Dubbo服务消费过程源码分析(九)
一、服务消费应具备的逻辑
如果要实现服务的消费,大致分以下几个步骤
- 通过@DubboReference注解生成远程服务的代理
- 获得目标服务的url地址
- 实现远程网络通信
- 实现负载均衡
- 实现集群容错
二、服务消费端流程
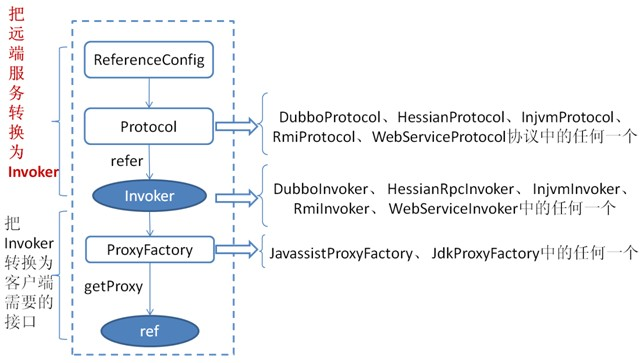
上图中可以看到,服务消费的流程与服务暴露的流程有点类似逆向的。同样,Dubbo 服务也是分为两个大步骤:
第一步就是将远程服务通过Protocol转换成Invoker。
第二步通过动态代理将Invoker转换成消费服务需要的接口。
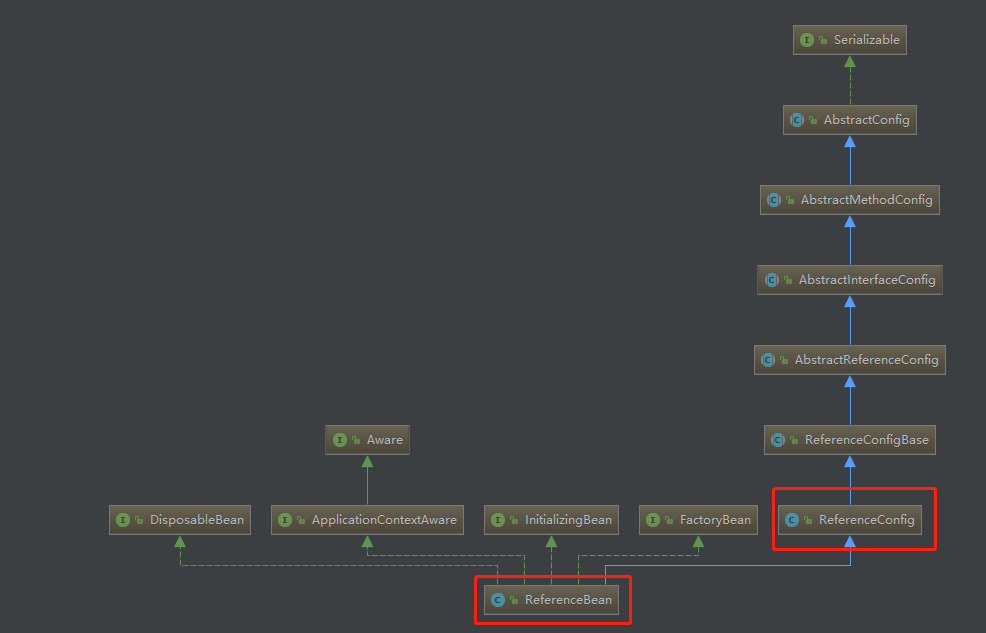
org.apache.dubbo.config.ReferenceConfig类是ReferenceBean的父类,与生产端服务的ServiceBean一样,存放着解析出来的 XML 和注解信息。类关系如下:
三、源码分析
xml的方式现在用的少,现在都是基于注解的方式进行开发,所以在讲切入点时就以注解的方式进行讲解,基于注解的方式无非就是扩展spring里面的东西,如果要扩展肯定是扩展BeanPostProcessor()中进行扩展(BeanPostProcessor是Spring IOC容器给我们提供的一个扩展接口。如果不了解可以先看下),因为最好是在Bean加载完成后去识别@DubboReference中的成员属性。所以接下来要找的就是什么时候进入到了BeanPostProcessor并且他是怎么做的,Dubbo中有个类叫DubboAutoConfiguration,他在里面配置一个自动装配机制。
@ConditionalOnMissingBean @Bean(name = ReferenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor.BEAN_NAME) public ReferenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor referenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() { return new ReferenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor(); }
进入ReferenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor类
public ReferenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor() { super(new Class[]{DubboReference.class, Reference.class, com.alibaba.dubbo.config.annotation.Reference.class}); this.referenceBeanCache = new ConcurrentHashMap(CACHE_SIZE); this.injectedFieldReferenceBeanCache = new ConcurrentHashMap(CACHE_SIZE); this.injectedMethodReferenceBeanCache = new ConcurrentHashMap(CACHE_SIZE); this.referencedBeanInvocationHandlersCache = new ConcurrentHashMap(); }
会发现他会把DubboReference、Reference、Reference这三种不同的注解传进来,最终会执行 ReferenceAnnotationBeanPostProcessor 中的重写方法 doGetInjectedBean执行获取依赖的Bean ,也就是实现bean的依赖注入的方法。在这个方法中,主要做两个事情
- 注册一个ReferenceBean到Spring IOC容器中
- 调用 getOrCreateProxy 返回一个动态代理对象
//由父类调用,实例化ReferenceBean
protected Object doGetInjectedBean(AnnotationAttributes attributes, Object bean, String beanName, Class<?> injectedType, InjectedElement injectedElement) throws Exception {
//需要注入引用Bean的名字 String referencedBeanName = this.buildReferencedBeanName(attributes, injectedType); String referenceBeanName = this.getReferenceBeanName(attributes, injectedType);
//初始化ReferenceBean ReferenceBean referenceBean = this.buildReferenceBeanIfAbsent(referenceBeanName, attributes, injectedType); boolean localServiceBean = this.isLocalServiceBean(referencedBeanName, referenceBean, attributes); this.registerReferenceBean(referencedBeanName, referenceBean, attributes, localServiceBean, injectedType); this.cacheInjectedReferenceBean(referenceBean, injectedElement); return this.getOrCreateProxy(referencedBeanName, referenceBean, localServiceBean, injectedType); }
getOrCreateProxy
获取或者创建一个动态代理对象。
private Object getOrCreateProxy(String referencedBeanName, ReferenceBean referenceBean, boolean localServiceBean, Class<?> serviceInterfaceType) { if (localServiceBean) { return Proxy.newProxyInstance(this.getClassLoader(), new Class[]{serviceInterfaceType}, this.newReferencedBeanInvocationHandler(referencedBeanName)); } else { this.exportServiceBeanIfNecessary(referencedBeanName); return referenceBean.get(); } }
可以看到,最终返回的动态代理对象,是通过referenceBean.get();来获得的。
ReferenceConfig.get
public synchronized T get() { if (destroyed) { throw new IllegalStateException("The invoker of ReferenceConfig(" + url + ") has already destroyed!"); } if (ref == null) { init(); } //返回的ref是个动态代理对象 return ref; }
init方法
开始调用init方法进行ref也就是代理对象的初始化动作.
