Struts学习总结(1)
Struts是一个开源框架,是apache的Jakarta项目组开发的,是对MVC设计模式的一种实现。
Struts2.x是基于WebWork的,因此Struts1.x和Struts2.x有很大的不同。
一、Struts和传统MVC之间的联系

二、Struts配置
因为Struts手工配置比较麻烦,因此一般都是通过MyEclipse进行配置。
新建web工程后,需要添加struts的包,可以发现,有一些文件都是预先建好了,比如
(1)struts-config.xml就是struts中核心的配置文件,在这个文件中可以配置Action和ActionForm等;
(2)web.xml配置ActionServlet和标签库的映射;
(3)ApplicationResource.properties是资源文件;
注意:资源文件不支持中文,因此如果想要在里面添加中文,则需要转换为Unicode码,通过native2ascii.exe转换;
常用配置:
(1)配置ActionForm:
<form-beans>
<form-bean name=" 名称 " type=" 所属类 "/>
</form-beans>
(2)配置Action:
<action-mappings>
<action attribute="form名称" input="错误页" name="form名称" path=" Action路径" scope="范围" type=" 所属类 " />
</action-mappings>
(3)配置forward:
<action>
<forward name="跳转名称" path="路径"></forward>
</action>
(4)配置资源名称:
<message-resources parameter="资源文件名称"/>
(5)配置tld文件:
struts也有自己的标签库,而标签库描述文件是在WEB-INF/lib/struts-taglib-1.3.10.jar\META-INF\tld中;
将tld文件放到WEB-INF文件夹中;
并且在web.xml中配置如下:
<jsp-config> <taglib> <taglib-uri>struts/bean</taglib-uri> <taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-bean.tld</taglib-location> </taglib> <taglib> <taglib-uri>struts/logic</taglib-uri> <taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-logic.tld</taglib-location> </taglib> <taglib> <taglib-uri>struts/html</taglib-uri> <taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-html.tld</taglib-location> </taglib> <taglib> <taglib-uri>struts/nested</taglib-uri> <taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-nested.tld</taglib-location> </taglib> <taglib> <taglib-uri>struts/tiles</taglib-uri> <taglib-location>/WEB-INF/struts-tiles.tld</taglib-location> </taglib> </jsp-config>
三、struts入门标签了解
<html:text property="info"></html:text>是一个名为info的文本框;
<html:errors/>表示显示全部的错误。这些错误都是通过ActionErrors进行保存的;
<logic:present name="info" scope="page">
${info}
</logic:present>
表示如果info这个属性存在,则输出;如果不存在,则跳过。
<html:form action=" " method=" "></html:form>
注意:action的提交路径需要根据struts-config.xml中的action的path属性+web.xml中的url-pattern决定;比如:url-pattern= *.do ; path属性为/hello,则提交路径为/hello.do;
四、ActionForm类入门
ActionForm主要用于验证,与JavaBean一样,比如提交了两个属性,String info1,String info2,则在继承ActionForm的类中也要用两个同名属性,并实现getter、setter方法;
ActionForm方法:
(1)public ActionErrors validate(ActionMapping mapping,HttpServletRequest req);验证功能:
(2)public void reset(ActionMapping mapping,HttpServletRequest req);重置功能;
注意:
(1)ActionForm中的属性是自动赋值的,而不需要手动赋值,即如果表单提交并进入ActionForm进行验证,则ActionForm的属性被赋值为提交的值;
(2)如果validate返回的ActionErrors为空即验证成功,则进行Action处理;如果验证失败,则跳转到struts-config.xml中的input属性的页面;
五、ActionErrors、ActionMessage类入门
ActionErrors用于保存很多的错误信息;ActionMessage用于保存一条错误信息;
ActionMessage常用方法:
(1)ActionMessage message = new ActionMessage(String key);
参数key是在ApplicationResource.properties中进行配置,比如在资源文件中配置:error.msg=abc;
则当执行ActionMessage messge = new ActionMessage("error.msg");时,就会保存abc;用以显示;
ActionErrors常用方法:
(1)ActionErrors errors = new ActionErrors();
(2)errors.add(String name,ActionMessage message);
六、Action类入门
Action类似于MVC中的Servlet,Action中常用方法:
(1)public ActionForward execute(ActionMapping mapping,ActionForm form,HttpServletRequest req,HttpServletResponse resp); 接受ActionForm的参数,并进行一些操作。
(2)public void saveErrors(HttpServletRequest req, ActionErrors errors); 保存错误信息,以供<html:errors/>显示;
(3)public void saveMessages(HttpServletRequest req,ActionMessages messages);
一般地,都是super.saveErrors(request,errors);进行调用;
七、ActionMapping类入门
用于跳转;常用方法:
(1)public ActionForward findForward(String forward); 在struts-config.xml 中已经配置好了<forward>标签,forward参数需要设置为标签的name属性;
(2)public ActionForward getInputForward();获得input属性设置的错误跳转页并进行跳转;
八、具体struts流程
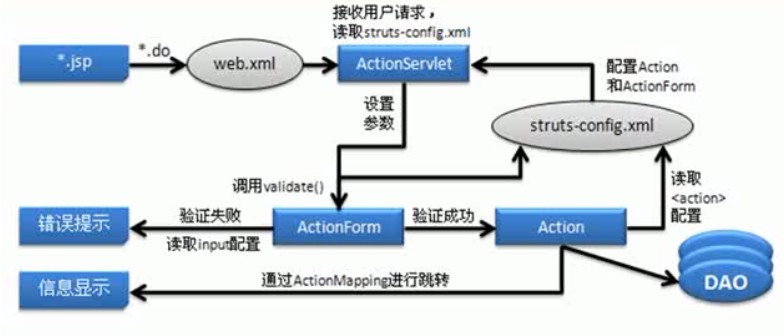
(1)JSP发送请求,并且ActionServlet接收;
(2)ActionServlet通过struts-config.xml调用ActionForm执行(调用validate方法);
(3)ActionServlet调用Action执行;
(4)Action进行跳转并显示结果;


