残差网络---ResNet
目录
———————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
论文:https://arxiv.org/pdf/1512.03385.pdf
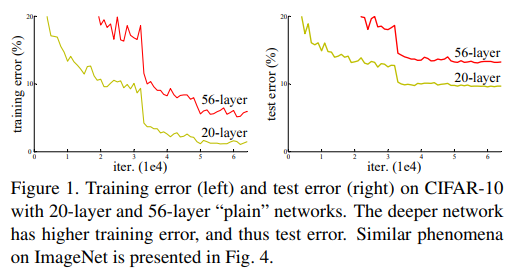
最近用到了ResNet残差网络,查看了原文和一些资料,在网易云课堂上学习了吴恩达老师介绍的残差网络,这里对学习的内容做一个简单的总结。我们都知道网络的宽度和深度可以很好的提高网络的性能,深的网络一般都比浅的的网络效果好,但训练一个很深的网络是非常困难的,一方面是网络越深越容易出现梯度消失和梯度爆炸问题, 然而这个问题通过BN层和ReLU激活函数等方法在很大程度上已经得到解决;另一方面当网络层数达到一定的数目以后,网络的性能就会趋于饱和,再增加网络层数的话性能就会开始退化,这说明当网络变得很深以后,网络就变得难以训练了。ResNet是2015年由何恺明等提出来的,曾在ImageNet中斩获图像分类、检测、定位三项的冠军,ResNet的提出很大程度上解决了网络退化问题(吴恩达老师解释的是梯度消失和爆炸问题)。
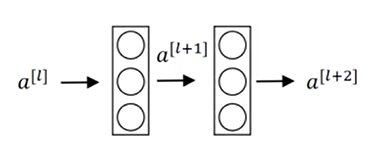
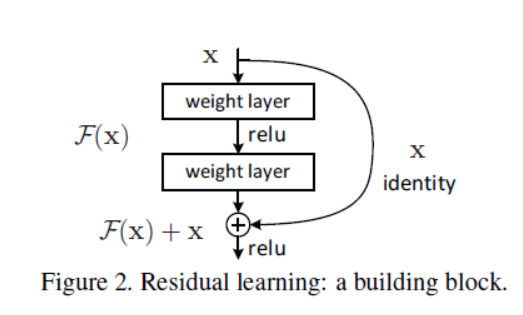
一、残差块(Residual Block)
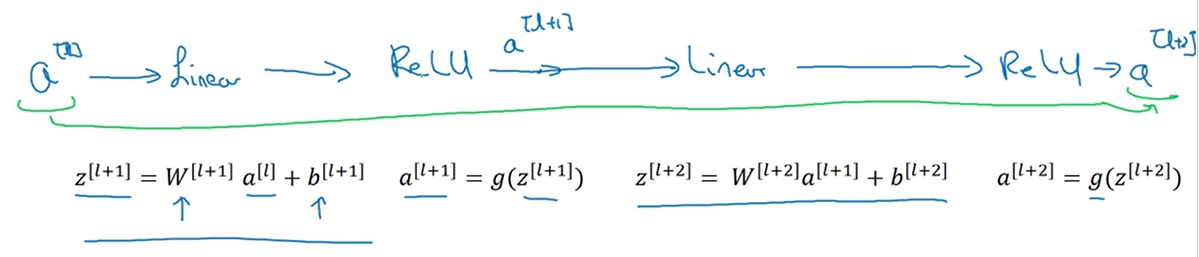
这里吴恩达老师课程中对残差块的介绍比较好理解,以一个两层神经网络为例,普通网络输入 首先经过线性变换生成,然后通过ReLU激活层输出 ,同样再经过一个线性变换生成,最后通过ReLU生成,最终
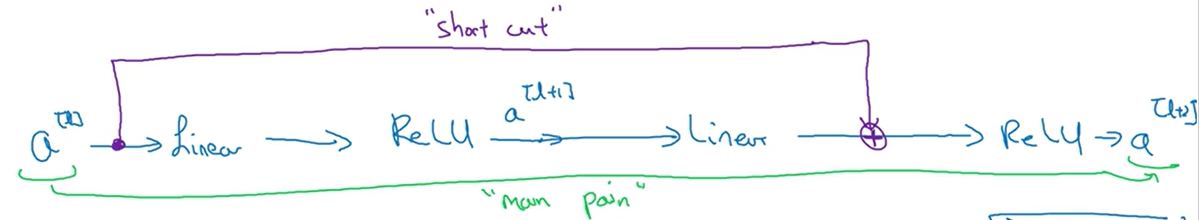
在残差网络中直接将连接到第二个线性变换和第二个ReLU激活层之间,形成一条更便捷的路径(short cut),此时变为,也就是加上后形成了一个残差块。
二、残差网络为什么有用?
