04 xlutils的使用
egon新书python全套来袭:https://egonlin.com/book.html
导语
xlrd和xlwt模块主要是针对excel表格的读取和写入,但是一些操作和处理数据的操作还是需要根据xlutils这个模块来实现。
1、拷贝原文件
import xlrd
from xlutils.copy import copy
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook('test.xlsx') # 打开工作薄
new_workbook = copy(workbook) # 将获取的xlrd文件对象,拷贝为xlwt对象
new_workbook.save('new_test.xlsx') # 保存工作薄
2、拷贝前获取原工作薄的信息
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook('test.xlsx') # 打开工作簿
sheets = workbook.sheet_names() # 获取工作簿中的所有工作表名字,形成列表元素
worksheet = workbook.sheet_by_name(sheets[0]) # 通过sheets[0]工作表名称获取工作簿中所有工作表中的的第一个工作表
rows_old = worksheet.nrows # 获取第一个工作表中已存在的数据的行数
print(sheets, sheets[0], worksheet, worksheet.nrows)
3、拷贝后获取新工作薄的信息
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook('test.xlsx') # 打开工作簿
new_workbook = copy(workbook) # 将xlrd对象拷贝转化为xlwt对象
new_worksheet = new_workbook.get_sheet(0) # 获取转化后工作簿中的第一个工作表对象
print(new_worksheet, new_workbook, new_worksheet.name) # 有时间整理下工作表对象的方法,工作表可以.name
4、拷贝后直接修改文件内容
# 打开想要更改的excel文件
old_excel = xlrd.open_workbook('test.xlsx', formatting_info=True)
# 将操作文件对象拷贝,变成可写的workbook对象
new_excel = copy(old_excel)
# 获得第一个sheet的对象
ws = new_excel.get_sheet(0)
# 写入数据
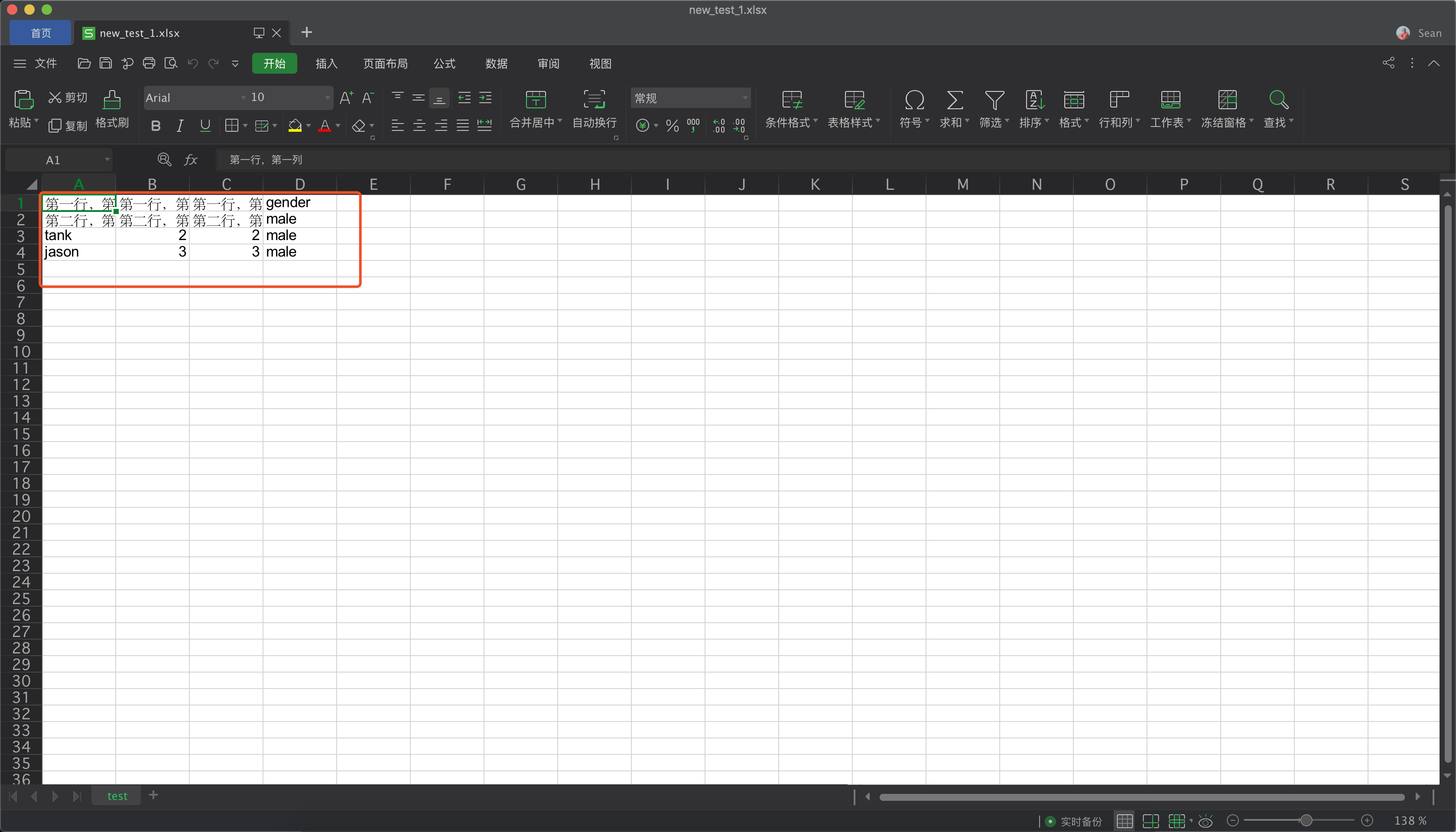
ws.write(0, 0, '第一行,第一列')
ws.write(0, 1, '第一行,第二列')
ws.write(0, 2, '第一行,第三列')
ws.write(1, 0, '第二行,第一列')
ws.write(1, 1, '第二行,第二列')
ws.write(1, 2, '第二行,第三列')
# 另存为excel文件,并将文件命名,可以重新命名,应该也可以覆盖掉
new_excel.save('new_test_1.xlsx')
