1概念具
集合Java的集合是工具类,可以存储任意数量的具有共同属性的对象。
2体系结构(分为2类一类为Collection一类为Map)
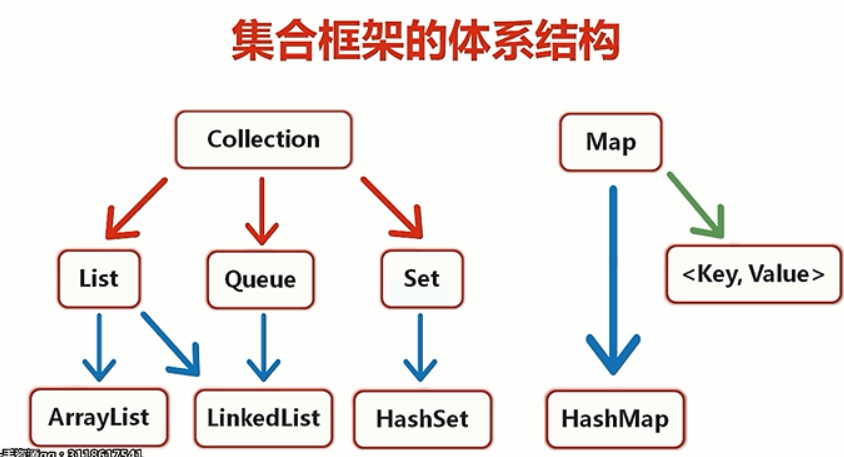
1Collection
1List
是元素有序并且可以重复的序列并且可以重复的集合
可以精确的控制每个元素的插入位置,或者删除某个位置
主要有两个类ArrayList和LinkedList
ArrayList
底层是由数组实现的
动态增长,以满足应用程序的需求
在列表尾部插入或者删除数据非常有效
更适合查找和更新元素
ArrayList可以为Null;
在ArrayList添加数据,删除数据,和输出数据

package com.jiedada.arraylist; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class ArrayListOne { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //创建一个ArrayList并且添加数据 List list=new ArrayList(); list.add("java"); list.add("C++"); list.add("GO"); list.add("C"); list.add("swit"); //输出结果 for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) { System.out.print(list.get(i)+" "); } //删除GO System.out.println("**************************"); list.remove(2); for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) { System.out.print(list.get(i)+" "); } } }
公告通知实列
1公告添加和显示
2在指定位置插入公告
3删除公告
4显示公告
注意:Data方法是JAVA中自带的方法,我们使用的时间函数在uitl中
在ArrayList中数组的长度方法为.size,删除方法为remove;set为修改数据;set不能更改ArrayList的长度;
创建广告类

package com.jiedada.arraylist; import java.util.Date; public class Notice { private int id; private String name; private Date date; private String title; public Notice(int id, String name, Date date, String title) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.date = date; this.title = title; } public int getId() { return id; } public void setId(int id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public Date getDate() { return date; } public void setDate(Date date) { this.date = date; } public String getTitle() { return title; } public void setTitle(String title) { this.title = title; } }
对广告类进行改动

package com.jiedada.arraylist; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.Date; public class NoticeTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //创建Notice类,生成公告 Notice notice1=new Notice(1, "jiedada",new Date(),"欢迎来到杰大大这里"); Notice notice2=new Notice(2, "jiedada",new Date(),"不准玩网络游戏"); Notice notice3=new Notice(3, "jiedada",new Date(),"不能在电脑上乱动东西哦"); //添加公告 ArrayList noticelist=new ArrayList(); noticelist.add(notice1); noticelist.add(notice2); noticelist.add(notice3); //显示内容 for(int i=0;i<noticelist.size();i++) { System.out.println(((Notice)(noticelist.get(i))).getTitle()); } System.out.println("**************************"); //在公告中添加一个杰是大帅哥 Notice notice4=new Notice(4, "jiedadadexiaomimei",new Date(), "杰是大帅哥"); noticelist.add(notice4); for(int i=0;i<noticelist.size();i++) { System.out.println(((Notice)(noticelist.get(i))).getTitle()); } System.out.println("**************************"); //删除数据 noticelist.remove(3); for(int i=0;i<noticelist.size();i++) { System.out.println(((Notice)(noticelist.get(i))).getTitle()); } System.out.println("**************************"); //修改数据 notice2.setTitle("杰大大不在的时候不准玩游戏"); noticelist.set(1,notice2); for(int i=0;i<noticelist.size();i++) { System.out.println(((Notice)(noticelist.get(i))).getTitle()); } } }
2Queue
3Set
是元素无序并且不重复的集合。
HashSet
是Set的重要实现类,叫哈希集
HashSet的元素无序并且不重复
HashSet中只允许一个null
具有良好的查找和存储功能
在这个类中没有get()方法需要使用迭代器
迭代器是一个接口也是在uitl中的,迭代器每次使用的时候最好在定义一次;
在迭代器中.next()方法中用用到向下转型,这样很容易出错,我们不知道。next()方法中是不是全部都是这样的类型的类;
所以我们引入泛型,在定义的时候这样定义Set<Cat> set=new HashSet<Cat>();
有hasNext()方法检测集合中是否还有元素;
next()返回集合中的下一个元素;
代码如下

package com.jiedada.arraylist; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Set; public class hashhanshu { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub //添加颜色 Set set=new HashSet(); set.add("blue"); set.add("red"); set.add("yellow"); set.add("wilte"); set.add("green"); //用迭代器进行输出 Iterator it=set.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { System.out.print(it.next()+" "); } System.out.println("**************************"); //添加wilte set.add("wilte"); it=set.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { System.out.print(it.next()+" "); } System.out.println("**************************"); } }
在添加相同属性时,HashSet不会自动判断需要重写HashCode和equles方法;
什么是哈希表:通过特定的规则把数据分为几份,在在数据中找到我们需要的数据;
如通过n%3分为3分,0为一份,1为一份,2为一份;
Cat的方法

package com.jiedada.arraylist; public class Cat { String name; int mouth; String speice; public Cat(String name, int mouth, String speice) { super(); this.name = name; this.mouth = mouth; this.speice = speice; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getMouth() { return mouth; } public void setMouth(int mouth) { this.mouth = mouth; } public String getSpeice() { return speice; } public void setSpeice(String speice) { this.speice = speice; } @Override public String toString() { return "Cat [name=" + name + ", mouth=" + mouth + ", speice=" + speice + "]"; } @Override public int hashCode() { final int prime = 31; int result = 1; result = prime * result + mouth; result = prime * result + ((name == null) ? 0 : name.hashCode()); result = prime * result + ((speice == null) ? 0 : speice.hashCode()); return result; } @Override public boolean equals(Object obj) { if(this==obj) { return false; } if(obj.getClass()==Cat.class) { Cat cat=(Cat)obj; return cat.getName().equals(name)&&(cat.getMouth()==mouth)&&cat.getSpeice().equals(speice); } return true; } }
test的方法

package com.jiedada.arraylist; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Set; public class CatTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Cat huahua=new Cat("花花",12,"英国猫"); Cat fanfan=new Cat("凡凡",3,"中国田园猫"); Set set=new HashSet(); set.add(huahua); set.add(fanfan); Iterator it=set.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); } System.out.println("**************"); //添加属性 Cat cat=new Cat("花花",12,"英国猫"); set.add(cat); it=set.iterator(); System.out.println("改变后的结果"); while(it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); } } }
上面的所有增,删,改,查的代码