- 检查配置信息
- 根据dubbo配置,构建map集合。
- 调用 createProxy 创建动态代理对象
public synchronized void init() { //如果已经初始化,则直接返回 if (initialized) { return; } if (bootstrap == null) { bootstrap = DubboBootstrap.getInstance(); bootstrap.init(); } //检查配置 checkAndUpdateSubConfigs(); //检查本地存根 local与stub checkStubAndLocal(interfaceClass); ConfigValidationUtils.checkMock(interfaceClass, this); Map<String, String> map = new HashMap<String, String>(); map.put(SIDE_KEY, CONSUMER_SIDE); //添加运行时参数 ReferenceConfigBase.appendRuntimeParameters(map); //检查是否为泛化接口 if (!ProtocolUtils.isGeneric(generic)) { //获取版本信息 String revision = Version.getVersion(interfaceClass, version); if (revision != null && revision.length() > 0) { map.put(REVISION_KEY, revision); } //获取接口方法列表,添加到map中 String[] methods = Wrapper.getWrapper(interfaceClass).getMethodNames(); if (methods.length == 0) { logger.warn("No method found in service interface " + interfaceClass.getName()); map.put(METHODS_KEY, ANY_VALUE); } else { map.put(METHODS_KEY, StringUtils.join(new HashSet<String>(Arrays.asList(methods)), COMMA_SEPARATOR)); } } //通过class加载配置信息 map.put(INTERFACE_KEY, interfaceName); AbstractConfig.appendParameters(map, getMetrics()); AbstractConfig.appendParameters(map, getApplication()); AbstractConfig.appendParameters(map, getModule()); // remove 'default.' prefix for configs from ConsumerConfig // appendParameters(map, consumer, Constants.DEFAULT_KEY); AbstractConfig.appendParameters(map, consumer); AbstractConfig.appendParameters(map, this); //将元数据配置信息放入到map中 MetadataReportConfig metadataReportConfig = getMetadataReportConfig(); if (metadataReportConfig != null && metadataReportConfig.isValid()) { map.putIfAbsent(METADATA_KEY, REMOTE_METADATA_STORAGE_TYPE); } //遍历methodConfig,组装method参数信息 Map<String, AsyncMethodInfo> attributes = null; if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(getMethods())) { attributes = new HashMap<>(); for (MethodConfig methodConfig : getMethods()) { AbstractConfig.appendParameters(map, methodConfig, methodConfig.getName()); String retryKey = methodConfig.getName() + ".retry"; if (map.containsKey(retryKey)) { String retryValue = map.remove(retryKey); if ("false".equals(retryValue)) { map.put(methodConfig.getName() + ".retries", "0"); } } AsyncMethodInfo asyncMethodInfo = AbstractConfig.convertMethodConfig2AsyncInfo(methodConfig); if (asyncMethodInfo != null) { // consumerModel.getMethodModel(methodConfig.getName()).addAttribute(ASYNC_KEY, asyncMethodInfo); attributes.put(methodConfig.getName(), asyncMethodInfo); } } } //获取服务消费者ip地址 String hostToRegistry = ConfigUtils.getSystemProperty(DUBBO_IP_TO_REGISTRY); if (StringUtils.isEmpty(hostToRegistry)) { hostToRegistry = NetUtils.getLocalHost(); } else if (isInvalidLocalHost(hostToRegistry)) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("Specified invalid registry ip from property:" + DUBBO_IP_TO_REGISTRY + ", value:" + hostToRegistry); } map.put(REGISTER_IP_KEY, hostToRegistry); serviceMetadata.getAttachments().putAll(map); //跟进 ref = createProxy(map); serviceMetadata.setTarget(ref); serviceMetadata.addAttribute(PROXY_CLASS_REF, ref); ConsumerModel consumerModel = repository.lookupReferredService(serviceMetadata.getServiceKey()); consumerModel.setProxyObject(ref); consumerModel.init(attributes); initialized = true; checkInvokerAvailable(); // dispatch a ReferenceConfigInitializedEvent since 2.7.4 dispatch(new ReferenceConfigInitializedEvent(this, invoker)); }
createProxy
创建动态代理对象这个过程中,它可能会有哪些操作步骤?首先我们需要注意一个点,这里是创建一个代理对象,而这个代理对象应该也和协议有关系,也就是不同的协议,使用的代理对象也应该不一样。
接下来分析下下面的代码
- 首先检查是不是本地调用,如果是,则使用injvm protocol的refer方法产生一个InjvmInvoker实例
- 否则,再判断是否是点对点通信,也就是url参数不为空,而url参数又可以配置多个,所以这里需要遍历
- 遍历所有注册中心的url,针对每个注册中心协议构建invoker,并保存到invokers中
- 通过Cluster的StaticDirectory把多个静态注册中心组件成一个集群
private T createProxy(Map<String, String> map) { if (shouldJvmRefer(map)) { URL url = new URL(LOCAL_PROTOCOL, LOCALHOST_VALUE, 0, interfaceClass.getName()).addParameters(map); invoker = REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, url); if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Using injvm service " + interfaceClass.getName()); } } else { urls.clear(); if (url != null && url.length() > 0) { // user specified URL, could be peer-to-peer address, or register center's address. String[] us = SEMICOLON_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(url); if (us != null && us.length > 0) { for (String u : us) { URL url = URL.valueOf(u); if (StringUtils.isEmpty(url.getPath())) { url = url.setPath(interfaceName); } if (UrlUtils.isRegistry(url)) { urls.add(url.addParameterAndEncoded(REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map))); } else { urls.add(ClusterUtils.mergeUrl(url, map)); } } } } else { // assemble URL from register center's configuration // if protocols not injvm checkRegistry //检查协议是否是injvm, if (!LOCAL_PROTOCOL.equalsIgnoreCase(getProtocol())) { checkRegistry(); //检查注册中心配置 //获取注册中心列表,由于可以配置多个注册中心,所以这里返回所有配置的注册中心 //信息 List<URL> us = ConfigValidationUtils.loadRegistries(this, false); //遍历注册中心列表,添加到urls中。 