01: docker 基本使用
docker其他篇
目录:
- 1.1 docker基础
- 1.2 docker技术应用场景
- 1.3 docker安装
- 1.4 镜像管理
- 1.5 docker常用命令
- 1.6 docker将数据挂载到容器的三种方式
- 1.7 容器网络
- 1.8 Dockerfile: 构建nginx项目镜像
- 1.9 Dockerfile: 构建php项目镜像
1.1 docker基础 返回顶部
参考博客:https://blog.51cto.com/lizhenliang
1、什么是docker
1. Docker是使用最广泛的开源容器引擎
2. 一种操作系统基本的虚拟化技术
3. 一种简单的应用程序打包工具
4. 依赖Linux内核特性:Namespace(资源隔离) 和 Cgroup(资源限制)
注:每个容器拥有一套和宿主机完全隔离的文件系统(共用linux内核),程序在这个虚拟容器里运行,就好像在真实的物理机上运行一样。
容器:
1)容器是一个操作系统级别下的虚拟化技术,运行一个容器就行运行一个进程一样
2)容器依赖linux内核特性:Namespace(资源隔离)和Cgroups(资源限制)
资源隔离:
1)Linux Namespaces机制提供一种资源隔离方案,每个namespace看上去就像一个单独的Linux系统。
2)PID,IPC(进程通信),Network等系统资源不再是全局性的,而是属于某个特定的Namespace。
3)每个namespace下的资源对于其他namespace下的资源都是透明,不可见的。
4)系统中可以同时存在两个进程号为0,1,2的进程,由于属于不同的namespace,所以它们之间并不冲突。
5)而在用户层面上只能看到属于用户自己namespace下的资源,例如使用ps命令只能列出自己namespace下的进程。
6)这样每个namespace看上去就像一个单独的Linux系统。
资源限制:
1)为了让容器中的进程更加可控,Docker 使用 Linux cgroups 来限制容器中的进程允许使用的系统资源。
2)可以在启动容器是指定每个容器可以使用的 网络、磁盘、CPU以及内存 等
2、docker思想
1. Docker的思想源于集装箱,集装箱解决了什么问题呢?
2. 在早期运输货物需要不同分类的船,例如运输水果的船,运输生活用品的船
3. 有了集装箱后,在大船上,可以把货物分类到不同的集装箱中,水果一个集装箱,生活用品一个集装箱
4. 它们之间互不影响,只要把货物封装好集装箱里,就可以把不同类的货物一起运走。
5. 通过Docker logo也可以看出所以然来,Docker就像大船,集装箱就是容器。
6. 一条鲸鱼拖着若干个集装箱的经典形象已经深入人心。

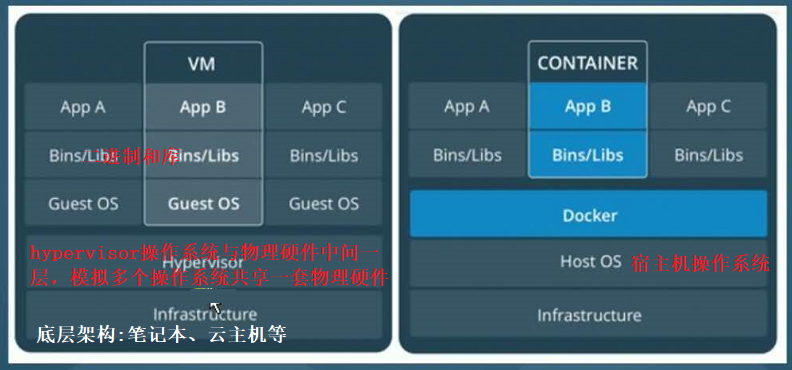
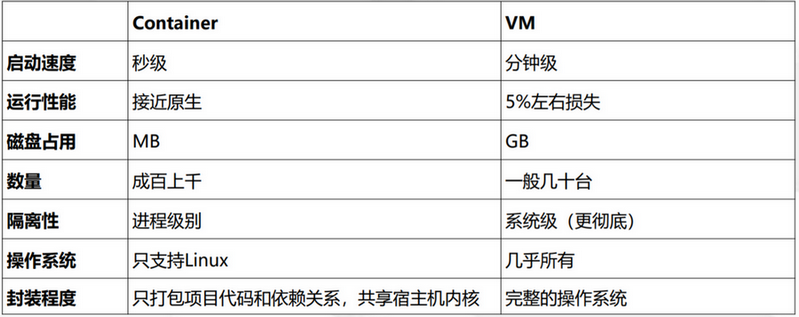
3、docker 与 虚拟机比较
1. docker设计小巧,部署迁移快速,运行高效,按照应用隔离,管理人员可以看到所有容器的内容。
2. 虚拟化技术比较臃肿,需要先创建新的系统,按照系统隔离,管理员无法看到系统内部信息。
举例:
1)Docker就是手机中的各种APP,只需要一个系统就可以下载自己所需的应用
2)虚拟化技术相当于苹果手机安装一个庞大软件,这个软件上安装安卓系统、魅族系统等,每个系统上还要安装各类应用。
4、docker解决的问题
1. 高效的利用资源
2. 单台机器得部署多个应用;
3. 应用之间互相隔离(微服务);
4. 应用之间不能发生资源抢占,每个应用只能使用事先注册申请的资源。
5、Docker架构
1. Docker客户端(Client): docker 命令行工具,用户也可以通过 REST API 与服务器通信
2. Docker服务器(Docker daemon): 服务器组件,以 Linux 后台服务的方式运行, Docker daemon 运行在 Docker host 上,负责创建、运行、监控容器,构建、存储镜像
3. Docker镜像(Image): 可将 Docker 镜像看着只读模板,通过它可以创建 Docker 容器
4. 镜像仓库(Registry): Registry 是存放 Docker 镜像的仓库,Registry 分私有和公有两种
5. Docker容器(Container): Docker 容器就是 Docker 镜像的运行实例

1.2 docker技术应用场景 返回顶部
1、场景一:节省项目环境部署时间
1)单项目打包
1. 每次部署项目到测试、生产等环境,都要部署一大堆依赖的软件、工具,时间久,出错概率大。
2. Docker主要理念就是环境打包部署,可在任意Docker Engine运行。
3. 我们只需要将每个项目环境打包到镜像,push到镜像仓库,当有需要部署这个项目时,
直接pull镜像启动容器,这个项目就可以访问了!一次构建多次部署,一劳永逸。
2)整套项目打包
1. 比如有一个产品可以整套部署到客户那里,以往都是派一名实施工程师到客户那部署。
2. 如果用了Docker,我们可以前期将这套项目封装打包起来,实现一键部署,分分钟钟搞定,就不需要再派人过去了。比如官方的Docker Compose编排工具。
3)新开源技术试用
1. 有时,我们想调研一些开源项目,我们可以直接从公共镜像仓库pull项目官方做好镜像启动容器即可。
2、场景二:环境一致性
1. 项目在开发电脑本地运行没问题,到了测试或生产环境就运行不起来。
2. Docker将项目环境打包成镜像,可以在任何Docker Engine部署。
3、场景三:持续集成
1. 一个项目版本快速迭代的测试场景,需要一个合理的CI(持续集成)/CD(持续部署)环境支撑。
2. CI/CD是一个周期性自动化项目测试流程,包括构建、部署、测试、发布等工作,很少需要人工干预。
3. Docker通过项目镜像构建和快速部署,打通测试环境与生产环境,高度保持多个环境之间一致性。
4、场景四:微服务
1. 微服务指尽可能细粒度拆分业务程序架构,由多个独立服务组成业务系统。
2. Docker容器作为这些独立服务的部署单元,每个服务单独部署到一个docker容器中。
1.3 docker安装 返回顶部
1、docker安装参考官方文档
1. docker官方文档:https://docs.docker.com/
2. centos安装docker:https://docs.docker.com/install/linux/docker-ce/centos/
注:docker CE只支持 centos7 不支持centos6
2、docker安装
# 1)安装依赖包 yum install -y yum-utils device-mapper-persistent-data lvm2
# 2)添加Docker软件包源(否则doker安装的不是新版本) yum-config-manager \ --add-repo \ https://download.docker.com/linux/centos/docker-ce.repo
# 3)安装Docker CE yum install -y docker-ce
# 4)启动Docker服务并设置开机启动 systemctl start docker systemctl enable docker
# 5)测试docker是否安装成功(hello-world是官方提供的一个测试镜像) docker run hello-world
# 6)查看docker基本信息 docker info
docker version
3、docker简单使用(创建一个ngixn容器)

# 1、创建一个nginx容器 docker run -it nginx # 2、查看docker运行的容器(可以获取到这个容器的id) docker ps # 3、访问这个容器 # 进入这个nginx容器(进入的文件系统和宿主机是完全隔离的,有自己独立的文件系统) docker exec -it 73877e65c07d bash # 4、查看当前容器的 IP docker inspect 73877e65c07d # 73877e65c07d是通过docekr ps查看到的容器ID curl 172.17.0.2 # 测试这个nginx容器是否可以访问
4、docker默认是国外源可以设置成国内镜像源

root@linux-node1 django-docker]# vim /etc/docker/deamon.json # 设置docker镜像源 { "registry-mirrors": ["http://hub-mirror.c.163.com"] } [root@linux-node2 ~]# systemctl restart docker # 重启docker生效
1.4 镜像管理 返回顶部
参考博客: https://www.cnblogs.com/sparkdev/p/9092082.html
1、什么是docker镜像
1. docker镜像不包含Linux内核而又精简的Linux操作系统
2. docker镜像是一个分层存储的文件,一个镜像可以创建N个容器
3. 可以这么理解,docker 镜像是 docker 容器的静态视角,docker 容器是 docker 镜像的运行状态。
4. 容器只是对docker镜像的引用,如果docker镜像删除,此镜像创建的容器也都失效
2、docker镜像与容器的区别
1. 当由 ubuntu:14.04 镜像启动容器时,ubuntu:14.04 镜像的镜像层内容将作为容器的 rootfs;
2. 而 ubuntu:14.04 镜像的 json 文件,会由 docker daemon 解析,并提取出其中的容器执行入口 CMD 信息,
以及容器进程的环境变量 ENV 信息,最终初始化容器进程。
3. 当然,容器进程的执行入口来源于镜像提供的 rootfs。
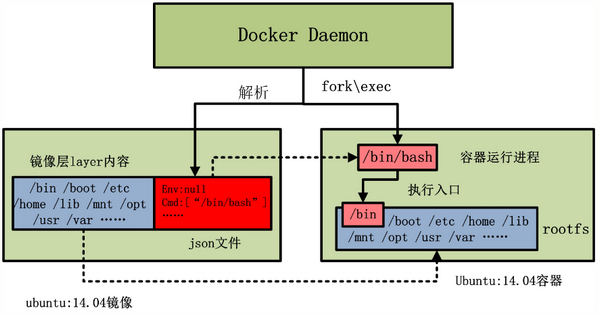
3、rootfs
1. rootfs 是 docker 容器在启动时内部进程可见的文件系统,即 docker 容器的根目录。
2. rootfs 通常包含一个操作系统运行所需的文件系统,例如可能包含典型的类 Unix 操作系统中的目录系统,
如 /dev、/proc、/bin、/etc、/lib、/usr、/tmp 及运行 docker 容器所需的配置文件、工具等。
3. 在传统的 Linux 操作系统内核启动时,首先挂载一个只读的 rootfs,当系统检测其完整性之后,再将其切换为读写模式。
4. 而在 docker 架构中,当 docker daemon 为 docker 容器挂载 rootfs 时,沿用了 Linux 内核启动时的做法,即将 rootfs 设为只读模式。
5. 在挂载完毕之后,利用联合挂载(union mount)技术在已有的只读 rootfs 上再挂载一个读写层。
6. 这样,可读写的层处于 docker 容器文件系统的最顶层,其下可能联合挂载了多个只读的层,
7. 只有在 docker 容器运行过程中文件系统发生变化时,才会把变化的文件内容写到可读写层,并隐藏只读层中的旧版本文件。
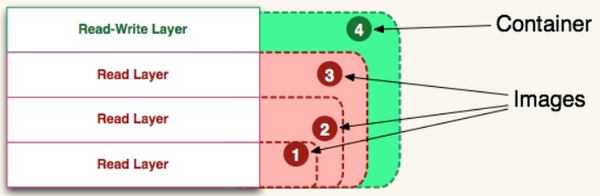
4、容器读写层
1. 容器其实是在镜像的最上面加了一层读写层,在运行容器里文件改动时,会先从镜像里要写的文件复制到容器自己的文件系统中(读写层)。
2. 如果容器删除了,最上面的读写层也就删除了,改动也就丢失了。
3. 所以无论多少个容器共享一个镜像,所做的写操作都是从镜像的文件系统中复制过来操作的,并不会修改镜像的源文件
4. 若想持久化这些改动,可以通过docker commit 将容器保存成一个新镜像

[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker run -itd --name=web1 -p 192.168.56.14:81:80 nginx:latest [root@linux-node4 diff]# docker inspect web1 [ { # 存储驱动 "GraphDriver": { "Data": { "LowerDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/51692869029f819494bb402dc70aa2869b8d1848c3b65c549a010a260e44cc13-init/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/09fa1314e484781dfc1fb25a6cf5df2502fe35dea9025a373a3cb0202732ccce/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/162ec5c9be56e5d718011c09ed087eda04b755e1a68bd1953c60f175e6635e68/diff:/var/lib/docker/overlay2/7c1b27ff59a397ae7d6bd106db579e90476f57bb1ecef9fcb1a6f1ad5ce43b7c/diff", "MergedDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/51692869029f819494bb402dc70aa2869b8d1848c3b65c549a010a260e44cc13/merged", "UpperDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/51692869029f819494bb402dc70aa2869b8d1848c3b65c549a010a260e44cc13/diff", "WorkDir": "/var/lib/docker/overlay2/51692869029f819494bb402dc70aa2869b8d1848c3b65c549a010a260e44cc13/work" }, "Name": "overlay2" }, "NetworkSettings": { "Ports": { "80/tcp": [ { "HostIp": "192.168.56.14", "HostPort": "81" } ] }, "MacAddress": "02:42:ac:11:00:02", "Networks": { "bridge": { "Gateway": "172.17.0.1", "IPAddress": "172.17.0.2", "IPPrefixLen": 16, } } } } ] [root@linux-node4 diff]# cd /var/lib/docker/overlay2/51692869029f819494bb402dc70aa2869b8d1848c3b65c549a010a260e44cc13 [root@linux-node4 51692869029f819494bb402dc70aa2869b8d1848c3b65c549a010a260e44cc13]# ll # 查看docker工作目录都哪些内容 diff link lower merged work diff # 读写层的差异(在读写层做的操作由这个容器单独管理) merged # 引用docker进行中的文件系统 work # 项目工作目录
5、docker镜像从哪里来
1. Docker Hub是由Docker公司负责维护的公共注册中心,包含大量的容器镜像,Docker工具默认从这个公共镜像库下载镜像。
2. 地址:https://hub.docker.com/explore # docker官方镜像和使用方法参考地址
3. 配置镜像加速器:https://www.daocloud.io/mirror
[root@linux-node2 ~]# curl -sSL https://get.daocloud.io/daotools/set_mirror.sh | sh -s http://f1361db2.m.daocloud.io
[root@linux-node2 ~]# cat /etc/docker/daemon.json # 执行上面命令后就会将镜像源修改成国内的地址
{"registry-mirrors": ["http://f1361db2.m.daocloud.io"]}
[root@linux-node2 ~]# systemctl restart docker # 重启docker生效
1.5 docker常用命令 返回顶部
1、docker镜像管理常用命令
[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker help # 查看docker帮助
[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker image --help # 查看 docker中 镜像相关帮助
[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker image ls # 查看当前所有镜像
[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker image inspect nginx # 查看指定镜像(nginx镜像)详细信息
[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker pull nginx:1.14 # 下载指定版本镜像 nginx
[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker image rm nginx:1.14 # 删除nginx 1.14版本
[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker image save nginx > nginx.tar # 导出niginx镜像
2、docker创建容器常用命令

-d # 后台运行容器,并返回容器ID; -i # 以交互模式运行容器,通常与 -t 同时使用; -t # 为容器重新分配一个伪输入终端,通常与 -i 同时使用; -P # 随机端口映射,容器内部端口随机映射到主机的高端口 -p # 指定端口映射,格式为:主机(宿主)端口:容器端口 --name="nginx-lb" # 为容器指定一个名称; --dns 8.8.8.8 # 指定容器使用的DNS服务器,默认和宿主一致;

--dns-search example.com: 指定容器DNS搜索域名,默认和宿主一致; -h "mars": 指定容器的hostname; -e username="ritchie": 设置环境变量; --env-file=[]: 从指定文件读入环境变量; --cpuset="0-2" or --cpuset="0,1,2": 绑定容器到指定CPU运行; -m :设置容器使用内存最大值; --net="bridge": 指定容器的网络连接类型,支持 bridge/host/none/container: 四种类型; --link=[]: 添加链接到另一个容器; --expose=[]: 开放一个端口或一组端口; --volume , -v: 绑定一个卷 -a stdin: 指定标准输入输出内容类型,可选 STDIN/STDOUT/STDERR 三项;
[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker run --help # 查看创建容器帮助
[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker run -it centos # 创建centos镜像并进入终端
[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker run -d nginx # 后台启动nginx容器
[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker stop 6bb09dce461f # 关闭一个容器
[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker ps -l # 查看最近运行的容器
[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker run -itd centos # 启用一个伪终端守护centos容器
[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker container run -d --name web3 -e test=123456 -p 8800:80 -h webhostname --restart always nginx
