算法初级面试题05——哈希函数/表、生成多个哈希函数、哈希扩容、利用哈希分流找出大文件的重复内容、设计RandomPool结构、布隆过滤器、一致性哈希、并查集、岛问题
今天主要讨论:哈希函数、哈希表、布隆过滤器、一致性哈希、并查集的介绍和应用。
题目一
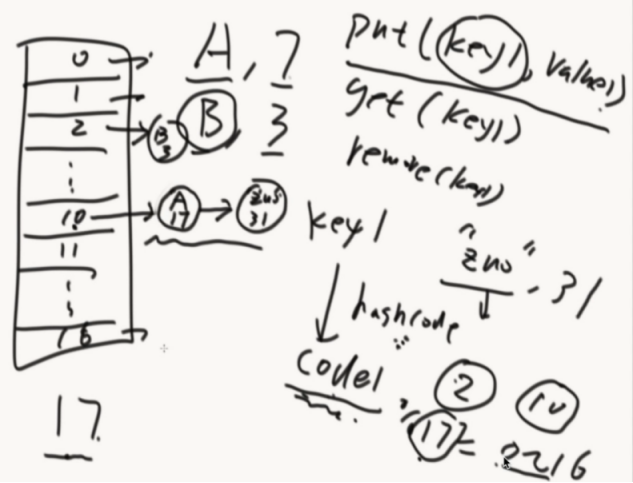
认识哈希函数和哈希表
1、输入无限大
2、输出有限的S集合
3、输入什么就输出什么
4、会发生哈希碰撞
5、会均匀分布,哈希函数的离散性,打乱输入规律

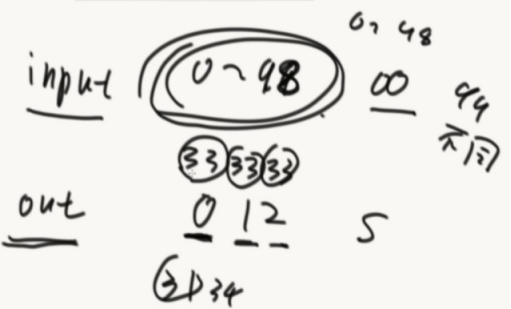
public class Code_01_HashMap { public static void main(String[] args) { HashMap<String, String> map = new HashMap<>(); map.put("zuo", "31"); System.out.println(map.containsKey("zuo")); System.out.println(map.containsKey("chengyun")); System.out.println("========================="); System.out.println(map.get("zuo")); System.out.println(map.get("chengyun")); System.out.println("========================="); System.out.println(map.isEmpty()); System.out.println(map.size()); System.out.println("========================="); System.out.println(map.remove("zuo")); System.out.println(map.containsKey("zuo")); System.out.println(map.get("zuo")); System.out.println(map.isEmpty()); System.out.println(map.size()); System.out.println("========================="); map.put("zuo", "31"); System.out.println(map.get("zuo")); map.put("zuo", "32"); System.out.println(map.get("zuo")); System.out.println("========================="); map.put("zuo", "31"); map.put("cheng", "32"); map.put("yun", "33"); for (String key : map.keySet()) { System.out.println(key); } System.out.println("========================="); for (String values : map.values()) { System.out.println(values); } System.out.println("========================="); map.clear(); map.put("A", "1"); map.put("B", "2"); map.put("C", "3"); map.put("D", "1"); map.put("E", "2"); map.put("F", "3"); map.put("G", "1"); map.put("H", "2"); map.put("I", "3"); for (Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) { String key = entry.getKey(); String value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key + "," + value); } System.out.println("========================="); // you