- 前向
假设输入通过一个很深的网络后通过ReLU激活函数输出为,根据ReLU的特性此时,再其后面再接一个两层的残差块输出,则可以表示为
当和偏置都为0时,,这说明残差块学习这个恒等变换并不难,另外如果中间这两层学习到了一些其他有用的特征信息的话,它可能比学习恒等变换的效果更好,但是如果不加入残差块的话随着网络的不断加深,学习一个恒等变换的参数都可能变得很难,因此残差网络能在不减慢学习效率(恒等变换)的情况下还有可能提高模型的性能。

原文中如下图所示,设 为浅层输出,为深层输出,为中间层结果,当 表示的特征已经达到一个很好的程度时,中间层继续学习会导致损失增大,就会慢慢趋近于0,将从short cut路径继续往下传播,这样就实现了当浅层特征很好时,后面的深层网络能达到一个恒等变换的效果。
- 反向传播
一方面是残差块将输出 分成了 ,变换后,即从原来学习一个到的映射变为学习 与 之间的差值,这样学习任务变得更简单。 另一方面因为前向过程中存在short cut路径下的恒等映射,因此在反向传播过程中也存在这样一条捷径,只需要通过一个ReLU函数就可以将梯度传到上一个模块。
三、ResNet网络结构

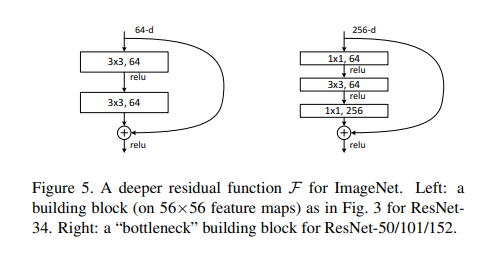
ResNet就是用这种残差块来作为网络的基本结构,在论文中,作者给出了不同层数的ResNet网络,包括18层、34层、50层、101层和152层,50层及以上的称为深度残差网络,它们网络结构如下图所示。深度残差网络和浅层残差网络的主要区别在于基本结构由原来的残差块(Residual Block)变为了瓶颈残差块(Residual Bottleneck),瓶颈残差块输出通道数为输入的四倍,而残差块输入和输出通道数相等,以50层的残差网络为例,在conv2_x层中包括了3个瓶颈残差块,第一层和最后一层的通道数相差4倍, 由原来的64变为了256。

四、代码实现
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 46 47 48 49 50 51 52 53 54 55 56 57 58 59 60 61 62 63 64 65 66 67 68 69 70 71 72 73 74 75 76 77 78 79 80 81 82 83 84 85 86 87 88 89 90 91 92 93 94 95 96 97 98 99 100 101 102 103 104 105 106 107 108 109 110 111 112 113 114 115 116 117 118 119 120 121 122 123 124 125 126 127 128 129 130 131 132 133 134 135 136 137 138 139 140 141 142 143 144 145 146 147 148 149 150 151 152 153 154 155 156 157 158 159 160 161 162 163 164 165 166 167 168 169 170 171 172 173 174 175 176 177 178 179 180 181 182 183 184 185 186 187 188 189 190 191 192 193 194 195 196 197 198 199 200 201 202 203 204 205 206 207 208 209 210 211 212 213 214 215 216 217 | from __future__ import print_function, division, absolute_importimport torch.nn as nnimport mathimport torch.utils.model_zoo as model_zoo__all__ = ['ResNet', 'resnet18', 'resnet34', 'resnet50', 'resnet101', 'resnet152']model_urls = { 'resnet18': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet18-5c106cde.pth', 'resnet34': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet34-333f7ec4.pth', 'resnet50': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet50-19c8e357.pth', 'resnet101': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet101-5d3b4d8f.pth', 'resnet152': 'https://download.pytorch.org/models/resnet152-b121ed2d.pth',}def conv3x3(in_planes, out_planes, stride=1): "3x3 convolution with padding" return nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=True)class BasicBlock(nn.Module): expansion = 1 def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None): super(BasicBlock, self).__init__() self.conv1 = conv3x3(inplanes, planes, stride) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes) self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) self.conv2 = conv3x3(planes, planes) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes) self.downsample = downsample self.stride = stride def forward(self, x): residual = x out = self.conv1(x) out = self.bn1(out) out = self.relu(out) out = self.conv2(out) out = self.bn2(out) if self.downsample is not None: residual = self.downsample(x) out += residual out = self.relu(out) return outclass Bottleneck(nn.Module): expansion = 4 def __init__(self, inplanes, planes, stride=1, downsample=None): super(Bottleneck, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(inplanes, planes, kernel_size=1, bias=True) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes) self.conv2 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=1, bias=True) self.bn2 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes) self.conv3 = nn.Conv2d(planes, planes * 4, kernel_size=1, bias=True) self.bn3 = nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * 4) self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) self.downsample = downsample self.stride = stride def forward(self, x): residual = x out = self.conv1(x) out = self.bn1(out) out = self.relu(out) out = self.conv2(out) out = self.bn2(out) out = self.relu(out) out = self.conv3(out) out = self.bn3(out) if self.downsample is not None: residual = self.downsample(x) out += residual out = self.relu(out) return outfrom torch.legacy import nn as nnlclass ResNet(nn.Module): def __init__(self, block, layers, num_classes=1000): self.inplanes = 64 super(ResNet, self).