Vue+Vuex 实现自动登录功能
刚刚实现了Vue+Vuex的自动登录功能,在实现的时候遇到了一些问题,这里记录一下:
因为这个还不够完善,在写完下列代码后,又进行了补充,可以从https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoxineryi/p/12405563.html 看到补充内容
一、对于vuex的简单理解:
可以参考这个:https://zhuanlan.zhihu.com/p/24357762、https://segmentfault.com/a/1190000009404727
还有官网文档:https://vuex.vuejs.org/zh/guide/getters.html
差不多理解就是,vuex里面,用state来存储数据,在mutations里面写保存数据的函数,并且提供给外部调用,在getters中写获取数据的函数,在actions里面写获取数据后、写入数据前的处理过程。
二、在看网上很多示例的时候,代码写得挺好的,但是没有总的项目目录,一个函数一个函数的写,却又不知道要放在哪里,就感觉很别扭,所以我先把项目目录列出来:因为只用到了src下的,其他的按新建项目的就好
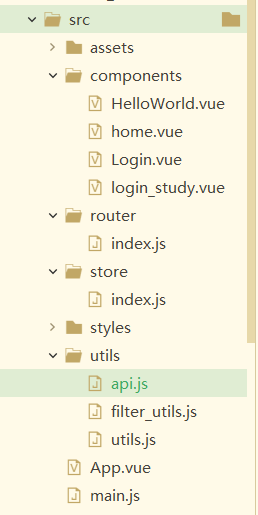
①:上一章的前后端分离里面,数据传递确实做到了,但是在Login.vue里面写的,很多重复的内容完全可以重用,所以这次干脆提出一个api来,专门用来传递数据。
另外,此次使用的是aoxis,本身就已经封装好很多了。

import axios from 'axios' let base = 'http://127.0.0.1:8090'; export const postRequest = (url, params) => { return axios({ method: 'post', url: `${base}${url}`, data: params, transformRequest: [function (data) { // Do whatever you want to transform the data let ret = '' for (let it in data) { ret += encodeURIComponent(it) + '=' + encodeURIComponent(data[it]) + '&' } return ret }], headers: { 'Content-Type': 'application/x-www-form-urlencoded' } }); }
base的路径,按照自己服务器的端口进行修改。
②:现在先在store里,定义好数据和方法(就相当于数据库):store/index.js
import Vue from 'vue'; import Vuex from 'vuex'; Vue.use(Vuex); const store = new Vuex.Store({ state: { // 存储token Authorization: localStorage.getItem('Authorization') ? localStorage.getItem('Authorization') : '' }, mutations: { // 修改token,并将token存入localStorage changeLogin (state, user) { // alert(user.Authorization); state.Authorization = user.Authorization; localStorage.setItem('Authorization', user.Authorization); } } }); export default store;
这里state里面就是存储的数据,这里就是存储用户的token,下面mutations,写了一个修改token的方法,这个方法将token写入localStorage,而且保存到自己的state中。
③:定义好了数据和方法以后,自动登录就是要在用户访问页面的时候,自动检查有没有token,token对不对:

// The Vue build version to load with the `import` command // (runtime-only or standalone) has been set in webpack.base.conf with an alias. import Vue from 'vue' import App from './App' import router from './router' import ElementUI from 'element-ui' import VueResource from 'vue-resource' import 'element-ui/lib/theme-chalk/index.css' // import './styles/element-variables.scss' import './styles/font-awesome-4.7.0/css/font-awesome.min.css' import './utils/filter_utils.js' import store from './store' import axios from 'axios' Vue.use(ElementUI) // Vue.use(VueResource) Vue.config.productionTip = false // Vue.http.options.emulateJSON = true /* eslint-disable no-new */ new Vue({ el: '#app', router, store:store, components: { App }, template: '<App/>' }) axios.interceptors.request.use( config => { if (localStorage.getItem('Authorization')) { config.headers.Authorization = localStorage.getItem('Authorization'); } return config; }, error => { return Promise.reject(error); });
在这里面,有两个需要注意的:
第一个就是,因为定义了store,所以在常规的main之外,还在Vue里面多加了一个store,否则的话,在使用的使用就相当于与没有注册,查找不到,经常有如下错误:
Cannot read property 'commit' of undefined
第二个就是下面的拦截器:因为只是对全局的访问都配置,所以直接就在全局中写了,而且前面是axios.interceptors.request.xx,前面的axios就表示了是全局的。
如果要对某个方法来使用,应该先创建一个axios,然后假设这个变量名为xx,则使用xx.interceptors来执行,后面用request或者response来表示是请求数据还是响应数据。
更详细的可以看https://www.jianshu.com/p/646ed4edf51f
④:在router/index.js中,也就是路由里面,也需要添加内容:
import Vue from 'vue' import Router from 'vue-router' import HelloWorld from '@/components/HelloWorld' import login from '@/components/login.vue' import home from '@/components/home.vue' import logo from '@/components/HelloWorld.vue' Vue.use(Router); const router = new Router({ mode:'history', routes:[ { path:'/login', name:'登录', component:login, }, { path:'/', name:'主页', component:logo, } ] }); router.beforeEach((to,from,next)=>{ if(to.path ==='/login'){ next(); }else { let token = localStorage.getItem('Authorization'); if(token ===null || token ===''){ next('/login'); }else { // alert(localStorage.getItem("Authorization")); next(); } } }); export default router;
