Spring学习笔记(三):面向切面的Spring
Spring之面向切面编程
一、理解何为面向切面编程
对于这个的理解,我觉得Spring实战中的例子讲得很明白:
假设我现在是一个小区用户,每个月小区都要收电费,这时候就会来人查看电表,算出来这个月电费是多少,然后让我去结账。
但在我很小的时候,其实电费是每个人家里有电表,要自己充电费,如果没电了就会断电,所以经常会出现在家里用着用着电,突然断电的情况,这时候就要下楼看电表,检查是没电费了还是跳闸了。
电对家庭而言十分重要,哪里都离不开用电,但是我们更关注吃饭、睡觉、游戏等等跟我们密切相关的事情,检查电表虽然很重要,但这更像是一个被动且必须的操作,而第一种情况就是实现了切面式编程,把检查电表的操作提取了出来,变成一个统一的行为,我们不需要再自己去检查电表了,而是不管我们干什么,总会有人在对应的时间处理电费的问题,让我们可以更专心于与自己密切相关的事物中。
二、AOP的实现
对于通知织入,有动态织入和静态织入两种方法,他们的实现原理并不相同,我们来看一看两种实现方法的区别:
静态织入:ApectJ采用的就是静态织入的方式。ApectJ主要采用的是编译期织入,在这个期间使用AspectJ的acj编译器(类似javac)把aspect类编译成class字节码后,在java目标类编译时织入,即先编译aspect类再编译目标类。
具体流程大概如下图所示:
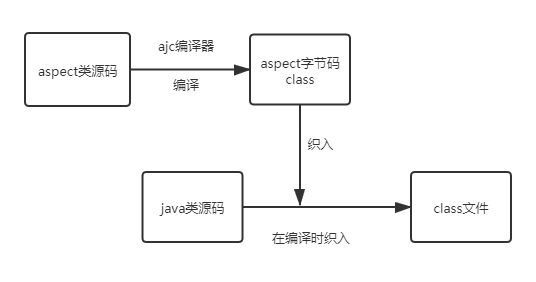
对于更详细的说明,可以参照 https://blog.csdn.net/javazejian/article/details/56267036#oop%E7%9A%84%E6%96%B0%E7%94%9F%E6%9C%BA ,有很详细的说明
动态织入:其原理主要是代理模式,如Java JDK的动态代理(Proxy,底层通过反射实现)或者CGLIB的动态代理(底层通过继承实现)。而Spring AOP的实现,也是基于动态代理的方法。因为Spring基于动态代理,所以Spring只支持方法连接点,对于字段、构造器连接点等,Spring无法实现,如果要实现对应功能,只能使用Aspect等来补充实现。
三、Spring基于注解实现切面编程
1、定义切点:
我们新建一个表示表演的接口,来作为可以织入的连接点:
public interface Performance { public void perform(); }
然后定义切点,一般使用execution()指示器,常见的格式为:

除了可以定义切点以外,还可以通过其他指示器添加限定:
@within(com.xiaoxin.xxx)指示器表示只有对应的类上有对应的注解,才可以被代理增强。
关于@Within更深一步的理解,可以参考 https://www.jianshu.com/p/fb109e03edec
@Bean("id")指示器表示,只有是ID为对应id的的Bean对象执行方法的时候,才可以被代理增强。
2、定义切面:
首先定义一个Audience类,该类的方法会织入到perform()方法之中。
在Spring AOP中,一共有五种通知,分别是:
前置通知[Before advice]:在连接点前面执行,前置通知不会影响连接点的执行,除非此处抛出异常。
正常返回通知[After returning advice]:在连接点正常执行完成后执行,如果连接点抛出异常,则不会执行。
异常返回通知[After throwing advice]:在连接点抛出异常后执行。
返回通知[After (finally) advice]:在连接点执行完成后执行,不管是正常执行完成,还是抛出异常,都会执行返回通知中的内容。
环绕通知[Around advice]:环绕通知围绕在连接点前后,比如一个方法调用的前后。这是最强大的通知类型,能在方法调用前后自定义一些操作。环绕通知还需要负责决定是继续处理join point(调用ProceedingJoinPoint的proceed方法)还是中断执行。
我们先看最基本的方法:
@Aspect public class Audience { @Before("execution(* com.xiaoxin.Concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void TakeSeat(){ System.out.println("Audience are taking seats"); } @AfterReturning("execution(* com.xiaoxin.Concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void applause(){ System.out.println("Clap!"); } @AfterThrowing("execution(* com.xiaoxin.Concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void demandFund(){ System.out.println("Audience are asking for fund"); } }
这里我们直接把对应指示器的内容传入,但很明显发现一个问题,这里的切点都是一样的,都写一遍太麻烦了,所以可以有下面的改进方法:
@Aspect public class Audience { @Pointcut("execution(* com.xiaoxin.Concert.Performance.perform(..))") public void performance(){} @Before("performance()") public void TakeSeat(){ System.out.println("Audience are taking seats"); } @AfterReturning("performance()") public void applause(){ System.out.println("Clap!"); } @AfterThrowing("performance()") public void demandFund(){ System.out.println("Audience are asking for fund"); } }
直接定义切点,然后在后续定义通知时,直接使用建立的切点即可。
与其他四个通知不同,环绕通知可以直接替代前置通知和后置通知,但使用方法有些许区别:
@Around("performance()")
public void aroundTest(ProceedingJoinPoint jp){
try{
System.out.println("Audience are taking seats Around");
jp.proceed();
System.out.println("Clap! Around");
} catch (Throwable throwable) {
throwable.printStackTrace();
System.out.println("Audience are asking fund Around");
}
}
在这里,我们可以看到jp.proceed(),就是执行对应的方法,而前面执行前置通知,后面是成功返回的通知,catch里面对应是抛出异常的通知。
现在定义好了切面和通知,但有一个问题就是,现在定义的通知,都是无参的,但比如我是查电表的,我需要获得电表数这样的参数,这时候需要怎么做呢?
