ASP.NET AJAX(一) Ajax的开始
Ajax的操作主要通过XMLHttpRequest,对于不同浏览器有不同的创建ActiveXObject的方法。其中XMLHttpRequest主要有open、send、setRequestHeader、getResponeHeader、getAllResponseHeader、abort方法和readyState、onreadystatechange、status、statusText、responseXML、的属性。
最原始的例子是这样的,html布局如下:
<body>
<form id="form1" runat="server">
<table id="credentials">
<tr><td>userName:</td><td><asp:TextBox ID="txtUserName" runat="server"></asp:TextBox></td></tr>
<tr><td>password</td><td><asp:TextBox ID="txtPassword" runat="server"></asp:TextBox></td></tr>
<tr><td></td><td><button id="btnSubmit" onclick="submitCallBack();" type="button">Submit</button></td></tr>
</table>
<table id="employeeInfo" style="display: none;">
<tr><td>Your Infomation</td></tr>
<tr><td>firstName:</td><td><span id="firstName"></span></td></tr>
<tr><td>lastName:</td><td><span id="lastName"></span></td></tr>
<tr><td>Employee ID:</td><td><span id="employeidName"></span></td></tr>
<tr><td>DepartmentName:</td><td><span id="departmentName"></span></td></tr>
</table>
</form>
</body>
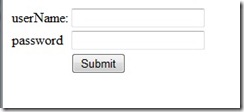
主要做了一个输入用户名和密码和隐藏的经ajax调用后显示用户信息的界面,如下所示。
其javascript代码如下:
var request;
if (!window.XMLHttpRequest) {
window.XMLHttpRequest = function window$XMLHttpRequest() {
var progIDS = ["Maxml2.XMLHTTP", "Microsoft.XMLHTTP"];
for (var i = 0; i < progIDS.length; i++) {
try {
var xmlHttp = new ActiveXObject(progIDS[i]);
return xmlHttp;
}
catch (ex) { };
}
return null;
}
}
window.employes = function window$employes(firstName, lastName, employeId, departmentName) {
this.firstName = firstName;
this.lastName = lastName;
this.employeId = employeId;
this.departmentName = departmentName;
}
function deserialize() {
var delimeter = "|";
var responseIndex = 0;
var delimiterIndex;
var response = request.responseText;
delimiterIndex = response.indexOf(delimeter, responseIndex);
var firstName = response.substring(responseIndex, delimiterIndex);
responseIndex = delimiterIndex + 1;
delimiterIndex = response.indexOf(delimeter, responseIndex);
var lastName = response.substring(responseIndex, delimiterIndex);
responseIndex = delimiterIndex + 1;
delimiterIndex = response.indexOf(delimeter, responseIndex);
var employeId = response.substring(responseIndex, delimiterIndex);
responseIndex = delimiterIndex + 1;
delimiterIndex = response.indexOf(delimeter, responseIndex);
var departmentName = response.substring(responseIndex, delimiterIndex);
return new employes(firstName, lastName, employeId, departmentName);
}
function readStateChangeCallback() {
if (request.readyState == 4 && request.status == 200) {
var credentials = document.getElementById("credentials");
credentials.style.display = "none";
var employeeInfoTable = document.getElementById("employeeInfo");
employeeInfoTable.style.display = "block";
var employee = new deserialize();
var firstNameSpan = document.getElementById("firstName");
firstNameSpan.innerText = employee.firstName;
var lastNameSpan = document.getElementById("lastName");
lastNameSpan.innerText = employee.firstName;
var employeidNameSpan = document.getElementById("employeidName");
employeidNameSpan.innerText = employee.employeid;
var departmentNameSpan = document.getElementById("departmentName");
departmentNameSpan.innerText = employee.departmentName;
}
}
window.credentials = function window$credentials(userName, password) {
this.userName = userName;
this.password = password;
}
function serialize(credentials) {
var requestBody = "";
requestBody += "txtUserName";
requestBody += "=";
requestBody += encodeURIComponent(credentials.userName);
requestBody += "&";
requestBody += "txtPassword";
requestBody += "=";
requestBody += encodeURIComponent(credentials.password);
return requestBody;
}
function submitCallBack() {
var userName = document.getElementById("txtUserName");
var password = document.getElementById("txtPassword");
var cred = new credentials(userName.value, password.value);
var body = serialize(cred);
request = new XMLHttpRequest();
request.open("POST", document.form1.action);
request.onreadystatechange = readStateChangeCallback;
request.setRequestHeader("MyCustomeHeader", "true");
request.setRequestHeader('Content-Type', 'Application/x-www-form-urlencoded');
request.send(body);
}
</script>
credentials是发往服务端进行验证的对象,employes是客户端要展现的信息对象,serialize和deserialize也就是将credentials和employes处理的函数,因为采用原始的字符串形式,显得稍复杂,可以用xml格式或json格式进行简化。
if (!window.XMLHttpRequest) {
window.XMLHttpRequest = function window$XMLHttpRequest() {
var progIDS = ["Maxml2.XMLHTTP", "Microsoft.XMLHTTP"];
for (var i = 0; i < progIDS.length; i++) {
try {
var xmlHttp = new ActiveXObject(progIDS[i]);
return xmlHttp;
}
catch (ex) { };
}
return null;
}
}
上面的代码也就是初始化XMLHttpRequest,根据不同的浏览器,初始化不同的对象而已。submitCallBack()也就是“确定”按钮的单击相应时间,将用户名、密码按Post格式组装好后发送HTTP请求,并设置回调函数为readStateChangeCallback,接着添加了自定义的http消息头部信息,其中"MyCustomeHeader”用于在服务端是否是异步加载,后者'Content-Type'的设置使得服务端可以用Request来访问提交的数据。回调函数readStateChangeCallback中request.readyState == 4 && request.status == 200表示异步调用成功返回,接着将http相应的值赋到给指定的位置,在设置employeeInfo为可见。
最后需要关注的是服务端代码:
void Page_Load(object sender, EventArgs e)
{
if (Request.Headers["MyCustomeHeader"] != null)
{
if (Request.Form["txtPassword"] == "password" &&
Request.Form["txtUserName"] == "username")
{
Response.Write("Shahrm|Khosravi|22223333|Some Department");
Response.End();
}
else
{
throw new Exception("Wrong credentials");
}
}
}
页面加载后根据MyCustomeHeader的头部信息判断是否是异步加载,再通过Request用户名和密码信息查看是否匹配,匹配则向客户端输入employee信息,最后停止页面继续输出。最后结果如下: