02-09 对数线性回归(波士顿房价预测)
对数线性回归(波士顿房价预测)
导入模块

import pandas as pd
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from matplotlib.font_manager import FontProperties
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.metrics import r2_score
%matplotlib inline
font = FontProperties(fname='/Library/Fonts/Heiti.ttc')
获取数据
在《代码-普通线性回归》的时候说到特征LSTAT和标记MEDV有最高的相关性,但是它们之间并不是线性关系,尝试多项式回归发现可以得到不错的结果,但是多项式可能会增加模型的复杂度容易导致过拟合的问题出现,是不是可以假设特征和标记之间可能符合对数线性回归呢?即\(y\)和\(x\)的关系为
\[ln(y) = x
\]
下面将使用对数线性回归做尝试。
df = pd.read_csv('housing-data.txt', sep='\s+', header=0)
X = df[['LSTAT']].values
y = df['MEDV'].values
# np.log()默认以$e$为底数
y_sqrt = np.log(y)
训练模型
# 增加x轴坐标点
X_fit = np.arange(X.min(), X.max(), 1)[:, np.newaxis]
lr = LinearRegression()
# 线性回归
lr.fit(X, y)
lr_predict = lr.predict(X_fit)
# 计算线性回归的R2值
lr_r2 = r2_score(y, lr.predict(X))
可视化
plt.scatter(X, y, c='gray', edgecolor='white', marker='s', label='训练数据')
plt.plot(X_fit, lr_predict, c='r',
label='线性,$R^2={:.2f}$'.format(lr_r2))
plt.xlabel('地位较低人口的百分比[LSTAT]', fontproperties=font)
plt.ylabel('ln(以1000美元为计价单位的房价[RM])', fontproperties=font)
plt.title('波士顿房价预测', fontproperties=font, fontsize=20)
plt.legend(prop=font)
plt.show()
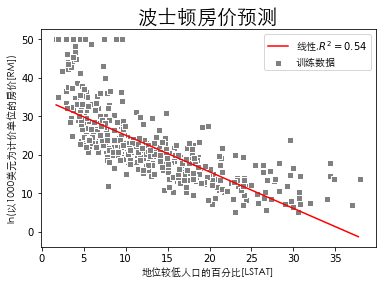
上图可以看出对数线性回归也能比较不错的拟合特征与标记之间的关系,这次只是使用了标准的对数线性回归拟合两者之间的关系,你也可以自行选择不同的关系函数\(g(·)\)去拟合两者之间的关系,也许可能会得到一个不错的结果。