if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(us)) { for (URL u : us) { URL monitorUrl = ConfigValidationUtils.loadMonitor(this, u); if (monitorUrl != null) { map.put(MONITOR_KEY, URL.encode(monitorUrl.toFullString())); } urls.add(u.addParameterAndEncoded(REFER_KEY, StringUtils.toQueryString(map))); } } if (urls.isEmpty()) { throw new IllegalStateException("No such any registry to reference " + interfaceName + " on the consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + " use dubbo version " + Version.getVersion() + ", please config <dubbo:registry address=\"...\" /> to your spring config."); } } } //如果urls=1,表示只配置了一个注册中心,则直接取一个。 if (urls.size() == 1) { invoker = REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, urls.get(0)); } else { //否则,它会把多个注册中心的协议都分别构建一个invoker。 List<Invoker<?>> invokers = new ArrayList<Invoker<?>>(); URL registryURL = null; for (URL url : urls) { invokers.add(REF_PROTOCOL.refer(interfaceClass, url)); if (UrlUtils.isRegistry(url)) { registryURL = url; // use last registry url } } //如果registryURL不为空 //则通过CLUSTER.join把invokers以静态的Directory形式构建一个invoker对象。 //目的是实现注册中心的路由 if (registryURL != null) { // registry url is available // for multi-subscription scenario, use 'zone-aware' policy by default String cluster = registryURL.getParameter(CLUSTER_KEY, ZoneAwareCluster.NAME); // The invoker wrap sequence would be: ZoneAwareClusterInvoker(StaticDirectory) -> FailoverClusterInvoker(RegistryDirectory, routing happens here) -> Invoker invoker = Cluster.getCluster(cluster, false).join(new StaticDirectory(registryURL, invokers)); } else { // not a registry url, must be direct invoke. String cluster = CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(invokers) ? (invokers.get(0).getUrl() != null ? invokers.get(0).getUrl().getParameter(CLUSTER_KEY, ZoneAwareCluster.NAME) : Cluster.DEFAULT) : Cluster.DEFAULT; invoker = Cluster.getCluster(cluster).join(new StaticDirectory(invokers)); } } } if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Refer dubbo service " + interfaceClass.getName() + " from url " + invoker.getUrl()); }
在上面这个方法中,有两个核心的代码需要关注,分别是。
- REF_PROTOCOL.refer, 这个是生成invoker对象,它是一个调用器,是dubbo中比较重要的领域对象,它在这里承担这服务调用的核心逻辑.
- PROXY_FACTORY.getProxy(invoker, ProtocolUtils.isGeneric(generic)), 构建一个代理对象,代理客户端的请求。
REF_PROTOCOL.ref
private static final Protocol REF_PROTOCOL = (Protocol)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getAdaptiveExtension();
RegistryProtocol.refer
- 组装注册中心协议的url
- 判断是否配置了group,如果有,则cluster=getMergeableCluster(),构建invoker
- doRefer构建invoker
public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException { //获得注册中心的url地址 // 此时,这里得到的是zookeeper:// url = getRegistryUrl(url); //registryFactory,是一个自适应扩展点,RegistryFactory$Adaptive // 定位到org.apache.dubbo.registry.RegistryFactory这个类可以知道,返回的实例是: ZookeeperRegistryFactory,并且是一个被RegistryFactoryWrapper包装的实例 Registry registry = registryFactory.getRegistry(url); if (RegistryService.class.equals(type)) { return proxyFactory.getInvoker((T) registry, type, url); } // group="a,b" or group="*" Map<String, String> qs = StringUtils.parseQueryString(url.getParameterAndDecoded(REFER_KEY)); String group = qs.get(GROUP_KEY); if (group != null && group.length() > 0) { if ((COMMA_SPLIT_PATTERN.split(group)).length > 1 || "*".equals(group)) { return doRefer(Cluster.getCluster(MergeableCluster.NAME), registry, type, url); } } Cluster cluster = Cluster.getCluster(qs.get(CLUSTER_KEY)); return doRefer(cluster, registry, type, url); }
doRefer
private <T> Invoker<T> doRefer(Cluster cluster, Registry registry, Class<T> type, URL url) { //初始化RegistryDirectory RegistryDirectory<T> directory = new RegistryDirectory<T>(type, url); directory.setRegistry(registry); directory.setProtocol(protocol); // all attributes of REFER_KEY Map<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<String, String>(directory.getConsumerUrl().getParameters()); //注册consumer://协议url URL subscribeUrl = new URL(CONSUMER_PROTOCOL, parameters.remove(REGISTER_IP_KEY), 0, type.getName(), parameters); if (directory.isShouldRegister()) { //注册服务消费者的url地址 directory.setRegisteredConsumerUrl(subscribeUrl); registry.register(directory.getRegisteredConsumerUrl()); } directory.buildRouterChain(subscribeUrl); //进行订阅 // subscribe订阅信息消费url、通知监听、配置监听、订阅url // toSubscribeUrl:订阅信息:category、providers、configurators、routers directory.subscribe(toSubscribeUrl(subscribeUrl)); //一个注册中心会存在多个服务提供者,所以在这里需要把多个服务提供者通过cluster.join合并成 一个 Invoker<T> invoker = cluster.join(directory); List<RegistryProtocolListener> listeners = findRegistryProtocolListeners(url); if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(listeners)) { return invoker; } //通过RegistryInvokerWrapper进行包装 RegistryInvokerWrapper<T> registryInvokerWrapper = new RegistryInvokerWrapper<>(directory, cluster, invoker); for (RegistryProtocolListener listener : listeners) { listener.onRefer(this, registryInvokerWrapper); } return registryInvokerWrapper; }
Cluster是什么
Invoker<T> invoker = cluster.join(directory);
public void setCluster(Cluster cluster) { this.cluster = cluster; }
@SPI(Cluster.DEFAULT)
public interface Cluster {
String DEFAULT = FailoverCluster.NAME;
/**
* Merge the directory invokers to a virtual invoker.
