RPC框架原理与实现
RPC,全称 Remote Procedure Call(远程过程调用),即调用远程计算机上的服务,就像调用本地服务一样。那么RPC的原理是什么呢?了解一个技术最好的思路就是寻找一个该类型麻雀虽小五脏俱全的开源项目,不负所期,找到一个轻量级分布式 RPC 框架,本文从这个项目入手来解读RPC的原理及其实现。
其实说到RPC,大家应该不会陌生才是,以往流行的Web Service就是一种RPC,一般来说RPC 可基于 HTTP 或 TCP 协议,因为Web Service 基于HTTP,所以具有良好的跨平台性,但由于HTTP是应用层协议,相比TCP性能有所损耗。
与本地调用不一样,远程调用需要通过网络层传输,因此涉及到的一个问题就是序列化,不同的序列化方式影响调用性能,流行的序列化包括Protobuf、Kryo、Hessian、Jackson、Thrift。
下面,让我们来一关如何从零开始实现分布式RPC框架。
RPC框架组件
建设一个框架,一个系统,首先要做的就是分析需要哪些组件,他们的关系是什么?
简单分析下,一个RPC框架需要包括:
- APP :应用端,调用服务
- Server 服务容器,对外提供服务
- Service Registry 服务注册表
我们需要将服务部署在分布式环境下的不同节点上,通过服务注册的方式,让客户端来自动发现当前可用的服务,并调用这些服务。这需要一种服务注册表(Service Registry)的组件,让它来注册分布式环境下所有的服务地址(包括:主机名与端口号)。
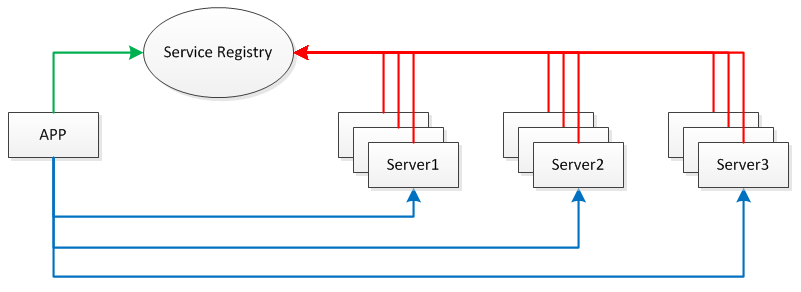
每台 Server 上可发布多个 Service,这些 Service 共用一个 host 与 port,在分布式环境下会提供 Server 共同对外提供 Service。此外,为防止 Service Registry 出现单点故障,因此需要将其搭建为集群环境。
RPC框架实现
定义服务
首先定义服务接口,接口可以单独放在一个jar包中
public interface HelloService {
String hello(String name);
String hello(Person person);
}
实现接口
然后,增加一种实现
@RpcService(HelloService.class)
public class HelloServiceImpl implements HelloService {
@Override
public String hello(String name) {
return "Hello! " + name;
}
@Override
public String hello(Person person) {
return "Hello! " + person.getFirstName() + " " + person.getLastName();
}
}
这里的RpcService注解,定义在服务接口的实现类上,可以让框架通过这个注解找到服务实现类。
更进一步,如果哪天服务版本升级了,但是历史服务还有人在使用,怎么办?解决方案就是服务需要分版本,按版本调用。
@RpcService(value = HelloService.class, version = "sample.hello2")
public class HelloServiceImpl2 implements HelloService {
@Override
public String hello(String name) {
return "你好! " + name;
}
@Override
public String hello(Person person) {
return "你好! " + person.getFirstName() + " " + person.getLastName();
}
}
再来看下 RPC 服务注解
/**
* RPC 服务注解(标注在服务实现类上)
*/
@Target({ElementType.TYPE})
@Retention(RetentionPolicy.RUNTIME)
@Component
public @interface RpcService {
/**
* 服务接口类
*/
Class<?> value();
/**
* 服务版本号
*/
String version() default "";
}
服务端实现
Server端主要基于Netty(一个NIO框架)+Spring
回到开头讲的,RPC关键点之一就是传输序列化,简单来说就是客户端调用service时,需要构建一个请求,然后将这个请求序列化传输到服务端,服务端完成调用后,再将结果 序列化后返回,简单画一下:
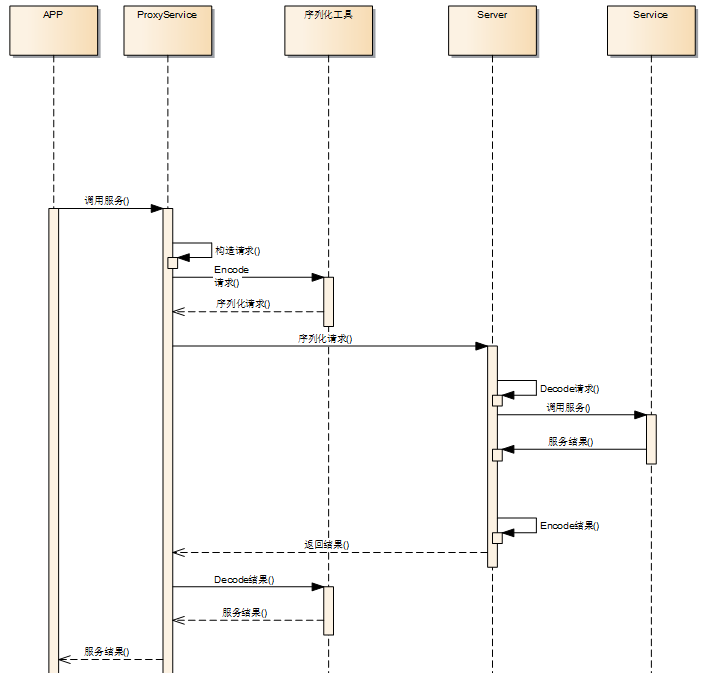
定义Request
public class RpcRequest {
private String requestId;
private String interfaceName;
private String serviceVersion;
private String methodName;
private Class<?>[] parameterTypes;
private Object[] parameters;
}
定义RpcResponse
public class RpcResponse {
private String requestId;
private Exception exception;
private Object result;
}
Encoder与Decoder
因为项目基于Netty,所以按Netty那一套搞就行,核心是SerializationUtil,这个根据需要可以采用不同的序列化框架,比如pb。
public class RpcEncoder extends MessageToByteEncoder {
private Class<?> genericClass;
public RpcEncoder(Class<?> genericClass) {
this.genericClass = genericClass;
}
@Override
public void encode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Object in, ByteBuf out) throws Exception {
if (genericClass.isInstance(in)) {
byte[] data = SerializationUtil.serialize(in);
out.writeInt(data.length);
out.writeBytes(data);
}
}
}
public class RpcDecoder extends ByteToMessageDecoder {
private Class<?> genericClass;
public RpcDecoder(Class<?> genericClass) {
this.genericClass = genericClass;
}
@Override
public void decode(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, ByteBuf in, List<Object> out) throws Exception {
if (in.readableBytes() < 4) {
return;
}
in.markReaderIndex();
int dataLength = in.readInt();
if (in.readableBytes() < dataLength) {
in.resetReaderIndex();
return;
}
byte[] data = new byte[dataLength];
in.readBytes(data);
out.add(SerializationUtil.deserialize(data, genericClass));
}
}
扫描服务
服务端采用Spring,并且服务加了RpcService注解,所以服务器启动的时候扫描一下带RpcService的就行
下面的代码实现了将服务找出来,并放到handlerMap里,这样,调用服务的时候就可以根据服务名称从Map里找到服务对象,知道了服务对象和服务方法,就能直接调用了。
private Map<String, Object> handlerMap = new HashMap<>();
public void setApplicationContext(ApplicationContext ctx) throws BeansException {
// 扫描带有 RpcService 注解的类并初始化 handlerMap 对象
Map<String, Object> serviceBeanMap = ctx.getBeansWithAnnotation(RpcService.class);
if (MapUtils.isNotEmpty(serviceBeanMap)) {
for (Object serviceBean : serviceBeanMap.values()) {
RpcService rpcService = serviceBean.getClass().getAnnotation(RpcService.class);
String serviceName = rpcService.value().getName();
String serviceVersion = rpcService.version();
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(serviceVersion)) {
serviceName += "-" + serviceVersion;
}
handlerMap.put(serviceName, serviceBean);
}
}
}
启动服务器
按照Netty服务器标准代码,启动服务,注意Encoder和Decoder
@Override
public void afterPropertiesSet() throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup bossGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
EventLoopGroup workerGroup = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 创建并初始化 Netty 服务端 Bootstrap 对象
ServerBootstrap bootstrap = new ServerBootstrap();
bootstrap.group(bossGroup, workerGroup);
bootstrap.channel(NioServerSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.childHandler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new RpcDecoder(RpcRequest.class)); // 解码 RPC 请求
pipeline.addLast(new RpcEncoder(RpcResponse.class)); // 编码 RPC 响应
pipeline.addLast(new RpcServerHandler(handlerMap)); // 处理 RPC 请求
}
});
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.SO_BACKLOG, 1024);
bootstrap.childOption(ChannelOption.SO_KEEPALIVE, true);
// 获取 RPC 服务器的 IP 地址与端口号
String[] addressArray = StringUtil.split(serviceAddress, ":");
String ip = addressArray[0];
int port = Integer.parseInt(addressArray[1]);
// 启动 RPC 服务器
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.bind(ip, port).sync();
// 注册 RPC 服务地址
if (serviceRegistry != null) {
for (String interfaceName : handlerMap.keySet()) {
serviceRegistry.register(interfaceName, serviceAddress);
LOGGER.debug("register service: {} => {}", interfaceName, serviceAddress);
}
}
LOGGER.debug("server started on port {}", port);
// 关闭 RPC 服务器
future.channel().closeFuture().sync();
} finally {
workerGroup.shutdownGracefully();
bossGroup.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
处理请求
RpcServerHandler负责处理请求,熟悉Netty的应该知道,继承SimpleChannelInboundHandler,在channelRead0函数里处理即可,注意,因为pipline里前面已经解码为RpcRequest对象了,所以在这里可以直接使用。
public class RpcServerHandler extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcRequest> {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RpcServerHandler.class);
private final Map<String, Object> handlerMap;
public RpcServerHandler(Map<String, Object> handlerMap) {
this.handlerMap = handlerMap;
}
@Override
public void channelRead0(final ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcRequest request) throws Exception {
// 创建并初始化 RPC 响应对象
RpcResponse response = new RpcResponse();
response.setRequestId(request.getRequestId());
try {
Object result = handle(request);
response.setResult(result);
} catch (Exception e) {
LOGGER.error("handle result failure", e);
response.setException(e);
}
// 写入 RPC 响应对象并自动关闭连接
ctx.writeAndFlush(response).addListener(ChannelFutureListener.CLOSE);
}
}
框架没什么说的,核心是怎么handle,无非就是从Reques里获取到服务名称和版本号,然后从handlerMap里寻找服务对象,然后调用方法。
已知方法名和Class,可以通过反射进行调用,但是反射性能较低,可以使用cglib里的FastClass来执行invoke,详情参见说说 cglib 动态代理
private Object handle(RpcRequest request) throws Exception {
// 获取服务对象
String serviceName = request.getInterfaceName();
String serviceVersion = request.getServiceVersion();
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(serviceVersion)) {
serviceName += "-" + serviceVersion;
}
Object serviceBean = handlerMap.get(serviceName);
if (serviceBean == null) {
throw new RuntimeException(String.format("can not find service bean by key: %s", serviceName));
}
// 获取反射调用所需的参数
Class<?> serviceClass = serviceBean.getClass();
String methodName = request.getMethodName();
Class<?>[] parameterTypes = request.getParameterTypes();
Object[] parameters = request.getParameters();
// 执行反射调用
// Method method = serviceClass.getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
// method.setAccessible(true);
// return method.invoke(serviceBean, parameters);
// 使用 CGLib 执行反射调用
FastClass serviceFastClass = FastClass.create(serviceClass);
FastMethod serviceFastMethod = serviceFastClass.getMethod(methodName, parameterTypes);
return serviceFastMethod.invoke(serviceBean, parameters);
}
服务发现与注册
在分布式系统里,服务的自动发现与注册是标配功能,一般来说都是使用集中配置中心,开源届有Zookeeper、etcd等实现。这里,使用zk作为配置中心。
服务发现与注册的核心是,服务启动时,将服务名称和服务地址写入到配置中心,客户端调用的时候,先从集中配置中心读取所要调用服务的服务器地址,如果有多个,随机挑选一个(当然随机的话会存在负载不均衡问题),连接服务器并调用。
个人认为较好的实现方式是,服务层面加一个HA层,客户端直接调用HA,HA负责负载Service。
回到代码解读,这里使用的zookeeper,我们来看怎么实现。
先是定义接口:
public interface ServiceRegistry {
/**
* 注册服务名称与服务地址
*
* @param serviceName 服务名称
* @param serviceAddress 服务地址
*/
void register(String serviceName, String serviceAddress);
}
public interface ServiceDiscovery {
/**
* 根据服务名称查找服务地址
*
* @param serviceName 服务名称
* @return 服务地址
*/
String discover(String serviceName);
}
再看谈实现,zk有两种类型的节点,永久节点和临时节点,这种特性非常适合做服务发现与注册。
试想:
- 新启动一台Server,自动注册到ZK,写一个临时节点,客户端调用的时候就能读取到这个节点
- 一台Server挂了,临时节点失效,客户端调用的时候就读取不到这个节点,自然不会调用
- 当服务调用量太大,可以新启动服务,服务小的时候再停掉
不再赘述,看代码:
public class ZooKeeperServiceRegistry implements ServiceRegistry {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ZooKeeperServiceRegistry.class);
private final ZkClient zkClient;
public ZooKeeperServiceRegistry(String zkAddress) {
// 创建 ZooKeeper 客户端
zkClient = new ZkClient(zkAddress, Constant.ZK_SESSION_TIMEOUT, Constant.ZK_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT);
LOGGER.debug("connect zookeeper");
}
@Override
public void register(String serviceName, String serviceAddress) {
// 创建 registry 节点(持久)
String registryPath = Constant.ZK_REGISTRY_PATH;
if (!zkClient.exists(registryPath)) {
zkClient.createPersistent(registryPath);
LOGGER.debug("create registry node: {}", registryPath);
}
// 创建 service 节点(持久)
String servicePath = registryPath + "/" + serviceName;
if (!zkClient.exists(servicePath)) {
zkClient.createPersistent(servicePath);
LOGGER.debug("create service node: {}", servicePath);
}
// 创建 address 节点(临时)
String addressPath = servicePath + "/address-";
String addressNode = zkClient.createEphemeralSequential(addressPath, serviceAddress);
LOGGER.debug("create address node: {}", addressNode);
}
}
原理就是创建了一个临时节点存储服务地址
再来看服务发现:
public class ZooKeeperServiceDiscovery implements ServiceDiscovery {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(ZooKeeperServiceDiscovery.class);
private String zkAddress;
public ZooKeeperServiceDiscovery(String zkAddress) {
this.zkAddress = zkAddress;
}
@Override
public String discover(String name) {
// 创建 ZooKeeper 客户端
ZkClient zkClient = new ZkClient(zkAddress, Constant.ZK_SESSION_TIMEOUT, Constant.ZK_CONNECTION_TIMEOUT);
LOGGER.debug("connect zookeeper");
try {
// 获取 service 节点
String servicePath = Constant.ZK_REGISTRY_PATH + "/" + name;
if (!zkClient.exists(servicePath)) {
throw new RuntimeException(String.format("can not find any service node on path: %s", servicePath));
}
List<String> addressList = zkClient.getChildren(servicePath);
if (CollectionUtil.isEmpty(addressList)) {
throw new RuntimeException(String.format("can not find any address node on path: %s", servicePath));
}
// 获取 address 节点
String address;
int size = addressList.size();
if (size == 1) {
// 若只有一个地址,则获取该地址
address = addressList.get(0);
LOGGER.debug("get only address node: {}", address);
} else {
// 若存在多个地址,则随机获取一个地址
address = addressList.get(ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(size));
LOGGER.debug("get random address node: {}", address);
}
// 获取 address 节点的值
String addressPath = servicePath + "/" + address;
return zkClient.readData(addressPath);
} finally {
zkClient.close();
}
}
}
客户端实现
服务代理
可以先查看(http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoqi/p/java-proxy.html)了解java的动态代理。
使用 Java 提供的动态代理技术实现 RPC 代理(当然也可以使用 CGLib 来实现),具体代码如下:
public class RpcProxy {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RpcProxy.class);
private String serviceAddress;
private ServiceDiscovery serviceDiscovery;
public RpcProxy(String serviceAddress) {
this.serviceAddress = serviceAddress;
}
public RpcProxy(ServiceDiscovery serviceDiscovery) {
this.serviceDiscovery = serviceDiscovery;
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T create(final Class<?> interfaceClass) {
return create(interfaceClass, "");
}
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
public <T> T create(final Class<?> interfaceClass, final String serviceVersion) {
// 创建动态代理对象
return (T) Proxy.newProxyInstance(
interfaceClass.getClassLoader(),
new Class<?>[]{interfaceClass},
new InvocationHandler() {
@Override
public Object invoke(Object proxy, Method method, Object[] args) throws Throwable {
// 创建 RPC 请求对象并设置请求属性
RpcRequest request = new RpcRequest();
request.setRequestId(UUID.randomUUID().toString());
request.setInterfaceName(method.getDeclaringClass().getName());
request.setServiceVersion(serviceVersion);
request.setMethodName(method.getName());
request.setParameterTypes(method.getParameterTypes());
request.setParameters(args);
// 获取 RPC 服务地址
if (serviceDiscovery != null) {
String serviceName = interfaceClass.getName();
if (StringUtil.isNotEmpty(serviceVersion)) {
serviceName += "-" + serviceVersion;
}
serviceAddress = serviceDiscovery.discover(serviceName);
LOGGER.debug("discover service: {} => {}", serviceName, serviceAddress);
}
if (StringUtil.isEmpty(serviceAddress)) {
throw new RuntimeException("server address is empty");
