设备。
2. Uevent在kernel中的位置
下面图片描述了Uevent模块在内核中的位置:
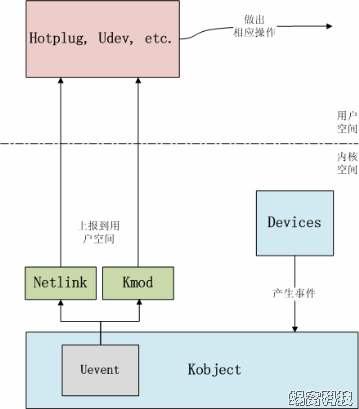
由此可知,Uevent的机制是比较简单的,设备模型中任何设备有事件需要上报时,会触发Uevent提供的接口。Uevent模块准备好上报事件的格式后,可以通过两个途径把事件上报到用户空间:一种是通过kmod模块,直接调用用户空间的可执行文件;另一种是通过netlink通信机制,将事件从内核空间传递给用户空间。
注1:有关kmod和netlink,会在其它文章中描述,因此本文就不再详细说明了。
3. Uevent的内部逻辑解析
source code: include/linux/kobject.h 和 lib/kobject_uevent.c
3.1相关数据结构
kobject.h定义了uevent相关的常量和数据结构,如下:
kobject_action
1 /* 2 * The actions here must match the index to the string array 3 * in lib/kobject_uevent.c 4 * 5 * Do not add new actions here without checking with the driver-core 6 * maintainers. Action strings are not meant to express subsystem 7 * or device specific properties. In most cases you want to send a 8 * kobject_uevent_env(kobj, KOBJ_CHANGE, env) with additional event 9 * specific variables added to the event environment. 10 */ 11 enum kobject_action { 12 KOBJ_ADD,//Kobject(或上层数据结构)的添加/移除事件 13 KOBJ_REMOVE,//Kobject(或上层数据结构)的添加/移除事件 14 KOBJ_CHANGE,//(或上层数据结构)的状态或者内容发生改变。如果设备驱动需要上报的事件不再上面事件的范围内,或者是自定义的事件,可以使用该event,并携带相应的参数 15 KOBJ_MOVE,//Kobject(或上层数据结构)更改名称或者更改Parent(意味着在sysfs中更改了目录结构)。 16 KOBJ_ONLINE, 17 KOBJ_OFFLINE, 18 KOBJ_MAX 19 };
kobj_uevent_env
1 #define UEVENT_HELPER_PATH_LEN 256 2 #define UEVENT_NUM_ENVP 32 /* number of env pointers */ 3 #define UEVENT_BUFFER_SIZE 2048 /* buffer for the variables */ 4 5 struct kobj_uevent_env { 6 char *envp[UEVENT_NUM_ENVP];//指针数组,用于保存每个环境变量的地址,数组中每个指针指向下面buf数组中每个环境变量。最多可支持的环境变量数量为UEVENT_NUM_ENVP。 7 int envp_idx;//用于访问环境变量指针数组的index 8 char buf[UEVENT_BUFFER_SIZE];//保存环境变量的buffer,最大为UEVENT_BUFFER_SIZE 9 int buflen;//环境变量buf的长度 10 };
前面有提到过,在利用Kmod向用户空间上报event事件时,会直接执行用户空间的可执行文件。而在Linux系统,可执行文件的执行,依赖于环境变量,因此kobj_uevent_env用于组织此次事件上报时的环境变量。
kset_uevent_ops
1 struct kset_uevent_ops { 2 int (* const filter)(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj); 3 const char *(* const name)(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj); 4 int (* const uevent)(struct kset *kset, struct kobject *kobj,struct kobj_uevent_env *env); 5 };
kset_uevent_ops是为kset量身订做的一个数据结构,里面包含filter和uevent两个回调函数,用处如下:
filter,当任何Kobject需要上报uevent时,它所属的kset可以通过该接口过滤,阻止不希望上报的event,从而达到从整体上管理的目的。
name,该接口可以返回kset的名称。如果一个kset没有合法的名称,则其下的所有Kobject将不允许上报uvent
uevent,当任何Kobject需要上报uevent时,它所属的kset可以通过该接口统一为这些event添加环境变量。因为很多时候上报uevent时的环境变量都是相同的,因此可以由kset统一处理,就不需要让每个Kobject独自添加了。
3.2相关API
3.2.1kobject_uevent_env
发送一个环境变量事件。
1 /** 2 * kobject_uevent_env - send an uevent with environmental data 3 * 4 * @action: action that is happening 5 * @kobj: struct kobject that the action is happening to 6 * @envp_ext: pointer to environmental data 7 * 8 * Returns 0 if kobject_uevent_env() is completed with success or the 9 * corresponding error when it fails. 