1066. Root of AVL Tree (25)
An AVL tree is a self-balancing binary search tree. In an AVL tree, the heights of the two child subtrees of any node differ by at most one; if at any time they differ by more than one, rebalancing is done to restore this property. Figures 1-4 illustrate the rotation rules.
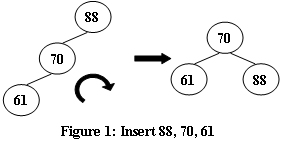

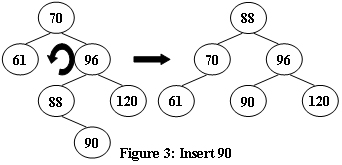
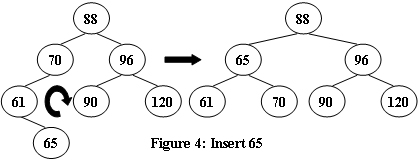
Now given a sequence of insertions, you are supposed to tell the root of the resulting AVL tree.
Input Specification:
Each input file contains one test case. For each case, the first line contains a positive integer N (<=20) which is the total number of keys to be inserted. Then N distinct integer keys are given in the next line. All the numbers in a line are separated by a space.
Output Specification:
For each test case, print ythe root of the resulting AVL tree in one line.
Sample Input 1:
5 88 70 61 96 120
Sample Output 1:
70
Sample Input 2:
7 88 70 61 96 120 90 65
Sample Output 2:
88
1 #include<stdio.h> 2 #include<vector> 3 #include<algorithm> 4 using namespace std; 5 6 struct node 7 { 8 node(int v):left(NULL),right(NULL),high(1),val(v){} 9 node* left,* right; 10 int val,high; 11 }; 12 13 int gethigh(node* root) 14 { 15 int a = 0, b = 0; 16 if(root->left!= NULL) 17 a = root->left->high; 18 if(root->right!= NULL) 19 b = root->right->high; 20 return a > b ? a+1:b+1; 21 } 22 23 void R(node* & root) 24 { 25 node* tem = root->left; 26 root->left = tem->right; 27 tem->right = root; 28 root->high = gethigh(root); 29 tem->high = gethigh(tem); 30 root = tem; 31 } 32 33 void L(node* & root) 34 { 35 node* tem = root->right; 36 root->right = tem->left; 37 tem->left = root; 38 root->high = gethigh(root); 39 tem->high = gethigh(tem); 40 root = tem; 41 } 42 43 void insert(node*& root,int val) 44 { 45 if(root == NULL) 46 { 47 root = new node(val); 48 return; 49 } 50 51 if(val < root->val) 52 { 53 insert(root->left,val); 54 root->high = gethigh(root); 55 int a = root->left == NULL ? 0 : root->left->high; 56 int b = root->right == NULL ? 0 : root->right->high; 57 if(a - b == 2) 58 { 59 int c = root->left->left == NULL ? 0:root->left->left->high; 60 int d = root->left->right == NULL ? 0:root->left->right->high; 61 if(c - d == 1 ) 62 { 63 R(root); 64 } 65 else if(c - d == -1) 66 { 67 L(root->left); 68 R(root); 69 } 70 } 71 } 72 else 73 { 74 insert(root->right,val); 75 root->high = gethigh(root); 76 int a = root->left == NULL ? 0 : root->left->high; 77 int b = root->right == NULL ? 0 : root->right->high; 78 if(a - b == -2) 79 { 80 int c = root->right->right == NULL ? 0:root->right->right->high; 81 int d = root->right->left == NULL ? 0:root->right->left->high; 82 if(c - d == 1) 83 { 84 L(root); 85 } 86 else if(c - d == -1) 87 { 88 R(root->right); 89 L(root); 90 } 91 } 92 } 93 } 94 95 int main() 96 { 97 int n,tem; 98 scanf("%d",&n); 99 node* Tree = NULL; 100 for(int i = 0;i < n;++i) 101 { 102 scanf("%d",&tem); 103 insert(Tree,tem); 104 } 105 printf("%d\n",Tree->val); 106 return 0; 107 }