-d # 后台启动nginx容器
--name web3 # 自定义容器名字(默认会是一段随机字符串)
-e test=123456 # 启动容器添加变量 test=123456 (echo $test)
-p 8800:80 # 宿主机的8800端口映射到docker容器的80端口中
-h webhostname # docker容器主机名 (a300f394af88)
--restart always # 宿主机重启自动拉起这个docker容器
nginx # 使用这个nginx镜像启动容器
注:http://192.168.56.12:8800/ 访问这个docker nginx
[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker logs web # 查看上面启动的web容器的日志
[root@linux-node4 diff]# docker exec -it web bash # 进入容器web
3、容器资源限制
1. 内存限额: 允许容器最多使用500M内存和100M的Swap,并禁用 OOM Killer
docker run -d --name nginx03 --memory="500m" --memory-swap="600m" --oom-kill-disable nginx
2. CPU限额:
docker run -d --name nginx04 --cpus="1.5" nginx # 允许容器最多使用一个半的CPU
docker run -d --name nginx05 --cpus=".5" nginx # 允许容器最多使用50%的CPU
4、docker管理容器常用命令
docker ps # 仅列出当前运行的容器
docker ps -l # 列出最新创建得容器
docker ps -a # 列出素有容器(包括 未运行的)
docker inspect web4 # 列出指定容器的详细信息
#### 持久化容器
docker exec -it web4 bash # 进入容器web4中
touch 1.txt 2.txt # 对容器进行修改
docker commit web4 nginx:web4 # 将修改后的web4容器提交为一个新镜像 nginx:web4
docker images # 可以看到 多了一个 TAG标记为 web4 的镜像
docker run -d --name web4-1 nginx:web4 # 使用刚刚提交的镜像web4创建一个容器web4-1
docker exec -it web4-1 bash # 进入web4-1的bash环境
#### 从宿主机复制文件到docker容器
docker cp nginx.tar web4-1:/home # 将宿主机nginx.tar文件拷贝到容器web4-1的/home目录中
docker exec -it web4-1 ls /home # 在容器web4-1中执行 "ls /home" 命令
#### 容器常用查询命令
docker logs web4-1 # 查看web4-1中控制台日志
docker port 55f870061ed9 # 查看指定容器端口映射
docker top 00f7ddc96622 # 查看容器中有哪些进程
docker stats 00f7ddc96622 # 查看容器资源使用情况
##### 启动、停止、删除 容器
docker ps -a # 列出素有容器(包括 未运行的)
docker start web # 启动容器web
docker stop web # 停止容器web
docker rm web
1.6 docker将数据挂载到容器的三种方式 返回顶部
1、Docker提供三种方式将数据从宿主机挂载到容器中
1)volumes:Docker管理宿主机文件系统的一部分(/var/lib/docker/volumes) 保存数据的最佳方式。
2)bind mounts:将宿主机上的任意位置的文件或者目录挂载到容器中, 就像软连接一样。
3)tmpfs:挂载存储在主机系统的内存中,而不会写入主机的文件系统(不常用)。
区别: volume : 是docker的宿主机文件系统一部分,只有docker可以进行更改,其他进程不能修改 bind mounts : 是挂载在宿主机文件系统的任意位置,除了docker所有进程都可以进行修改、
2、管理卷
docker volume create nginx-vol # 创建一个数据卷 nginx-vol
docker volume ls # 查看宿主机数据卷信息
docker volume inspect nginx-vol # 查看 nginx-vol 这个数据卷详细信息
ls /var/lib/docker/volumes/nginx-vol/_data # 详细信息中会显示 nginx-vol 这个卷实际在宿主机位置
docker rm -f $(docker ps -a |awk '{print $1}') # 删除所有容器
3、volumes:将容器中的数据持久化到宿主机中
1)用卷创建一个容器:
docker run -d --name=nginx-test -p 88:80 --mount src=nginx-vol,dst=/usr/share/nginx/html nginx
run -d # 后台启动一个nginx容器
--name=nginx-test # 自定义容器名字(默认会是一段随机字符串)
-p 88:80 # 将宿主机的88端口映射到容器的80端口
--mount
src=nginx-vol, # 挂载数据卷名称nginx-vol
dst=/usr/share/nginx/html # 将/usr/share/nginx/html文件挂载到nginx-vol数据卷中
nginx # 使用这个nginx镜像启动容器
vim /var/lib/docker/volumes/nginx-vol/_data/index.html # 修改nginx的 index.html文件可以发现页面发生改变
http://192.168.56.12:88/
2)清理卷:
docker stop nginx-test # 关闭正在使用卷nginx-vol的容器nginx-test
docker rm nginx-test # 删除容器 nginx-test
docker volume rm nginx-vol # 删除卷 nginx-vol
4、bind mounts:将宿主机中的数据挂载到容器中
1)用卷创建一个容器:
docker run -d --name=nginx-test -p 88:80 --mount type=bind,src=/mnt/,dst=/usr/share/nginx/html nginx
run -d # 后台启动一个nginx容器
--name=nginx-test # 自定义容器名字(默认会是一段随机字符串)
-p 88:80 # 将宿主机的88端口映射到容器的80端口
--mount type=bind # 将/usr/share/nginx/html文件夹挂载到宿主机/mnt/文件夹中
src=/mnt/, # 宿主机中挂载目录 /mnt/
dst=/usr/share/nginx/html # 容器中/usr/share/nginx/html文件夹
nginx # 使用这个nginx镜像启动容器
docker exec -it nginx-test bash # 进入容器
cd /usr/share/nginx/html # 进入容器的挂载目录
echo "hello I come here" > index.html # 在目录中创建一个 index.html文件
http://192.168.56.12:88/ # 可以在页面访问到 index.html首页
vim /mnt/index.html # 修改 /mnt/index.html 就等同修改容器中的index.html页面
2)清理:
docker stop nginx-test # 关闭正在使用卷nginx-vol的容器nginx-test
docker rm nginx-test # 删除容器 nginx-test
注意:
1. 如果源文件/目录没有存在,不会自动创建,会抛出一个错误。
2. 如果挂载目标在容器中非空目录,则该目录现有内容将被隐藏。
5、Volume特点:
1. 多个运行容器之间共享数据。
2. 当容器停止或被移除时,该卷依然存在。
3. 多个容器可以同时挂载相同的卷。
4. 当明确删除卷时,卷才会被删除。
5. 将容器的数据存储在远程主机或其他存储上
6. 将数据从一台Docker主机迁移到另一台时,先停止容器,然后备份卷的目录(/var/lib/docker/volumes/)
6、Bind Mounts特点:
1. 从主机共享配置文件到容器。默认情况下,挂载主机/etc/resolv.conf到每个容器,提供DNS解析。
2. 在Docker主机上的开发环境和容器之间共享源代码。例如,可以将Maven target目录挂载到容器中,每次在Docker主机
上构建Maven项目时,容器都可以访问构建的项目包。
3. 当Docker主机的文件或目录结构保证与容器所需的绑定挂载一致时
1.7 容器网络
1、网络模式
• bridge(常用)
–net=bridge
默认网络,Docker启动后创建一个docker0网桥,默认创建的容器也是添加到这个网桥中。
• host(常用)
–net=host
容器不会获得一个独立的network namespace,而是与宿主机共用一个。这就意味着容器不会有自己的网卡信息,而是使用宿主
机的。容器除了网络,其他都是隔离的。
• none(不常用)
–net=none
获取独立的network namespace,但不为容器进行任何网络配置,需要我们手动配置。
• container(不常用)
–net=container:Name/ID
与指定的容器使用同一个network namespace,具有同样的网络配置信息,两个容器除了网络,其他都还是隔离的。
• 自定义网络(最佳方式)
与默认的bridge原理一样,但自定义网络具备内部DNS发现,可以通过容器名或者主机名容器之间网络通信。
'''开启Linux系统的IP转发功能 '''
# 1. 出于安全考虑,Linux系统默认是禁止数据包转发的。
# 2. 所谓转发即当主机拥有多于一块的网卡时,将收到的数据包转发给其他网卡
[root@linux-node4 ~]# vim /etc/sysctl.conf