需要增加参数,使用args()指示器,现在添加一个售票的电影院类,而作为观众,需要再进入之前看看自己有没有足够的钱来购买电影票:
public interface Cinema { public void sell(int money); }
@Component public class ChinaCinema implements Cinema { @Override public void sell(int money) { System.out.println("the price of ticket is "+money); } }
现在已经添加好电影院类以后,增加切点和通知:
@AfterReturning("execution(* com.xiaoxin.Concert.Cinema.sell(int)) &&args(money)")
public void check(int money){
System.out.println("i will check if i have money more than "+money);
}
这里的关注点是:&&angs(money)还有sell(int)这两个要搭配使用,前面加入int的参数后,在后面默认为这个的参数,这样就可以使用了。
这里第三个问题就是上面的注解@Aspect,该注解表示Audience不仅仅是一个POJO,还是一个切面。Audience类中的方法都使用注解来定义切面的具体行为。
但仅仅配置了@Aspect注解还不够,如果注解不被解析的话,Audience也只能被当做一个普通的Java类来使用,因此我们需要对切面的解析进行配置。
3、配置自动代理:
配置既可以使用java配置类来实现,也可以使用xml文件来实现:
对于Java配置类,可以用如下注解实现:
@Configuration @EnableAspectJAutoProxy @ComponentScan public class ConcertConfig { @Bean public Audience audience(){ return new Audience(); } }
前面几个注解已经很熟悉了,@Configuration表示这是一个注解类,@ComponentScan表示自动扫描该配置类所在包的所有内容,里面的@Bean注解,表示注册了一个Audience的对象进入Spring容器,唯一没见过的就是这个@EnableAspectJAutoProxy注解,这个注解表示启用自动代理。
如果使用xml配置,那么xml文件应该如此:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <beans xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop/spring-aop.xsd" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:aop="http://www.springframework.org/schema/aop"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.xiaoxin.Concert"/> <aop:aspectj-autoproxy/> <bean class="com.xiaoxin.Concert.Audience"/> </beans>
4、测试使用
@RunWith(SpringJUnit4ClassRunner.class) @ContextConfiguration(classes = com.xiaoxin.Concert.ConcertConfig.class) public class AOPTest { @Autowired Performance artist; @Autowired Cinema chinaCinema; @Test public void test(){ chinaCinema.sell(50); //这里刚刚犯的一个很大的错误:不应该直接new 而是从容器里面获得建立好的Bean对象 artist.perform(); } }
这里要不然就获得ApplicationContext(应用上下文对象)来获得容器里的Bean,要不然就使用@Autowired来自动装配对应对象,不要在里面直接new,这样new出来的是新的对象,但AOP的原理是代理机制,是获得出来的对象不再是之前的类对象,而是经过代理增强后的对象,因此不能直接new,必须要从Spring容器中获取才可以。
四、Spring基于xml文件配置切面:
其实配置方法大同小异,就是把注解中的@Component变为一个<bean>标签声明,然后把切面方法都声明在<aop:config>中:
<aop:aspectj-autoproxy/>
<bean id="artist" class="com.xiaoxin.ConcertXml.Artist"/>
<bean id="audience" class="com.xiaoxin.ConcertXml.Audience"/>
<bean id="cinema" class="com.xiaoxin.ConcertXml.ChinaCinema"/>
<bean id="DefaultEncoreable" class="com.xiaoxin.ConcertXml.DefaultEncoreable"/>
<aop:config>
<aop:aspect ref="audience">
<aop:pointcut id="perform" expression="execution(* com.xiaoxin.ConcertXml.Performance.perform(..))"/>
<aop:before method="TakeSeat" pointcut-ref="perform"/>
<aop:before method="check" pointcut="execution(* com.xiaoxin.ConcertXml.Cinema.sell(int)) and args(money)"/>
</aop:aspect>
</aop:config>
这里要注意的就是:不要忘记配置自动代理。
用xml配置的好处就是,在有些时候,我们是不能修改源代码来增加注解的,比如从其他地方下载的jar包等,这时候就要用xml配置来完成切面的装配。



