基本MVVM 和 ICommand用法举例(转)
引言
在本贴中,我们将学习WPF Commands。 Commands 可以很好地与 MVVM 模式 (Model- View-ViewModel)结合在一起。我们也将看到,视图(view)实际上是怎样知道和怎样调用它的使用WPF 命令( Commands )的视图模型(ViewModel)。
背景
下面我们一步一步讨论而不是立即查看完整的代码,这也可以较好地帮助我们理解代码的每一部分。
让我们看一下MVVM的体系结构。
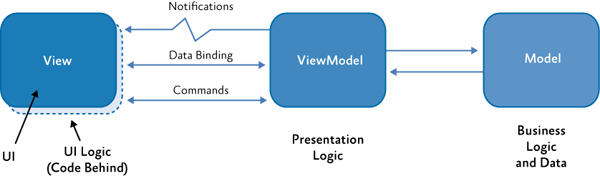
我们约定使用下列标准术语:
Views 表示后缀为view的文件名。(例如:StudentListView)ViewModels 表示后缀为ViewModel的文件。(例如:StudentListViewModel)Models 表示后缀为Model的文件。StudentModel).
使用代码
原理介绍已经足够了。下面深入代码了解一个可以工作的MVVM例子,了解怎样在MVVM使用命令。
使用 Visual Studio 建立一个新WPF项目。按照上面的约定,把文件名MainWindow更改为 MainWindowView。
接着,我们需要建立一个新的类,名字为 MainWindowViewModel ,它将担当视图MainWindowView的视图模型(ViewModel)。
我们在这里所做的是,在MVVM内,我们告诉视图,它的视图模型是什么。这可以通过为视图设置 Data Context来完成。在视图模型文件里有ViewModel,然而他们现在还不具有某些特定的视图之间的任何连接。
设置Datacontext的代码看起来是下面的样子。
打开 MainWindowView.xaml.cs并设置 data context 如下。
MainWindowView.xaml.cs
<Window x:Class="WpfExample.MainWindowView"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="MainWindow" Height="350" Width="525"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WpfExample">
<Window.DataContext>
<local:MainWindowViewModel/>
</Window.DataContext>
<Grid>
</Grid>
</Window>
这里的本地命名空间别名为WpfExample。这是必要的,这样 framework知道MainWindowViewModel在哪里可以找到。
我们通过一个简单的绑定来验证这个。
让我们添加一个button查看,使用视图模型的一个实例设置button的content 。
视图
添加一个查看按钮并设置它的绑定内容如下。
MainWindowView.xaml.cs
<Window x:Class=" WpfMvvmExample.MainWindow"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WpfMvvmExample"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="MainWindow" Height="350" Width="525">
<Window.DataContext>
<local:MainWindowViewModel/>
</Window.DataContext>
<Grid>
<Button Width="100"
Height="100" Content="{Binding ButtonContent}"/>
</Grid>
</Window>
视图模型
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
|
namespace WpfExample{ class MainWindowViewModel { public string ButtonContent { get { return "Click Me"; } } }} |
在上面代码中,我们告诉视图,从视图模型所呈现的ButtonContent属性获取按钮的内容。
<Button Width="100" Height="100" Content="{Binding ButtonContent}"/>
现在如果运行应用,我们可以看到按钮的内容为 字符串(string) “Click Me”.

这表明我们的MVVM可以正常工作。
现在我们转移到ICommand 接口(ICommand Interface)
现在,我们使用WPF命令为按钮添加一个点击功能。
在MVVM中,命令为通过视图更新模型提供了一种机制。
首先,我们看一下ICommand接口。
bool CanExecute(object parameter); void Execute(object parameter); event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged;
我们建立一个应用样板。当点击按钮时显示一个“HI"消息框,我们添加另一个按钮,切换hi按钮是否可以点击。
我们建立一个RelayCommand类,实现ICommand接口。这个类增强ICommand并分离代码作为一个独立的类。
This class acts as Enhancement for the ICommand and extracts the boiler plate code to a separate class.
