分水岭
一、问题
最近遇到一个需要统计物体个数的问题,由于有些物体贴的比较近,直接二值化后会存在相交区域,统计后会不太准确,本文借助分水岭算法先进行分割,然后再进行个数统计,这里对实现过程做一个记录。
二、分水岭算法
分水岭算法是一种基于拓扑理论的数学形态学的分割方法,其基本思想是把图像看作是测地学上的拓扑地貌,图像中每一像素的灰度值表示该点的海拔高度,每一个局部极小值及其影响区域称为集水盆地,而集水盆地的边界则形成分水岭。分水岭的概念和形成可以通过模拟浸入过程来说明,这里可以参考CMM(Centre de Morphologie Mathématique)提供的一个动图进行理解。

三、OpenCV分水岭算法
但是这种基于梯度的分水岭算法容易受到图片中噪声或者其他非规则区域形成很多小的盆地,从而造成图片过分割,针对这一缺点,Opencv提供了一种基于标记区域的分水岭算法,OpenCV提供的分水岭教程是分割硬币的例子,和我的情况有点类似,大致流程可以分为以下几步:
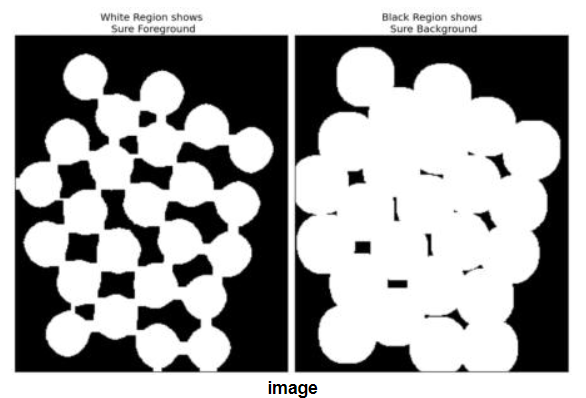
- step1: 确定背景区域
- step2: 确定前景区域
- step3: 确定未知区域
- step4: 得到标记区域
- step5: 原图和标记区域共同作为输入

