JAVA 集合三(Set、HashSet、TreeSet、LinkedHashSet)
一、Set概述和特点
概述:一个不包含重复元素的 collection。更确切地讲,set 不包含满足 e1.equals(e2) 的元素对 e1 和 e2,并且最多包含一个 null 元素。正如其名称所暗示的,此接口模仿了数学上的 set 抽象。
特点:不包含重复的集合;没有带索引的方法,所以不能使用普通for循环遍历
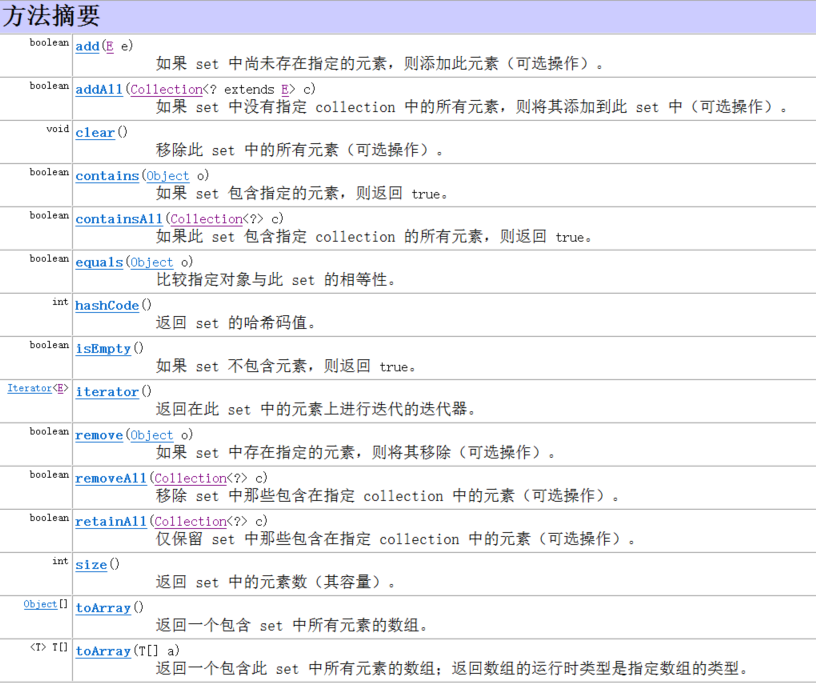
二、方法
三、哈希值
概述:是JDK根据对象的地址或者字符串或者数学算出来的int类型的数值
获取方式:Object类中的方法获取对象的哈希值 public int hashCode()
四、HasSet
概述:此类实现一个哈希表,该哈希表将键映射到相应的值。任何非 null 对象都可以用作键或值。
特点:底层数据结构是哈希表
对集合的迭代顺序不做任何保证,也就是说不保证存储和取出的元素顺序一致
没有带索引的方法,所以不能使用普通for循环遍历
由于Set集合,所以是不是包含重复元素的集合
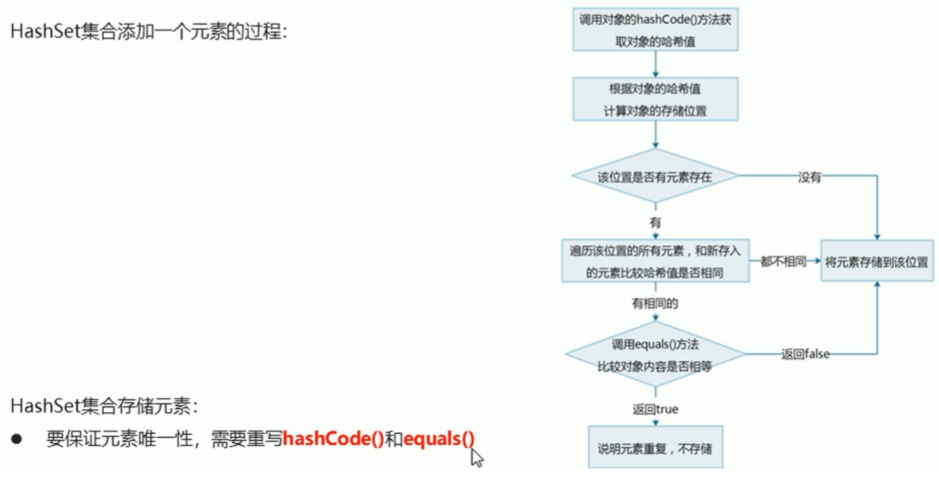
五、HashSet集合保证元素唯一性源码分析
@Override
public boolean equals(Object o) {
if (this == o) return true;
if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
Student student=(Student) o;
return Age == student.Age && Objects.equals(Name, student.Name);
}
@Override
public int hashCode() {
return Objects.hash(Name, Age);
}
六、LinkedHashSet集合
概述:具有可预知迭代顺序的 Set 接口的哈希表和链接列表实现。此实现与 HashSet 的不同之外在于,后者维护着一个运行于所有条目的双重链接列表。此链接列表定义了迭代顺序,即按照将元素插入到 set 中的顺序(插入顺序)进行迭代。注意,插入顺序不 受在 set 中重新插入的 元素的影响。(如果在 s.contains(e) 返回 true 后立即调用 s.add(e),则元素 e 会被重新插入到 set s 中。)
特点:哈希表和链表实现的Set接口,具有可预测的迭代次序
由链表保证元素有序,也就是说元素的存储和取出顺序是一致的
由哈希表保证元素唯一,也就是说没有重复的元素
Set set=new LinkedHashSet();
七、TreeSet集合
概述:基于 TreeMap 的 NavigableSet 实现。使用元素的自然顺序对元素进行排序,或者根据创建 set 时提供的 Comparator 进行排序,具体取决于使用的构造方法。
特点:元素有序,这里的顺序不是指的存储和取出的顺序,而是按照一定的规则进行排序,具体排序方式取决于构造方法
TreeSet():根据其元素的自然排序进行排序
TreeSet(Comparator comparator):根据指定的比较器进行排序
没有带索引的方法,所以不能使用普通的for循环遍历
由于是Set集合,所以不包含重复元素的集合
八、自然排序Comparable的使用
方式一:重新自然排序方法
public class Student implements Comparable {
public Student() {
}
public Student(String name, int age) {
this.Name=name;
this.Age=age;
}
private String Name;
private int Age;
public String GetName() {
return this.Name;
}
public void SetName(String name) {
this.Name=name;
}
public void SetAge(int age) {
this.Age=age;
}
public int GetAge() {
return this.Age;
}
//继承接口:Comparable 重写比较器
@Override
public int compareTo(Object o) {
Student st=(Student) o;
int num=this.GetAge()- st.GetAge();
num=num==0?this.GetName().compareTo(st.GetName()):num;
return num;
}
// @Override
// public boolean equals(Object o) {
// if (this == o) return true;
// if (o == null || getClass() != o.getClass()) return false;
// Student student=(Student) o;
// return Age == student.Age && Objects.equals(Name, student.Name);
// }
//
// @Override
// public int hashCode() {
// return Objects.hash(Name, Age);
// }
}
方式二:初始化TreeSet用匿名函数写比较器
TreeSet<Student> ts=new TreeSet<Student>(new Comparator<Student>() {
@Override
public int compare(Student s1, Student s2) {
int num=s1.GetAge()- s2.GetAge();
num=num==0?s1.GetName().compareTo(s2.GetName()):num;
return num;
}
});