can not remove item in map when you use the iterator of map // for(Entry<String,String> entry : map.entrySet()){ // if(!entry.getValue().equals("1")){ // map.remove(entry.getKey()); // } // } // if you want to remove items, collect them first, then remove them by // this way. List<String> removeKeys = new ArrayList<String>(); for (Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) { if (!entry.getValue().equals("1")) { removeKeys.add(entry.getKey()); } } for (String removeKey : removeKeys) { map.remove(removeKey); } for (Entry<String, String> entry : map.entrySet()) { String key = entry.getKey(); String value = entry.getValue(); System.out.println(key + "," + value); } System.out.println("========================="); } }
推论:如果结果都%一个M,那么0~m-1这个区域也是均匀分布的。
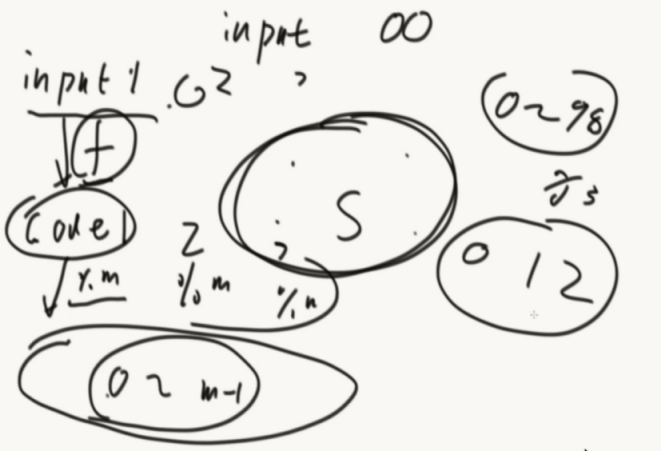
怎么拥有1000个相对独立的哈希函数。
把h计算出的16位数,分成高8位h1和低8位h2,然后h1 + 1*h2 =h3
生成新的哈希函数。(每个位置都是独立的,都是通过hash函数不断异或处理计算出来的)
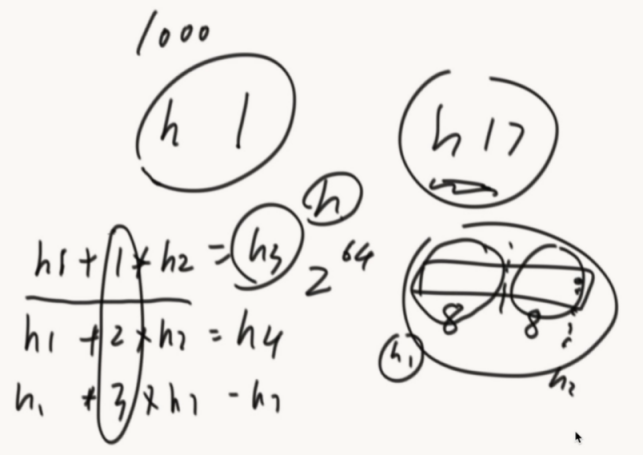
哈希表经典结构:
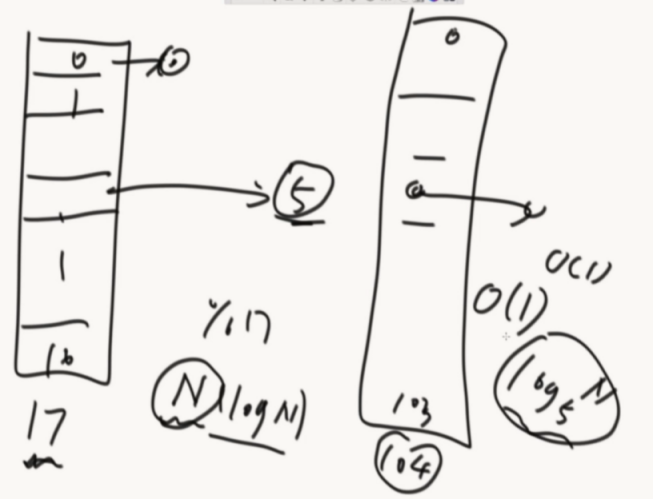
哈希扩容:
扩容要把以前的元素拿出来,重新计算然后放入新的空间,为了不影响效率也可以使用离线时间进行扩容(push就同时两个都push,get的话先从原来的地方拿)。
增删改查,全为o(1)

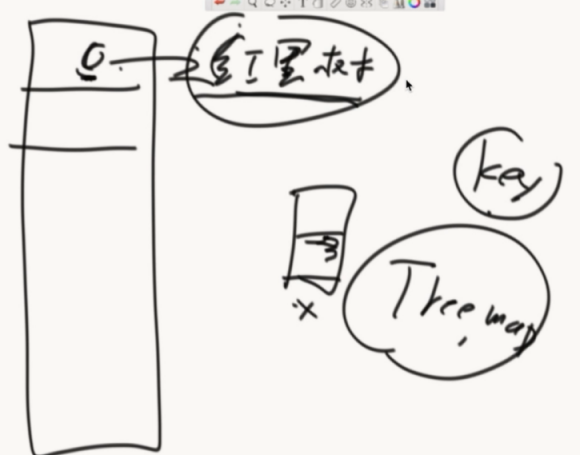
JVM里面的实现:
利用了平衡搜索二叉树
数组+红黑色的哈希表,使用了TreeMap结构
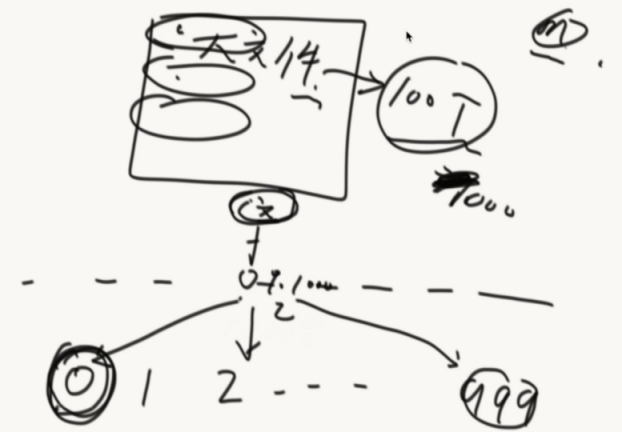
哈希表多有用?引入一道题目:
有一个大文件(100T),每行是一个字符串,想把大文件里面重复的内容打印出来
问面试官:你给我多少台机器?1000台机器
给机器编号0~999
然后从100T里面开始读文本,然后把文本按照hash函数算出hashcode再%上1000,如果是0就扔到0机器...,这样就把大文件分到1000台机器上。
根据hash的性质,相同的文本会来到同一台机器上。然后再单台机器上统计哪些重复的。
如果还太大的话,可以再机器里面再分文件。(hash函数做分流)
题目二
设计RandomPool结构
【题目】 设计一种结构,在该结构中有如下三个功能:insert(key):将某个key加入到该结构,做到不重复加入。delete(key):将原本在结构中的某个key移除。 getRandom():等概率随机返回结构中的任何一个key。
【要求】 Insert、delete和getRandom方法的时间复杂度都是 O(1)
做法:准备两张hash表和整形变量size,每加入一个数就分别存在两个hash表中,利用math.random随机从第二个hash表中返回一个数。
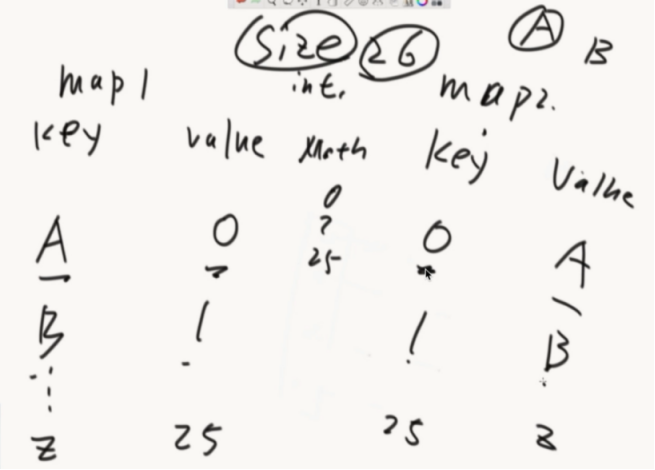
怎么解决删的问题?
拿最后一个值去填这个洞,然后删了最后一个。size再减一。

