java基础,集合,HashMap,源码解析
最怕,你以为你懂咯,其实你还不懂;
见贤思齐,看看那些我们习以为常的集合,通过相关定义、源码,思考分析,加深对其的理解,提高编码能力,能做一个略懂的程序员;
做几个我们常用的集合类。开篇HashMap
HashMap
1、基于哈希表的 Map 接口的实现。此实现提供所有可选的映射操作,并允许使用 null 值和 null 键。
2、为什么允许null的key呢?
因为在put方法,会对是null值的可以进行特殊处理
1 private V putForNullKey(V value) { 2 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[0]; e != null; e = e.next) { 3 if (e.key == null) { 4 V oldValue = e.value; 5 e.value = value; 6 e.recordAccess(this); 7 return oldValue; 8 } 9 } 10 modCount++; 11 addEntry(0, null, value, 0); 12 return null; 13 }
3、默认大小:16,临界因子是:0.75,达到临界因子的时候,初始时候的长度就会扩大一倍,即 length*2,永永是2的倍数,当达到
内部的table 使用while循环将原来entry 赋值到新的entry 中(这一步往往影响性能)
HashMap由数组+链表组成的
1 //初始化大小 2 static final int DEFAULT_INITIAL_CAPACITY = 16; 3 //1左移30位 4 static final int MAXIMUM_CAPACITY = 1 << 30; 5 //临界因子 6 static final float DEFAULT_LOAD_FACTOR = 0.75f; 7 8 9 void addEntry(int hash, K key, V value, int bucketIndex) { 10 if ((size >= threshold) && (null != table[bucketIndex])) { 11 resize(2 * table.length);//长度扩大两倍,进行交换 12 hash = (null != key) ? hash(key) : 0; 13 bucketIndex = indexFor(hash, table.length); 14 } 15 16 createEntry(hash, key, value, bucketIndex); 17 } 18 19 20 void resize(int newCapacity) { 21 Entry[] oldTable = table; 22 int oldCapacity = oldTable.length; 23 if (oldCapacity == MAXIMUM_CAPACITY) { 24 threshold = Integer.MAX_VALUE; 25 return; 26 } 27 28 Entry[] newTable = new Entry[newCapacity]; 29 boolean oldAltHashing = useAltHashing; 30 useAltHashing |= sun.misc.VM.isBooted() && 31 (newCapacity >= Holder.ALTERNATIVE_HASHING_THRESHOLD); 32 boolean rehash = oldAltHashing ^ useAltHashing; 33 transfer(newTable, rehash); 34 table = newTable; 35 threshold = (int)Math.min(newCapacity * loadFactor, MAXIMUM_CAPACITY + 1); 36 } 37 38 //交换元素 39 void transfer(Entry[] newTable, boolean rehash) { 40 int newCapacity = newTable.length; 41 for (Entry<K,V> e : table) { 42 while(null != e) { 43 Entry<K,V> next = e.next; 44 if (rehash) { 45 e.hash = null == e.key ? 