*
* @param <T>
* @param directory
* @return cluster invoker
* @throws RpcException
*/
@Adaptive
<T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException;
static Cluster getCluster(String name) {
return getCluster(name, true);
}
static Cluster getCluster(String name, boolean wrap) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(name)) {
name = Cluster.DEFAULT;
}
return ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Cluster.class).getExtension(name, wrap);
}
}
Cluster$Adaptive
public class Cluster$Adaptive implements org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster { public org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker join(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory arg0) throws org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcException { if (arg0 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory argument == null"); if (arg0.getUrl() == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Directory argument getUrl() == null"); org.apache.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0.getUrl(); String extName = url.getParameter("cluster", "failover"); if(extName == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to get extension (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster) name from url (" + url.toString() + ") use keys([cluster])"); org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster extension = (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apa che.dubbo.rpc.cluster.Cluster.class).getExtension(extName); return extension.join(arg0); } }
cluster.join
private Cluster cluster; public MockClusterWrapper(Cluster cluster) { this.cluster = cluster; } @Override public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException { return new MockClusterInvoker<T>(directory, this.cluster.join(directory)); } }
@Override public <T> Invoker<T> join(Directory<T> directory) throws RpcException { return buildClusterInterceptors(doJoin(directory), directory.getUrl().getParameter(REFERENCE_INTERCEPTOR_KEY)); }
private <T> Invoker<T> buildClusterInterceptors(AbstractClusterInvoker<T> clusterInvoker, String key) { AbstractClusterInvoker<T> last = clusterInvoker; //通过激活扩展点来获得ClusterInterceptor集合. 如果没有配置激活参数,默认会有一个 ConsumerContextClusterInterceptor拦截器. List<ClusterInterceptor> interceptors = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(ClusterInterceptor.class).getActivateExtension(clusterInvoker.getUrl(), key); if (!interceptors.isEmpty()) { //遍历拦截器集合,构建一个拦截器链. for (int i = interceptors.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { final ClusterInterceptor interceptor = interceptors.get(i); final AbstractClusterInvoker<T> next = last; last = new InterceptorInvokerNode<>(clusterInvoker, interceptor, next); } } //最终返回的last= InterceptorInvokerNode // ConsumerContextClusterInterceptor -next- FailoverClusterInvoker return last; }
context=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.interceptor.ConsumerContextClusterIntercept or
zone-aware=org.apache.dubbo.rpc.cluster.interceptor.ZoneAwareClusterInterceptor
Cluster.join总结
ReferenceConfifig.createProxy
return (T) PROXY_FACTORY.getProxy(invoker, ProtocolUtils.isGeneric(generic));
import org.apache.dubbo.common.extension.ExtensionLoader;
public class ProxyFactory$Adaptive implements org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory {
public java.lang.Object getProxy(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker arg0) throws org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg0 == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument == null"); if (arg0.getUrl() == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument getUrl() == null");
org.apache.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0.getUrl();
String extName = url.getParameter("proxy", "javassist");
if(extName == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to get extension (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory) name from url (" + url.toString() + ") use keys([proxy])");
org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory extension = (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache .dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.getProxy(arg0);
}
public java.lang.Object getProxy(org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker arg0, boolean arg1) throws org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg0 == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument == null");
if (arg0.getUrl() == null)
throw new IllegalArgumentException("org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker argument getUrl() == null");
org.apache.dubbo.common.URL url = arg0.getUrl();
String extName = url.getParameter("proxy", "javassist");
if(extName == null)
throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to get extension (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory) name from url (" + url.toString() + ") use keys([proxy])");
org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory extension = (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache .dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.getProxy(arg0, arg1);
}
public org.apache.dubbo.rpc.Invoker getInvoker(java.lang.Object arg0, java.lang.Class arg1, org.apache.dubbo.common.URL arg2) throws org.apache.dubbo.rpc.RpcException {
if (arg2 == null) throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null");
org.apache.dubbo.common.URL url = arg2;
String extName = url.getParameter("proxy", "javassist");
