dotnetCore增加MiddleWare的Run,Use Map MapThen四个扩展方法
什么是中间件
中间件是在管道中处理Request请求与Responses响应的一种组件,每种组件可以选择是否让Request进入到下一个组件去处理。
译得不好,大家可以自己看原文Middleware
更详细的还可以参照园中大神的作品;
有汤姆大叔的解读ASP.NET 5 & MVC6系列(6):Middleware详解
artech大神的 ASP.NET Core真实管道详解[1]:中间件是个什么东西?
怎么创建一个Middleware请参考英文文档Middleware 或者
LineZero的 ASP.NET Core 开发-中间件(Middleware)
要正确使用Middleware来构建自己的应该程序,需要理解Run,Use,Map,MapThen这四个方法是如何使用的, 下面Ricman将自己的理解与大家分享。
一、Run扩展方法
Run方法在说明上是这样的:在管道的尾端增加一个Middleware;它是执行的最后一个Middleware。即它执行完就不再执行下一个Middleware了。如下代码示例。
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline. public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory) { loggerFactory.AddConsole(Configuration.GetSection("Logging")); loggerFactory.AddDebug(); var loger = loggerFactory.CreateLogger("TestLogger"); //第一个Run 执行了 app.Run(async context => { loger.LogInformation("run 1 start"); await context.Response.WriteAsync("hello world!,run 1"); loger.LogInformation("run 1 end"); }); //第二个Run 没的执行 app.Run(async context => { loger.LogInformation("run 2 start"); await context.Response.WriteAsync("hello world!,run 2"); loger.LogInformation("run 2 end"); }); }
输出的结果为:
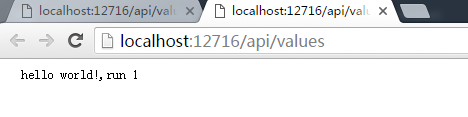
只打印出了第一个Run中的内容。而程序也不会响应第二个Run方法中的内容。
二、Use扩展方法
Use方法,则是在管道中增加一个Middleware。如果调用了next.Invoke()方法,它会去执行下一个Middleware 。我们把上面的例子稍作修改:
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline. public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory) { loggerFactory.AddConsole(Configuration.GetSection("Logging")); loggerFactory.AddDebug(); var loger = loggerFactory.CreateLogger("TestLogger"); //use 方法 执行了 app.Use (async (context,next) => { loger.LogInformation("Use 1 start"); await context.Response.WriteAsync("hello world!,Use 1"); loger.LogInformation("Use 1 end"); }); //Run 方法没的执行 app.Run(async context => { loger.LogInformation("run 1 start"); await context.Response.WriteAsync("hello world!,run 1"); loger.LogInformation("run 1 end"); }); }
输出结果是什么?
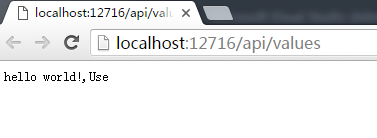
没有调用next.Invoke();尾端的Middleware即Run方法内没有执行。使用Use方法,而没有调用next.Invoke(),Use的效果与Run的效果是一致的。为了验证Use 的效果,我们再修改代码。
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline. public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory) { loggerFactory.AddConsole(Configuration.GetSection("Logging")); loggerFactory.AddDebug(); var loger = loggerFactory.CreateLogger("TestLogger"); //执行了 app.Use (async (context,next) => { loger.LogInformation("Use 1 start"); await context.Response.WriteAsync("hello world!,Use "); await next.Invoke(); loger.LogInformation("Use 1 end"); }); //没的执行 app.Run(async context => { loger.LogInformation("run 1 start"); await context.Response.WriteAsync(" hello world!,run "); loger.LogInformation("run 1 end"); }); }
此时,输入以下的结果
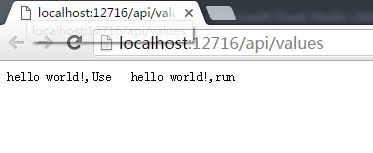
即Use与Run代码段都被执行了。需要注意的是,管道中可以增加多个middleware,他们是按顺序执行的,执行的顺序与在Configure方法中代码的顺序是一致的。
三、Map与MapThen
Map比较不同,它将Middleware添加到管道中,它是在管道中增加了分枝。通过影射路径的方式,增加管道分枝。我们保留上面例子,并增加代码。如下:
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline. public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory) { loggerFactory.AddConsole(Configuration.GetSection("Logging")); loggerFactory.AddDebug(); var loger = loggerFactory.CreateLogger("TestLogger"); //执行了 app.Use (async (context,next) => { loger.LogInformation("Use 1 start"); await context.Response.WriteAsync("hello world!,Use "); await next.Invoke(); loger.LogInformation("Use 1 end"); }); app.Map("/mapTest", HandleMap); //没的执行 app.Run(async context => { loger.LogInformation("run 1 start"); await context.Response.WriteAsync(" hello world!,run "); loger.LogInformation("run 1 end"); }); } private static void HandleMap(IApplicationBuilder app) { app.Run(async context => { await context.Response.WriteAsync("Hello ,that is Handle Map "); }); }
运行起来,我们在浏览器中输入” http://localhost:12716/mapTest” 得到的结果如下:

mapTest分枝被执行了。
MapThen就更有意思,从字面上感觉有点类似查询的意思。对了。它就是处理符合条件的Request去执行给定的方法。我们修改代码
// This method gets called by the runtime. Use this method to configure the HTTP request pipeline. public void Configure(IApplicationBuilder app, IHostingEnvironment env, ILoggerFactory loggerFactory) { loggerFactory.AddConsole(Configuration.GetSection("Logging")); loggerFactory.AddDebug(); var loger = loggerFactory.CreateLogger("TestLogger"); //执行了 app.Use (async (context,next) => { loger.LogInformation("Use 1 start"); await context.Response.WriteAsync("hello world!,Use "); await next.Invoke(); loger.LogInformation("Use 1 end"); }); app.MapWhen(context => { return context.Request.Query.ContainsKey("q"); }, HandleQuery); //没的执行 app.Run(async context => { loger.LogInformation("run 1 start"); await context.Response.WriteAsync(" hello world!,run "); loger.LogInformation("run 1 end"); }); } private static void HandleQuery(IApplicationBuilder app) { app.Run(async context => { await context.Response.WriteAsync(" Hello ,this is Handle Query "); }); }
我们要处理的是:如果有URL中的参数包含了q字母的话,就去执行HandleQuery方法。看一下结果

可以看出来,MapWhen可以处理很多的东西,比如我们要处理Request表头中某特定的内容,可以使用MapWhen来处理。
如果你觉得本文对你有帮助,请点击“推荐”



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号