0 : hash(e.key); 46 } 47 int i = indexFor(e.hash, newCapacity); 48 e.next = newTable[i]; 49 newTable[i] = e; 50 e = next; 51 } 52 } 53 }
1 public synchronized V put(K key, V value) { 2 // hashtable 是不允许null值的 3 if (value == null) { 4 throw new NullPointerException(); 5 } 6 ...}
3、由于hashmap扩容的问题,所以使用hashmap保存较大的数的时候,尽量设置好长度,不然影响效率;
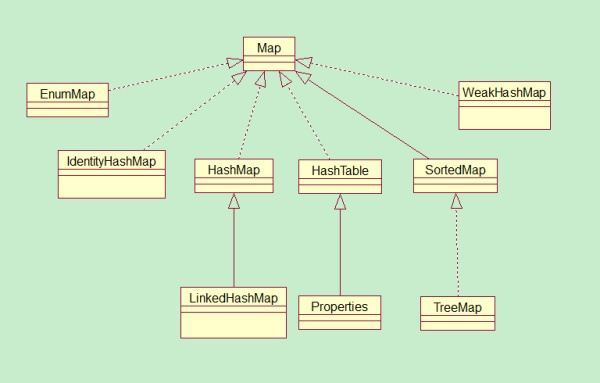
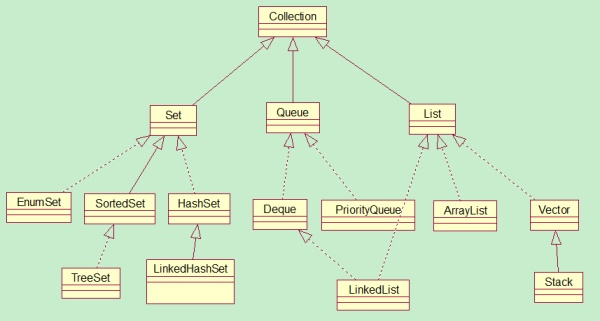
4、hashmap继承关系 对比右边是hashtable的继承关系,一个继承的是AbstractMap,另外一个是Dictionary
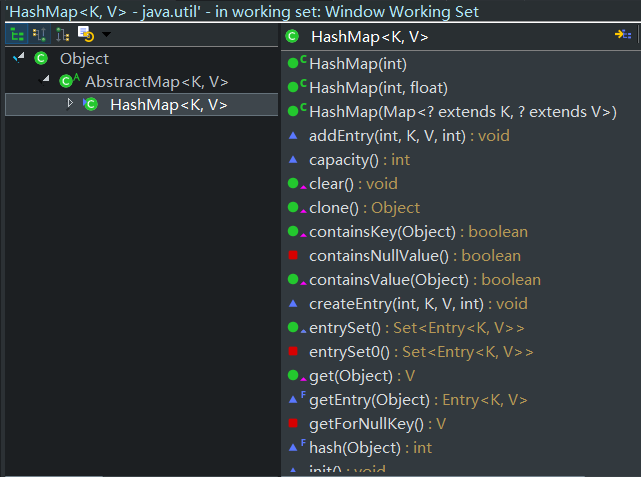
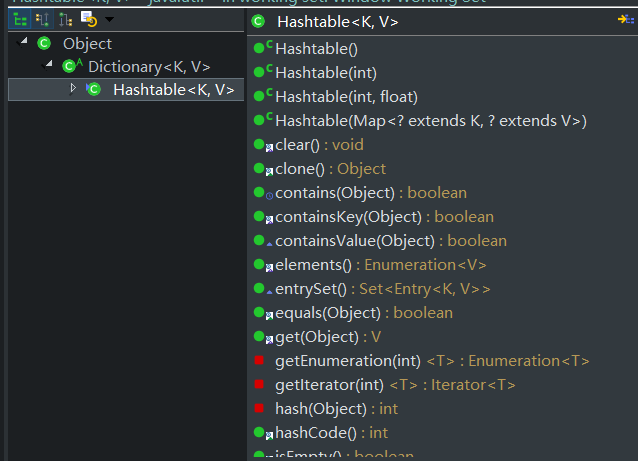
5、当put新key值相同,value值不同的时候,hashmap中entry会将,会将新的值付给原来key中的value,
put方法有返回值,出现value值替换的时候会返回原来的值,其他情况返回的是 null
1 public V put(K key, V value) { 2 if (key == null) 3 return putForNullKey(value); 4 int hash = hash(key); 5 int i = indexFor(hash, table.length); 6 for (Entry<K,V> e = table[i]; e != null; e = e.next) { 7 Object k; 8 if (e.hash == hash && ((k = e.key) == key || key.equals(k))) { 9 V oldValue = e.value; 10 e.value = value; 11 e.recordAccess(this); 12 return oldValue; 13 } 14 } 15 16 modCount++; 17 addEntry(hash, key, value, i); 18 return null; 19 }
6、对比的话,不是线程安全
hashtable,hashmap对比主要是线程安全问题;hashtable的方法中很多都有synchronized的同步设置;
LinkedHashMap 是HashMap的一个子类,保存了记录的插入顺序,在用Iterator遍历LinkedHashMap时,先得到的记录肯定是先插入的.也可以在构造时用带参数,按照应用次数排序。
LinkedHashMap在遍历的时候会比HashMap慢,
LinkedHashMapkey可以是null,只是重写init 以及get的方法
7、有containkey containvalue 方法
8、hashmap遍历的方法有什么?
hashmap实现map接口,所以就可以使用keyset,entrySet(),values(),以及Iterator<Map.Entry<String, String>> it = map.entrySet().iterator(); (map实现的iterator接口实现遍历)



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号