if(extName == null) throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to get extension (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory) name from url (" + url.toString() + ") use keys([proxy])");
org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory extension = (org.apache.dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory)ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(org.apache .dubbo.rpc.ProxyFactory.class).getExtension(extName);
return extension.getInvoker(arg0, arg1, arg2);
}
}
JavassistProxyFactory.getProxy
public <T> T getProxy(Invoker<T> invoker, Class<?>[] interfaces) {
return (T) Proxy.getProxy(interfaces).newInstance(new InvokerInvocationHandler(invoker));
}
proxy.getProxy
proxy = (Proxy) pc.newInstance();

public java.lang.String sayHello(java.lang.String arg0){
Object[] args = new Object[1];
args[0] = ($w)$1;
Object ret = handler.invoke(this, methods[0], args);
return (java.lang.String)ret;
}
小结
- 构建一个RegistryDirectory对象
- 生成远程服务的代理
RegistryDirectory
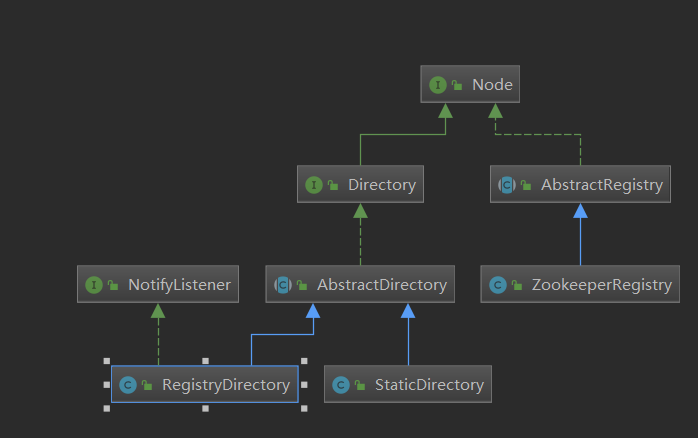
之前在写服务注册发布时提过RegistryProtocol的doRefer这个方法,这个doRefer方法中,构建了一个RegistryDirectory,之前我们不明白Directory的含义,所以暂时没有管,但是它的作用很重要,它负责动态维护服务提供者列表。
private <T> Invoker<T> doRefer(Cluster cluster, Registry registry, Class<T> type, URL url) { //初始化RegistryDirectory RegistryDirectory<T> directory = new RegistryDirectory<T>(type, url); directory.setRegistry(registry); directory.setProtocol(protocol); // all attributes of REFER_KEY Map<String, String> parameters = new HashMap<String, String>(directory.getConsumerUrl().getParameters()); //注册consumer://协议url URL subscribeUrl = new URL(CONSUMER_PROTOCOL, parameters.remove(REGISTER_IP_KEY), 0, type.getName(), parameters); if (directory.isShouldRegister()) { //注册服务消费者的url地址 directory.setRegisteredConsumerUrl(subscribeUrl); registry.register(directory.getRegisteredConsumerUrl()); } directory.buildRouterChain(subscribeUrl); //进行订阅 // subscribe订阅信息消费url、通知监听、配置监听、订阅url // toSubscribeUrl:订阅信息:category、providers、configurators、routers directory.subscribe(toSubscribeUrl(subscribeUrl)); //一个注册中心会存在多个服务提供者,所以在这里需要把多个服务提供者通过cluster.join合并成 一个 Invoker<T> invoker = cluster.join(directory); List<RegistryProtocolListener> listeners = findRegistryProtocolListeners(url); if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(listeners)) { return invoker; } //通过RegistryInvokerWrapper进行包装 RegistryInvokerWrapper<T> registryInvokerWrapper = new RegistryInvokerWrapper<>(directory, cluster, invoker); for (RegistryProtocolListener listener : listeners) { listener.onRefer(this, registryInvokerWrapper); } return registryInvokerWrapper; }
服务目录
RegistryDirectory.subscribe
public void subscribe(URL url) { setConsumerUrl(url); //把当前RegistryDirectory作为listener,去监听zk上节点的变化 CONSUMER_CONFIGURATION_LISTENER.addNotifyListener(this); serviceConfigurationListener = new ReferenceConfigurationListener(this, url); registry.subscribe(url, this);//订阅 -> 这里的registry是zookeeperRegsitry }
由于找不到ZookeeperRegistry类,所以找他的父类FailbackRegistry
FailbackRegistry.subscribe
@Override public void subscribe(URL url, NotifyListener listener) { super.subscribe(url, listener); //移除失效的listener,调用doSubscribe进行订阅 removeFailedSubscribed(url, listener); try { // Sending a subscription request to the server side // 发送订阅请求到服务端 doSubscribe(url, listener); } catch (Exception e) { Throwable t = e; List<URL> urls = getCacheUrls(url); if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(urls)) { notify(url, listener, urls); logger.error("Failed to subscribe " + url + ", Using cached list: " + urls + " from cache file: " + getUrl().getParameter(FILE_KEY, System.getProperty("user.home") + "/dubbo-registry-" + url.getHost() + ".cache") + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t); } else { // If the startup detection is opened, the Exception is thrown directly. boolean check = getUrl().getParameter(Constants.CHECK_KEY, true) && url.getParameter(Constants.CHECK_KEY, true); boolean skipFailback = t instanceof SkipFailbackWrapperException; if (check || skipFailback) { if (skipFailback) { t = t.getCause(); } throw new IllegalStateException("Failed to subscribe " + url + ", cause: " + t.getMessage(), t); } else { logger.error("Failed to subscribe " + url + ", waiting for retry, cause: " + t.getMessage(), t); } } // Record a failed registration request to a failed list, retry regularly // 记录失败的注册订阅请求,根据规则进行重试 addFailedSubscribed(url, listener); } }
ZookeeperRegistry.doSubscribe
@Override public void doSubscribe(final URL url, final NotifyListener listener) { try { if (ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface())) { //针对所有service层发起的定于 String root = toRootPath(); ConcurrentMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener> listeners = zkListeners.computeIfAbsent(url, k -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>()); ChildListener zkListener = listeners.computeIfAbsent(listener, k -> (parentPath, currentChilds) -> { for (String child : currentChilds) { child = URL.decode(child); if (!anyServices.contains(child)) { anyServices.add(child); subscribe(url.setPath(child).addParameters(INTERFACE_KEY, child, Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false)), k); } } }); zkClient.create(root, false); List<String> services = zkClient.addChildListener(root, zkListener); if (CollectionUtils.isNotEmpty(services)) { for (String service : services) { service = URL.decode(service); anyServices.add(service); subscribe(url.setPath(service).addParameters(INTERFACE_KEY, service, Constants.CHECK_KEY, String.valueOf(false)), listener); } } } else { //针对指定的服务地址发起订阅 // toCategoriesPath 会返回三个结果,分别 是/providers、/configurations、/routers。 