public class Code_02_RandomPool { public static class Pool<K> { private HashMap<K, Integer> keyIndexMap; private HashMap<Integer, K> indexKeyMap; private int size; public Pool() { this.keyIndexMap = new HashMap<K, Integer>(); this.indexKeyMap = new HashMap<Integer, K>(); this.size = 0; } public void insert(K key) { if (!this.keyIndexMap.containsKey(key)) { this.keyIndexMap.put(key, this.size); this.indexKeyMap.put(this.size++, key); } } public void delete(K key) { if (this.keyIndexMap.containsKey(key)) { int deleteIndex = this.keyIndexMap.get(key); int lastIndex = --this.size; K lastKey = this.indexKeyMap.get(lastIndex); this.keyIndexMap.put(lastKey, deleteIndex); this.indexKeyMap.put(deleteIndex, lastKey); this.keyIndexMap.remove(key); this.indexKeyMap.remove(lastIndex); } } public K getRandom() { if (this.size == 0) { return null; } int randomIndex = (int) (Math.random() * this.size); // 0 ~ size -1 return this.indexKeyMap.get(randomIndex); } } public static void main(String[] args) { Pool<String> pool = new Pool<String>(); pool.insert("zuo"); pool.insert("cheng"); pool.insert("yun"); System.out.println(pool.getRandom()); System.out.println(pool.getRandom()); System.out.println(pool.getRandom()); System.out.println(pool.getRandom()); System.out.println(pool.getRandom()); System.out.println(pool.getRandom()); } }
题目三
认识布隆过滤器(面试搜索相关的公司几乎都会问到)
就是一个某种类型的集合,不过会有失误率。
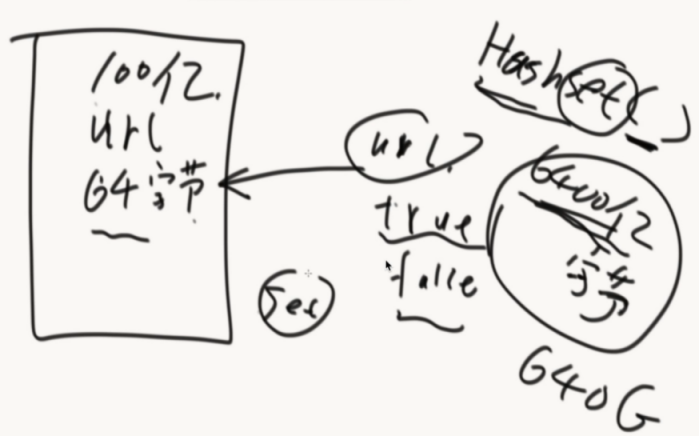
实现0~m-1比特的数组(处理黑名单问题)
原本的数 | 1 << 16 就可以把32字节里面的第16位改为1
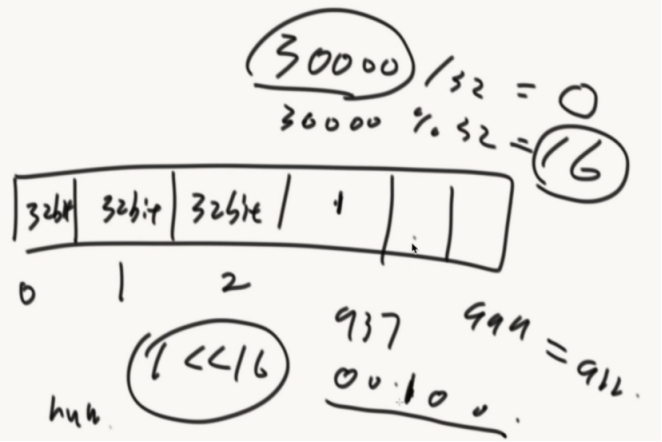
public class c05_03BloemFilter { //实现0~m-1比特的数组 public static void main(String[] args) { //int 4个字节 32个比特 int[] arr = new int[1000];//4*8*1000 = 32000; //数量不够可以使用二维数组实现 long[][] map = new long[1000][1000]; int index = 30000;//想把第30000位置描黑 int intIndex = index / 4 / 8;//查看这个bit来自哪个整数位置 int bitIndex = index % 32;//在定位来自这个整数的哪个bit位 arr[intIndex] = arr[intIndex] | (1 << bitIndex); } }
一个URL经过K个hash函数,计算出K个位置都描黑。(这个URL就进入到布隆过滤器当中了)
接下来每个URL都这样计算加入到bit类型的数组里面。(数组要够大)
怎么查?