package com.jiedada.arraylist; import java.util.HashSet; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Set; public class CatTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Cat huahua=new Cat("花花",12,"英国猫"); Cat fanfan=new Cat("凡凡",3,"中国田园猫"); Set<Cat> set=new HashSet<Cat>(); set.add(huahua); set.add(fanfan); Iterator<Cat> it=set.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); } System.out.println("**************"); //添加属性 System.out.println("*****************"); Cat cat=new Cat("花花",12,"英国猫"); set.add(cat); it=set.iterator(); System.out.println("改变后的结果"); while(it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); } Cat huahua2=new Cat("花花2",1,"英国猫"); //通过对想找到元素 System.out.println("*****************"); set.add(huahua2); if(set.contains(huahua)) { System.out.println("找到了花花!"); System.out.println(huahua); } else { System.out.println("没有找到"); } //通过名字找到元素 System.out.println("*****************"); Cat cat1=new Cat(); boolean flag=false; it=set.iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { cat1=(Cat)it.next(); if(cat1.getName()=="花花") { flag=true; break; } } if(flag) { System.out.println("找到了花花!"); System.out.println(cat1); } else { System.out.println("没有找到!"); } System.out.println("*****************"); //删除花花的数据并且用增强型FOR循环 /* for(Cat cat2:set) { if(cat2.getName().equals("花花")) { set.remove(cat2); break; } }*/ //删除多个数据的方法; Set<Cat> set1=new HashSet<Cat>(); for(Cat cat2:set) { if(cat2.getMouth()<5) { set1.add(cat2); } } set.removeAll(set1); for(Cat cat2:set) { System.out.println(cat2); } System.out.println("*****************"); //删除所有数据 boolean flag1=set.removeAll(set); if(set.isEmpty()) { System.out.println("没有数据了!"); } else { System.out.println("还有数据"); } } }
Map
map中的数据是以键值对(key-value)的形式储存的
key-value以Entry类型的对象实例存在
可以通过key值快速查找value
一个映射不能包含重复的键:一个key只能对应一个value,但是一个value可以对应多个key
HashMap
基于哈希表的Map接口的实现
允许使用null值和null键
key值不允许重复
HashMap中的Entry对象是无序排列的
实现一个字典的添加和输出数据;
通过对象.put输入数据
再通过把key和values的值通过对象.entrySet()存入Set<Entry<String,String>>的方法

package com.jiedada.arraylist; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Map.Entry; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Set; public class Dictionliry { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Map<String,String> animal=new HashMap<String,String>(); Scanner console=new Scanner(System.in); int i=0; //添加key和value的值 while(i<3) { System.out.println("请输入key(单词)的值"); String key=console.next(); System.out.println("请输入value(注释)的值"); String value=console.next(); animal.put(key, value); i++; } //通过迭代器的方法输出value的值 Iterator<String> it=animal.values().iterator(); System.out.println("迭代器输出values:"); while(it.hasNext()) { System.out.print(it.next()+" "); } System.out.println(); System.out.println("*******************"); //输出key和values Set<Entry<String, String>> set=animal.entrySet(); for(Entry<String, String> a:set) { System.out.print(a.getKey()+"-"); System.out.println(a.getValue()); } } }
完整的货物存储代码
Goods代码

package com.jiedada.arraylist; public class Goods { private String id; private String name; private int price; public Goods(String id, String name, int price) { super(); this.id = id; this.name = name; this.price = price; } public String getId() { return id; } public void setId(String id) { this.id = id; } public String getName() { return name; } public void setName(String name) { this.name = name; } public int getPrice() { return price; } public void setPrice(int price) { this.price = price; } @Override public String toString() { return "Goods [id=" + id + ", name=" + name + ", price=" + price + "]"; } }
Goodstest

package com.jiedada.arraylist; import java.util.HashMap; import java.util.InputMismatchException; import java.util.Iterator; import java.util.Map; import java.util.Map.Entry; import java.util.Scanner; import java.util.Set; public class GoodsTest { public static void main(String[] args) { // TODO Auto-generated method stub Map<String,Goods> goodsMap=new HashMap<String,Goods>(); System.out.println("请输入三天信息:"); Scanner console=new Scanner(System.in); //录入信息 int i=0; while(i<3) { System.out.println("请输入商品编号:"); String id=console.next(); if(goodsMap.containsKey(id)) { System.out.println("商品名称重复,请在此输入"); continue; } System.out.println("请输入商品名字:"); String name=console.next(); int price; try { System.out.println("请输入商品价格:"); price=console.nextInt(); }catch(java.util.InputMismatchException e) { System.out.println("价格为整数请重新输入数字"); console.next(); continue; } Goods goods=new Goods(id,name,price); //把值输入其中 goodsMap.put(id, goods); i++; } //遍历找出 Iterator<Goods> it=goodsMap.values().iterator(); while(it.hasNext()) { System.out.println(it.next()); } //输出values和key的数据 } }




 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号