5、获取所有单元格索引坐标
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook('test.xlsx') # 打开工作簿
Data_sheet = workbook.sheets()[0]
row1 = Data_sheet.row_values(0) # 取出第一行
dic_col_s = {str(i): row1[i] for i in
range(0, len(row1))} # 将第一行的每个元素加个序数标记,标记列表索引,让列表索引和标题对应,由标题则可以从字典获取列号,即列表索引+1,这里需要的是索引
col2 = Data_sheet.col_values(0) # 取出第一列,
dic_row_s = {str(i): col2[i] for i in
range(0, len(col2))} # 将第一列的每个元素加个序数标记,标记为第一列的列表索引。让名字和列表索引对应,就可以在字典中由名字得行号,即列表索引+1。这里需要的是这个索引
mtitle = "gender" # 需要修改哪个标题
mname = "tank" # 需要修改哪个人的
rindex = "".join([i for i in dic_row_s if dic_row_s[i] == mname]) # 获取要修改的标题所在行的索引
cindex = "".join([i for i in dic_col_s if dic_col_s[i] == mtitle]) # 获取要修改的那个人所在的列索引
print(f"rindex:{rindex},cindex:{cindex}")
---------------------------------执行结果-------------------------------------
{'0': 'name', '1': 'class', '2': 'cid', '3': 'gender'}
{'0': 'name', '1': 'sean', '2': 'tank', '3': 'jason'}
rindex:2,cindex:3
6、修改单元格内元素
rindex = list(rindex)
rindex = "".join(rindex)
rindex = int(rindex)
cindex = list(cindex)
cindex = "".join(cindex)
cindex = int(cindex)
# 打开想要更改的excel文件
old_excel = xlrd.open_workbook('test.xlsx', formatting_info=True)
# 将操作文件对象拷贝,变成可写的workbook对象
new_excel = copy(old_excel)
# 获得第一个sheet的对象
ws = new_excel.get_sheet(0)
# 写入数据
ws.write(rindex, cindex, 'dsb') # 修改第3行第4列
# 另存为excel文件,并将文件命名,可以重新命名,应该也可以覆盖掉
new_excel.save('new_test_2.xlsx')
7、(改)函数:读取单元格索引,修改单元格内元素
fpath = 'test.xlsx'
mname = "sean"
mtitle = "hobby"
