实验2 类和对象_基础编程1
实验任务1:
代码:
t.h
查看代码
#pragma once
#include <string>
class T {
public:
T(int x = 0, int y = 0);
T(const T &t);
T(T &&t);
~T();
void adjust(int ratio);
void display() const;
private:
int m1, m2;
public:
static int get_cnt();
public:
static const std::string doc;
static const int max_cnt;
private:
static int cnt;
friend void func();
};
void func();t.cpp
查看代码
#include "t.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::string;
const std::string T::doc{"a simple class sample"};
const int T::max_cnt = 999;
int T::cnt = 0;
T::T(int x, int y): m1{x}, m2{y} {
++cnt;
cout << "T constructor called.\n";
}
T::T(const T &t): m1{t.m1}, m2{t.m2} {
++cnt;
cout << "T copy constructor called.\n";
}
T::T(T &&t): m1{t.m1}, m2{t.m2} {
++cnt;
cout << "T move constructor called.\n";
}
T::~T() {
--cnt;
cout << "T destructor called.\n";
}
void T::adjust(int ratio) {
m1 *= ratio;
m2 *= ratio;
}
void T::display() const {
cout << "(" << m1 << ", " << m2 << ")" ;
}
int T::get_cnt() {
return cnt;
}
void func() {
T t5(42);
t5.m2 = 2049;
cout << "t5 = "; t5.display(); cout << endl;
}task1.cpp
查看代码
#include "t.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "t.cpp"
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
void test();
int main() {
test();
cout << "\nmain: \n";
cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl;
}
void test() {
cout << "test class T: \n";
cout << "T info: " << T::doc << endl;
cout << "T objects'max count: " << T::max_cnt << endl;
cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl << endl;
T t1;
cout << "t1 = "; t1.display(); cout << endl;
T t2(3, 4);
cout << "t2 = "; t2.display(); cout << endl;
T t3(t2);
t3.adjust(2);
cout << "t3 = "; t3.display(); cout << endl;
T t4(std::move(t2));
cout << "t3 = "; t4.display(); cout << endl;
cout << "T objects'current count: " << T::get_cnt() << endl;
func();
}运行结果:
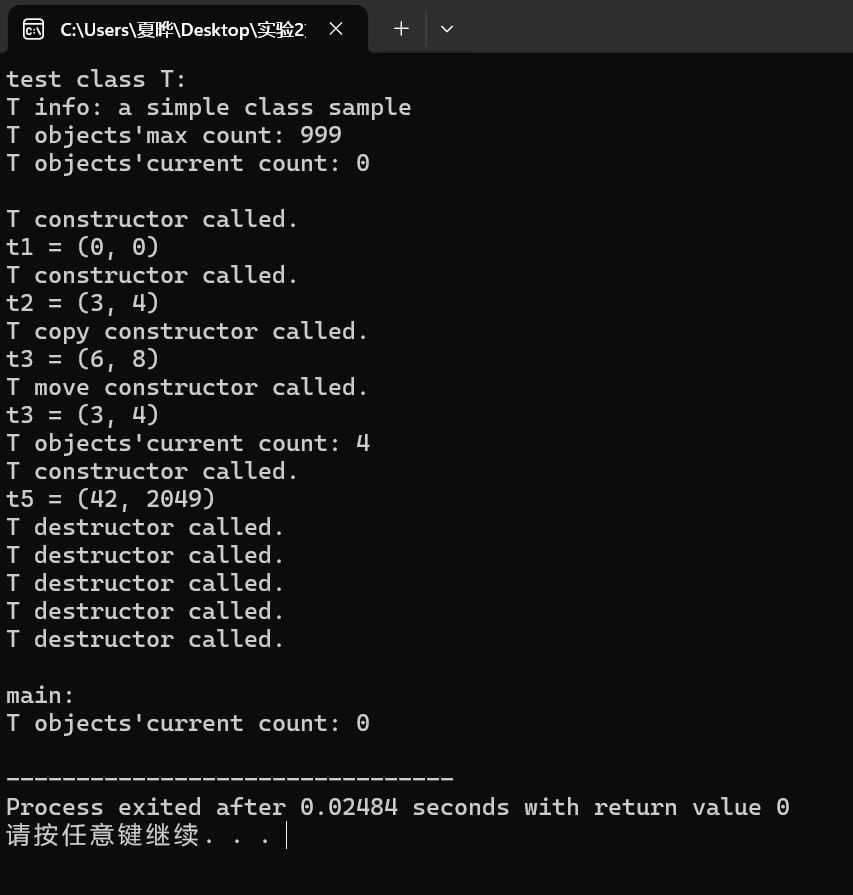
问题1:
不能运行,报错为![]()
可能是func不能访问T类的私有成员
问题2:
普通构造函数 T(int x = 0, int y = 0);
功能:创建 T 类对象,允许指定 m1 和 m2 的初始值
调用时机:参数创建对象
复制构造函数 T(const T &t);
功能:通过现有 T 类对象初始化新对象
调用时机:以现有对象初始化新对象
移动构造函数 T(T &&t);
功能:移动资源,减少不必要的拷贝
调用时机:使用 std::move 转换为右值引用
析构函数 ~T();
功能:执行清理操作
调用时机:程序结束时,调用析构函数
问题3:
不能,如果将静态成员变量的定义和初始化从t.cpp移动到t.h,会导致链接错误。
实验任务2:
代码:
Complex.h
查看代码
#ifndef COMPLEX_H
#define COMPLEX_H
#include <iostream>
#include <cmath>
class Complex {
public:
static const std::string doc;