10 */ 11 int kobject_uevent_env(struct kobject *kobj, enum kobject_action action, 12 char *envp_ext[]) 13 { 14 struct kobj_uevent_env *env; 15 const char *action_string = kobject_actions[action]; 16 const char *devpath = NULL; 17 const char *subsystem; 18 struct kobject *top_kobj; 19 struct kset *kset; 20 const struct kset_uevent_ops *uevent_ops; 21 int i = 0; 22 int retval = 0; 23 #ifdef CONFIG_NET 24 struct uevent_sock *ue_sk; 25 #endif 26 27 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s\n", 28 kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__); 29 30 /* search the kset we belong to 知道到该kobj从属的kset*/ 31 top_kobj = kobj; 32 while (!top_kobj->kset && top_kobj->parent) 33 top_kobj = top_kobj->parent; /* 找的方法很简单,若它的kset不存在,则查找其父节点的kset是否存在,不存在则继续查找父父节点.... */ 34 35 if (!top_kobj->kset) { 36 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: attempted to send uevent " 37 "without kset!\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj, 38 __func__); 39 return -EINVAL; /* 最终还没找到就报错 */ 40 } 41 42 kset = top_kobj->kset; /* 找到与之相关的kset */ 43 uevent_ops = kset->uevent_ops; 44 45 /* skip the event, if uevent_suppress is set*/ 46 if (kobj->uevent_suppress) { /* uevent_suppress被置位,则忽略上报uevent */ 47 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: uevent_suppress " 48 "caused the event to drop!\n", 49 kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__); 50 return 0; 51 } 52 /* skip the event, if the filter returns zero. */ 53 if (uevent_ops && uevent_ops->filter) /* 所属的筛选函数存在则筛选,返回0表示被筛掉了,不再上报 */ 54 if (!uevent_ops->filter(kset, kobj)) { 55 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: filter function " 56 "caused the event to drop!\n", 57 kobject_name(kobj), kobj, __func__); 58 return 0; 59 } 60 61 /* originating subsystem */ 62 if (uevent_ops && uevent_ops->name) 63 subsystem = uevent_ops->name(kset, kobj); /* name函数存在,则使用kset返回的kset的name */ 64 else 65 subsystem = kobject_name(&kset->kobj); /* 否则用kset里kobj的name做kset的name */ 66 if (!subsystem) { /* kset的name不存在,也不允许上报 */ 67 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: unset subsystem caused the " 68 "event to drop!\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj, 69 __func__); 70 return 0; 71 } 72 73 /* environment buffer */ 74 env = kzalloc(sizeof(struct kobj_uevent_env), GFP_KERNEL); /* 分配一个用于此次环境变量的buffer */ 75 if (!env) 76 return -ENOMEM; 77 78 /* complete object path */ 79 devpath = kobject_get_path(kobj, GFP_KERNEL); /* 根据kobj得到它在sysfs中的路径 */ 80 if (!devpath) { 81 retval = -ENOENT; 82 goto exit; 83 } 84 85 /* default keys 添加当前要上报的行为,path,name到env的buffer中 */ 86 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "ACTION=%s", action_string); 87 if (retval) 88 goto exit; 89 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "DEVPATH=%s", devpath); 90 if (retval) 91 goto exit; 92 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "SUBSYSTEM=%s", subsystem); 93 if (retval) 94 goto exit; 95 96 /* keys passed in from the caller */ 