Python一路走来 - 模块
模块,用一砣代码实现了某个功能的代码集合。
类似于函数式编程和面向过程编程,函数式编程则完成一个功能,其他代码用来调用即可,提供了代码的重用性和代码间的耦合。而对于一个复杂的功能来,可能需要多个函数才能完成(函数又可以在不同的.py文件中),n个 .py 文件组成的代码集合就称为模块。
如:os 是系统相关的模块;file是文件操作相关的模块
模块分为三种:
- 自定义模块
- 内置模块
- 开源模块
1. 自定义模块:
自己写的代码模块
2. 导入模块
Python之所以应用越来越广泛,在一定程度上也依赖于其为程序员提供了大量的模块以供使用,如果想要使用模块,则需要导入。导入模块有一下几种方法:
|
1
2
3
4
|
import modulefrom module.xx.xx import xxfrom module.xx.xx import xx as rename from module.xx.xx import * |
导入模块其实就是告诉Python解释器去解释那个py文件
- 导入一个py文件,解释器解释该py文件
- 导入一个包,解释器解释该包下的 __init__.py 文件
导入模块时是根据那个路径作为基准来进行的呢?即:sys.path
import sys print(sys.path) 结果: ['/Users/zhwang/PycharmProjects/S13/Day6', '/usr/local/Cellar/python3/3.4.2_1/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.4/lib/python3.4/site-packages/setuptools-12.0.5-py3.4.egg', '/usr/local/Cellar/python3/3.4.2_1/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.4/lib/python3.4/site-packages/pip-6.0.7-py3.4.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python3.4/site-packages/setuptools-12.0.5-py3.4.egg', '/usr/local/lib/python3.4/site-packages/pip-6.0.7-py3.4.egg', '/Users/zhwang/PycharmProjects/S13', '/usr/local/Cellar/python3/3.4.2_1/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.4/lib/python34.zip', '/usr/local/Cellar/python3/3.4.2_1/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.4/lib/python3.4', '/usr/local/Cellar/python3/3.4.2_1/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.4/lib/python3.4/plat-darwin', '/usr/local/Cellar/python3/3.4.2_1/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.4/lib/python3.4/lib-dynload', '/usr/local/Cellar/python3/3.4.2_1/Frameworks/Python.framework/Versions/3.4/lib/python3.4/site-packages', '/usr/local/lib/python3.4/site-packages'] Process finished with exit code 0
内置模块:
re
re模块用于对python的正则表达式的操作。
字符:
. 匹配除换行符以外的任意字符
\w 匹配字母或数字或下划线或汉字
\s 匹配任意的空白符
\d 匹配数字
\b 匹配单词的开始或结束
^ 匹配字符串的开始
$ 匹配字符串的结束
次数:
* 重复零次或更多次
+ 重复一次或更多次
? 重复零次或一次
{n} 重复n次
{n,} 重复n次或更多次
{n,m} 重复n到m次
IP:
^(25[0-5]|2[0-4]\d|[0-1]?\d?\d)(\.(25[0-5]|2[0-4]\d|[0-1]?\d?\d)){3}$
手机号:
^1[3|4|5|8][0-9]\d{8}$
1、match(pattern, string, flags=0)
从起始位置开始根据模型去字符串中匹配指定内容,匹配单个
- 正则表达式
- 要匹配的字符串
- 标志位,用于控制正则表达式的匹配方式
import re
obj = re.match('\d+', '123uuasf')
if obj:
print obj.group()

# flags I = IGNORECASE = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_IGNORECASE # ignore case L = LOCALE = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_LOCALE # assume current 8-bit locale U = UNICODE = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_UNICODE # assume unicode locale M = MULTILINE = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_MULTILINE # make anchors look for newline S = DOTALL = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_DOTALL # make dot match newline X = VERBOSE = sre_compile.SRE_FLAG_VERBOSE # ignore whitespace and comments
2、search(pattern, string, flags=0)
根据模型去字符串中匹配指定内容,匹配单个
import re
obj = re.search('\d+', 'u123uu888asf')
if obj:
print obj.group()
3、group和groups
a = "123abc456"
print re.search("([0-9]*)([a-z]*)([0-9]*)", a).group()
print re.search("([0-9]*)([a-z]*)([0-9]*)", a).group(0)