也就是服务启动时需要监听这三个节点下的数据变化 List<URL> urls = new ArrayList<>(); for (String path : toCategoriesPath(url)) { //构建一个listeners集合,其中key是NotifyListener,其中前面我们知道 RegistryDirectory实现了这个接口,所以这里的key应该是RegistryDirectory // value表示针对这个RegistryDirectory注册的子节点监听。 ConcurrentMap<NotifyListener, ChildListener> listeners = zkListeners.computeIfAbsent(url, k -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>()); ChildListener zkListener = listeners.computeIfAbsent(listener, k -> (parentPath, currentChilds) -> ZookeeperRegistry.this.notify(url, k, toUrlsWithEmpty(url, parentPath, currentChilds))); zkClient.create(path, false);//创建一个/providers or /configurators、/routers节点 List<String> children = zkClient.addChildListener(path, zkListener); if (children != null) { urls.addAll(toUrlsWithEmpty(url, path, children)); } } //调用notify方法触发监听 notify(url, listener, urls); } } catch (Throwable e) { throw new RpcException("Failed to subscribe " + url + " to zookeeper " + getUrl() + ", cause: " + e.getMessage(), e); } }
FailbackRegistry.notify
@Override protected void notify(URL url, NotifyListener listener, List<URL> urls) { if (url == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("notify url == null"); } if (listener == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("notify listener == null"); } try { doNotify(url, listener, urls); } catch (Exception t) { // Record a failed registration request to a failed list, retry regularly addFailedNotified(url, listener, urls); logger.error("Failed to notify for subscribe " + url + ", waiting for retry, cause: " + t.getMessage(), t); } }
AbstractRegistry.notify
protected void notify(URL url, NotifyListener listener, List<URL> urls) { if (url == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("notify url == null"); } if (listener == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("notify listener == null"); } if ((CollectionUtils.isEmpty(urls)) && !ANY_VALUE.equals(url.getServiceInterface())) { logger.warn("Ignore empty notify urls for subscribe url " + url); return; } if (logger.isInfoEnabled()) { logger.info("Notify urls for subscribe url " + url + ", urls: " + urls); } // keep every provider's category. Map<String, List<URL>> result = new HashMap<>(); for (URL u : urls) { //urls表示三个empty://协议的地址 if (UrlUtils.isMatch(url, u)) { String category = u.getParameter(CATEGORY_KEY, DEFAULT_CATEGORY); List<URL> categoryList = result.computeIfAbsent(category, k -> new ArrayList<>()); categoryList.add(u); } } if (result.size() == 0) { return; } Map<String, List<URL>> categoryNotified = notified.computeIfAbsent(url, u -> new ConcurrentHashMap<>()); for (Map.Entry<String, List<URL>> entry : result.entrySet()) { String category = entry.getKey(); List<URL> categoryList = entry.getValue(); categoryNotified.put(category, categoryList); listener.notify(categoryList); //通过listener监听categoryList //保存到本地文件中,作为服务地址的缓存信息 // We will update our cache file after each notification. // When our Registry has a subscribe failure due to network jitter, we can return at least the existing cache URL. saveProperties(url); } }
RegistryDirectory.notify
@Override public synchronized void notify(List<URL> urls) { //对数据进行过滤。 Map<String, List<URL>> categoryUrls = urls.stream() .filter(Objects::nonNull) .filter(this::isValidCategory) .filter(this::isNotCompatibleFor26x) .collect(Collectors.groupingBy(this::judgeCategory)); //假设当前进来的通知是 providers节点 //判断configurator是否为空,这个节点下的配置,是在dubbo-admin控制台上修改配置时,会先 创建一个配置节点到这个路径下, // 注册中心收到这个变化时会通知服务消费者,服务消费者会根据新的配置重 新构建Invoker List<URL> configuratorURLs = categoryUrls.getOrDefault(CONFIGURATORS_CATEGORY, Collections.emptyList()); this.configurators = Configurator.toConfigurators(configuratorURLs).orElse(this.configurators); //判断路由规则配置是否为空,如果不为空,同样将路由规则添加到url中。 List<URL> routerURLs = categoryUrls.getOrDefault(ROUTERS_CATEGORY, Collections.emptyList()); toRouters(routerURLs).ifPresent(this::addRouters); // providers // providers 得到服务提供者的地址列表 List<URL> providerURLs = categoryUrls.getOrDefault(PROVIDERS_CATEGORY, Collections.emptyList()); /** * 3.x added for extend URL address */ //获得一个地址监听的激活扩展点。 这里目前应该还没有任何实现,可以先不用管 ExtensionLoader<AddressListener> addressListenerExtensionLoader = ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(AddressListener.class); List<AddressListener> supportedListeners = addressListenerExtensionLoader.getActivateExtension(getUrl(), (String[]) null); if (supportedListeners != null && !supportedListeners.isEmpty()) { for (AddressListener addressListener : supportedListeners) { providerURLs = addressListener.notify(providerURLs, getConsumerUrl(),this); } } refreshOverrideAndInvoker(providerURLs); }
refreshOverrideAndInvoker
- 逐个调用注册中心里面的配置,覆盖原来的url,组成最新的url 放入overrideDirectoryUrl 存储,此时我们没有在dubbo-admin中修改任何配置,所以这里没必要去分析
- 根据 provider urls,重新刷新Invoker
private void refreshOverrideAndInvoker(List<URL> urls) { // mock zookeeper://xxx?mock=return null //付给DirectoryUrl overrideDirectoryUrl(); //刷新invoker refreshInvoker(urls); }
refreshInvoker