public class RelayCommand : ICommand
{
private Action<object> execute; //定义成员
private Predicate<object> canExecute;//Predicate:述语//定义成员
private event EventHandler CanExecuteChangedInternal;//事件
public RelayCommand(Action<object> execute) //定义Action,CanExecute
: this(execute, DefaultCanExecute)
{
}
public RelayCommand(Action<object> execute, Predicate<object> canExecute)//定义
{
if (execute == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("execute");
}
if (canExecute == null)
{
throw new ArgumentNullException("canExecute");
}
this.execute = execute;
this.canExecute = canExecute;
}
public event EventHandler CanExecuteChanged //CanExecuteChanged事件处理方法
{
add
{
CommandManager.RequerySuggested += value;
this.CanExecuteChangedInternal += value;
}
remove
{
CommandManager.RequerySuggested -= value;
this.CanExecuteChangedInternal -= value;
}
}
public bool CanExecute(object parameter) //CanExecute方法
{
return this.canExecute != null && this.canExecute(parameter);
}
public void Execute(object parameter) //Execute方法
{
this.execute(parameter);
}
public void OnCanExecuteChanged() //OnCanExecute方法
{
EventHandler handler = this.CanExecuteChangedInternal;
if (handler != null)
{
//DispatcherHelper.BeginInvokeOnUIThread(() => handler.Invoke(this, EventArgs.Empty));
handler.Invoke(this, EventArgs.Empty);
}
}
public void Destroy() //销毁方法
{
this.canExecute = _ => false;
this.execute = _ => { return; };
}
private static bool DefaultCanExecute(object parameter) //DefaultCanExecute方法
{
return true;
}
}
CommandManager.RequerySuggested 负责使能和禁用 "Click to Hii" 按钮.
视图
<Window x:Class="WpfExample.MainWindowView"
xmlns="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml/presentation"
xmlns:x="http://schemas.microsoft.com/winfx/2006/xaml"
Title="MainWindow" Height="350" Width="525"
xmlns:local="clr-namespace:WpfExample">
<Window.DataContext>
<local:MainWindowViewModel/>
</Window.DataContext>
<Grid>
<Grid.RowDefinitions>
<RowDefinition />
<RowDefinition/>
</Grid.RowDefinitions>
<Button Grid.Row="0" Command="{Binding HiButtonCommand}"
CommandParameter="Hai" Content="{Binding HiButtonContent}"
Width="100"
Height="100" />
<Button Grid.Row="1" Content="Toggle Can Click"
Command="{Binding ToggleExecuteCommand}" Width="100" Height="100"/>
</Grid>
</Window>
视图模型
class MainWindowViewModel
{
private ICommand hiButtonCommand;
private ICommand toggleExecuteCommand { get; set; }
private bool canExecute = true; //初始化为true
public string HiButtonContent //定义公开属性
{
get
{
return "click to hi";
}
}
public bool CanExecute //定义公开属性
{
get
{
return this.canExecute;
}
set
{
if (this.canExecute == value)
{
return;
}
this.canExecute = value;
}
}
public ICommand ToggleExecuteCommand //定义接口
{
get
{
return toggleExecuteCommand;
}
set
{
toggleExecuteCommand = value;
}
}
public ICommand HiButtonCommand //定义接口
{
get
{
return hiButtonCommand;
}
set
{
hiButtonCommand = value;
}
}
public MainWindowViewModel() //构造函数
{
HiButtonCommand = new RelayCommand(ShowMessage, param => this.canExecute);
toggleExecuteCommand = new RelayCommand(ChangeCanExecute);
}
public void ShowMessage(object obj) //消息 方法
{
MessageBox.Show(obj.ToString());
}
public void ChangeCanExecute(object obj) //方法
{
canExecute = !canExecute;
}
}
最后的运行结果好像是这样:



