Java使用AES算法进行加密解密
一、加密
/** * 加密 * @param src 源数据字节数组 * @param key 密钥字节数组 * @return 加密后的字节数组 */ public static byte[] Encrypt(byte[] src, byte[] key) throws Exception { SecretKeySpec skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key, "AES"); Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/NoPadding");//"算法/模式/补码方式" cipher.init(Cipher.ENCRYPT_MODE, skeySpec); return cipher.doFinal(src); }
二、解密
/** * 解密 * @param src 加密后的字节数据 * @param key 密钥字节数组 * @return 加密后的字节数组 * @throws Exception 异常 */ public static byte[] Decrypt(byte[] src, byte[] key) throws Exception { try { SecretKeySpec skeySpec = new SecretKeySpec(key, "AES"); Cipher cipher = Cipher.getInstance("AES/ECB/NoPadding"); cipher.init(Cipher.DECRYPT_MODE, skeySpec); try { return cipher.doFinal(key); } catch (Exception e) { System.out.println(e.toString()); return null; } } catch (Exception ex) { System.out.println(ex.toString()); return null; } }
三、hex字符串与字节数组互转
/** * 将二进制转换成16进制字符串 * @param buf 字节数组 * @return 字符串 */ public static String parseByte2HexStr(byte buf[]) { StringBuffer sb = new StringBuffer(); for (int i = 0; i < buf.length; i++) { String hex = Integer.toHexString(buf[i] & 0xFF); if (hex.length() == 1) { hex = '0' + hex; } sb.append(hex.toUpperCase()); } return sb.toString(); } /** * 将16进制字符串转换为二进制 * @param hexStr 字符串 * @return 字节数组 */ public static byte[] parseHexStr2Byte(String hexStr) { if (hexStr.length() < 1) return null; byte[] result = new byte[hexStr.length() / 2]; for (int i = 0; i < hexStr.length() / 2; i++) { int high = Integer.parseInt(hexStr.substring(i * 2, i * 2 + 1), 16); int low = Integer.parseInt(hexStr.substring(i * 2 + 1, i * 2 + 2), 16); result[i] = (byte) (high * 16 + low); } return result; }
注:因工作内容常与单片机进行数据传输,所以不能直接使用字符串进行加密解密,需要多进行一次hex字符串的转换
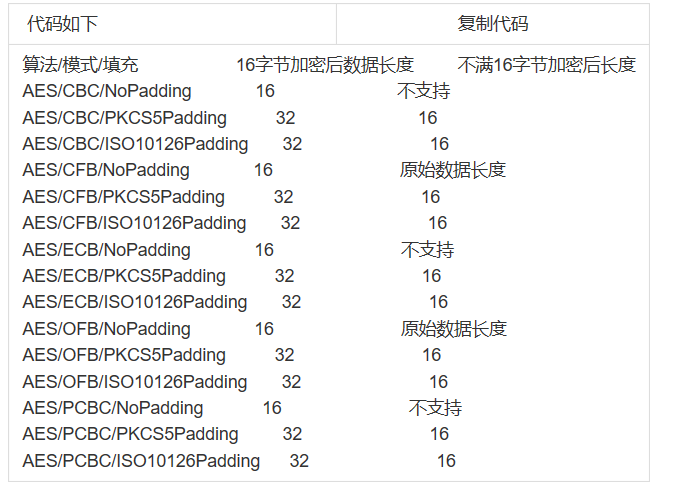
因为上述加密解密使用的补码模式是NoPadding,所以输入的字节必须是128位对应的16个字节的倍数,如有需要可以将补码模式改为以下模式