private void refreshInvoker(List<URL> invokerUrls) { Assert.notNull(invokerUrls, "invokerUrls should not be null"); //如果只有一个服务提供者,并且如果是空协议,那么这个时候直接返回进制访问,并且销毁所有的 invokers if (invokerUrls.size() == 1 && invokerUrls.get(0) != null && EMPTY_PROTOCOL.equals(invokerUrls.get(0).getProtocol())) { this.forbidden = true; // Forbid to access this.invokers = Collections.emptyList(); routerChain.setInvokers(this.invokers); destroyAllInvokers(); // Close all invokers } else { //第一次初始化的时候,invokerUrls为空 this.forbidden = false; // Allow to access //获取老的invoker集合 Map<String, Invoker<T>> oldUrlInvokerMap = this.urlInvokerMap; // local reference if (invokerUrls == Collections.<URL>emptyList()) {//为null则初始化 invokerUrls = new ArrayList<>(); } if (invokerUrls.isEmpty() && this.cachedInvokerUrls != null) { invokerUrls.addAll(this.cachedInvokerUrls); } else { this.cachedInvokerUrls = new HashSet<>(); this.cachedInvokerUrls.addAll(invokerUrls);//Cached invoker urls, convenient for comparison } if (invokerUrls.isEmpty()) { return; } //把invokerUrls转化为InvokerMap Map<String, Invoker<T>> newUrlInvokerMap = toInvokers(invokerUrls);// Translate url list to Invoker map /** * If the calculation is wrong, it is not processed. * * 1. The protocol configured by the client is inconsistent with the protocol of the server. * eg: consumer protocol = dubbo, provider only has other protocol services(rest). * 2. The registration center is not robust and pushes illegal specification data. * */ if (CollectionUtils.isEmptyMap(newUrlInvokerMap)) { logger.error(new IllegalStateException("urls to invokers error .invokerUrls.size :" + invokerUrls.size() + ", invoker.size :0. urls :" + invokerUrls .toString())); return; } //转化为list List<Invoker<T>> newInvokers = Collections.unmodifiableList(new ArrayList<>(newUrlInvokerMap.values())); // pre-route and build cache, notice that route cache should build on original Invoker list. // toMergeMethodInvokerMap() will wrap some invokers having different groups, those wrapped invokers not should be routed. routerChain.setInvokers(newInvokers); //如果服务配置了分组,则把分组下的provider包装成StaticDirectory,组成一个invoker // 实际上就是按照group进行合并 this.invokers = multiGroup ? toMergeInvokerList(newInvokers) : newInvokers; this.urlInvokerMap = newUrlInvokerMap; try { //旧的url 是否在新map里面存在,不存在,就是销毁url对应的Invoker destroyUnusedInvokers(oldUrlInvokerMap, newUrlInvokerMap); // Close the unused Invoker } catch (Exception e) { logger.warn("destroyUnusedInvokers error. ", e); } } }
toInvokers
invoker = new InvokerDelegate<>(protocol.refer(serviceType, url), url, providerUrl);
private Map<String, Invoker<T>> toInvokers(List<URL> urls) { Map<String, Invoker<T>> newUrlInvokerMap = new HashMap<>(); if (urls == null || urls.isEmpty()) { return newUrlInvokerMap; } Set<String> keys = new HashSet<>(); String queryProtocols = this.queryMap.get(PROTOCOL_KEY); for (URL providerUrl : urls) { // If protocol is configured at the reference side, only the matching protocol is selected if (queryProtocols != null && queryProtocols.length() > 0) { boolean accept = false; String[] acceptProtocols = queryProtocols.split(","); for (String acceptProtocol : acceptProtocols) { if (providerUrl.getProtocol().equals(acceptProtocol)) { accept = true; break; } } if (!accept) { continue; } } if (EMPTY_PROTOCOL.equals(providerUrl.getProtocol())) { continue; } if (!ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).hasExtension(providerUrl.getProtocol())) { logger.error(new IllegalStateException("Unsupported protocol " + providerUrl.getProtocol() + " in notified url: " + providerUrl + " from registry " + getUrl().getAddress() + " to consumer " + NetUtils.getLocalHost() + ", supported protocol: " + ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Protocol.class).getSupportedExtensions())); continue; } URL url = mergeUrl(providerUrl); String key = url.toFullString(); // The parameter urls are sorted if (keys.contains(key)) { // Repeated url continue; } keys.add(key); // Cache key is url that does not merge with consumer side parameters, regardless of how the consumer combines parameters, if the server url changes, then refer again Map<String, Invoker<T>> localUrlInvokerMap = this.urlInvokerMap; // local reference Invoker<T> invoker = localUrlInvokerMap == null ? null : localUrlInvokerMap.get(key); if (invoker == null) { // Not in the cache, refer again try { boolean enabled = true; if (url.hasParameter(DISABLED_KEY)) { enabled = !url.getParameter(DISABLED_KEY, false); } else { enabled = url.getParameter(ENABLED_KEY, true); } if (enabled) { invoker = new InvokerDelegate<>(protocol.refer(serviceType, url), url, providerUrl); } } catch (Throwable t) { logger.error("Failed to refer invoker for interface:" + serviceType + ",url:(" + url + ")" + t.getMessage(), t); } if (invoker != null) { // Put new invoker in cache newUrlInvokerMap.put(key, invoker); } } else { newUrlInvokerMap.put(key, invoker); } } keys.clear(); return newUrlInvokerMap; }
总结
- 定于指定注册中心的以下三个路径的子节点变更事件
/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/providers 、/dubbo/org.apache.dubbo.demo.DemoService/configurators、/dubbo/org.apache. dubbo.demo.DemoService/routers
- 触发时间变更之后,把变更的节点信息转化为Invoker
Protocol.refer
invoker = new InvokerDelegate<>(protocol.refer(serviceType, url), url, providerUrl);
- 这个invoker应该和通信有关系
- 那么这里应该会建立一个网络通信的连接
QosProtocolWrapper(ProtocolFilterWrapper(ProtocolListenerWrapper(DubboProtocol)))
AbstractProtocol.refer
@Override public <T> Invoker<T> refer(Class<T> type, URL url) throws RpcException { return new AsyncToSyncInvoker<>(protocolBindingRefer(type, url)); }
protocolBindingRefer
- 优化序列化
- 构建DubboInvoker
@Override public <T> Invoker<T> protocolBindingRefer(Class<T> serviceType, URL url) throws RpcException { optimizeSerialization(url); // create rpc invoker. DubboInvoker<T> invoker = new DubboInvoker<T>(serviceType, url, getClients(url), invokers); invokers.add(invoker); return invoker; }