第一点就是将router加上mode:'history',这个也不知道为啥,反正我写的时候,没有这个就不管什么页面都跳转到首页,怎么调都不管用,加上这一句话就好了。
第二个就是定义了一个beforeEach的函数,这个可以检测来的请求路径、去的请求路径,加上token检测,可以让用户如果没有登录就自动跳转到登录界面。
⑤:再写登录页面:
<template> <el-form :rules="rules" class="login-container" label-position="left" label-width="0px" v-loading="loading"> <h3 class="login_title">系统登录</h3> <el-form-item prop="account"> <el-input type="text" v-model="loginForm.username" auto-complete="off" placeholder="账号"></el-input> </el-form-item> <el-form-item prop="checkPass"> <el-input type="password" v-model="loginForm.password" auto-complete="off" placeholder="密码"></el-input> </el-form-item> <el-checkbox class="login_remember" v-model="checked" label-position="left">记住密码</el-checkbox> <el-form-item style="width: 100%"> <el-button type="primary" @click.native.prevent="submitClick" style="width: 100%">登录</el-button> </el-form-item> </el-form> </template> <script> import {postRequest} from '../utils/api' import {putRequest} from '../utils/api' import { mapMutations } from 'vuex'; export default{ data(){ return { rules: { account: [{required: true, message: '请输入用户名', trigger: 'blur'}], checkPass: [{required: true, message: '请输入密码', trigger: 'blur'}] }, checked: true, loginForm: { username: '11', password: '123' }, loading: false } }, methods: { ...mapMutations(['changeLogin']), submitClick: function () { var _this = this; this.loading = true; postRequest('/login', { username: this.loginForm.username, password: this.loginForm.password }).then(resp=> { _this.loading = false; if (resp.status == 200) { //成功 var json = resp.data; if (json.status == 'success') { _this.userToken = 123; // localStorage.setItem('Authorization',_this.userToken); _this.changeLogin({Authorization:_this.userToken}); _this.$router.replace({path: '/'}); } else { _this.$alert('登录失败!', '失败!'); } } else { //失败 _this.$alert('登录失败!', '失败!'); } }, resp=> { _this.loading = false; _this.$alert('找不到服务器⊙﹏⊙∥!', '失败!'); }); } } } </script> <style> .login-container { border-radius: 15px; background-clip: padding-box; margin: 180px auto; width: 350px; padding: 35px 35px 15px 35px; background: #fff; border: 1px solid #eaeaea; box-shadow: 0 0 25px #cac6c6; } .login_title { margin: 0px auto 40px auto; text-align: center; color: #505458; } .login_remember { margin: 0px 0px 35px 0px; text-align: left; } </style>
这里一定不要忘了引入函数
⑥在这里我们可以看到,返回的是json数据,对应后台可以:先创建一个Bean,用来专门返回响应内容:
package com.example.Bean; public class RespBean { private String status; private String msg; public RespBean() { } public RespBean(String status, String msg) { this.status = status; this.msg = msg; } public String getStatus() { return status; } public void setStatus(String status) { this.status = status; } public String getMsg() { return msg; } public void setMsg(String msg) { this.msg = msg; } }
而在controller中,直接调用即可:
package com.example.Controller; import com.example.Bean.RespBean; import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller; import org.springframework.ui.Model; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.CrossOrigin; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestParam; import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RestController; @RestController public class TestController { @CrossOrigin(origins = "*") @RequestMapping("/login") public RespBean login( @RequestParam(value = "username", required = false) String username, @RequestParam(value = "password",required = false) String password, Model model ){ System.out.println("用户名为"+username); System.out.println("密码为"+password); if (username.equals("11")){ return new RespBean("success","登录成功"); }else{ return new RespBean("fail","登录失败"); } } }