97 if (envp_ext) { /* 传的外部环境变量要不为空,则解析并添加到env的buffer中 */ 98 for (i = 0; envp_ext[i]; i++) { 99 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "%s", envp_ext[i]); 100 if (retval) 101 goto exit; 102 } 103 } 104 105 /* let the kset specific function add its stuff */ 106 if (uevent_ops && uevent_ops->uevent) { /* 如果uevent_ops中的uevent存在,则调用该接口发送该kobj的env */ 107 retval = uevent_ops->uevent(kset, kobj, env); 108 if (retval) { 109 pr_debug("kobject: '%s' (%p): %s: uevent() returned " 110 "%d\n", kobject_name(kobj), kobj, 111 __func__, retval); 112 goto exit; 113 } 114 } 115 116 /* 117 * Mark "add" and "remove" events in the object to ensure proper 118 * events to userspace during automatic cleanup. If the object did 119 * send an "add" event, "remove" will automatically generated by 120 * the core, if not already done by the caller. 121 */ 122 if (action == KOBJ_ADD) /* 如果action是add或remove的话要更新kobj中的state */ 123 kobj->state_add_uevent_sent = 1; 124 else if (action == KOBJ_REMOVE) 125 kobj->state_remove_uevent_sent = 1; 126 127 mutex_lock(&uevent_sock_mutex); 128 /* we will send an event, so request a new sequence number */ 129 /* 每次发送一个事件,都要有它的事件号,该事件号不能重复,u64 uevent_seqnum,把它也作为环境变量添加到buffer最后面 */ 130 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "SEQNUM=%llu", (unsigned long long)++uevent_seqnum); 131 if (retval) { 132 mutex_unlock(&uevent_sock_mutex); 133 goto exit; 134 } 135 136 #if defined(CONFIG_NET) 137 /* send netlink message 如果定义了"CONFIG_NET”,则使用netlink发送该uevent */ 138 list_for_each_entry(ue_sk, &uevent_sock_list, list) { 139 struct sock *uevent_sock = ue_sk->sk; 140 struct sk_buff *skb; 141 size_t len; 142 143 if (!netlink_has_listeners(uevent_sock, 1)) 144 continue; 145 146 /* allocate message with the maximum possible size */ 147 len = strlen(action_string) + strlen(devpath) + 2; 148 skb = alloc_skb(len + env->buflen, GFP_KERNEL); 149 if (skb) { 150 char *scratch; 151 152 /* add header */ 153 scratch = skb_put(skb, len); 154 sprintf(scratch, "%s@%s", action_string, devpath); 155 156 /* copy keys to our continuous event payload buffer */ 157 for (i = 0; i < env->envp_idx; i++) { 158 len = strlen(env->envp[i]) + 1; 159 scratch = skb_put(skb, len); 160 strcpy(scratch, env->envp[i]); 161 } 162 163 NETLINK_CB(skb).dst_group = 1; 164 retval = netlink_broadcast_filtered(uevent_sock, skb, 165 0, 1, GFP_KERNEL, 166 kobj_bcast_filter, 167 kobj); 168 /* ENOBUFS should be handled in userspace */ 169 if (retval == -ENOBUFS || retval == -ESRCH) 170 retval = 0; 171 } else 172 retval = -ENOMEM; 173 } 174 #endif 175 mutex_unlock(&uevent_sock_mutex); 176 177 /* call uevent_helper, usually only enabled during early boot */ 178 if (uevent_helper[0] && !kobj_usermode_filter(kobj)) { 179 char *argv [3]; 180 181 /* 添加helper和 kset的name */ 182 argv [0] = uevent_helper; 183 argv [1] = (char *)subsystem; 184 argv [2] = NULL; 185 186 /* 添加了标准环境变量 (HOME=/,PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin)*/ 187 retval = add_uevent_var(env, "HOME=/"); 188 if (retval) 189 goto exit; 190 retval = add_uevent_var(env, 191 "PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin"); 192 if (retval) 193 goto exit; 194 /* 调用kmod模块提供的call_usermodehelper函数,上报uevent。