使用mysql-proxy实现mysql的读写分离
前言:
MySQL读写分离是指让master处理写操作,让slave处理读操作,非常适用于读操作量比较大的场景,可减轻master的压力。使用mysql-proxy实现mysql的读写分离,mysql-proxy实际上是作为后端mysql主从服务器的代理,它直接接受客户端的请求,对SQL语句进行分析,判断出是读操作还是写操作,然后分发至对应的mysql服务器上。mysql-proxy是官方提供的mysql中间件产品可以实现负载平衡,读写分离,failover等MySQL Proxy就是这么一个中间层代理,简单的说,MySQL Proxy就是一个连接池,负责将前台应用的连接请求转发给后台的数据库,并且通过使用lua脚本,可以实现复杂的连接控制和过滤,从而实现读写分离和负载平衡。对于应用来说,MySQL Proxy是完全透明的,应用则只需要连接到MySQL Proxy的监听端口即可。当然,这样proxy机器可能成为单点失效,但完全可以使用多个proxy机器做为冗余,在应用服务器的连接池配置中配置到多 个proxy的连接参数即可。
实验系统:CentOS 6.6_x86_64
实验前提:防火墙和selinux都关闭
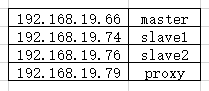
实验说明:本实验共有4台主机,IP分配如拓扑
实验软件:mariadb-10.0.20 mysql-proxy-0.8.5-linux-el6-x86-64bit
下载地址:http://pan.baidu.com/s/1i3F5Pop
实验拓扑:

一、准备工作:
1.将主机名称改为如下所示:
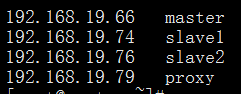
2.将hosts文件添加如下内容:
3.master、slave1和slave2安装mariadb:
tar xf mariadb-10.0.20-linux-x86_64.tar.gz -C /usr/local/ cd /usr/local/ ln -sv mariadb-10.0.20-linux-x86_64 mysql useradd -r mysql mkdir -pv /mydata/data chown -R mysql.mysql /mydata/data/ cd mysql/ chown -R root.mysql . scripts/mysql_install_db --user=mysql --datadir=/mydata/data/ cp support-files/my-large.cnf /etc/my.cnf cp support-files/mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysqld chkconfig --add mysqld chkconfig mysqld on
二、配置主从复制
1.master上配置my.cnf:
[mysqld] server-id = 1 datadir = /mydata/data log-bin = /mydata/data/master-bin binlog_format = ROW sync_binlog = 1 //确保每次事务提交之前都能将二进制日志同步磁盘上
2.slave1上配置my.cnf:
[mysqld] #log-bin=mysql-bin #binlog_format=mixed server-id = 2 datadir = /mydata/data relay_log = /mydata/data/relay-log read_only = 1 sync_master_info = 1 //及时同步master文件 sync_relay_log = 1 //及时同步relay-log文件 sync_relay_log_info = 1 //及时同步relay-log-info文件
3.slave2上配置my.cnf:
[mysqld] #log-bin=mysql-bin #binlog_format=mixed server-id = 3 datadir = /mydata/data relay_log = /mydata/data/relay-log read_only = 1 sync_master_info = 1 sync_relay_log = 1 sync_relay_log_info = 1
4.在master上创建复制用户:
service mysqld start /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql -------------------------------------------> GRANT REPLICATION SLAVE,REPLICATION CLIENT ON *.* TO 'slave'@'192.168.19.%' IDENTIFIED BY '123456'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
5.在master上查看二进制日志位置:
SHOW MASTER LOGS;

6.两台slave上操作:
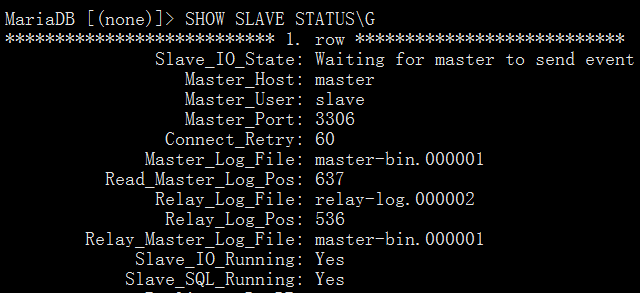
CHANGE MASTER TO MASTER_HOST='master',MASTER_USER='slave',MASTER_PASSWORD='123456',MASTER_LOG_FILE='master-bin.000001',MASTER_LOG_POS=637; START SLAVE; SHOW SLAVE STATUS\G
三、安装mysql-proxy
1.此实验中19.79为mysql-proxy服务器,所以软件安装在此主机上:
tar xf mysql-proxy-0.8.5-linux-el6-x86-64bit.tar.gz -C /usr/local/ cd /usr/local/ ln -sv mysql-proxy-0.8.5-linux-el6-x86-64bit mysql-proxy useradd -r mysql-proxy
2.提供服务脚本:
vim /etc/init.d/mysql-proxy ---------------------------------------------------------> #!/bin/bash # # mysql-proxy This script starts and stops the mysql-proxy daemon # # chkconfig: - 78 30 # processname: mysql-proxy # description: mysql-proxy is a proxy daemon for mysql # Source function library. . /etc/rc.d/init.d/functions prog="/usr/local/mysql-proxy/bin/mysql-proxy" # Source networking configuration. if [ -f /etc/sysconfig/network ]; then . /etc/sysconfig/network fi # Check that networking is up. [ ${NETWORKING} = "no" ] && exit 0 # Set default mysql-proxy configuration. ADMIN_USER="admin" ADMIN_PASSWD="admin" ADMIN_LUA_SCRIPT="/usr/local/mysql-proxy/share/doc/mysql-proxy/admin.lua" PROXY_OPTIONS="--daemon" PROXY_PID=/var/run/mysql-proxy.pid PROXY_USER="mysql-proxy" # Source mysql-proxy configuration. if [ -f /etc/sysconfig/mysql-proxy ]; then . /etc/sysconfig/mysql-proxy fi RETVAL=0 start() { echo -n $"Starting $prog: " daemon $prog $PROXY_OPTIONS --pid-file=$PROXY_PID --proxy-address="$PROXY_ADDRESS" --user=$PROXY_USER --admin-username="$ADMIN_USER" --admin-lua-script="$ADMIN_LUA_SCRIPT" --admin-password="$ADMIN_PASSWORD" RETVAL=$? echo if [ $RETVAL -eq 0 ]; then touch /var/lock/subsys/mysql-proxy fi } stop() { echo -n $"Stopping $prog: " killproc -p $PROXY_PID -d 3 $prog RETVAL=$? echo if [ $RETVAL -eq 0 ]; then rm -f /var/lock/subsys/mysql-proxy rm -f $PROXY_PID fi } # See how we were called. case "$1" in start) start ;; stop) stop ;; restart) stop start ;; condrestart|try-restart) if status -p $PROXY_PIDFILE $prog >&/dev/null; then stop start fi ;; status) status -p $PROXY_PID $prog ;; *) echo "Usage: $0 {start|stop|restart|reload|status|condrestart|try-restart}" RETVAL=1 ;; esac exit $RETVAL
<---------------------------------------------------------
chmod +x /etc/init.d/mysql-proxy
chkconfig --add mysql-proxy
3.为服务脚本提供配置文件:
vim /etc/sysconfig/mysql-proxy ---------------------------------------------------------> # Options for mysql-proxy ADMIN_USER="admin" ADMIN_PASSWORD="admin" ADMIN_ADDRESS="" ADMIN_LUA_SCRIPT="/usr/local/mysql-proxy/share/doc/mysql-proxy/admin.lua" PROXY_ADDRESS="" PROXY_USER="mysql-proxy" PROXY_OPTIONS="--daemon --log-level=info --log-use-syslog --plugins=proxy --plugins=admin --proxy-backend-addresses=192.168.19.66:3306 --proxy-read-only-backend-addresses=192.168.19.74:3306 --proxy-read-only-backend-addresses=192.168.19.76:3306 --proxy-lua-script=/usr/local/mysql-proxy/share/doc/mysql-proxy/rw-splitting.lua"
//--daemon:以守护进程模式启动mysql-proxy
//--proxy-backend-addresses:后端可读写的mysql服务器的地址和端口
//--proxy-read-only-backend-addresses:后端只读mysql服务器的地址和端口
//--proxy-lua-script:完成mysql代理功能的Lua脚本
4.提供admin.lua文件:
vim /usr/local/mysql-proxy/share/doc/mysql-proxy/admin.lua ------------------------------------------------------------------------------> --[[ $%BEGINLICENSE%$ Copyright (c) 2007, 2012, Oracle and/or its affiliates. All rights reserved. This program is free software; you can redistribute it and/or modify it under the terms of the GNU General Public License as published by the Free Software Foundation; version 2 of the License. This program is distributed in the hope that it will be useful, but WITHOUT ANY WARRANTY; without even the implied warranty of MERCHANTABILITY or FITNESS FOR A PARTICULAR PURPOSE. See the GNU General Public License for more details. You should have received a copy of the GNU General Public License along with this program; if not, write to the Free Software Foundation, Inc., 51 Franklin St, Fifth Floor, Boston, MA 02110-1301 USA $%ENDLICENSE%$ --]] function set_error(errmsg) proxy.response = { type = proxy.MYSQLD_PACKET_ERR, errmsg = errmsg or "error" } end function read_query(packet) if packet:byte() ~= proxy.COM_QUERY then set_error("[admin] we only handle text-based queries (COM_QUERY)") return proxy.PROXY_SEND_RESULT end local query = packet:sub(2) local rows = { } local fields = { } if query:lower() == "select * from backends" then fields = { { name = "backend_ndx", type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_LONG }, { name = "address", type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING }, { name = "state", type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING }, { name = "type", type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING }, { name = "uuid", type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING }, { name = "connected_clients", type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_LONG }, } for i = 1, #proxy.global.backends do local states = { "unknown", "up", "down" } local types = { "unknown", "rw", "ro" } local b = proxy.global.backends[i] rows[#rows + 1] = { i, b.dst.name, -- configured backend address states[b.state + 1], -- the C-id is pushed down starting at 0 types[b.type + 1], -- the C-id is pushed down starting at 0 b.uuid, -- the MySQL Server's UUID if it is managed b.connected_clients -- currently connected clients } end elseif query:lower() == "select * from help" then fields = { { name = "command", type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING }, { name = "description", type = proxy.MYSQL_TYPE_STRING }, } rows[#rows + 1] = { "SELECT * FROM help", "shows this help" } rows[#rows + 1] = { "SELECT * FROM backends", "lists the backends and their state" } else set_error("use 'SELECT * FROM help' to see the supported commands") return proxy.PROXY_SEND_RESULT end proxy.response = { type = proxy.MYSQLD_PACKET_OK, resultset = { fields = fields, rows = rows } } return proxy.PROXY_SEND_RESULT end
5.为了使实验结果更明显,编辑rw-splitting.lua文件中的其中2个数值:
vim /usr/local/mysql-proxy/share/doc/mysql-proxy/rw-splitting.lua ---------------------------------------------------------------------------> if not proxy.global.config.rwsplit then proxy.global.config.rwsplit = { min_idle_connections = 1, //默认为4 max_idle_connections = 1, //默认为8 is_debug = false } end
//mysql-proxy会检测客户端连接,当连接没有超过min_idle_connections预设值时, 不会进行读写分离, 即查询操作会发生到Master上。
5.启动mysql-proxy:
service mysql-proxy start ss -tnlp //查看端口

