java通过异常处理错误
1.创建自定义异常
要自己定义异常类,必须从已有的异常类继承
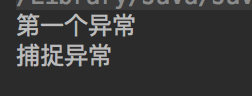
package demo3; class FirstException extends Exception { } public class InheritingException{ public void f() throws FirstException{ System.out.println("第一个异常"); throw new FirstException(); } public static void main(String[] args){ InheritingException exception = new InheritingException(); try { exception.f(); }catch (FirstException e){ System.out.println("捕捉异常"); } } }
运行结果
也可以为异常类定义一个接受字符串参数的构造器
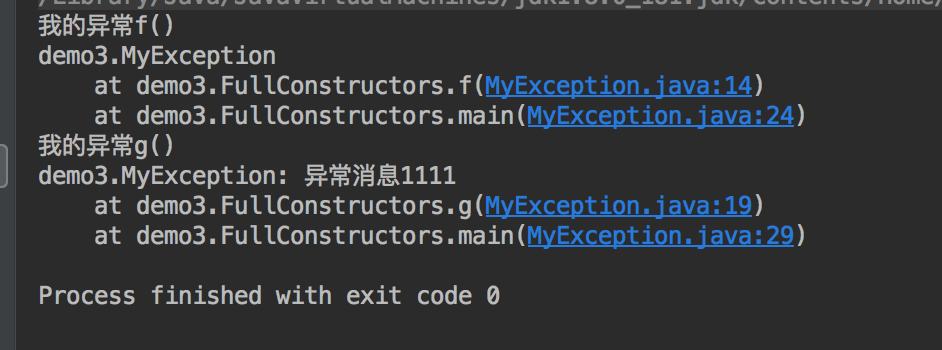
package demo3; public class MyException extends Exception{ public MyException() { } public MyException(String msg) { super(msg); } } class FullConstructors{ public static void f() throws MyException{ System.out.println("我的异常f()"); throw new MyException(); } public static void g() throws MyException{ System.out.println("我的异常g()"); throw new MyException("异常消息1111"); } public static void main(String[] args){ try { f(); }catch (MyException e){ e.printStackTrace(System.out); } try { g(); }catch (MyException e){ e.printStackTrace(System.out); } } }
运行结果
2.异常与记录日志
public class LoggingException extends Exception { private static Logger logger = Logger.getLogger("LoggingException"); public LoggingException() { StringWriter trace = new StringWriter(); printStackTrace(new PrintWriter(trace)); logger.severe(trace.toString()); } } class testException{ public static void main(String[] args){ try { throw new LoggingException(); } catch (LoggingException e){ System.err.println("捕捉到异常:"+e); } try { throw new LoggingException(); }catch (LoggingException e){ System.err.println("捕捉到异常"+e); } } }
运行结果

3.使用finally进行清理
对于一些代码,可能会希望无论try块中的一场是否抛出,他们都能得到执行,这通常适用于内存回收之外的情况。可以再异常处理程序后面加上finally子句。
package demo3; class ThreeException extends Exception {} public class Finally { static int count = 0; public static void main(String[] args){ while (true){ try { if (count++ == 0){ throw new ThreeException(); } System.out.println("无异常"); }catch (ThreeException e){ System.out.println("ThreeException"); }finally { System.out.println("finally"); if (count ==2){ break; } } } } }
运行结果

在return中使用finally
因为finally自居总是会执行的,所以在一个方法中,可以从多个点返回,并且可以保证重要的清理工作仍旧会执行
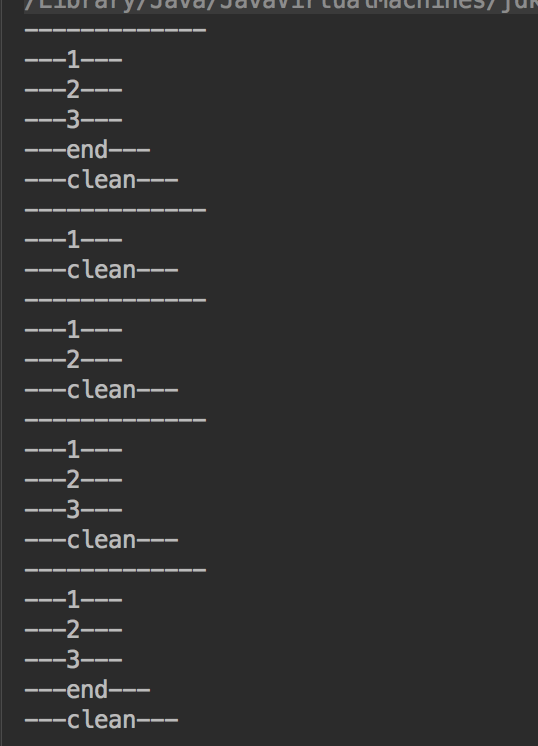
package demo3; public class MultipleReturns { public static void f(int i ){ System.out.println("-------------"); try { System.out.println("---1---"); if (i == 1){ return; } System.out.println("---2---"); if (i == 2) return; System.out.println("---3---"); if (i==3)return; System.out.println("---end---"); return; }finally { System.out.println("---clean---"); } } public static void main(String[] args){ for (int i = 0;i<= 4 ;i++){ f(i); } } }
运行结果