call_usermodehelper的作用,就是fork一个进程,以uevent为参数,执行uevent_helper */ 195 retval = call_usermodehelper(argv[0], argv, 196 env->envp, UMH_WAIT_EXEC); 197 } 198 199 exit: 200 kfree(devpath); 201 kfree(env); 202 return retval; 203 }
kobject_uevent_env,以envp为环境变量,上报一个指定action的uevent。环境变量的作用是为执行用户空间程序指定运行环境。整个流程总结如下:
(1)查找kobj本身或者其parent是否从属于某个kset,如果不是,则报错返回(注2:由此可以说明,如果一个kobject没有加入kset,是不允许上报uevent的)
(2)查看kobj->uevent_suppress是否设置,如果设置,则忽略所有的uevent上报并返回(注3:由此可知,可以通过Kobject的uevent_suppress标志,管控Kobject的uevent的上报)
(3)如果所属的kset有uevent_ops->filter函数,则调用该函数,过滤此次上报(注4:这佐证了3.2小节有关filter接口的说明,kset可以通过filter接口过滤不希望上报的event,从而达到整体的管理效果)
(4)判断所属的kset是否有合法的名称(称作subsystem,和前期的内核版本有区别),否则不允许上报uevent
(5)分配一个用于此次上报的、存储环境变量的buffer(结果保存在env指针中),并获得该Kobject在sysfs中路径信息(用户空间软件需要依据该路径信息在sysfs中访问它)
(6)调用add_uevent_var接口(下面会介绍),将Action、路径信息、subsystem等信息,添加到env指针中
(7)如果传入的envp不空,则解析传入的环境变量中,同样调用add_uevent_var接口,添加到env指针中
(8)如果所属的kset存在uevent_ops->uevent接口,调用该接口,添加kset统一的环境变量到env指针
(9)根据ACTION的类型,设置kobj->state_add_uevent_sent和kobj->state_remove_uevent_sent变量,以记录正确的状态
(10)调用add_uevent_var接口,添加格式为"SEQNUM=%llu”的序列号
(11)如果定义了"CONFIG_NET”,则使用netlink发送该uevent
(12)以uevent_helper、subsystem以及添加了标准环境变量(HOME=/,PATH=/sbin:/bin:/usr/sbin:/usr/bin)的env指针为参数,调用kmod模块提供的call_usermodehelper函数,上报uevent。
其中uevent_helper的内容是由内核配置项CONFIG_UEVENT_HELPER_PATH(位于./drivers/base/Kconfig)决定的(可参考lib/kobject_uevent.c, line 32),该配置项指定了一个用户空间程序(或者脚本),用于解析上报的uevent,例如"/sbin/hotplug”。 call_usermodehelper的作用,就是fork一个进程,以uevent为参数,执行uevent_helper。
3.2.2kobject_uevent
和kobject_uevent_env功能一样,只是没有指定任何的环境变量。
还是call kobject_uevent_env(),向用户空间发送一个事件。
1 /** 2 * kobject_uevent - notify userspace by sending an uevent 3 * 4 * @action: action that is happening 5 * @kobj: struct kobject that the action is happening to 6 * 7 * Returns 0 if kobject_uevent() is completed with success or the 8 * corresponding error when it fails. 9 */ 10 int kobject_uevent(struct kobject *kobj, enum kobject_action action) 11 { 12 return kobject_uevent_env(kobj, action, NULL); 13 }
kobject_uevent(),最终被kset_register() 调用,向用户空间发送一个事件。
1 int kset_register(struct kset *k) 2 { 3 int err; 4 5 if (!k) 6 return -EINVAL; 7 8 kset_init(k); 9 err = kobject_add_internal(&k->kobj); 10 if (err) 11 return err; 12 kobject_uevent(&k->kobj, KOBJ_ADD);//向用户空间发送事件 13 return 0; 14 }
3.2.3add_uevent_var
以格式化字符的形式(类似printf、printk等),将环境变量copy到env指针中。