getClients
- 判断是否为共享连接,默认是共享同一个连接进行通信
- 是否配置了多个连接通道 connections,默认只有一个共享连接
private ExchangeClient[] getClients(URL url) { // whether to share connection boolean useShareConnect = false; int connections = url.getParameter(CONNECTIONS_KEY, 0); List<ReferenceCountExchangeClient> shareClients = null; // if not configured, connection is shared, otherwise, one connection for one service // 如果没有配置的情况下,默认是采用共享连接,否则,就是针对一个服务提供一个连接。 // 所谓共享连接,实际上就是 if (connections == 0) { useShareConnect = true; /* * The xml configuration should have a higher priority than properties. */ String shareConnectionsStr = url.getParameter(SHARE_CONNECTIONS_KEY, (String) null); connections = Integer.parseInt(StringUtils.isBlank(shareConnectionsStr) ? ConfigUtils.getProperty(SHARE_CONNECTIONS_KEY, DEFAULT_SHARE_CONNECTIONS) : shareConnectionsStr); //返回共享连接 shareClients = getSharedClient(url, connections); } //从共享连接中获得客户端连接进行返回 ExchangeClient[] clients = new ExchangeClient[connections]; for (int i = 0; i < clients.length; i++) { if (useShareConnect) { clients[i] = shareClients.get(i); } else {//如果不是使用共享连接,则初始化一个新的客户端连接进行返回 clients[i] = initClient(url); } } return clients; }
getSharedClient
private List<ReferenceCountExchangeClient> getSharedClient(URL url, int connectNum) { String key = url.getAddress(); List<ReferenceCountExchangeClient> clients = referenceClientMap.get(key); //检查当前的key检查连接是否已经创建过并且可用,如果是,则直接返回并且增加连接的个数的统计 if (checkClientCanUse(clients)) { batchClientRefIncr(clients); return clients; } //如果连接已经关闭或者连接没有创建过 locks.putIfAbsent(key, new Object()); synchronized (locks.get(key)) { clients = referenceClientMap.get(key); // dubbo check // 双重检查 if (checkClientCanUse(clients)) { batchClientRefIncr(clients); return clients; } // connectNum must be greater than or equal to 1 // 连接数必须大于等于1 connectNum = Math.max(connectNum, 1); // If the clients is empty, then the first initialization is //如果当前消费者还没有和服务端产生连接,则初始化 if (CollectionUtils.isEmpty(clients)) { clients = buildReferenceCountExchangeClientList(url, connectNum); referenceClientMap.put(key, clients); } else {//如果clients不为空,则从clients数组中进行遍历 for (int i = 0; i < clients.size(); i++) { ReferenceCountExchangeClient referenceCountExchangeClient = clients.get(i); // If there is a client in the list that is no longer available, create a new one to replace him. // 如果在集合中存在一个连接但是这个连接处于closed状态,则重新构建一个进行替换 if (referenceCountExchangeClient == null || referenceCountExchangeClient.isClosed()) { clients.set(i, buildReferenceCountExchangeClient(url)); continue; } //增加个数 referenceCountExchangeClient.incrementAndGetCount(); } } /* * I understand that the purpose of the remove operation here is to avoid the expired url key * always occupying this memory space. */ locks.remove(key); return clients; } }
buildReferenceCountExchangeClient
private List<ReferenceCountExchangeClient> buildReferenceCountExchangeClientList(URL url, int connectNum) { List<ReferenceCountExchangeClient> clients = new ArrayList<>(); for (int i = 0; i < connectNum; i++) { clients.add(buildReferenceCountExchangeClient(url)); } return clients; } /** * Build a single client * * @param url * @return */ private ReferenceCountExchangeClient buildReferenceCountExchangeClient(URL url) { ExchangeClient exchangeClient = initClient(url); return new ReferenceCountExchangeClient(exchangeClient); }
initClient
private ExchangeClient initClient(URL url) { // 获取客户端通信类型,默认是netty // client type setting. String str = url.getParameter(CLIENT_KEY, url.getParameter(SERVER_KEY, DEFAULT_REMOTING_CLIENT)); //获取编码解码类型,默认是Dubbo自定义类型 url = url.addParameter(CODEC_KEY, DubboCodec.NAME); // 开启心跳并设置心跳间隔,默认60s // enable heartbeat by default url = url.addParameterIfAbsent(HEARTBEAT_KEY, String.valueOf(DEFAULT_HEARTBEAT)); // 如果没有找到指定类型的通信扩展点,则抛出异常。 // BIO is not allowed since it has severe performance issue. if (str != null && str.length() > 0 && !ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).hasExtension(str)) { throw new RpcException("Unsupported client type: " + str + "," + " supported client type is " + StringUtils.join(ExtensionLoader.getExtensionLoader(Transporter.class).getSupportedExtensions(), " ")); } ExchangeClient client; try { // 是否延迟建立连接 // connection should be lazy if (url.getParameter(LAZY_CONNECT_KEY, false)) { client = new LazyConnectExchangeClient(url, requestHandler); //默认是直接在启动时建立连接 } else { client = Exchangers.connect(url, requestHandler); } } catch (RemotingException e) { throw new RpcException("Fail to create remoting client for service(" + url + "): " + e.getMessage(), e); } return client; }
Exchangers.connect
public static ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException { if (url == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("url == null"); } if (handler == null) { throw new IllegalArgumentException("handler == null"); } url = url.addParameterIfAbsent(Constants.CODEC_KEY, "exchange"); return getExchanger(url).connect(url, handler); }
HeaderExchange.connect
@Override public ExchangeClient connect(URL url, ExchangeHandler handler) throws RemotingException { return new HeaderExchangeClient(Transporters.connect(url, new DecodeHandler(new HeaderExchangeHandler(handler))), true); }
NettyTransport.connect
@Override public Client connect(URL url, ChannelHandler handler) throws RemotingException { return new NettyClient(url, handler); }



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号