Complex();
Complex(double real);
Complex(double real, double imag);
Complex(const Complex& other);
double get_real() const;
double get_imag() const;
void add(const Complex& other);
friend Complex add(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2);
friend bool is_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2);
friend bool is_not_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2);
friend void output(const Complex& c);
friend double abs(const Complex& c);
private:
double real;
double imag;
};
#endifComplex.cpp
查看代码
#include "Complex.h"
const std::string Complex::doc = "a simplified complex class";
Complex::Complex() : real(0.0), imag(0.0) {}
Complex::Complex(double real) : real(real), imag(0.0) {}
Complex::Complex(double real, double imag) : real(real), imag(imag) {}
Complex::Complex(const Complex& other) : real(other.real), imag(other.imag) {}
double Complex::get_real() const {
return real;
}
double Complex::get_imag() const {
return imag;
}
void Complex::add(const Complex& other) {
real += other.real;
imag += other.imag;
}
Complex add(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2) {
return Complex(c1.real + c2.real, c1.imag + c2.imag);
}
bool is_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2) {
return (c1.real == c2.real) && (c1.imag == c2.imag);
}
bool is_not_equal(const Complex& c1, const Complex& c2) {
return !(is_equal(c1, c2));
}
void output(const Complex& c) {
std::cout << c.real << (c.imag >= 0 ? " + " : " - ") << std::abs(c.imag) << "i";
}
double abs(const Complex& c) {
return std::sqrt(c.real * c.real + c.imag * c.imag);
}task2.cpp
查看代码
#include "Complex.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "Complex.cpp"
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::boolalpha;
void test() {
cout << "类成员测试: " << endl;
cout << Complex::doc << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "Complex对象测试: " << endl;
Complex c1;
Complex c2(3, -4);
const Complex c3(3.5);
Complex c4(c3);
cout << "c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl;
cout << "c2 = "; output(c2); cout << endl;
cout << "c3 = "; output(c3); cout << endl;
cout << "c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl;
cout << "c4.real = " << c4.get_real() << ", c4.imag = " << c4.get_imag() << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl;
cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl;