这个URL经过K个hash函数,算出来K个位置,如果K个位置都是黑的就说这个URL在黑名单中,如果有一个不是黑的就不在黑名单里
数组空间越大,失误率会降低,空间多大和样本量、预计失误率有关系
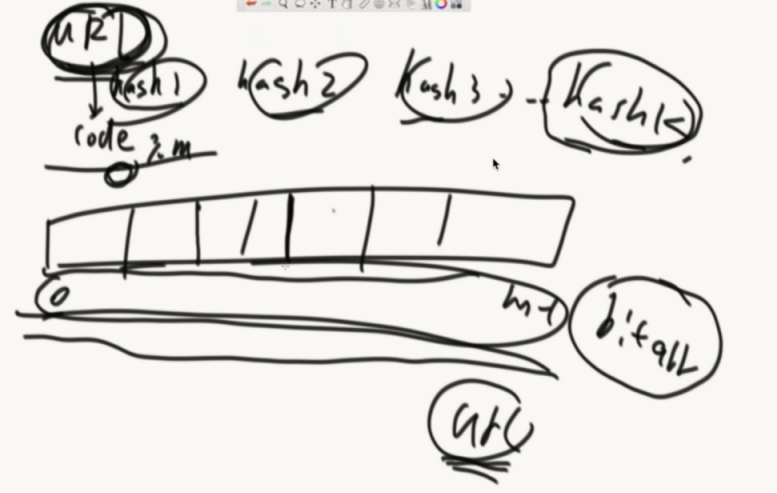
数组的大小M(bit)有一个公式计算。22.3G
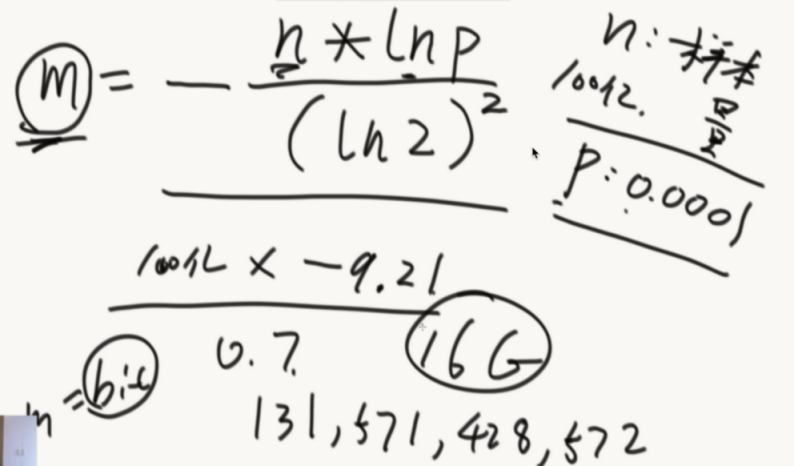
确定hash函数的个数K,最后P会在确定了M和K后计算出来
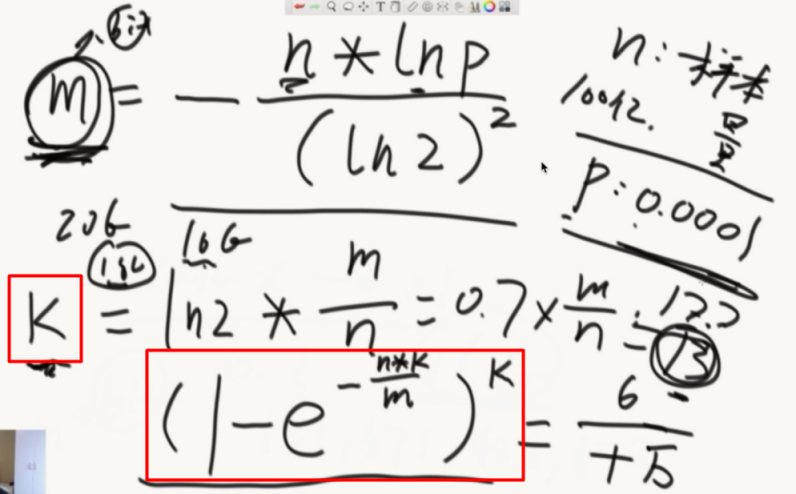
如果面试官感觉经典结构太费,就问面试官允不允许有失误率,失误率是多少,允许就讲布隆过滤器的原理,URL经过K个hash然后描黑数组,检查URL的时候通过K个hash来检查。都黑就在,否则就不在。
数组开多大,由样本量、失误率,计算出bit后还要除以8才是字节数。
