对拍
对拍
对拍是什么
对拍,是一个比较实用的工具。它能够非常方便地对于两个程序的输出文件进行比较,可以帮助我们实现一些自动化的比较输出结果的问题。
众所周知,几乎每一道编程题目,都会有某种正解能拿到满分;当我们想不出正解时,我们往往可以打暴力代码来获取部分分数。
但是,当我们觉得有思路写正解,但又担心自己正解写的不对,而恰好,我们又有一个能够暴力骗分的代码。这个时候就可以用到对拍。 暴力骗分代码必须保证正确性,只是超出时间限制,不能出现答案错误的情况。
这样,我们可以造多组数据,让暴力骗分的程序跑一遍,再让我们自己写的正解跑一遍,二者进行多次对比。如果多组数据都显示二者的输出结果一样,那么这个正解大概率没问题。相反地,如果两组数据不同,我们就找到了一组错误数据,方便调试,找到正解哪里出了问题。
对拍代码
正解代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("std.txt", "w", stdout);
/*
正解代码
*/
return 0;
}
暴力代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("baoli.txt", "w", stdout);
/*
暴力代码
*/
return 0;
}
生成数据代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
struct _timeb T;
_ftime(&T);
srand(T.millitm);
freopen("in.txt", "w", stdout);
/*
生成将要读入的数据,并读出
例如:int x = rand(), cout << x << '\n';
*/
return 0;
}
对拍代码
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <windows.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
while (1) {
system("data.exe");
system("baoli.exe");
DWORD t1, t2; // 统计 std 的时间
t1 = GetTickCount();
system("std.exe");
t2 = GetTickCount();
double tim = ((t2 - t1) * 1.0 / 1000); // 计算 std 的时间
cout << tim << '\n';
if (system("fc std.txt baoli.txt")) { // 比较 std 与 baoli 的答案
cout << "Wrong Answer\n";
break;
}
if (tim > 1) { // 看是否超时
cout << "Time Limited Exceeded\n";
break;
}
cout << "Accepted\n";
}
return 0;
}
示例(最短路问题)
- std
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int kMaxN = 1e6 + 10;
struct node {
int y, z, ne;
} a[kMaxN << 1];
int h[kMaxN], d[kMaxN], v[kMaxN], n, m, K;
priority_queue<pair<int, int> > p;
void add(int x, int y, int z) { a[++K] = (node){y, z, h[x]}, h[x] = K; }
int main() {
freopen("paths.in", "r", stdin);
freopen("paths.out", "w", stdout);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i < n; i++) {
add(i, i + 1, 1), add(i + 1, i, 1);
}
for (int i = 1, x, y, z; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> x >> y >> z, add(x, y, z), add(y, x, z);
}
memset(d, 0x3f, sizeof(d));
for (d[1] = 0, p.push({0, 1}); p.size();) {
int x = p.top().second;
p.pop();
if (v[x]) {
continue;
}
v[x] = 1;
for (int i = h[x]; i; i = a[i].ne) {
(d[a[i].y] > d[x] + a[i].z) && (d[a[i].y] = d[x] + a[i].z, p.push({-d[a[i].y], a[i].y}), 0);
}
}
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
cout << d[i] << ' ';
}
return cout << '\n', 0;
}
- baoli
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#define int long long
using namespace std;
const int kMaxN = 5e5 + 10;
int vis[kMaxN], dis[kMaxN], n, m;
vector<pair<int, int> > g[kMaxN];
queue<int> q;
void D() {
fill(dis + 1, dis + 1 + n, kMaxN), dis[1] = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
int now, maxn = kMaxN;
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
if (!vis[j] && dis[j] < maxn) {
maxn = dis[j], now = j;
}
}
vis[now] = 1;
for (int j = 0; j < g[now].size(); j++) {
dis[g[now][j].first] = min(dis[g[now][j].first], dis[now] + g[now][j].second);
}
}
}
signed main() {
freopen("in.txt", "r", stdin);
freopen("baoli.txt", "w", stdout);
ios::sync_with_stdio(0), cin.tie(0), cout.tie(0);
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= n; j++) {
g[i].push_back({j, abs(i - j)});
}
}
for (int i = 1, x, y, z; i <= m; i++) {
cin >> x >> y >> z;
if (abs(x - y) <= z) {
continue;
}
g[x].push_back({y, z}), g[y].push_back({x, z});
}
D();
for (int i = 2; i <= n; i++) {
cout << dis[i] << ' ';
}
return cout << '\n', 0;
}
- data
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
struct _timeb T;
_ftime(&T);
srand(T.millitm);
freopen("in.txt", "w", stdout);
int n = rand() % 500000 + 1, m = rand() % 500000;
printf("%d %d\n", n, m);
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++) {
int x = rand() % n + 1, y = rand() % n + 1;
(x == y) && ((x == n) ? (y--) : (y++));
int xx = abs(x - y), z = rand() % xx;
printf("%d %d %d\n", x, y, z);
}
return 0;
}
- duipai
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
#include <windows.h>
using namespace std;
int main() {
while (1) {
system("data.exe");
system("baoli.exe");
DWORD t1, t2;
t1 = GetTickCount();
system("std.exe");
t2 = GetTickCount();
double tim = ((t2 - t1) * 1.0 / 1000);
cout << tim << '\n';
if (system("fc std.txt baoli.txt")) {
cout << "Wrong Answer\n";
break;
}
if (tim > 1) {
cout << "Time Limited Exceeded\n";
break;
}
cout << "Accepted\n";
}
return 0;
}
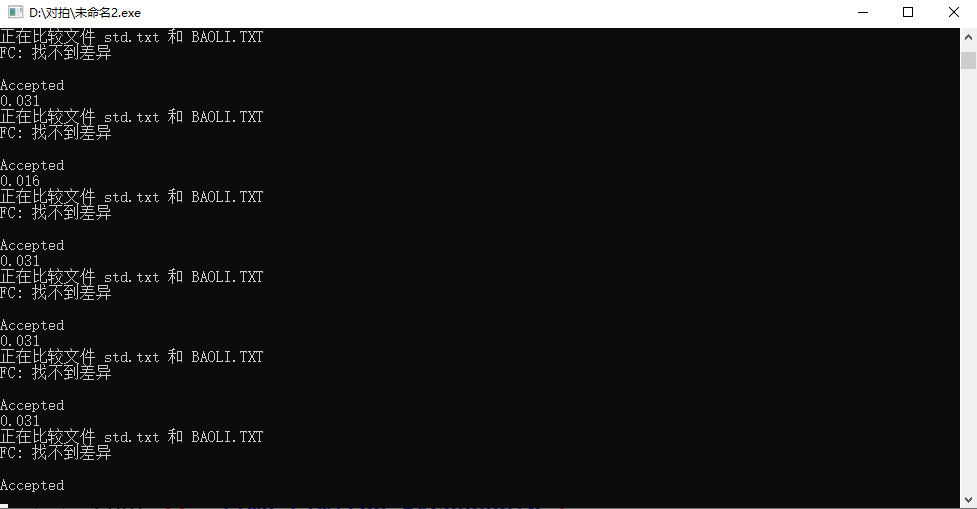
- 运行结果