【设计模式】—— 迭代模式Iterator
前言:【模式总览】——————————by xingoo
模式意图
提供一个方法按顺序遍历一个集合内的元素,而又不需要暴露该对象的内部表示。
应用场景
1 访问一个聚合的对象,而不需要暴露对象的内部表示
2 支持对聚合对象的多种遍历
3 对遍历不同的对象,提供统一的接口。
模式结构
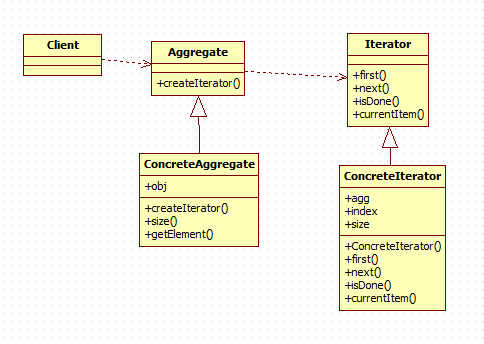
Iterator 定义访问的接口
/** * 抽象的迭代,有判断结束和下一个,获取当前元素等函数 * @author xingoo * */ interface Iterator{ void first(); void next(); boolean isDone(); Object currentItem(); }
ConcreteIterator 具体的迭代器,跟踪聚合内的元素
/** * 具体的迭代类 * @author xingoo * */ class ConcreteIterator implements Iterator{ private ConreteAggregate agg; private int index = 0; private int size = 0; public ConcreteIterator(ConreteAggregate agg) { this.agg = agg; size = agg.size(); index = 0; } public void first() { index = 0; } public void next() { if(index < size){ index++; } } public boolean isDone() { return (index >= size); } public Object currentItem() { return agg.getElement(index); } }
Aggregate 提供聚合的接口
/** * 聚合的类 * @author xingoo * */ abstract class Aggregate{ public Iterator createIterator(){ return null; } }
ConcreteAggregate 具体的聚合
/** * 具体的聚合对象,拥有大小,创建迭代子等函数 * @author xingoo * */ class ConreteAggregate extends Aggregate{ private Object[] obj = {"test1","test2","test3","test4"}; public Iterator createIterator(){ return new ConcreteIterator(this); } public Object getElement(int index){ if(index < obj.length){ return obj[index]; }else{ return null; } } public int size(){ return obj.length; } }
全部代码

1 package com.xingoo.Iterator; 2 /** 3 * 聚合的类 4 * @author xingoo 5 * 6 */ 7 abstract class Aggregate{ 8 public Iterator createIterator(){ 9 return null; 10 } 11 } 12 /** 13 * 抽象的迭代,有判断结束和下一个,获取当前元素等函数 14 * @author xingoo 15 * 16 */ 17 interface Iterator{ 18 void first(); 19 void next(); 20 boolean isDone(); 21 Object currentItem(); 22 } 23 /** 24 * 具体的聚合对象,拥有大小,创建迭代子等函数 25 * @author xingoo 26 * 27 */ 28 class ConreteAggregate extends Aggregate{ 29 private Object[] obj = {"test1","test2","test3","test4"}; 30 public Iterator createIterator(){ 31 return new ConcreteIterator(this); 32 } 33 public Object getElement(int index){ 34 if(index < obj.length){ 35 return obj[index]; 36 }else{ 37 return null; 38 } 39 } 40 public int size(){ 41 return obj.length; 42 } 43 } 44 /** 45 * 具体的迭代类 46 * @author xingoo 47 * 48 */ 49 class ConcreteIterator implements Iterator{ 50 private ConreteAggregate agg; 51 private int index = 0; 52 private int size = 0; 53 54 public ConcreteIterator(ConreteAggregate agg) { 55 this.agg = agg; 56 size = agg.size(); 57 index = 0; 58 } 59 60 public void first() { 61 index = 0; 62 } 63 64 public void next() { 65 if(index < size){ 66 index++; 67 } 68 } 69 70 public boolean isDone() { 71 return (index >= size); 72 } 73 74 public Object currentItem() { 75 return agg.getElement(index); 76 } 77 78 } 79 /** 80 * 客户端 使用方法 81 * @author xingoo 82 * 83 */ 84 public class Client { 85 private Iterator it; 86 private Aggregate agg = new ConreteAggregate(); 87 public void operation(){ 88 it = agg.createIterator(); 89 while(!it.isDone()){ 90 System.out.println(it.currentItem().toString()); 91 it.next(); 92 } 93 } 94 public static void main(String[] args) { 95 Client client = new Client(); 96 client.operation(); 97 } 98 }
运行结果
test1
test2
test3
test4