net.ipv4.ip_forward=1
[root@linux-node4 ~]# systemctl restart network
[root@linux-node4 ~]# sysctl net.ipv4.ip_forward # 输出为1时则证明是成功的

##### 1、下载busybox镜像用于测试 docker pull busybox # 下载一个测试镜像,一些工具都有了 docker run -it busybox # 进入busybox 默认 bash docker run -it --net=host busybox # 以 host 网络模式进入bash ##### 2、自定义网络模式 docker network create bs-test # 创建一个网络 bs-test docker run -it --name bs3 --net bs-test busybox # 创建容器bst加入网络bs-test docker run -it --name bs4 --net bs-test busybox # 创建容器bst加入网络bs-test ping bs3 # 在bs3和bs4容器中可以通过主机名ping通 ping bs4 docker start bs3 # 启动容器bs3 docker exec -it bs3 sh # 进入bs3 bash环境 ####3、container网络模式 docker run -itd --name bs -p 99:80 busybox # 创建一个名字为bs的容器,并将宿主机99端口映射到80端口 docker run -d --name nginx01 --net container:bs nginx # 使用nginx镜像创建一个容器名nginx01,加入到bs容器中 http://192.168.56.12:99/ docker exec -it bs sh # 注:bs容器中虽然没有nginx服务,但是可以访问nginx服务,因为nginx01容器加入了
1.8 Dockerfile: 构建nginx项目镜像 返回顶部
'''1.DOckerfile常用命令 '''
FROM python:3.6 # 指定拉取镜像版本
ENV PYTHONUNBUFFERED 1 # 不缓冲stdin、stdout和stderr,直接把输出重定向到文件
MAINITAINER zhangsan # 指定作者
RUN mkdri /code # 运行的linux命令
WORKDIR /code # 指定项目工作根路径
ADD . /code/ # 将宿主机文件复制到镜像中
COPY dj.conf /etc/nginx/conf.d # docker内部文件拷贝
VOLUME ["/data1","/data2"] # 将宿主机文件夹挂载到容器中
EXPOSE 8080 # 暴露端口
CMD ["sh","/code/start.sh"] # 容器启动时要运行的命令
CMD ["python", "manage.py", "runserver", "0:8000"]
'''2.生成镜像并运行容器'''
docker build -t nginx:v1 -f Dockerfile-nginx . # 使用Dockerfile-nginx文件生成镜像 nginx:v1
docker push linux-node4.example.com/test/nginx:v1 # 推送镜像到harbor中
docker run -d -p 192.168.56.14:8000:8080 nginx:v1 # 运行docker容器

'''COPY与ADD指令比较 ''' #1.COPY指令: 能够将构建命令所在的主机本地的文件或目录,复制到镜像文件系统 #2.ADD指令: 不仅能够将构建命令所在的主机本地的文件或目录,复制到镜像文件系统 而且可以是一个 URL,这种情况下,Docker 引擎会试图去下载这个链接的文件放到 <目标路径> 去 所以,可以认为ADD是增强版的COPY,支持将远程URL的资源加入到镜像的文件系统 例:ADD http://example.com/big.tar.xz /usr/src/things/
1、使用 Dockerfile-nginx 文件构建一个基础镜像 nginx:v1

FROM centos:7 MAINTAINER www.ctnrs.com RUN yum install -y gcc gcc-c++ make \ openssl-devel pcre-devel gd-devel \ iproute net-tools telnet wget curl && \ yum clean all && \ rm -rf /var/cache/yum/* RUN wget http://nginx.org/download/nginx-1.15.5.tar.gz && \ tar zxf nginx-1.15.5.tar.gz && \ cd nginx-1.15.5 && \ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/nginx \ --with-http_ssl_module \ --with-http_stub_status_module && \ make -j 4 && make install && \ rm -rf /usr/local/nginx/html/* && \ echo "ok" >> /usr/local/nginx/html/status.html && \ cd / && rm -rf nginx-1.12.2* && \ ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime ENV PATH $PATH:/usr/local/nginx/sbin #COPY nginx.conf /usr/local/nginx/conf/nginx.conf WORKDIR /usr/local/nginx EXPOSE 80 CMD ["nginx", "-g", "daemon off;"]
docker build -t nginx:v1 -f Dockerfile-nginx . # 使用 Dockerfile-nginx 文件构建一个基础镜像 nginx:v1
-t nginx:v1 # 指定版本tag=v1
-f Dockerfile-nginx # 指定dockerfile的名称
. # 指定上下文(比如配置文件在那个位置等)
docker images # 查看 nginx:v1 镜像是否创建成功
docker run -d --name nginx01 -p 88:80 nginx:v1 # 使用 nginx:v1 镜像创建一个容器 nginx01
http://192.168.56.12:88/status.html # 测试是否可以访问容器nginx01的web服务
2、使用nginx:v1 基础镜像构建一个项目镜像
vim Dockerfile
FROM nginx:v1
COPY index.html /usr/local/nginx/html # 需要在当前目录中创建index.html文件
docker build -t nginx:v2 -f Dockerfile . # 使用Dockerfile创建一个项目镜像 nginx:v2
docker run -d --name nginx02 -p 89:80 nginx:v2 # 使用 nginx:v2 创建一个容器 nginx02
http://192.168.56.12:89/ # 测试访问 容器 nginx:v2中的nginx服务
1.9 Dockerfile: 构建php项目镜像 返回顶部
1、使用 Dockerfile-nginx 文件构建一个基础镜像 nginx:v1

FROM centos:7 MAINTAINER www.ctnrs.com RUN yum install epel-release -y && \ yum install -y gcc gcc-c++ make gd-devel libxml2-devel \ libcurl-devel libjpeg-devel libpng-devel openssl-devel \ libmcrypt-devel libxslt-devel libtidy-devel autoconf \ iproute net-tools telnet wget curl && \ yum clean all && \ rm -rf /var/cache/yum/* RUN wget http://docs.php.net/distributions/php-5.6.36.tar.gz && \ tar zxf php-5.6.36.tar.gz && \ cd php-5.6.36 && \ ./configure --prefix=/usr/local/php \ --with-config-file-path=/usr/local/php/etc \ --enable-fpm --enable-opcache \ --with-mysql --with-mysqli --with-pdo-mysql \ --with-openssl --with-zlib --with-curl --with-gd \ --with-jpeg-dir --with-png-dir --with-freetype-dir \ --enable-mbstring --with-mcrypt --enable-hash && \ make -j 4 && make install && \ cp php.ini-production /usr/local/php/etc/php.ini && \ cp sapi/fpm/php-fpm.conf /usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.conf && \ sed -i "90a \daemonize = no" /usr/local/php/etc/php-fpm.conf && \ mkdir /usr/local/php/log && \ cd / && rm -rf php* && \ ln -sf /usr/share/zoneinfo/Asia/Shanghai /etc/localtime ENV PATH $PATH:/usr/local/php/sbin COPY php.ini /usr/local/php/etc/ COPY php-fpm.conf /usr/local/php/etc/ WORKDIR /usr/local/php EXPOSE 9000 CMD ["php-fpm"]