如果计算出16G,面试官给出20G空间就适当调整大到18G
接着就计算hash的个数K,向上取整。
最后再计算下失误率。
题目四
认识一致性哈希(服务器设计)
服务器经典结构怎么做到负载均衡,前端通过同一份hash函数,计算出hashcode再%3,得到0/1/2然后存在不同的服务器中。由于hash函数的性质,这个服务器巨均衡。
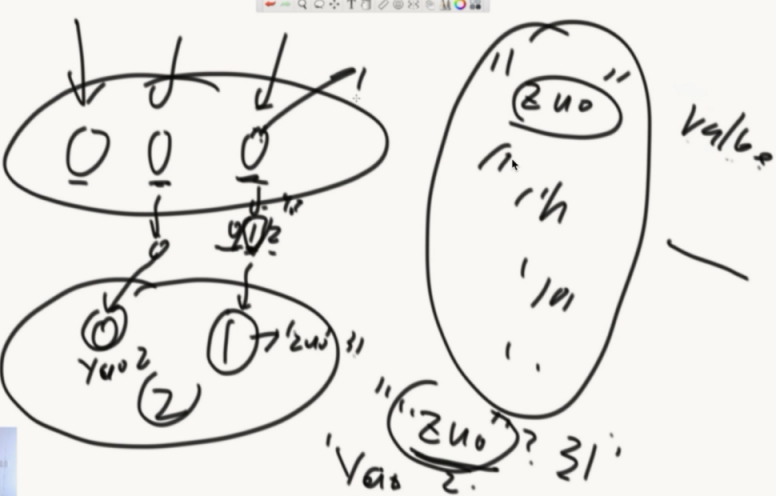
当想加减机器的时候,这个结构就干了。和hash表扩容一样。所有的数据归属全变了。(代价很大)
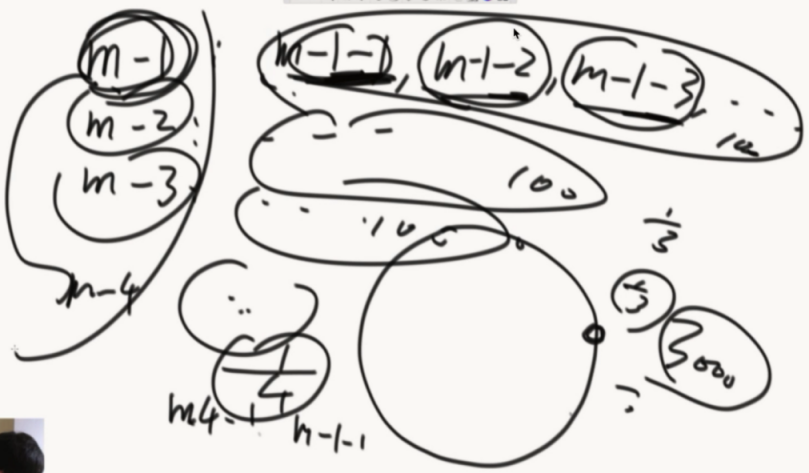
引入一致性哈希结构。
把hash函数的返回值想象成一个环。再把机器M1/M2/M3的IP经过hash计算放在环里面,接着要进入一个数据”zuo”就入环,顺时针找到最近的机器存进去。
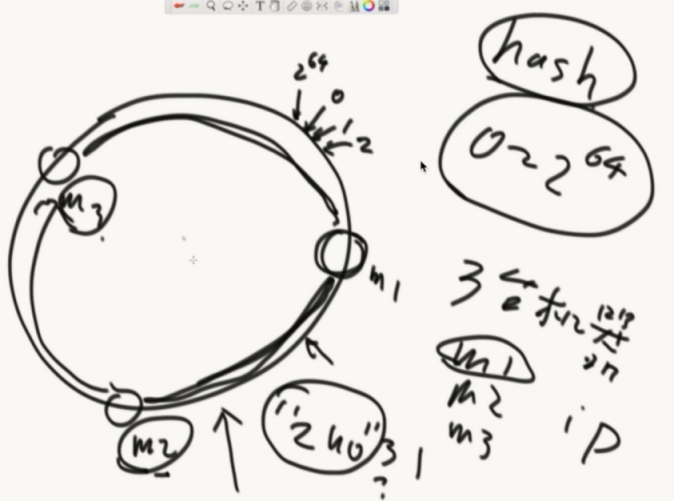
怎么实现?
