OpenCV中Mat与二维数组之间的转换
---恢复内容开始---
在OpenCV中将Mat(二维)与二维数组相对应,即将Mat中的每个像素值赋给一个二维数组。
全部代码如下:
#include <iostream> #include <opencv2/core/core.hpp> #include <opencv2/highgui/highgui.hpp> //包含imread, imshow等标识符 #include "opencv2/imgproc/imgproc.hpp" //包含cvtColor等 using namespace std; using namespace cv; //测试Mat void main(){ //读入图像 Mat mat = imread("trabeculae.jpg"); //判断读入图片是否有误 if(mat.empty()) { if (!mat.data) { printf("Oh,no,读取图片文件错误~! \n"); } cout << "error" << endl; } // 进行图像灰度化操作 cvtColor(mat, mat, CV_BGR2GRAY); //获取 mat 的行和列 int row = mat.rows; int col = mat.cols; cout << " mat.rows : " << mat.rows << endl; cout << " mat.cols : " << mat.cols << endl; //动态创建二维数组,row行col列 int **La = new int *[row]; for (int i = 0; i < row; i ++){ La[i] = new int[col]; } // 循环二维数组和mat,并将mat对应值赋给二维数组对应值, for (int i = 0; i < row; i ++){ for (int j = 0; j < col; j ++){ La[i][j] = mat.at<uchar>(i, j); } } // 释放分配空间 for (int i = 0; i < row; i ++){ delete []La[i]; } delete [] La; cout << endl; waitKey(0); system("pause"); }
分析:
1. 读入一幅图像
//读入图像 Mat mat = imread("trabeculae.jpg"); //判断读入图片是否有误 if(mat.empty()) { if (!mat.data) { printf("Oh,no,读取图片文件错误~! \n"); } cout << "error" << endl; }
2. 对图像进行灰度化操作,将Mat转为二维。
// 进行图像灰度化操作 cvtColor(mat, mat, CV_BGR2GRAY);
3. Mat有rows和cols属性,rows表示对应矩阵行数,cols表示对应矩阵列数:
//保存mat的行和列 int row = mat.rows; int col = mat.cols;
4. Mat还具有size () 方法,该方法可以得到width宽度和height高度:
Size s = mat.size(); int width = s.width; int height = s.height;
5. rows,cols,width,height 之间的关系:
cout << " s.width : " << s.width << endl; cout << " s.height : " << s.height << endl;
cout << " mat.rows : " << mat.rows << endl; cout << " mat.cols : " << mat.cols << endl;
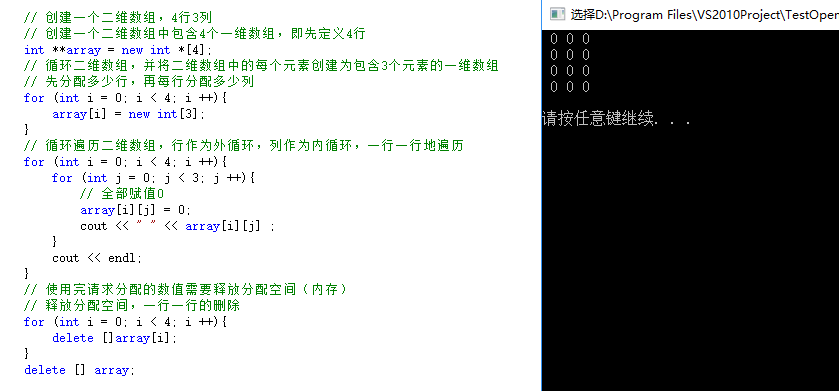
6. 打印结果:

7. 结论:
由第5步和第6步可得:
mat.size().width = mat.cols;
mat.size().height = mat.rows;
8. 动态创建二维数组:
例:创建一个4行3列的二维数组,如下:
{ { 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0 }, { 0, 0, 0 } }
即:{ { 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0 },
{ 0, 0, 0 }
}
// 创建一个二维数组中包含4个一维数组,即先定义4行 int **array = new int *[4]; // 循环二维数组,并将二维数组中的每个元素创建为包含3个元素的一维数组 // 先分配多少行,再每行分配多少列 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++){ array[i] = new int[3]; } // 循环遍历二维数组,行作为外循环,列作为内循环,一行一行地遍历 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++){ for (int j = 0; j < 3; j ++){ array[i][j] = 0; cout << " " << array[i][j] ; } cout << endl; } // 使用完请求分配的数值需要释放分配空间(内存) // 释放分配空间,一行一行的删除 for (int i = 0; i < 4; i ++){ delete []array[i]; } delete [] array;
结果:
9. 使用Mat图像的宽度和高度进行动态创建二维数组,Height(row)代表具有多少行,width(col)代表具有多少列。
// 创建一个二维数组,height(row)行width(col)列 int **La = new int *[height]; for (int i = 0; i < height; i ++){ La[i] = new int[width]; } // 循环将Mat中对应的值赋给La二维数组 for (int i = 0; i < row; i ++){ for (int j = 0; j < col; j ++){ La[i][j] = mat.at<uchar>(i, j); //cout << " " << La[i][j] ; } //cout << endl; } // 释放分配空间 for (int i = 0; i < height; i ++){ delete []La[i]; } delete [] La;
10. 创建一个和二维数组行列大小的Mat:
当知道二维数组的大小,需要将二维数组中的值赋给同样大小的Mat,使用Mat显示。
//创建一个Mat变量 height(row)行width(col)列 Mat temp = Mat(height, width, CV_8U, Scalar::all(0)); // 循环赋值 for (int i = 0; i < height; i ++){ for (int j = 0; j < width; j ++){ mat.at<uchar>(i, j) = La[i][j]; } }
---恢复内容结束---




【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】凌霞软件回馈社区,博客园 & 1Panel & Halo 联合会员上线
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】博客园社区专享云产品让利特惠,阿里云新客6.5折上折
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步