[PHP] ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; About php.ini ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; PHP's initialization file, generally called php.ini, is responsible for ; configuring many of the aspects of PHP's behavior. ; PHP attempts to find and load this configuration from a number of locations. ; The following is a summary of its search order: ; 1. SAPI module specific location. ; 2. The PHPRC environment variable. (As of PHP 5.2.0) ; 3. A number of predefined registry keys on Windows (As of PHP 5.2.0) ; 4. Current working directory (except CLI) ; 5. The web server's directory (for SAPI modules), or directory of PHP ; (otherwise in Windows) ; 6. The directory from the --with-config-file-path compile time option, or the ; Windows directory (C:\windows or C:\winnt) ; See the PHP docs for more specific information. ; http://php.net/configuration.file ; The syntax of the file is extremely simple. Whitespace and lines ; beginning with a semicolon are silently ignored (as you probably guessed). ; Section headers (e.g. [Foo]) are also silently ignored, even though ; they might mean something in the future. ; Directives following the section heading [PATH=/www/mysite] only ; apply to PHP files in the /www/mysite directory. Directives ; following the section heading [HOST=www.example.com] only apply to ; PHP files served from www.example.com. Directives set in these ; special sections cannot be overridden by user-defined INI files or ; at runtime. Currently, [PATH=] and [HOST=] sections only work under ; CGI/FastCGI. ; http://php.net/ini.sections ; Directives are specified using the following syntax: ; directive = value ; Directive names are *case sensitive* - foo=bar is different from FOO=bar. ; Directives are variables used to configure PHP or PHP extensions. ; There is no name validation. If PHP can't find an expected ; directive because it is not set or is mistyped, a default value will be used. ; The value can be a string, a number, a PHP constant (e.g. E_ALL or M_PI), one ; of the INI constants (On, Off, True, False, Yes, No and None) or an expression ; (e.g. E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE), a quoted string ("bar"), or a reference to a ; previously set variable or directive (e.g. ${foo}) ; Expressions in the INI file are limited to bitwise operators and parentheses: ; | bitwise OR ; ^ bitwise XOR ; & bitwise AND ; ~ bitwise NOT ; ! boolean NOT ; Boolean flags can be turned on using the values 1, On, True or Yes. ; They can be turned off using the values 0, Off, False or No. ; An empty string can be denoted by simply not writing anything after the equal ; sign, or by using the None keyword: ; foo = ; sets foo to an empty string ; foo = None ; sets foo to an empty string ; foo = "None" ; sets foo to the string 'None' ; If you use constants in your value, and these constants belong to a ; dynamically loaded extension (either a PHP extension or a Zend extension), ; you may only use these constants *after* the line that loads the extension. ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; About this file ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; PHP comes packaged with two INI files. One that is recommended to be used ; in production environments and one that is recommended to be used in ; development environments. ; php.ini-production contains settings which hold security, performance and ; best practices at its core. But please be aware, these settings may break ; compatibility with older or less security conscience applications. We ; recommending using the production ini in production and testing environments. ; php.ini-development is very similar to its production variant, except it is ; much more verbose when it comes to errors. We recommend using the ; development version only in development environments, as errors shown to ; application users can inadvertently leak otherwise secure information. ; This is php.ini-production INI file. ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Quick Reference ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; The following are all the settings which are different in either the production ; or development versions of the INIs with respect to PHP's default behavior. ; Please see the actual settings later in the document for more details as to why ; we recommend these changes in PHP's behavior. ; display_errors ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: Off ; display_startup_errors ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: Off ; error_reporting ; Default Value: E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED ; Development Value: E_ALL ; Production Value: E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT ; html_errors ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: On ; Production value: On ; log_errors ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: On ; max_input_time ; Default Value: -1 (Unlimited) ; Development Value: 60 (60 seconds) ; Production Value: 60 (60 seconds) ; output_buffering ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: 4096 ; Production Value: 4096 ; register_argc_argv ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: Off ; Production Value: Off ; request_order ; Default Value: None ; Development Value: "GP" ; Production Value: "GP" ; session.gc_divisor ; Default Value: 100 ; Development Value: 1000 ; Production Value: 1000 ; session.hash_bits_per_character ; Default Value: 4 ; Development Value: 5 ; Production Value: 5 ; short_open_tag ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: Off ; Production Value: Off ; track_errors ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: Off ; url_rewriter.tags ; Default Value: "a=href,area=href,frame=src,form=,fieldset=" ; Development Value: "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry" ; Production Value: "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry" ; variables_order ; Default Value: "EGPCS" ; Development Value: "GPCS" ; Production Value: "GPCS" ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; php.ini Options ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Name for user-defined php.ini (.htaccess) files. Default is ".user.ini" ;user_ini.filename = ".user.ini" ; To disable this feature set this option to empty value ;user_ini.filename = ; TTL for user-defined php.ini files (time-to-live) in seconds. Default is 300 seconds (5 minutes) ;user_ini.cache_ttl = 300 ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Language Options ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Enable the PHP scripting language engine under Apache. ; http://php.net/engine engine = On ; This directive determines whether or not PHP will recognize code between ; <? and ?> tags as PHP source which should be processed as such. It is ; generally recommended that <?php and ?> should be used and that this feature ; should be disabled, as enabling it may result in issues when generating XML ; documents, however this remains supported for backward compatibility reasons. ; Note that this directive does not control the <?= shorthand tag, which can be ; used regardless of this directive. ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: Off ; Production Value: Off ; http://php.net/short-open-tag short_open_tag = Off ; Allow ASP-style <% %> tags. ; http://php.net/asp-tags asp_tags = Off ; The number of significant digits displayed in floating point numbers. ; http://php.net/precision precision = 14 ; Output buffering is a mechanism for controlling how much output data ; (excluding headers and cookies) PHP should keep internally before pushing that ; data to the client. If your application's output exceeds this setting, PHP ; will send that data in chunks of roughly the size you specify. ; Turning on this setting and managing its maximum buffer size can yield some ; interesting side-effects depending on your application and web server. ; You may be able to send headers and cookies after you've already sent output ; through print or echo. You also may see performance benefits if your server is ; emitting less packets due to buffered output versus PHP streaming the output ; as it gets it. On production servers, 4096 bytes is a good setting for performance ; reasons. ; Note: Output buffering can also be controlled via Output Buffering Control ; functions. ; Possible Values: ; On = Enabled and buffer is unlimited. (Use with caution) ; Off = Disabled ; Integer = Enables the buffer and sets its maximum size in bytes. ; Note: This directive is hardcoded to Off for the CLI SAPI ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: 4096 ; Production Value: 4096 ; http://php.net/output-buffering output_buffering = 4096 ; You can redirect all of the output of your scripts to a function. For ; example, if you set output_handler to "mb_output_handler", character ; encoding will be transparently converted to the specified encoding. ; Setting any output handler automatically turns on output