c1.add(c2);
cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = "; output(c1); cout << endl;
cout << boolalpha;
cout << "c1 == c2 : " << is_equal(c1, c2) << endl;
cout << "c1 != c3 : " << is_not_equal(c1, c3) << endl;
c4 = add(c2, c3);
cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = "; output(c4); cout << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
}运行结果:
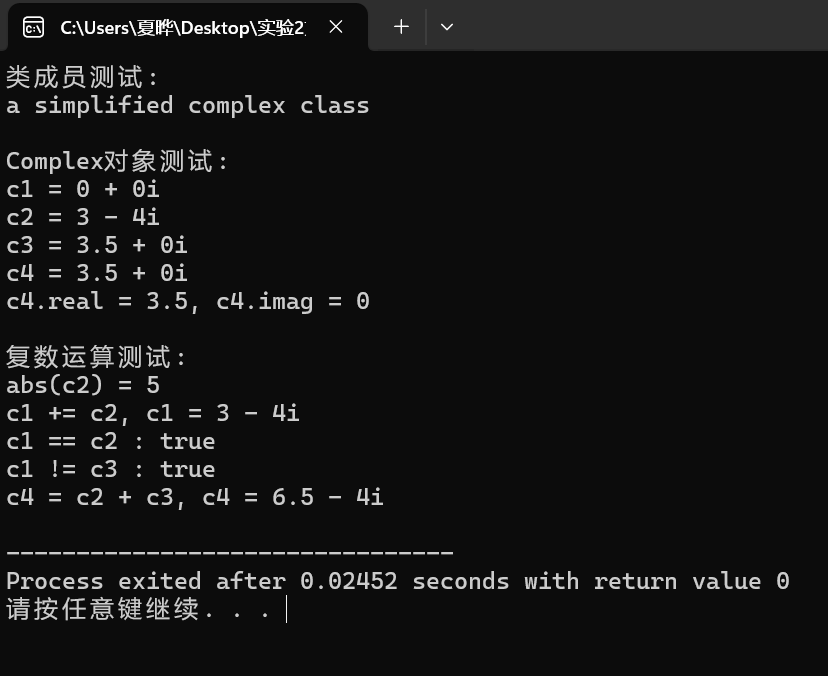
实验任务3:
代码:
task3.cpp
查看代码
#include <iostream>
#include <complex>
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
using std::boolalpha;
using std::complex;
void test() {
cout << "标准库模板类comple测试: " << endl;
complex<double> c1;
complex<double> c2(3, -4);
const complex<double> c3(3.5);
complex<double> c4(c3);
cout << "c1 = " << c1 << endl;
cout << "c2 = " << c2 << endl;
cout << "c3 = " << c3 << endl;
cout << "c4 = " << c4 << endl;
cout << "c4.real = " << c4.real() << ", c4.imag = " << c4.imag() << endl;
cout << endl;
cout << "复数运算测试: " << endl;
cout << "abs(c2) = " << abs(c2) << endl;
c1 += c2;
cout << "c1 += c2, c1 = " << c1 << endl;
cout << boolalpha;
cout << "c1 == c2 : " << (c1 == c2) << endl;
cout << "c1 != c3 : " << (c1 != c3) << endl;
c4 = c2 + c3;
cout << "c4 = c2 + c3, c4 = " << c4 << endl;
}
int main() {
test();
}运行结果:
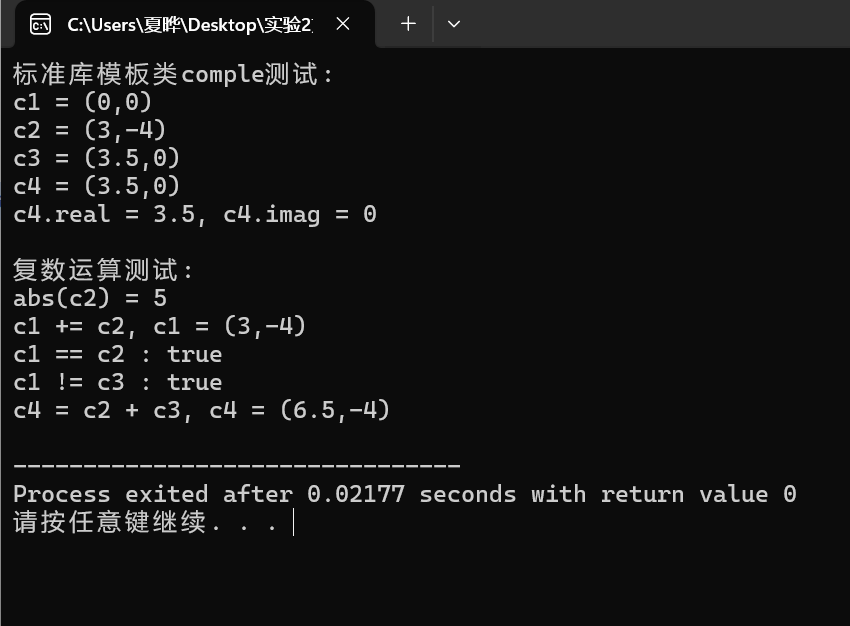
默认构造函数:
complex<double> c1;
带实部和虚部的构造函数:
complex<double> c2(3, -4);
仅带实部的构造函数:
const complex<double> c3(3.5);
复制构造函数:
complex<double> c4(c3);
成员函数:
c4.real();
算术运算符重载:
c1 += c2;
比较运算符重载:
c1 == c2;
非成员函数:
abs(c2);
输出运算符重载:
cout << c1;
实验任务4:
代码:
Fraction.h
查看代码
#ifndef FRACTION_H
#define FRACTION_H
#include <string>
class Fraction {
public:
static const std::string doc;
Fraction(int up = 0, int down = 1);
Fraction(const Fraction &other);
int get_up() const;
int get_down() const;
Fraction negative() const;
friend void output(const Fraction &f);
friend Fraction add(const Fraction &f1, const Fraction &f2);
friend Fraction sub(const Fraction &f1, const Fraction &f2);
friend Fraction mul(const Fraction &f1, const Fraction &f2);
friend Fraction div(const Fraction &f1, const Fraction &f2);
private:
int up;
int down;
void reduce();
};
#endifFraction.cpp
查看代码
#include "Fraction.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
using namespace std;
static int gcd(int a, int b) {
return b == 0 ? a : gcd(b, a % b);
}
const string Fraction::doc = "Fraction类 v 0.01版.\n目前仅支持分数对象的构造、输出、加/减/乘/除运算.";