}
// 从 RPC 服务地址中解析主机名与端口号
String[] array = StringUtil.split(serviceAddress, ":");
String host = array[0];
int port = Integer.parseInt(array[1]);
// 创建 RPC 客户端对象并发送 RPC 请求
RpcClient client = new RpcClient(host, port);
long time = System.currentTimeMillis();
RpcResponse response = client.send(request);
LOGGER.debug("time: {}ms", System.currentTimeMillis() - time);
if (response == null) {
throw new RuntimeException("response is null");
}
// 返回 RPC 响应结果
if (response.hasException()) {
throw response.getException();
} else {
return response.getResult();
}
}
}
);
}
}
RPC客户端
使用RpcClient类实现 RPC 客户端,只需扩展 Netty 提供的SimpleChannelInboundHandler抽象类即可,代码如下:
public class RpcClient extends SimpleChannelInboundHandler<RpcResponse> {
private static final Logger LOGGER = LoggerFactory.getLogger(RpcClient.class);
private final String host;
private final int port;
private RpcResponse response;
public RpcClient(String host, int port) {
this.host = host;
this.port = port;
}
@Override
public void channelRead0(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, RpcResponse response) throws Exception {
this.response = response;
}
@Override
public void exceptionCaught(ChannelHandlerContext ctx, Throwable cause) throws Exception {
LOGGER.error("api caught exception", cause);
ctx.close();
}
public RpcResponse send(RpcRequest request) throws Exception {
EventLoopGroup group = new NioEventLoopGroup();
try {
// 创建并初始化 Netty 客户端 Bootstrap 对象
Bootstrap bootstrap = new Bootstrap();
bootstrap.group(group);
bootstrap.channel(NioSocketChannel.class);
bootstrap.handler(new ChannelInitializer<SocketChannel>() {
@Override
public void initChannel(SocketChannel channel) throws Exception {
ChannelPipeline pipeline = channel.pipeline();
pipeline.addLast(new RpcEncoder(RpcRequest.class)); // 编码 RPC 请求
pipeline.addLast(new RpcDecoder(RpcResponse.class)); // 解码 RPC 响应
pipeline.addLast(RpcClient.this); // 处理 RPC 响应
}
});
bootstrap.option(ChannelOption.TCP_NODELAY, true);
// 连接 RPC 服务器
ChannelFuture future = bootstrap.connect(host, port).sync();
// 写入 RPC 请求数据并关闭连接
Channel channel = future.channel();
channel.writeAndFlush(request).sync();
channel.closeFuture().sync();
// 返回 RPC 响应对象
return response;
} finally {
group.shutdownGracefully();
}
}
}
服务测试
public class HelloClient {
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
ApplicationContext context = new ClassPathXmlApplicationContext("spring.xml");
RpcProxy rpcProxy = context.getBean(RpcProxy.class);
HelloService helloService = rpcProxy.create(HelloService.class);
String result = helloService.hello("World");
System.out.println(result);
HelloService helloService2 = rpcProxy.create(HelloService.class, "sample.hello2");
String result2 = helloService2.hello("世界");
System.out.println(result2);
System.exit(0);
}
}
输出结果
connect zookeeper
get only address node: address-0000000001
discover service: com.xxx.rpc.sample.api.HelloService => 127.0.0.1:8000
time: 569ms
Hello! World
connect zookeeper
get only address node: address-0000000001
discover service: com.xxx.rpc.sample.api.HelloService-sample.hello2 => 127.0.0.1:8000
time: 36ms
你好! 世界
作者:Jadepeng
出处:jqpeng的技术记事本--http://www.cnblogs.com/xiaoqi
您的支持是对博主最大的鼓励,感谢您的认真阅读。
本文版权归作者所有,欢迎转载,但未经作者同意必须保留此段声明,且在文章页面明显位置给出原文连接,否则保留追究法律责任的权利。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号