__init__() self.conv1 = nn.Conv2d(3, 64, kernel_size=7, stride=2, padding=3, bias=True) #self.conv1 = nnl.SpatialConvolution(3, 64, 7, 7, 2, 2, 3, 3) self.bn1 = nn.BatchNorm2d(64) self.relu = nn.ReLU(inplace=True) self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1) self.layer1 = self._make_layer(block, 64, layers[0]) self.layer2 = self._make_layer(block, 128, layers[1], stride=2) self.layer3 = self._make_layer(block, 256, layers[2], stride=2) self.layer4 = self._make_layer(block, 512, layers[3], stride=2) self.avgpool = nn.AvgPool2d(7) self.fc = nn.Linear(512 * block.expansion, num_classes) for m in self.modules(): if isinstance(m, nn.Conv2d): n = m.kernel_size[0] * m.kernel_size[1] * m.out_channels m.weight.data.normal_(0, math.sqrt(2. / n)) elif isinstance(m, nn.BatchNorm2d): m.weight.data.fill_(1) m.bias.data.zero_() def _make_layer(self, block, planes, blocks, stride=1): downsample = None if stride != 1 or self.inplanes != planes * block.expansion: downsample = nn.Sequential( nn.Conv2d(self.inplanes, planes * block.expansion, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, bias=True), nn.BatchNorm2d(planes * block.expansion), ) layers = [] layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes, stride, downsample)) self.inplanes = planes * block.expansion for i in range(1, blocks): layers.append(block(self.inplanes, planes)) return nn.Sequential(*layers) def forward(self, x): x = self.conv1(x) self.conv1_input = x.clone() x = self.bn1(x) x = self.relu(x) x = self.maxpool(x) x = self.layer1(x) x = self.layer2(x) x = self.layer3(x) x = self.layer4(x) x = self.avgpool(x) x = x.view(x.size(0), -1) x = self.fc(x) return xdef resnet18(pretrained=False, **kwargs): """Constructs a ResNet-18 model. Args: pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet """ model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [2, 2, 2, 2], **kwargs) if pretrained: model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet18'])) return modeldef resnet34(pretrained=False, **kwargs): """Constructs a ResNet-34 model. Args: pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet """ model = ResNet(BasicBlock, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs) if pretrained: model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet34'])) return modeldef resnet50(pretrained=False, **kwargs): """Constructs a ResNet-50 model. Args: pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet """ model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 6, 3], **kwargs) if pretrained: model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet50'])) return modeldef resnet101(pretrained=False, **kwargs): """Constructs a ResNet-101 model. Args: pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet """ model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 4, 23, 3], **kwargs) if pretrained: model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet101'])) return modeldef resnet152(pretrained=False, **kwargs): """Constructs a ResNet-152 model. Args: pretrained (bool): If True, returns a model pre-trained on ImageNet """ model = ResNet(Bottleneck, [3, 8, 36, 3], **kwargs) if pretrained: model.load_state_dict(model_zoo.load_url(model_urls['resnet152'])) return model |
参考连接




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:基于图像分类模型对图像进行分类
· go语言实现终端里的倒计时
· 如何编写易于单元测试的代码
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 25岁的心里话
· 闲置电脑爆改个人服务器(超详细) #公网映射 #Vmware虚拟网络编辑器
· 零经验选手,Compose 一天开发一款小游戏!
· 因为Apifox不支持离线,我果断选择了Apipost!
· 通过 API 将Deepseek响应流式内容输出到前端