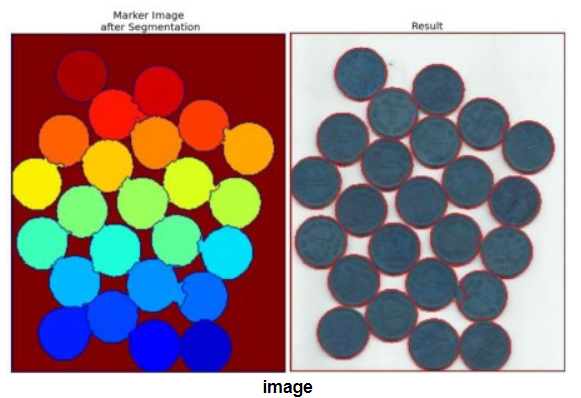
四、实现脚本
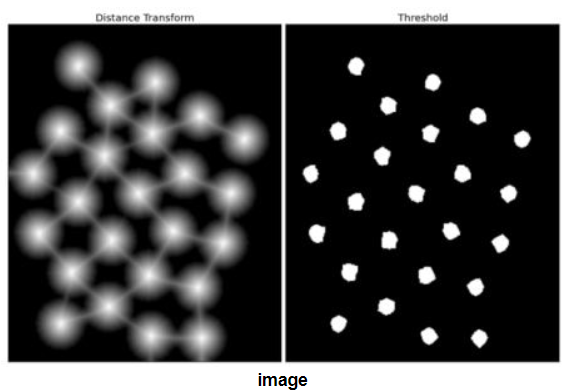
在查找种子区域的时候,依据实际情况设置了自动调节阈值, 最终得到的结果通过后处理即可统计个数。C++的实现过程可以见github
-
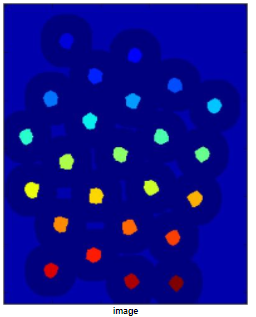
处理过程中热力图
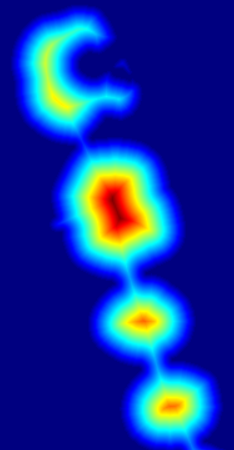
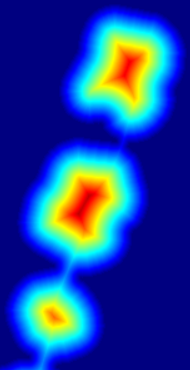
-
Python
import cv2
import numpy as np
def findBestSeed(dist):
ratio = 0.70
minVal, maxVal, minLoc, maxLoc = cv2.minMaxLoc(dist)
print("maxVal: ", maxVal, "minVal: ", minVal)
_, sure_fg = cv2.threshold(dist, ratio * maxVal, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
sure_fg = np.uint8(sure_fg)
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(sure_fg, 2, 2)
cnt_num = len(contours)
cnt_ratio = ratio
step = 0.05
# 根据具体情况进行设置,实现自动调节
while ratio >= 0.25:
if cnt_num >= 12:
break
ratio -= step
_, sure_fg = cv2.threshold(dist, ratio * maxVal, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
sure_fg = np.uint8(sure_fg)
contours, _ = cv2.findContours(sure_fg, 2, 2)
if len(contours) > cnt_num:
cnt_num = len(contours)
cnt_ratio = ratio
_, sure_fg = cv2.threshold(dist, cnt_ratio * maxVal, 255, cv2.THRESH_BINARY)
print("cnt_ratio", cnt_ratio)
return sure_fg
def watershed(img_path):
img = cv2.imread(img_path)
img_gray = cv2.cvtColor(img, cv2.COLOR_BGR2GRAY)
_, thresh = cv2.threshold(img_gray, 127, 255, 0)
kernel = cv2.getStructuringElement(cv2.MORPH_ELLIPSE, (3, 3))
thresh = cv2.morphologyEx(thresh, cv2.MORPH_OPEN, kernel)
# 生成种子区域
dist_img = cv2.distanceTransform(thresh, cv2.DIST_L2, cv2.DIST_MASK_PRECISE)
dist2 = cv2.normalize(dist_img, None, 255, 0, cv2.NORM_MINMAX, cv2.CV_8UC1)
heat_img = cv2.applyColorMap(dist2, cv2.COLORMAP_JET) # 生成热力图
cv2.imshow("heat", heat_img)
sure_fg = findBestSeed(dist2) # sure_fg.convertTo(sure_fg, CV_8U);
contours, hierarchy = cv2.findContours(sure_fg, 2, 2)
print("mark: ", len(contours))
# 查找未知区域
sure_fg = np.uint8(sure_fg)
sure_bg = cv2.dilate(thresh, kernel)
unknown = cv2.subtract(sure_bg, sure_fg)
# 查找标记区域
_, markers = cv2.connectedComponents(sure_fg)
# Add one to all labels so that sure background is not 0, but 1
markers = markers+1
# Now, mark the region of unknown with zero
markers[unknown == 255] = 0
# 分水岭算法
markers = cv2.watershed(img, markers)
img[markers == -1] = [0, 0, 0]
return img
if __name__ == "__main__":
img_path = r'E:\test.png'
img = watershed(img_path)
cv2.waitKey(0)
参考链接
Image Segmentation with Watershed Algorithm
python数字图像处理(19):骨架提取与分水岭算法
图像分割的经典算法:分水岭算法
OpenCV—图像分割中的分水岭算法原理与应用
基于opencv的重叠图像的凹点分割




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 因为Apifox不支持离线,我果断选择了Apipost!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端
2018-06-20 pandas练习(三)------ 数据分组