概率
一、基本概率论——模拟骰子
1、导入必要包
1 2 3 4 5 | # matplotlib inline jupyter常用于生成画布%matplotlib inlineimport torchfrom torch.distributions import multinomialfrom d2l import torch as d2l |
2、相对概率做真实概率
1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 21 22 23 24 25 26 27 28 29 30 31 32 33 34 35 36 37 38 39 40 41 42 43 44 45 | # 进行500组实验,每组抽取10个样本# 数据将存在一个500*6的矩阵中counts = multinomial.Multinomial(10, fair_probs).sample((500,))print(counts)# dim=0,逐行相加# cumsum保持维度cum_counts = counts.cumsum(dim=0)print(cum_counts)# keepdims=True非降维# 生成只有500*1的矩阵(只有一列)# print(cum_counts.sum(dim=1, keepdims=True))# 计算相对频率模拟真实概率estimates = cum_counts / cum_counts.sum(dim=1, keepdims=True)print(estimates)# figsize: 指定figure的宽和高,单位为英寸d2l.set_figsize((6, 4.5))for i in range(6): d2l.plt.plot(estimates[:, i].numpy(), label=("P(die=" + str(i + 1) + ")"))d2l.plt.axhline(y=0.167, color='black', linestyle='dashed')d2l.plt.gca().set_xlabel('Groups of experiments')d2l.plt.gca().set_ylabel('Estimated probability')d2l.plt.legend();<br><br>#输出结果<br><br>tensor([[2., 1., 1., 1., 3., 2.], [1., 3., 3., 1., 1., 1.], [2., 0., 3., 1., 4., 0.], ..., [3., 1., 3., 0., 0., 3.], [3., 1., 2., 1., 1., 2.], [3., 1., 1., 1., 2., 2.]])tensor([[ 2., 1., 1., 1., 3., 2.], [ 3., 4., 4., 2., 4., 3.], [ 5., 4., 7., 3., 8., 3.], ..., [803., 782., 860., 829., 857., 849.], [806., 783., 862., 830., 858., 851.], [809., 784., 863., 831., 860., 853.]])tensor([[0.2000, 0.1000, 0.1000, 0.1000, 0.3000, 0.2000], [0.1500, 0.2000, 0.2000, 0.1000, 0.2000, 0.1500], [0.1667, 0.1333, 0.2333, 0.1000, 0.2667, 0.1000], ..., [0.1612, 0.1570, 0.1727, 0.1665, 0.1721, 0.1705], [0.1615, 0.1569, 0.1727, 0.1663, 0.1719, 0.1705], [0.1618, 0.1568, 0.1726, 0.1662, 0.1720, 0.1706]])<br><br>绘图略 |
二、概率论公理
1、样本空间:也称结果空间。在处理骰子掷出时,我们将集合 S={1,2,3,4,5,6}称为样本空间
2、样本空间中每个元素称为结果
3、事件是来自样本空间的一组结果
4、联合概率: P(A=a,B=b):表示事件A和事件B同时发生的概率
5、条件概率:P(B=b∣A=a):表示在事件A发生的前提下,事件B发生的概率
6、贝叶斯定理 :
P(A,B)=P(B∣A)P(A)
P(A,B)=P(A∣B)P(B)

1、随机变量X的期望(或平均值)

2、函数f(x)的期望

3、随机变量X的方差:衡量随机变量X与期望值的偏差

4、函数f(x)的方差
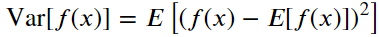




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· Linux系列:如何用heaptrack跟踪.NET程序的非托管内存泄露
· 开发者必知的日志记录最佳实践
· winform 绘制太阳,地球,月球 运作规律
· AI与.NET技术实操系列(五):向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 超详细:普通电脑也行Windows部署deepseek R1训练数据并当服务器共享给他人
· 【硬核科普】Trae如何「偷看」你的代码?零基础破解AI编程运行原理
· 上周热点回顾(3.3-3.9)