把机器的hash值排序后做成数组,存在每个前端服务器中。
在数据访问的时候,通过计算hash值,二分的方式查询机器数组,查询出最近的大于等于机器。
前端服务器二分的查找服务器过程,就是一个顺时针找最近服务器的过程。
新增一个机器的情况:
M4通过IP计算出位置,数据迁移只需要一小部分。新增和删除都只需要一小部分数据。
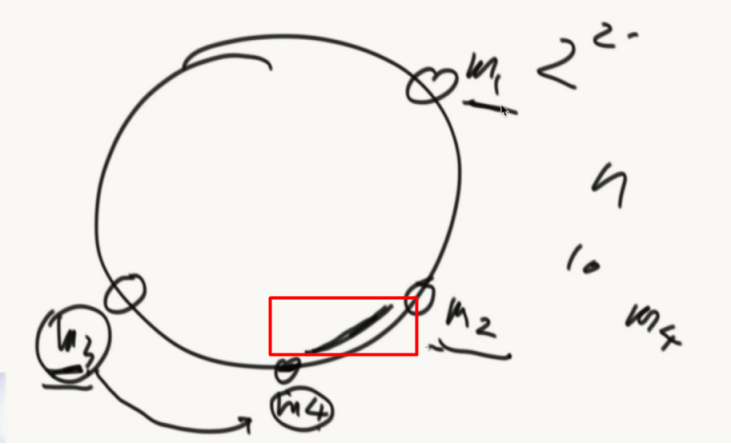
在机器数量小的时候,不能确保机器均匀分布。
什么技术可以解决这个问题?
虚拟节点技术。
给M1/M2/M3,1000个虚拟节点。
准备一张路由表,虚拟节点可以找到自己对应的节点。
把3000个节点。存入环中,那么机器们负责的数据就差不多一样了
新增了M4之后,也加入1000个节点,把相应的数据进行调整。
几乎所有需要集群化都进行了一致性哈希的改造。
题目五
岛问题
一个矩阵中只有0和1两种值,每个位置都可以和自己的上、下、左、右四个位置相连,如果有一片1连在一起,这个部分叫做一个岛,求一个矩阵中有多少个岛?
举例:
0 0 1 0 1 0
1 1 1 0 1 0
1 0 0 1 0 0
0 0 0 0 0 0
这个矩阵中有三个岛。
如果矩阵巨大无比,但是有几个CPU,设计一个多任务并行的算法。
经典解法:
遍历矩阵,碰到1就启动感染函数(递归改变数值的函数),把1周围的变为2,岛屿+1,直到遍历结束。

public class Code_03_Islands { public static int countIslands(int[][] m) { if (m == null || m[0] == null) { return 0; } int N = m.length; int M = m[0].length; int res = 0; for (int i = 0; i < N; i++) { for (int j = 0; j < M; j++) { if (m[i][j] == 1) { res++; infect(m, i, j, N, M); } } } return res; } public static void infect(int[][] m, int i, int j, int N, int M) { if (i < 0 || i >= N || j < 0 || j >= M || m[i][j] != 1) { return; } m[i][j] = 2; infect(m, i + 1, j, N, M); infect(m, i - 1, j, N, M); infect(m, i, j + 1, N, M); infect(m, i, j - 1, N, M); } public static void main(String[] args) { int[][] m1 = { { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0 }, { 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 }, { 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, }; System.out.println(countIslands(m1)); int[][] m2 = { { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1, 0 }, { 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 0 }, { 0, 1, 1, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0, 0 }, }; System.out.println(countIslands(m2)); } }
多任务解题思路:
要解决合并岛的问题
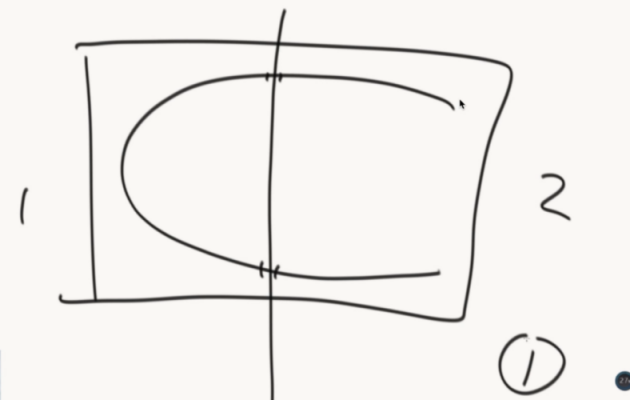
把岛的数量和边界信息存储起来。
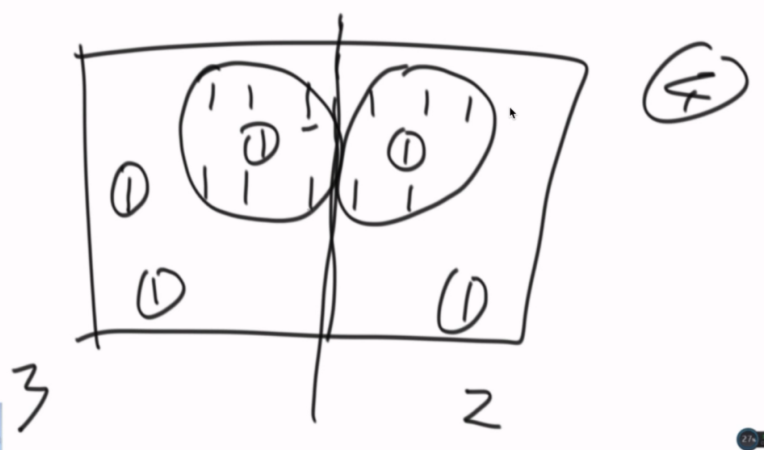
边界信息要如何合并:
标记感染中心。(并查集应用)
看边界A和边界C是否合并过,没有就合并(指向同一个标记),岛数量减一。
如何一路下去会碰到B和C,再次检查,合并,岛减一。
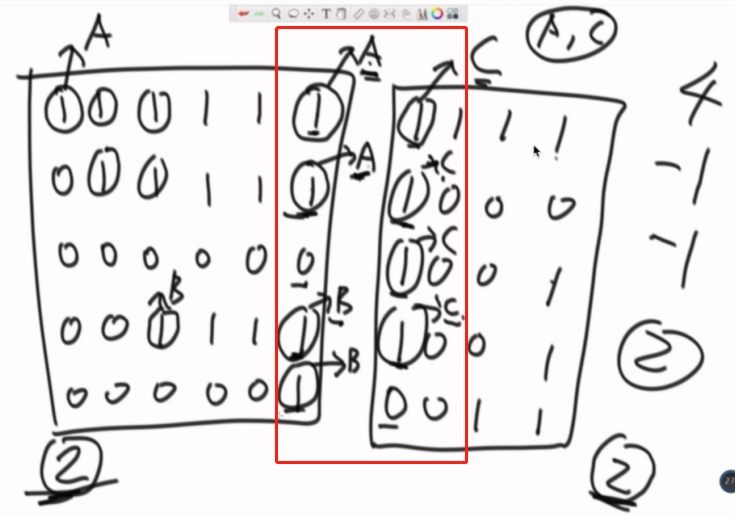
连成一片的这个概念,用并查集这个结构能非常好做,在结构上,怎么避免已经合完的部分,不重复减岛这个问题,用并查集来解决。
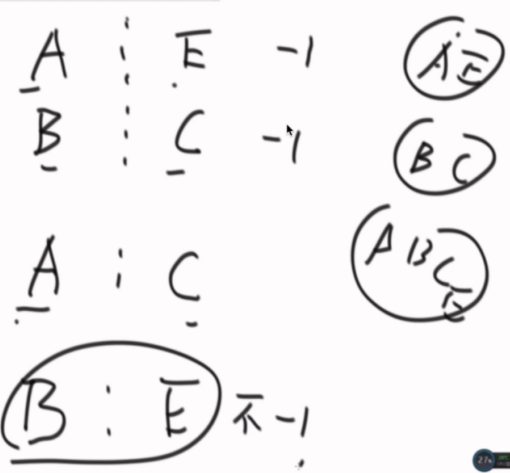
多边界的话就是收集的信息多一点而已,合并思路是一样的。
可以把边界信息都扔在一个并查集里面合并。(和面试官吹水的部分)
可以分成多个部分给多个CPU操作,得到结果后再合并最后的结果。(看具体情况,可使用二分法)

题目六
认识并查集结构(用之前给所有的数据)
1、非常快的检查两个元素是否在同一个集合。isSameSet
2、两个元素各种所在的集合,合并在一起。Union(元素,元素)

使用list的话合并快,查询是否在同一个集合慢。
使用set的话查询快,合并慢。
自己指向自己的就是代表节点。
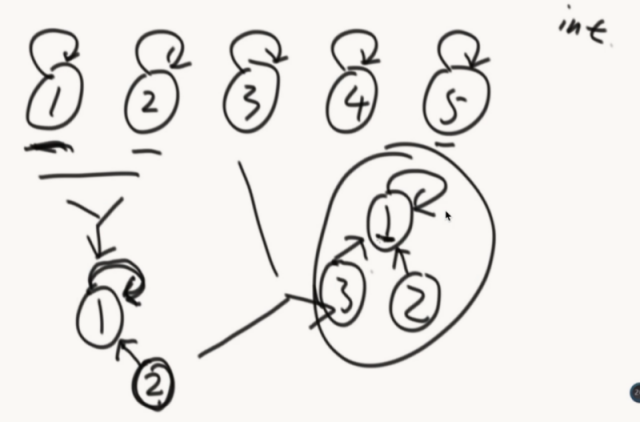
A/B向上找代表节点,相同就是在同一个集合。
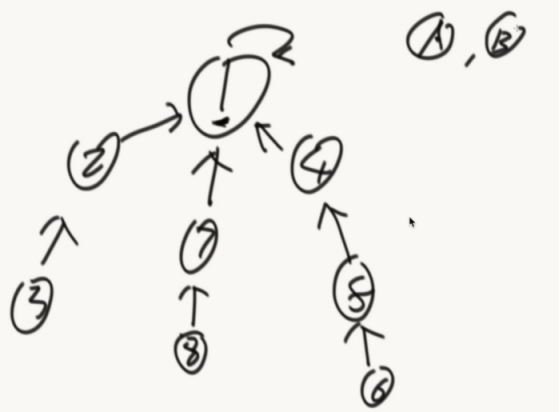
怎么合并
少元素的挂在多元素的底下。
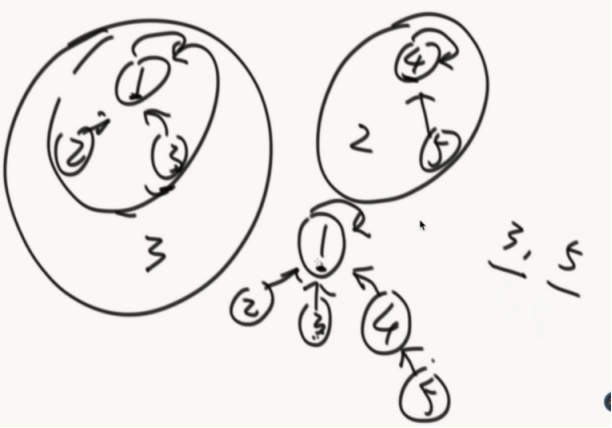
优化:(路径压缩)
在一次查询后,把路径上的节点统一打平。

public class Code_04_UnionFind { public static class Node { // whatever you like } public static class UnionFindSet { public HashMap<Node, Node> fatherMap; public HashMap<Node, Integer> sizeMap; //创建的时候就要一次性导入所有的节点 public UnionFindSet(List<Node> nodes) { fatherMap = new HashMap<Node, Node>(); sizeMap = new HashMap<Node, Integer>(); makeSets(nodes); } private void makeSets(List<Node> nodes) { fatherMap.clear(); sizeMap.clear(); for (Node node : nodes) { fatherMap.put(node, node);//一开始自己是自己的父亲 sizeMap.put(node, 1);//大小为1 } } private Node findHead(Node node) { //非递归版本 Stack<Node> Nodes = new Stack<>(); Node cur = node; Node parent = fatherMap.get(cur); while(cur != parent){ Nodes.push(cur); cur = parent; parent = fatherMap.get(cur); } while(!Nodes.isEmpty()){ fatherMap.put(Nodes.pop(),parent); } return parent; //递归版本 /* //获得节点的父节点 Node father = fatherMap.get(node); if (father != node) {//这样找是因为头节点是自己指向自己的 //一路向上找父节点 father = findHead(father); } fatherMap.put(node, father);//路径压缩 return father;*/ } public boolean isSameSet(Node a, Node b) { return findHead(a) == findHead(b); } public void union(Node a, Node b) { if (a == null || b == null) { return; } Node aHead = findHead(a); Node bHead = findHead(b); if (aHead != bHead) { int aSetSize= sizeMap.get(aHead); int bSetSize = sizeMap.get(bHead); if (aSetSize <= bSetSize) {//a小于b fatherMap.put(aHead, bHead); sizeMap.put(bHead, aSetSize + bSetSize); } else {//a大于b fatherMap.put(bHead, aHead); sizeMap.put(aHead, aSetSize + bSetSize); } } } } public static void main(String[] args) { } }
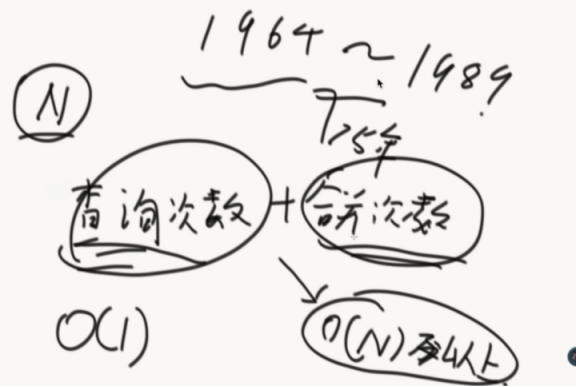
并查集是1964年别人脑补的一个算法,到证明结束是1989年,这个证明也是够漫长的。
并查集的效率非常高,当有N个数据的时候,假设查询次数到了N之后,其时间复杂度仅为o(1)!!
查询次数+合并次数逼近o(n)以上,平均时间复杂度o(1)
作者: kent鹏
出处: http://www.cnblogs.com/xieyupeng/
关于作者:专注JAVAEE领域,请多多赐教!
本文版权归作者和博客园共有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文链接。