modifycontent = "read"
def recindex(path, mname, mtitle):
'''
定位单元格,返回单元格行列索引供modify_cell函数使用
:param path: Excel文件路径
:param mname: 要修改的名字
:param mtitile: 要修改的标题
:return: 单元格的行列索引号。rindex:行,cindex:列索引
'''
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook(path)
Data_sheet = workbook.sheets()[0]
row1 = Data_sheet.row_values(0)
dic_col_s = {str(i): row1[i] for i in range(0, len(row1))}
col2 = Data_sheet.col_values(0)
dic_row_s = {str(i): col2[i] for i in range(0, len(col2))}
rindex = "".join([i for i in dic_row_s if dic_row_s[i] == mname])
cindex = "".join([i for i in dic_col_s if dic_col_s[i] == mtitle])
rindex = int("".join(list(rindex)))
cindex = int("".join(list(cindex)))
return rindex, cindex
def modify_cell(path, rindex, cindex, modifycontent):
"""
修改文件指定单元格内容,由recindex函数返回值获取rindex和cindex参数
:param path: 要修改的Excel文件路径
:param rindex:recindex返回值元组第一个元素,行索引
:param cindex:recindex返回值元组第二个元素,列索引
:param modifycontent: 要修改的单元格新的内容
:return:
"""
old_excel = xlrd.open_workbook(path, formatting_info=True)
new_excel = copy(old_excel)
ws = new_excel.get_sheet(0)
ws.write(rindex, cindex, modifycontent)
new_excel.save(path)
val = recindex(fpath, mname, mtitle)
modify_cell(fpath, val[0], val[1], modifycontent)
8、(增)函数:添加多条数据
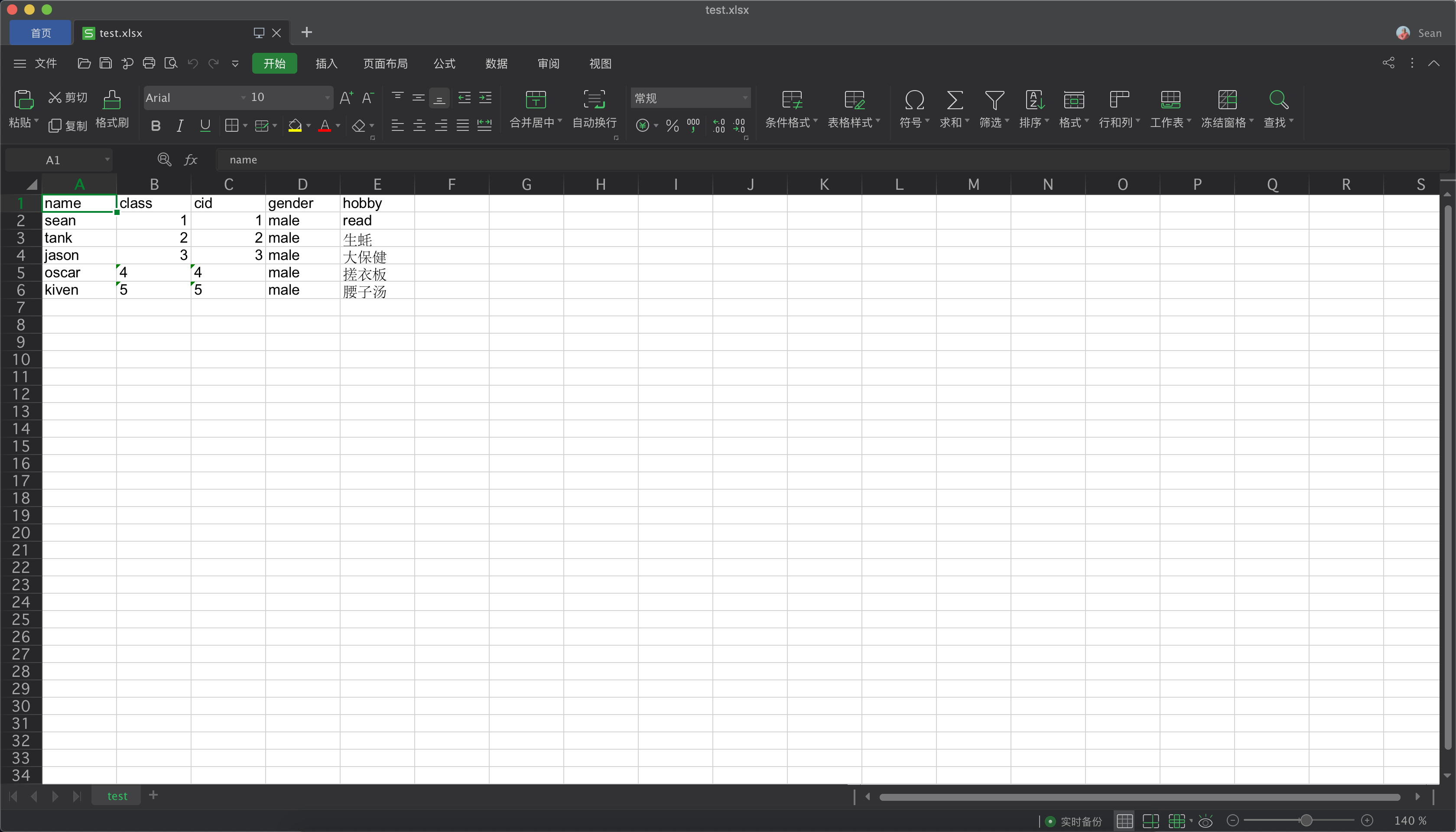
fpath = 'test.xlsx'
valueli = [["oscar", "4", "4", "male", "搓衣板"],
["kiven", "5", "5", "male", "腰子汤"], ]
def write_excel_xls_append(path, value):
index = len(value) # 获取需要写入数据的行数