buffering. ; Note: People who wrote portable scripts should not depend on this ini ; directive. Instead, explicitly set the output handler using ob_start(). ; Using this ini directive may cause problems unless you know what script ; is doing. ; Note: You cannot use both "mb_output_handler" with "ob_iconv_handler" ; and you cannot use both "ob_gzhandler" and "zlib.output_compression". ; Note: output_handler must be empty if this is set 'On' !!!! ; Instead you must use zlib.output_handler. ; http://php.net/output-handler ;output_handler = ; Transparent output compression using the zlib library ; Valid values for this option are 'off', 'on', or a specific buffer size ; to be used for compression (default is 4KB) ; Note: Resulting chunk size may vary due to nature of compression. PHP ; outputs chunks that are few hundreds bytes each as a result of ; compression. If you prefer a larger chunk size for better ; performance, enable output_buffering in addition. ; Note: You need to use zlib.output_handler instead of the standard ; output_handler, or otherwise the output will be corrupted. ; http://php.net/zlib.output-compression zlib.output_compression = Off ; http://php.net/zlib.output-compression-level ;zlib.output_compression_level = -1 ; You cannot specify additional output handlers if zlib.output_compression ; is activated here. This setting does the same as output_handler but in ; a different order. ; http://php.net/zlib.output-handler ;zlib.output_handler = ; Implicit flush tells PHP to tell the output layer to flush itself ; automatically after every output block. This is equivalent to calling the ; PHP function flush() after each and every call to print() or echo() and each ; and every HTML block. Turning this option on has serious performance ; implications and is generally recommended for debugging purposes only. ; http://php.net/implicit-flush ; Note: This directive is hardcoded to On for the CLI SAPI implicit_flush = Off ; The unserialize callback function will be called (with the undefined class' ; name as parameter), if the unserializer finds an undefined class ; which should be instantiated. A warning appears if the specified function is ; not defined, or if the function doesn't include/implement the missing class. ; So only set this entry, if you really want to implement such a ; callback-function. unserialize_callback_func = ; When floats & doubles are serialized store serialize_precision significant ; digits after the floating point. The default value ensures that when floats ; are decoded with unserialize, the data will remain the same. serialize_precision = 17 ; open_basedir, if set, limits all file operations to the defined directory ; and below. This directive makes most sense if used in a per-directory ; or per-virtualhost web server configuration file. ; http://php.net/open-basedir ;open_basedir = ; This directive allows you to disable certain functions for security reasons. ; It receives a comma-delimited list of function names. ; http://php.net/disable-functions disable_functions = ; This directive allows you to disable certain classes for security reasons. ; It receives a comma-delimited list of class names. ; http://php.net/disable-classes disable_classes = ; Colors for Syntax Highlighting mode. Anything that's acceptable in ; <span style="color: ???????"> would work. ; http://php.net/syntax-highlighting ;highlight.string = #DD0000 ;highlight.comment = #FF9900 ;highlight.keyword = #007700 ;highlight.default = #0000BB ;highlight.html = #000000 ; If enabled, the request will be allowed to complete even if the user aborts ; the request. Consider enabling it if executing long requests, which may end up ; being interrupted by the user or a browser timing out. PHP's default behavior ; is to disable this feature. ; http://php.net/ignore-user-abort ;ignore_user_abort = On ; Determines the size of the realpath cache to be used by PHP. This value should ; be increased on systems where PHP opens many files to reflect the quantity of ; the file operations performed. ; http://php.net/realpath-cache-size ;realpath_cache_size = 16k ; Duration of time, in seconds for which to cache realpath information for a given ; file or directory. For systems with rarely changing files, consider increasing this ; value. ; http://php.net/realpath-cache-ttl ;realpath_cache_ttl = 120 ; Enables or disables the circular reference collector. ; http://php.net/zend.enable-gc zend.enable_gc = On ; If enabled, scripts may be written in encodings that are incompatible with ; the scanner. CP936, Big5, CP949 and