Fraction::Fraction(int up, int down) : up(up), down(down) {
if (down < 0) {
this->up = -this->up;
this->down = -this->down;
}
reduce();
}
Fraction::Fraction(const Fraction &other) : up(other.up), down(other.down) {
}
int Fraction::get_up() const {
return up;
}
int Fraction::get_down() const {
return down;
}
Fraction Fraction::negative() const {
return Fraction(-up, down);
}
void Fraction::reduce() {
int gcd_val = gcd(abs(up), abs(down));
if (gcd_val != 0) {
up /= gcd_val;
down /= gcd_val;
}
}
void output(const Fraction &f) {
if (f.down == 1) {
cout << f.up;
} else {
cout << f.up << "/" << f.down;
}
}
Fraction add(const Fraction &f1, const Fraction &f2) {
int numerator = f1.up * f2.down + f2.up * f1.down;
int denominator = f1.down * f2.down;
return Fraction(numerator, denominator);
}
Fraction sub(const Fraction &f1, const Fraction &f2) {
int numerator = f1.up * f2.down - f2.up * f1.down;
int denominator = f1.down * f2.down;
return Fraction(numerator, denominator);
}
Fraction mul(const Fraction &f1, const Fraction &f2) {
int numerator = f1.up * f2.up;
int denominator = f1.down * f2.down;
return Fraction(numerator, denominator);
}
Fraction div(const Fraction &f1, const Fraction &f2) {
if (f2.up == 0) {
cout << "分母不能为0" << endl;
exit(1);
}
int numerator = f1.up * f2.down;
int denominator = f1.down * f2.up;
if (denominator < 0) {
numerator = -numerator;
denominator = -denominator;
}
return Fraction(numerator, denominator);
}task4.cpp
查看代码
#include "Fraction.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "Fraction.cpp"
using std::cout;
using std::endl;
void test1() {
cout << "Fraction类测试: " << endl;
cout << Fraction::doc << endl << endl;
Fraction f1(5);
Fraction f2(3, -4), f3(-18, 12);
Fraction f4(f3);
cout << "f1 = "; output(f1); cout << endl;
cout << "f2 = "; output(f2); cout << endl;
cout << "f3 = "; output(f3); cout << endl;
cout << "f4 = "; output(f4); cout << endl;
Fraction f5(f4.negative());
cout << "f5 = "; output(f5); cout << endl;
cout << "f5.get_up() = " << f5.get_up() << ", f5.get_down() = " << f5.get_down() << endl;
cout << "f1 + f2 = "; output(add(f1, f2)); cout << endl;
cout << "f1 - f2 = "; output(sub(f1, f2)); cout << endl;
cout << "f1 * f2 = "; output(mul(f1, f2)); cout << endl;
cout << "f1 / f2 = "; output(div(f1, f2)); cout << endl;
cout << "f4 + f5 = "; output(add(f4, f5)); cout << endl;
}
