React Hooks: everything you need to know! 🚀(译)
原文地址:React Hooks: everything you need to know! 🚀
从React 16.8.0开始,有新的方法可以优雅地调用异步代码,从而更轻松地在组件之间重用逻辑。
作为reactjs开发人员,您有责任了解最新的react框架功能。不是为了取悦您的老板,而是要在该领域和市场中保持相关性。
我仍然记得过去的美好时光,当时没人在谈论redux模式,而我的react应用程序是状态混乱的(2014年中)。
最初引入flux模式时,它很难理解,实现起来似乎很复杂,但是几年后,这是每个基于React Framework的项目中的标准。
与react hooks将发生的相同,是类组件的替换和React框架的未来。
好的,这将是一篇漫长的文章,所以我添加了一个目录,以便您可以阅读一些内容,然后继续进行项目,然后在需要休息时再回来。
我是唯一阅读技术文章以清理思想,减轻日常工作压力的人吗?
内容列表
- 什么是React hooks?
- React Hook与React Class
- 现有的React hooks
- 表示含义
- useState hook
- useEffect hook
- useReducer hook
- useRef hook
- 关注点分离
- 预先使用案例
- 现实世界中的例子
- 显示在线状态
- 跟踪地理位置
- 很棒的资源
- 结论
什么是React hooks? 🤔
当您使用Reactjs类组件时,可以使用状态,这就是为什么这些组件也称为有状态的原因,而且每个类组件都有生命周期方法,例如:componentDidMount(),componentDidUpdate()等。
您不能在函数组件中使用任何一种。 函数组件不能使用自己的状态,也没有生命周期方法。
现在,您可以使用React hooks了。
React钩子使我们能够使用Reactjs功能组件并为其添加状态和生命周期方法。
简而言之,React钩子是特殊函数,可以扩展功能组件的函数,并使其具有生命周期事件和管理状态的可能性。
让我们比较一下使用React钩子时类与功能组件的不同之处。
基于类方式,陈旧且良好的写法
import React from 'react';
class ClickCounter extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.state = {
count: 0 // Initial value for our counter
};
}
setCount(numb) {
this.setState({
count: numb
})
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<p>You clicked {count} times</p>
<button onClick={() => this.setCount(this.state.count + 1).bind(this)}>
Click me
</button>
</div>
);
}
}
使用React hooks
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function ClickCounter() {
/**
useState creates a "count" variable that will store the state and a "setCount" function that will mute the "count" variable state.
**/
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
return (
<div>
<p>You clicked {count} times</p>
<button onClick={() => setCount(count + 1)}>
Click me
</button>
</div>
);
}
使用useState hook将状态存储在函数组件中的示例
更少的代码行可以完成相同的工作!
不仅如此,借助React钩子,您现在可以重用状态逻辑并更好地分离关注点。
刚开始,这个新的API可能对您来说很奇怪,但继续与我一起,您将学习如何充分利用它。
现有的React hooks 🍱
新的API带有两个主要的预先存在的钩子,还有一些用于其他用例
基本React hooks
所有React钩子的基础,您将看到的所有其他钩子都是这三个钩子的变体,或者将它们用作基本体。
- useState是状态钩子,用于在组件中声明状态
- useEffect是副作用挂钩,用于将其用于数据提取,手动更改DOM等。
- useContext与Reactjs Context API结合使用。 当React Context提供程序更新时,此挂钩将触发具有最新上下文值的渲染。
先进的React钩子
这些是库附带的其他内置React钩子中最重要的。
useReducer是useState的替代方法,如果您具有复杂的状态逻辑,则应该使用它,如果您对Redux熟悉的话,会喜欢它。
useRef使用它来访问带有可变ref对象的DOM元素。 比ref属性更有用
那些特殊的括号
您可能会问 const [age,setAge] = useState(24)的语法含义,但这只是解构数组的新方法,下面让我向您展示另一种方法。
const ageStateVariable = useState(24); // Returns a tuple or an array of length 2
const age = ageStateVariable[0]; // First item
const setAge = ageStateVariable[1]; // Second item
// ES6 way to do this
const [age, setAge] = useState(24);
我喜欢简单而优雅的单行代码,不像使用python的人那么多,而且我绝对不喜欢像使用python的人一样疯狂的单行代码
规则
- 切勿从循环,条件或嵌套函数内部调用hooks
- 切勿从常规函数调用hooks
- 仅在函数组件或自定义hooks中调用它们
- Hooks应位于组件的顶层
- Hooks可以调用其他Hooks
useState hook 🎲
最容易使用和理解所有的钩子。 其目的是将状态存储在函数组件中。
嗯,从技术上讲,我们不是将状态存储在其中,而是将其连接到由底层React库处理的状态的字典(键值)中。 但是我们暂时不会深入了解这些细节
import React, { useState } from 'react';
function myAwesomeComponent () {
const [name, setName] = useState('John');
...
}
useState返回具有状态持有者属性和setter方法的元组。
您使用状态的初始值调用useState。
要更新状态,请调用setName函数
useEffect hook 🍯
在React类中,通常会在componentDidMount中设置一个订阅,并在componentWillUnmount中对其进行清理。
通过react hook useEffect,我们通过返回一个清除或取消订阅效果的函数来执行此操作。
如果您使用过mobx,这种模式可能会让您感到熟悉,这类似于反应。
useEffect(() => {
PlacesAPI.subscribeToPlaceNews(props.place.id, handlePlacesNews);
return () => {
PlacesAPI.unsubscribeFromPlaceNews(props.place.id, handlePlacesNews);
};
});
为什么我们从effect中返回一个函数?
这是用于effect的可选择的清理机制。 每个effect都可能返回一个函数,在之后执行清除操作。
这使我们可以保持彼此之间添加和删除订阅的逻辑。
useReducer hook 🎣
当您具有复杂的状态逻辑时,最好使用reducer。 如果您熟悉Redux之类的库或flux模式,那么您将一眼就理解了。
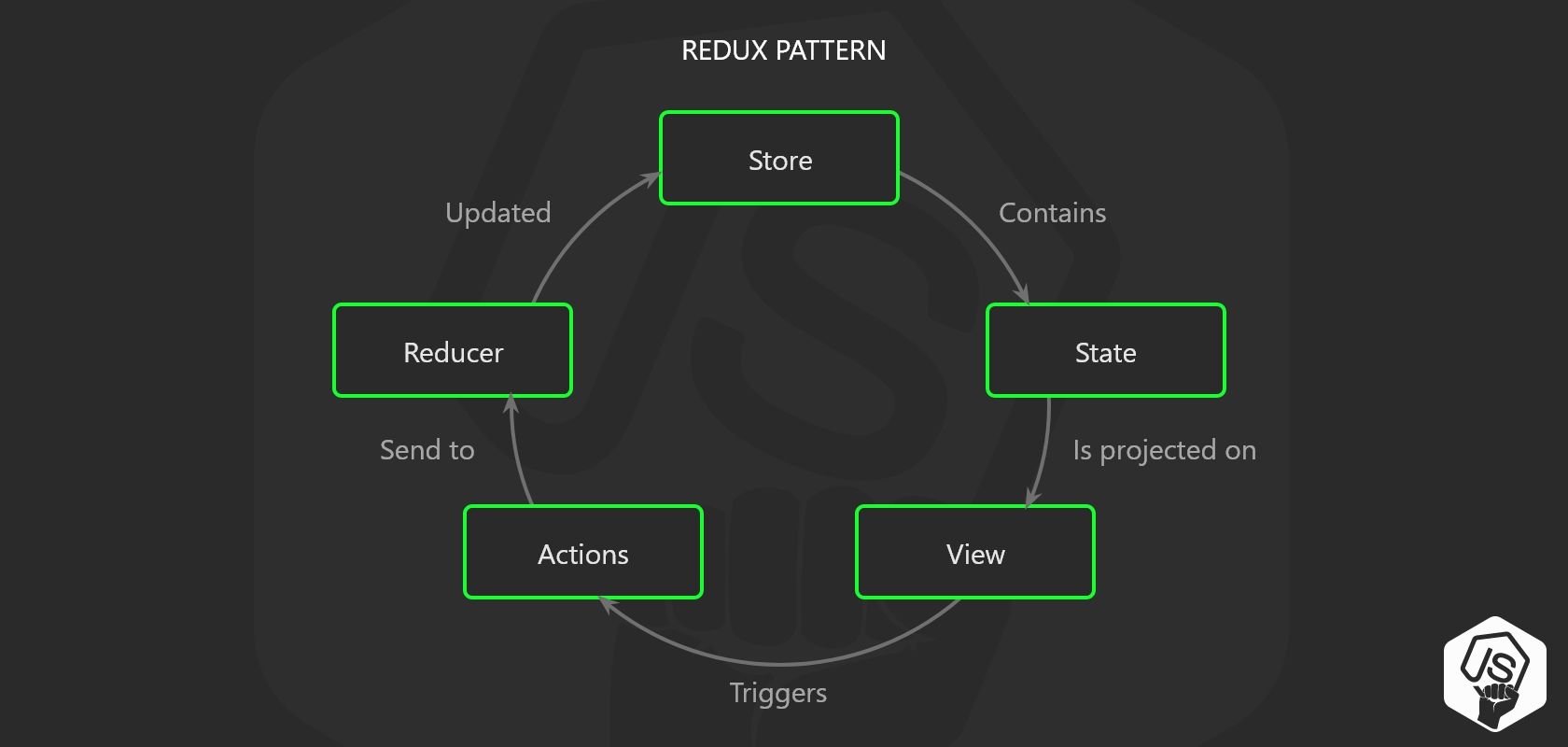
基本上,在您使用reducer调度或触发视图中的某些操作的情况下,这些事件将由reducer监听,这些reducer具有内部逻辑来更新状态所在的商店。 现在,当商店更新时,您的组件将重新渲染。
import React, { useReducer, useState } from 'react';
import produce from 'immer';
function reducer(state, action) {
switch (action.type) {
case 'toggle':
return produce(state, (draftState) => {
draftState[action.payload].isCompleted = !draftState[action.payload].isCompleted;
});
case 'add':
return produce(state, (draftState) => {
draftState.push({ label: action.payload });
});
default:
return state;
}
}
function Todo({ isCompleted, label, onChange }) {
return <p>
<label style={{
textDecoration: isCompleted && 'line-through'
}}>
<input
type="checkbox"
checked={isCompleted || false}
onChange={onChange}
/>
<span>{label}</span>
</label>
</p>
}
function TodoList() {
const todos = [
{ label: 'Do something' },
{ label: 'Buy dinner' }
];
const [state, dispatch] = useReducer(reducer, todos);
const [newTodo, setNewTodo] = useState('');
return <>
{state.map((todo, i) => (
<Todo
key={i}
{...todo}
onChange={() => dispatch({ type: 'toggle', payload: i })}
/>
))}
<input
type="text"
value={newTodo}
onChange={(e) => setNewTodo(e.target.value)}
/>
<button onClick={() => {
dispatch({ type: 'add', payload: newTodo });
setNewTodo('');
}}>
Add
</button>
</>;
}
export default TodoList;
useRef hook 🔮
Refs用于访问render函数中渲染后的React元素或DOM元素。 useRef hook返回一个可变的ref对象,该对象的.current属性已初始化为传递的参数initialValue。 使用非常简单
function TextInputWithFocusButton() {
const inputEl = useRef(null);
const onButtonClick = () => {
// `current` points to the mounted text input element
inputEl.current.focus();
};
return (
<>
<input ref={inputEl} type="text" />
<button onClick={onButtonClick}>Focus the input</button>
</>
);
}
关注点分离 🎎

使用Hooks,您可以从组件中提取状态逻辑,以便可以对其进行独立测试和重用。