print re.search("([0-9]*)([a-z]*)([0-9]*)", a).group(1)
print re.search("([0-9]*)([a-z]*)([0-9]*)", a).group(2)
print re.search("([0-9]*)([a-z]*)([0-9]*)", a).groups()
4、findall(pattern, string, flags=0)
上述两中方式均用于匹配单值,即:只能匹配字符串中的一个,如果想要匹配到字符串中所有符合条件的元素,则需要使用 findall。
import re
obj = re.findall('\d+', 'fa123uu888asf')
print obj
5、sub(pattern, repl, string, count=0, flags=0)
用于替换匹配的字符串
content = "123abc456"
new_content = re.sub('\d+', 'sb', content)
# new_content = re.sub('\d+', 'sb', content, 1)
print new_content
相比于str.replace功能更加强大
6、split(pattern, string, maxsplit=0, flags=0)
根据指定匹配进行分组
content = "'1 - 2 * ((60-30+1*(9-2*5/3+7/3*99/4*2998+10*568/14))-(-4*3)/(16-3*2) )'"
new_content = re.split('\*', content)
# new_content = re.split('\*', content, 1)
print new_content
content = "'1 - 2 * ((60-30+1*(9-2*5/3+7/3*99/4*2998+10*568/14))-(-4*3)/(16-3*2) )'"
new_content = re.split('[\+\-\*\/]+', content)
# new_content = re.split('\*', content, 1)
print new_content
inpp = '1-2*((60-30 +(-40-5)*(9-2*5/3 + 7 /3*99/4*2998 +10 * 568/14 )) - (-4*3)/ (16-3*2))'
inpp = re.sub('\s*','',inpp)
new_content = re.split('\(([\+\-\*\/]?\d+[\+\-\*\/]?\d+){1}\)', inpp, 1)
print new_content
相比于str.split更加强大
Re mind map:

logging
用于便捷记录日志且线程安全的模块
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
|
import logginglogging.basicConfig(filename='log.log', format='%(asctime)s - %(name)s - %(levelname)s -%(module)s: %(message)s', datefmt='%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S %p', level=10)logging.debug('debug')logging.info('info')logging.warning('warning')logging.error('error')logging.critical('critical')logging.log(10,'log') |
对于等级:
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
|
CRITICAL = 50FATAL = CRITICALERROR = 40WARNING = 30WARN = WARNINGINFO = 20DEBUG = 10NOTSET = 0 |
只有大于当前日志等级的操作才会被记录。
对于格式,有如下属性可是配置:

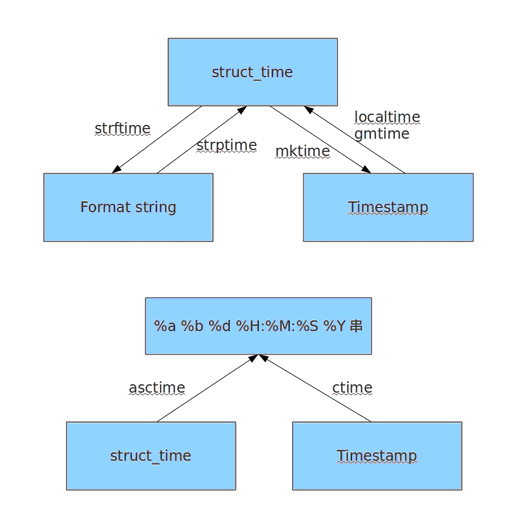
time
时间相关的操作,时间有三种表示方式:
- 时间戳 1970年1月1日之后的秒,即:time.time()
- 格式化的字符串 2014-11-11 11:11, 即:time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d')
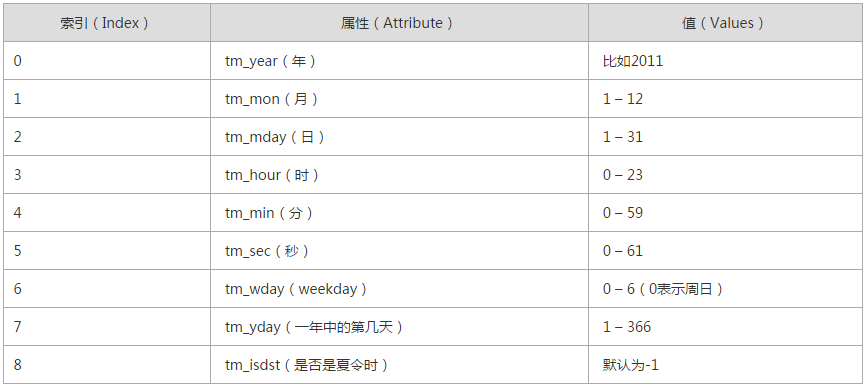
- 结构化时间 元组包含了:年、日、星期等... time.struct_time 即:time.localtime()
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
|
print time.time()print time.mktime(time.localtime()) print time.gmtime() #可加时间戳参数print time.localtime() #可加时间戳参数print time.strptime('2014-11-11', '%Y-%m-%d') print time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d') #默认当前时间print time.strftime('%Y-%m-%d',time.localtime()) #默认当前时间print time.asctime()print time.asctime(time.localtime())print time.ctime(time.time()) import datetime'''datetime.date:表示日期的类。常用的属性有year, month, daydatetime.time:表示时间的类。常用的属性有hour, minute, second, microseconddatetime.datetime:表示日期时间datetime.timedelta:表示时间间隔,即两个时间点之间的长度timedelta([days[, seconds[, microseconds[, milliseconds[, minutes[, hours[, weeks]]]]]]])strftime("%Y-%m-%d")'''import datetimeprint datetime.datetime.now()print datetime.datetime.now() - datetime.timedelta(days=5) |
os
用于提供系统级别的操作
os.getcwd() 获取当前工作目录,即当前python脚本工作的目录路径
os.chdir("dirname") 改变当前脚本工作目录;相当于shell下cd
os.curdir 返回当前目录: ('.')