void test2() {
Fraction f6(42, 55), f7(0, 3);
cout << "f6 = "; output(f6); cout << endl;
cout << "f7 = "; output(f7); cout << endl;
cout << "f6 / f7 = "; output(div(f6, f7)); cout << endl;
}
int main() {
cout << "测试1: Fraction类基础功能测试\n";
test1();
cout << "\n测试2: 分母为0测试: \n";
test2();
}
实验任务5:
代码:
account.h
查看代码
#ifndef __ACCOUNT_H__
#define __ACCOUNT_H__
class SavingAccount{
private:
int id;
double balance;
double rate;
double lastData;
double accumulation;
static double total;
void record(int data,double amount);
double accumulate(int data) const
{
return accumulation+balance*(data-lastData);
}
public:
SavingAccount(int data,int id,double rate);
int getId() const {return id;}
double getBalance() const {return balance;}
double getRate() const {return rate;}
static double getTotal() {return total;}
void deposit(int data,double amount);
void withdraw(int data,double amount);
void settle(int data);
void show() const;
};
#endifaccount.cpp
查看代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include "account.h"
using namespace std;
double SavingAccount::total=0;
SavingAccount::SavingAccount(int data,int id,double rate)
:id(id),balance(0),rate(rate),lastData(data),accumulation(0)
{
cout<<data<<"\t#"<<id<<" is created"<<endl;
}
void SavingAccount::record(int data,double amount)
{
accumulation=accumulate(data);
lastData=data;
amount=floor(amount*100+0.5)/100;
balance+=amount;
total+=amount;
cout<<data<<"\t#"<<id<<"\t"<<amount<<"\t"<<balance<<endl;
}
void SavingAccount::deposit(int data,double amount)
{
record(data,amount);
}
void SavingAccount::withdraw(int data,double amount)
{
if (amount>getBalance())
cout<<"Error:not enough money"<<endl;
else
record(data,-amount);
}
void SavingAccount::settle(int data)
{
double interest=accumulate(data)*rate/365;
if (interest!=0)
record(data,interest);
accumulation=0;
}
void SavingAccount::show() const
{
cout<<"#"<<id<<"\tBalance:"<<balance;
}task5.cpp
查看代码
#include "account.h"
#include <iostream>
#include "account.cpp"
using namespace std;
int main ()
{
SavingAccount sa0(1,21325302,0.015);
SavingAccount sa1(1,58320212,0.015);
sa0.deposit(5,5000);
sa1.deposit(25,10000);
sa0.deposit(45,5500);
sa1.deposit(60,-4000);
sa0.settle(90);
sa1.settle(90);
sa0.show();cout<<endl;
sa1.show();cout<<endl;
cout<<"Total:"<<SavingAccount::getTotal()<<endl;
return 0;
}实验结果:

代码合理
改进:
常量成员函数,所有不修改变量的成员都被声明为 const,有助于提高代码的安全性