Hooks允许您重用状态逻辑,而无需更改组件层次结构。
例如,组件可能在componentDidMount和componentDidUpdate中执行某些数据获取。
但是,同一componentDidMount方法也可能包含设置事件侦听器的无关逻辑,并在componentWillUnmount中执行清理。
在一起变化的相互关联的代码被分开,但是完全不相关的代码最终以单个方法组合在一起。
import React from 'react';
import PlacesAPI from '../services/place';
class PlaceNewsWithCounter extends React.Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props);
this.handlePlacesNews = this.handlePlacesNews.bind(this);
this.state = { count: 0, currentEvent: null };
}
// Unrelated stateful logic
componentDidMount() {
document.title = `You clicked ${this.state.count} times`;
PlacesAPI.subscribeToPlaceNews(
this.props.place.id,
this.handlePlacesNews
);
}
componentDidUpdate() {
document.title = `You clicked ${this.state.count} times`;
}
componentWillUnmount() {
PlacesAPI.unsubscribeFromPlaceNews(
this.props.place.id,
this.handlePlacesNews
);
}
handlePlacesNews(place) {
this.setState({
currentEvent: place.currentEvent
});
}
...
}
使用React钩子的更好方法
import React, { useState, useEffect } from 'react';
import PlacesAPI from '../services/place';
function PlaceNewsWithCounter() {
// Logic for counter here...
const [count, setCount] = useState(0);
useEffect(() => {
document.title = `You clicked ${count} times`;
});
// Logic for place API here...
const [currentEvent, setCurrentEvent] = useState(null);
function handlePlacesNews(place) {
setCurrentEvent(place.currentEvent);
}
useEffect(() => {
PlacesAPI.subscribeToPlaceNews(props.place.id, handlePlacesNews);
return () => {
PlacesAPI.unsubscribeFromPlaceNews(props.place.id, handlePlacesNews);
};
});
return ...;
}
提前使用示例

使用useEffect进行数据提取
通过结合使用useEffect和useState,可以使用useEffect进行API调用,并将空数组或对象作为第二个参数传递,使其具有与componentDidMount相同的行为。
这里的关键是第二个参数。 如果您不提供空数组或对象作为第二个参数,则将在每个渲染器上调用API调用,并且该调用实际上与componentDidUpdate相同
const [todo, setTodo] = useState(null);
const [id, setId] = useState(1);
useEffect(() => {
if (!id) {
return;
}
fetch(`https://jsonplaceholder.typicode.com/todos/${id}`)
.then(results => results.json())
.then(data => {
setTodo(data);
});
}, [id]); // Don't forget to add this!
通过将第二个参数传递给useEffect,我们将在id属性更改时设置订阅,从而重新触发效果
如果相反,我们只想在该组件挂载时进行API调用
const [fullName, setFullName] = useState(null);
useEffect(() => {
fetch('https://randomuser.me/api/')
.then(results => results.json())
.then(data => {
const {name} = data.results[0];
setFullName(`${name.first} ${name.last}`);
});
}, []); // <-- Have to pass in [] here!