1 /** 2 * add_uevent_var - add key value string to the environment buffer 3 * @env: environment buffer structure 4 * @format: printf format for the key=value pair 5 * 6 * Returns 0 if environment variable was added successfully or -ENOMEM 7 * if no space was available. 8 */ 9 int add_uevent_var(struct kobj_uevent_env *env, const char *format, ...) 10 { 11 va_list args; 12 int len; 13 14 if (env->envp_idx >= ARRAY_SIZE(env->envp)) { 15 WARN(1, KERN_ERR "add_uevent_var: too many keys\n"); 16 return -ENOMEM; 17 } 18 19 va_start(args, format); 20 len = vsnprintf(&env->buf[env->buflen], 21 sizeof(env->buf) - env->buflen, 22 format, args); 23 va_end(args); 24 25 if (len >= (sizeof(env->buf) - env->buflen)) { 26 WARN(1, KERN_ERR "add_uevent_var: buffer size too small\n"); 27 return -ENOMEM; 28 } 29 30 env->envp[env->envp_idx++] = &env->buf[env->buflen]; 31 env->buflen += len + 1; 32 return 0; 33 }
3.2.4kobject_action_type
将enum kobject_action类型的Action,转换为字符串。
1 /* the strings here must match the enum in include/linux/kobject.h */ 2 static const char *kobject_actions[] = { 3 [KOBJ_ADD] = "add", 4 [KOBJ_REMOVE] = "remove", 5 [KOBJ_CHANGE] = "change", 6 [KOBJ_MOVE] = "move", 7 [KOBJ_ONLINE] = "online", 8 [KOBJ_OFFLINE] = "offline", 9 }; 10 11 /** 12 * kobject_action_type - translate action string to numeric type 13 * 14 * @buf: buffer containing the action string, newline is ignored 15 * @len: length of buffer 16 * @type: pointer to the location to store the action type 17 * 18 * Returns 0 if the action string was recognized. 19 */ 20 int kobject_action_type(const char *buf, size_t count, 21 enum kobject_action *type) 22 { 23 enum kobject_action action; 24 int ret = -EINVAL; 25 26 if (count && (buf[count-1] == '\n' || buf[count-1] == '\0')) 27 count--; 28 29 if (!count) 30 goto out; 31 32 for (action = 0; action < ARRAY_SIZE(kobject_actions); action++) { 33 if (strncmp(kobject_actions[action], buf, count) != 0) /* 把buf和全局变量kobject_actions字符串比较 */ 34 continue; 35 if (kobject_actions[action][count] != '\0') /* 不是结束符 */ 36 continue; 37 *type = action; /* 比较成功则数字cation就是对应的action */ 38 ret = 0; 39 break; 40 } 41 out: 42 return ret; 43 }
说明:怎么指定处理uevent的用户空间程序(简称uevent helper)?
上面介绍kobject_uevent_env的内部动作时,有提到,Uevent模块通过Kmod上报Uevent时,会通过call_usermodehelper函数,调用用户空间的可执行文件(或者脚本,简称uevent helper )处理该event。而该uevent helper的路径保存在uevent_helper数组中。
char uevent_helper[UEVENT_HELPER_PATH_LEN] = CONFIG_UEVENT_HELPER_PATH;
配置内核.config文件把CONFIG_UEVENT_HELPER_PATH设置为空,则热插拔的路径这个全局数组默认是为空的。
可以在编译内核时,通过CONFIG_UEVENT_HELPER_PATH配置项,静态指定uevent helper。但这种方式会为每个event fork一个进程,随着内核支持的设备数量的增多,这种方式在系统启动时将会是致命的(可以导致内存溢出等)。因此只有在早期的内核版本中会使用这种方式,现在内核不再推荐使用该方式。因此内核编译时,需要把该配置项留空。
在系统启动后,大部分的设备已经ready,可以根据需要,重新指定一个uevent helper,以便检测系统运行过程中的热拔插事件。这可以通过把helper的路径写入到"/sys/kernel/uevent_helper”文件中实现。实际上,内核通过sysfs文件系统的形式,将uevent_helper数组开放到用户空间,供用户空间程序修改访问,具体可参考"./kernel/ksysfs.c”中相应的代码,这里不再详细描述。
参考博文:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_16777851/java/article/details/81395281