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook(path) # 打开工作簿
sheets = workbook.sheet_names() # 获取工作簿中的所有表格
worksheet = workbook.sheet_by_name(sheets[0]) # 获取工作簿中所有表格中的的第一个表格
rows_old = worksheet.nrows # 获取表格中已存在的数据的行数
new_workbook = copy(workbook) # 将xlrd对象拷贝转化为xlwt对象
new_worksheet = new_workbook.get_sheet(0) # 获取转化后工作簿中的第一个表格
for i in range(0, index):
for j in range(0, len(value[i])):
new_worksheet.write(i + rows_old, j, value[i][j]) # 追加写入数据,注意是从i+rows_old行开始写入
new_workbook.save(path) # 保存工作簿
print("xls/xlsx格式表格【追加】写入数据成功!")
write_excel_xls_append(fpath, valueli)
9、(查1)函数:以制表符分割,显示每行数据
fpath = "test.xlsx"
def read_excel_xls(path):
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook(path) # 打开工作簿
sheets = workbook.sheet_names() # 获取工作簿中的所有表格
worksheet = workbook.sheet_by_name(sheets[0]) # 获取工作簿中所有表格中的的第一个表格
for i in range(0, worksheet.nrows):
for j in range(0, worksheet.ncols):
print(worksheet.cell_value(i, j), "\t", end="") # 逐行逐列读取数据#分隔符加空格实现对其点的
print()
read_excel_xls(fpath)

10、(查2)函数:
fpath = "test.xlsx"
def read_excel_xls(path):
"""
打印所有行的内容,每行内容以列表形式展示
:param path: 要查看的Excel文件路径
"""
workbook = xlrd.open_workbook(path) # 打开工作簿
sheets = workbook.sheet_names() # 获取工作簿中的所有表格
worksheet = workbook.sheet_by_name(sheets[0]) # 获取工作簿中所有表格中的的第一个表格
rows = worksheet.row_values(0)
for i in range(0, worksheet.nrows):
rows = worksheet.row_values(i) # 逐行逐列读取数据#分隔符加空格实现对其点的
print(rows)
read_excel_xls(fpath)