os.pardir 获取当前目录的父目录字符串名:('..')
os.makedirs('dirname1/dirname2') 可生成多层递归目录
os.removedirs('dirname1') 若目录为空,则删除,并递归到上一级目录,如若也为空,则删除,依此类推
os.mkdir('dirname') 生成单级目录;相当于shell中mkdir dirname
os.rmdir('dirname') 删除单级空目录,若目录不为空则无法删除,报错;相当于shell中rmdir dirname
os.listdir('dirname') 列出指定目录下的所有文件和子目录,包括隐藏文件,并以列表方式打印
os.remove() 删除一个文件
os.rename("oldname","newname") 重命名文件/目录
os.stat('path/filename') 获取文件/目录信息
os.sep 输出操作系统特定的路径分隔符,win下为"\\",Linux下为"/"
os.linesep 输出当前平台使用的行终止符,win下为"\t\n",Linux下为"\n"
os.pathsep 输出用于分割文件路径的字符串
os.name 输出字符串指示当前使用平台。win->'nt'; Linux->'posix'
os.system("bash command") 运行shell命令,直接显示
os.environ 获取系统环境变量
os.path.abspath(path) 返回path规范化的绝对路径
os.path.split(path) 将path分割成目录和文件名二元组返回
os.path.dirname(path) 返回path的目录。其实就是os.path.split(path)的第一个元素
os.path.basename(path) 返回path最后的文件名。如何path以/或\结尾,那么就会返回空值。即os.path.split(path)的第二个元素
os.path.exists(path) 如果path存在,返回True;如果path不存在,返回False
os.path.isabs(path) 如果path是绝对路径,返回True
os.path.isfile(path) 如果path是一个存在的文件,返回True。否则返回False
os.path.isdir(path) 如果path是一个存在的目录,则返回True。否则返回False
os.path.join(path1[, path2[, ...]]) 将多个路径组合后返回,第一个绝对路径之前的参数将被忽略
os.path.getatime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后存取时间
os.path.getmtime(path) 返回path所指向的文件或者目录的最后修改时间
更多猛击这里
sys
用于提供对解释器相关的操作
sys.argv 命令行参数List,第一个元素是程序本身路径
sys.exit(n) 退出程序,正常退出时exit(0)
sys.version 获取Python解释程序的版本信息
sys.maxint 最大的Int值
sys.path 返回模块的搜索路径,初始化时使用PYTHONPATH环境变量的值
sys.platform 返回操作系统平台名称
sys.stdout.write('please:')
val = sys.stdin.readline()[:-1]
更多猛击这里
hashlib
用于加密相关的操作,代替了md5模块和sha模块,主要提供 SHA1, SHA224, SHA256, SHA384, SHA512 ,MD5 算法
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
18
19
20
21
22
23
24
25
26
27
28
29
30
31
32
|
import hashlib# ######## md5 ########hash = hashlib.md5()hash.update('admin')print hash.hexdigest()# ######## sha1 ########hash = hashlib.sha1()hash.update('admin')print hash.hexdigest()# ######## sha256 ########hash = hashlib.sha256()hash.update('admin')print hash.hexdigest()# ######## sha384 ########hash = hashlib.sha384()hash.update('admin')print hash.hexdigest()# ######## sha512 ########hash = hashlib.sha512()hash.update('admin')print hash.hexdigest() |
以上加密算法虽然依然非常厉害,但时候存在缺陷,即:通过撞库可以反解。所以,有必要对加密算法中添加自定义key再来做加密。
|
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
|
import hashlib# ######## md5 ########hash = hashlib.md5('898oaFs09f')hash.update('admin')print hash.hexdigest() |
还不够吊?python 还有一个 hmac 模块,它内部对我们创建 key 和 内容 再进行处理然后再加密
|
1
2
3
4
|
import hmach = hmac.new('wueiqi')h.update('hellowo')print h.hexdigest() |
不能再TM牛逼了!!!


