Java 多线程假唤醒及解决方法
参考
描述
线程可以在没有被通知,中断或超时的情况下唤醒 ,即所谓的虚假唤醒 。---jdk11中文版文档
虚假唤醒就是在多线程执行过程中,线程间的通信未按照我们幻想的顺序唤醒,故出现数据不一致等不符合我们预期的结果。Java多线程— —线程 虚假唤醒 问题剖析
当代码 wait() 之后,当前代码释放锁并等待 notifyAll() 唤醒,如果有多个线程被唤醒,他们就会争抢锁,某一个线程获得锁之后,按照 wait() 的代码位置继续执行(执行完毕后释放锁给其他被唤醒的线程争抢),而不会重新走到 if 判断处而导致结果没有按照预期进行输出,如果使用 while ,就会按照代码流程重新走到 判断 代码处,判断是否符合要求。
代码
问题代码
package thread;
/**
* @Author 夏秋初
* @Date 2022/2/28 09:36
*/
public class Thread3 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Dog dog = new Dog();
new Thread(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
dog.buy();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "A").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
dog.sell();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"B").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
dog.buy();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}, "C").start();
new Thread(()->{
try {
Thread.sleep(200);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
try {
dog.sell();
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
},"D").start();
// Thread3 thread3 = new Thread3();
// thread3.wait();
}
}
class Dog{
public Integer count = 1;
/**
* 买狗
*/
public synchronized void buy() throws InterruptedException {
if(count == 1){
this.wait();
}
count += 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"买了狗"+count);
this.notifyAll();
}
/**
* 卖狗
*/
public synchronized void sell() throws InterruptedException {
if(count == 0){
this.wait();
}
count -= 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"卖了狗"+count);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
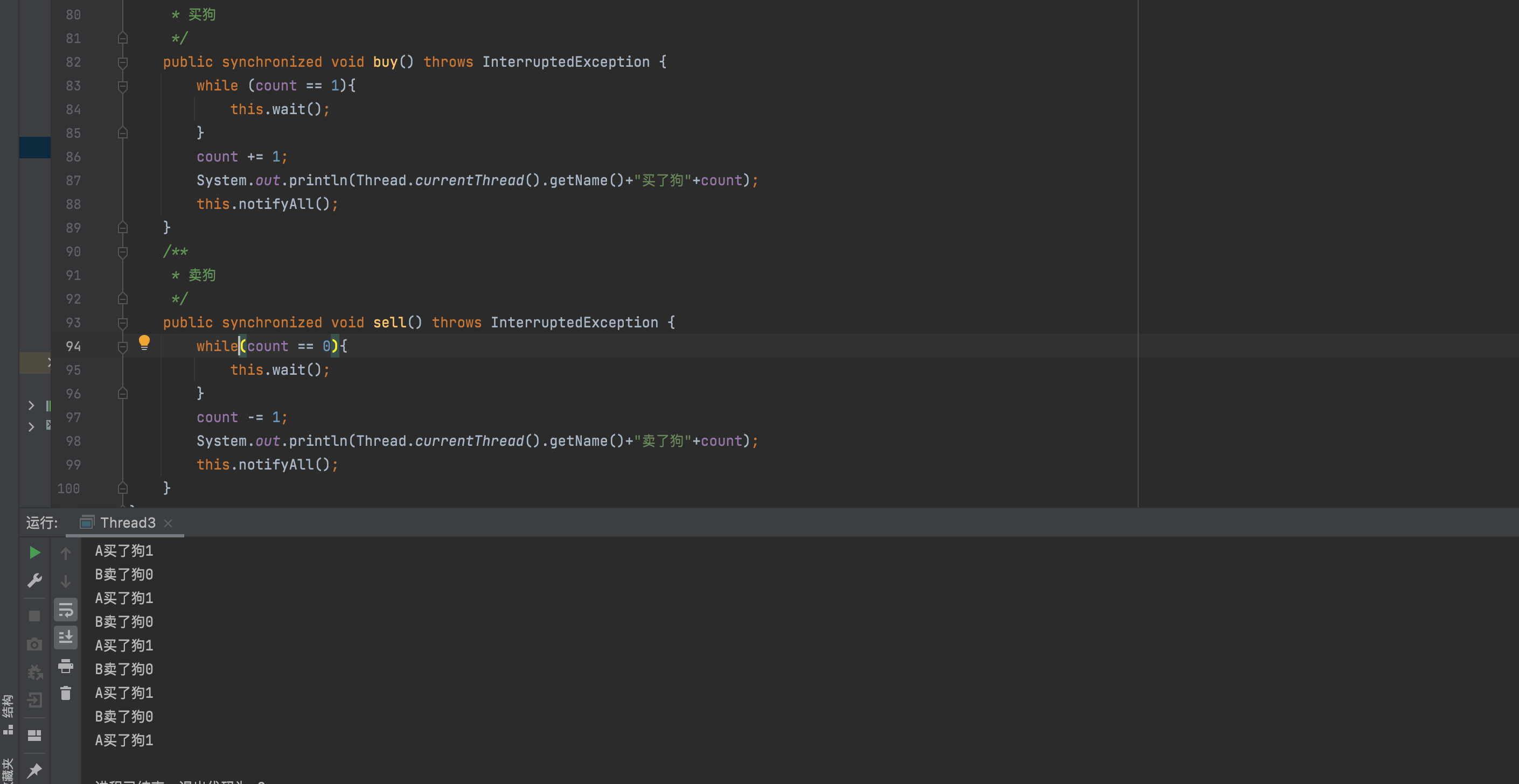
正确代码
解决办法就是将数量修改方法内的
if判断修改为while循环
1. synchronized 版本
/**
* @Author 夏秋初
* @Date 2022/2/28 09:36
*/
class Dog{
public Integer count = 1;
/**
* 买狗
*/
public synchronized void buy() throws InterruptedException {
while (count == 1){
this.wait();
}
count += 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"买了狗"+count);
this.notifyAll();
}
/**
* 卖狗
*/
public synchronized void sell() throws InterruptedException {
while(count == 0){
this.wait();
}
count -= 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName()+"卖了狗"+count);
this.notifyAll();
}
}
2. ReentrantLock版本
将synchronized 替换为 ReentrantLock
class Dog {
public Integer count = 1;
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
Condition condition = lock.newCondition();
/**
* 买狗
*/
public void buy() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (count == 1) {
condition.await();
}
count += 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "买了狗" + count);
condition.signalAll();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
/**
* 卖狗
*/
public void sell() throws InterruptedException {
lock.lock();
try {
while (count == 0) {
condition.await();
}
count -= 1;
System.out.println(Thread.currentThread().getName() + "卖了狗" + count);
condition.signalAll();
} finally {
lock.unlock();
}
}
}
Synchronized和Lock的区别 Synchronized和Lock的区别
- Synchronized是关键字,内置语言实现,Lock是接口。
- Synchronized在线程发生异常时会自动释放锁,因此不会发生异常死锁。Lock异常时不会自动释放锁,所以需要在finally中实现释放锁。
- Lock是可以中断锁,Synchronized是非中断锁,必须等待线程执行完成释放锁。
- Lock可以使用读锁提高多线程读效率。
博 主 :夏秋初
地 址 :https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaqiuchu/p/15944478.html
如果对你有帮助,可以点一下 推荐 或者 关注 吗?会让我的分享变得更有动力~
转载时请带上原文链接,谢谢。
地 址 :https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaqiuchu/p/15944478.html
如果对你有帮助,可以点一下 推荐 或者 关注 吗?会让我的分享变得更有动力~
转载时请带上原文链接,谢谢。




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· TypeScript + Deepseek 打造卜卦网站:技术与玄学的结合
· 阿里巴巴 QwQ-32B真的超越了 DeepSeek R-1吗?
· 【译】Visual Studio 中新的强大生产力特性
· 【设计模式】告别冗长if-else语句:使用策略模式优化代码结构
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义