package Test;
public class Computer {
public static int getFac(int n) {
if(n == 1|| n==0)
return 1;
else
//递归调用
return n*getFac(n-1);
}
}
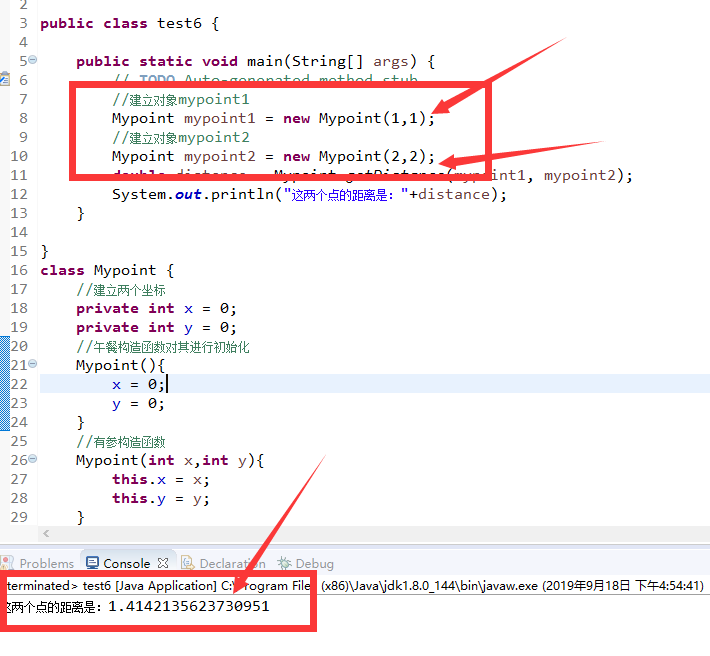
package Apppackage;
import Test.Computer;
public class app {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
Computer computer = new Computer();
int total = computer.getFac(5);
System.out.println(total);
}
}
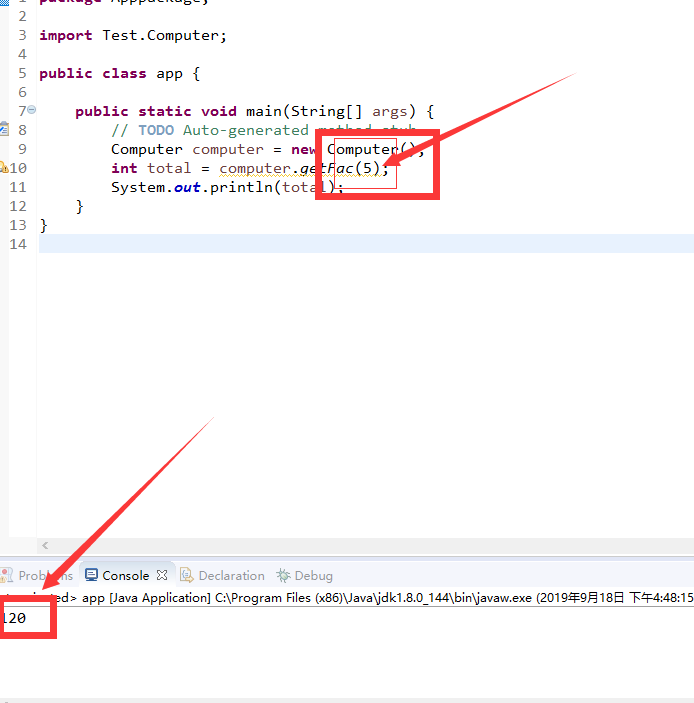
package Test;
public class test6 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// TODO Auto-generated method stub
//建立对象mypoint1
Mypoint mypoint1 = new Mypoint(1,1);
//建立对象mypoint2
Mypoint mypoint2 = new Mypoint(2,2);
double distance = Mypoint.getDistance(mypoint1, mypoint2);
System.out.println("这两个点的距离是:"+distance);
}
}
class Mypoint {
//建立两个坐标
private int x = 0;
private int y = 0;
//午餐构造函数对其进行初始化
Mypoint(){
x = 0;
y = 0;
}
//有参构造函数
Mypoint(int x,int y){
this.x = x;
this.y = y;
}
//设置一系列的访问器和修改器
public int getX() {
return x;
}
public void setX(int x) {
this.x = x;
}
public int getY() {
return y;
}
public void setY(int y) {
this.y = y;
}
public static double getDistance(Mypoint mypoint1,Mypoint mypoint2) {
//通过数学类对传进来的两个点进行计算两个点的距离
double distance = Math.sqrt(Math.pow((mypoint1.getX()-mypoint2.getX()), 2)+Math.pow((mypoint1.getY()-mypoint2.getY()), 2));
//返回给调用者
return distance;
}
}