6.连接测试:
yum -y install mysql //如果没有mysql客户端的话执行此步 mysql -uadmin -padmin -h192.168.19.79 --port=4041 ------------------------------------------------------------> SELECT * FROM backends; +-------------+--------------------+---------+------+------+-------------------+ | backend_ndx | address | state | type | uuid | connected_clients | +-------------+--------------------+---------+------+------+-------------------+ | 1 | 192.168.19.66:3306 | unknown | rw | NULL | 0 | | 2 | 192.168.19.74:3306 | unknown | ro | NULL | 0 | | 3 | 192.168.19.76:3306 | unknown | ro | NULL | 0 | +-------------+--------------------+---------+------+------+-------------------+
四、读写分离测试:
1.在master上创建测试用户:
GRANT ALL ON *.* TO 'jason'@'192.168.19.%' IDENTIFIED BY '123456'; FLUSH PRIVILEGES;
2.分别在三台mariadb服务器上抓包:
master:
tcpdump -i eth0 -nn -XX ip dst 192.168.19.66 and tcp dst port 3306 //目标是19.66并且端口是3306
slave1:
tcpdump -i eth0 -nn -XX ip dst 192.168.19.74 and tcp dst port 3306
slave2:
tcpdump -i eth0 -nn -XX ip dst 192.168.19.76 and tcp dst port 3306
3.mysql-proxy上进行数据库操作:
mysql -ujason -p123456 -h192.168.19.79 -------------------------------------------------> CREATE DATABASE hello;
USE mysql;
SELECT * FROM user; //可以用额外的主机多执行几次
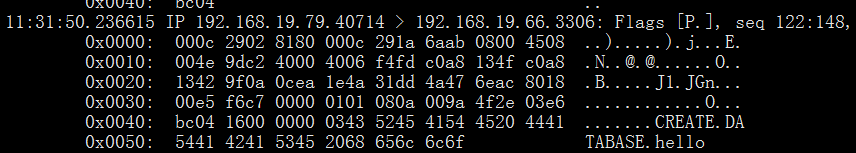
在master上的抓包信息:
在slave上的抓包信息:

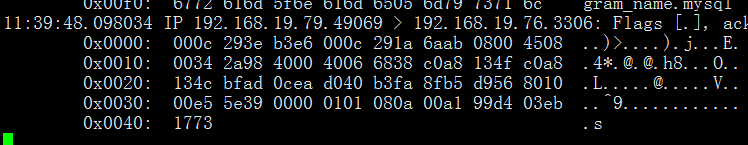
4.查看状态,在proxy上操作,可以看到状态全部为up:
mysql -uadmin -padmin -h192.168.19.79 --port=4041 -------------------------------------------------------------> SELECT * FROM backends; +-------------+--------------------+-------+------+------+-------------------+ | backend_ndx | address | state | type | uuid | connected_clients | +-------------+--------------------+-------+------+------+-------------------+ | 1 | 192.168.19.66:3306 | up | rw | NULL | 0 | | 2 | 192.168.19.74:3306 | up | ro | NULL | 0 | | 3 | 192.168.19.76:3306 | up | ro | NULL | 0 | +-------------+--------------------+-------+------+------+-------------------+
五、拓展实验
1.在proxy上安装httpd和php:
yum install httpd php php-mysql service httpd start
2.让httpd可以支持index.php首页,然后放入wordpress页面文件,创建wordpress数据库并安装:
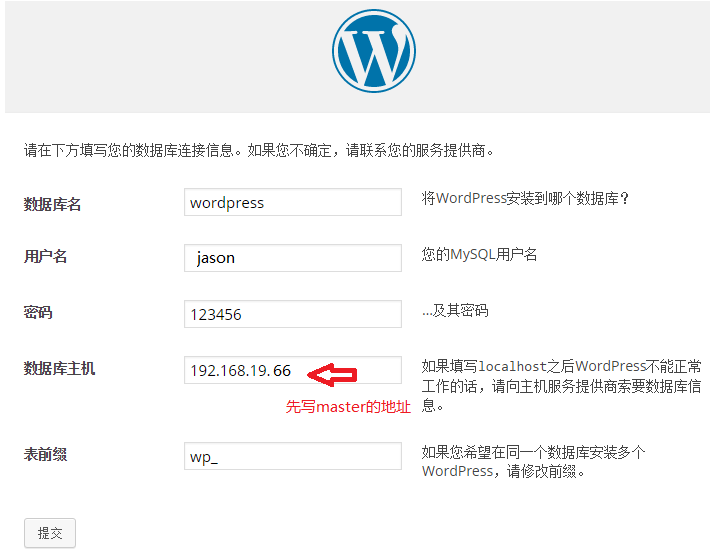
3.安装完后修改wordpress的配置文件,将master地址改为proxy的:
vim /var/www/html/wp-config.php

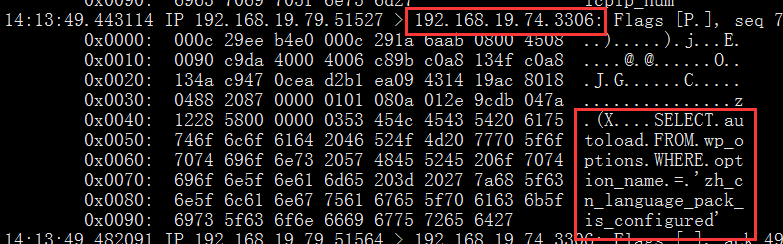
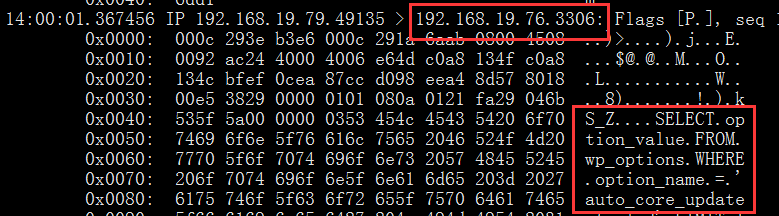
4.访问测试并抓包:
master:

slave:
转载链接:https://www.cnblogs.com/tae44/p/4701226.html







【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· SQL Server 2025 AI相关能力初探
· Linux系列:如何用 C#调用 C方法造成内存泄露
· 无需6万激活码!GitHub神秘组织3小时极速复刻Manus,手把手教你使用OpenManus搭建本
· Manus爆火,是硬核还是营销?
· 终于写完轮子一部分:tcp代理 了,记录一下
· 别再用vector<bool>了!Google高级工程师:这可能是STL最大的设计失误
· 单元测试从入门到精通