Shift_JIS are the examples of such ; encodings. To use this feature, mbstring extension must be enabled. ; Default: Off ;zend.multibyte = Off ; Allows to set the default encoding for the scripts. This value will be used ; unless "declare(encoding=...)" directive appears at the top of the script. ; Only affects if zend.multibyte is set. ; Default: "" ;zend.script_encoding = ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Miscellaneous ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Decides whether PHP may expose the fact that it is installed on the server ; (e.g. by adding its signature to the Web server header). It is no security ; threat in any way, but it makes it possible to determine whether you use PHP ; on your server or not. ; http://php.net/expose-php expose_php = On ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Resource Limits ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Maximum execution time of each script, in seconds ; http://php.net/max-execution-time ; Note: This directive is hardcoded to 0 for the CLI SAPI max_execution_time = 30 ; Maximum amount of time each script may spend parsing request data. It's a good ; idea to limit this time on productions servers in order to eliminate unexpectedly ; long running scripts. ; Note: This directive is hardcoded to -1 for the CLI SAPI ; Default Value: -1 (Unlimited) ; Development Value: 60 (60 seconds) ; Production Value: 60 (60 seconds) ; http://php.net/max-input-time max_input_time = 60 ; Maximum input variable nesting level ; http://php.net/max-input-nesting-level ;max_input_nesting_level = 64 ; How many GET/POST/COOKIE input variables may be accepted ; max_input_vars = 1000 ; Maximum amount of memory a script may consume (128MB) ; http://php.net/memory-limit memory_limit = 128M ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Error handling and logging ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; This directive informs PHP of which errors, warnings and notices you would like ; it to take action for. The recommended way of setting values for this ; directive is through the use of the error level constants and bitwise ; operators. The error level constants are below here for convenience as well as ; some common settings and their meanings. ; By default, PHP is set to take action on all errors, notices and warnings EXCEPT ; those related to E_NOTICE and E_STRICT, which together cover best practices and ; recommended coding standards in PHP. For performance reasons, this is the ; recommend error reporting setting. Your production server shouldn't be wasting ; resources complaining about best practices and coding standards. That's what ; development servers and development settings are for. ; Note: The php.ini-development file has this setting as E_ALL. This ; means it pretty much reports everything which is exactly what you want during ; development and early testing. ; ; Error Level Constants: ; E_ALL - All errors and warnings (includes E_STRICT as of PHP 5.4.0) ; E_ERROR - fatal run-time errors ; E_RECOVERABLE_ERROR - almost fatal run-time errors ; E_WARNING - run-time warnings (non-fatal errors) ; E_PARSE - compile-time parse errors ; E_NOTICE - run-time notices (these are warnings which often result ; from a bug in your code, but it's possible that it was ; intentional (e.g., using an uninitialized variable and ; relying on the fact it is automatically initialized to an ; empty string) ; E_STRICT - run-time notices, enable to have PHP suggest changes ; to your code which will ensure the best interoperability ; and forward compatibility of your code ; E_CORE_ERROR - fatal errors that occur during PHP's initial startup ; E_CORE_WARNING - warnings (non-fatal errors) that occur during PHP's ; initial startup ; E_COMPILE_ERROR - fatal compile-time errors ; E_COMPILE_WARNING - compile-time warnings (non-fatal errors) ; E_USER_ERROR - user-generated error message ; E_USER_WARNING - user-generated warning message ; E_USER_NOTICE - user-generated notice message ; E_DEPRECATED - warn about code that will not work in future versions ; of PHP ; E_USER_DEPRECATED - user-generated deprecation warnings ; ; Common Values: ; E_ALL (Show all errors, warnings and notices including coding standards.) ; E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE (Show all errors, except for notices) ; E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT (Show all errors, except for notices and coding standards warnings.) ; E_COMPILE_ERROR|E_RECOVERABLE_ERROR|E_ERROR|E_CORE_ERROR (Show only errors) ; Default Value: E_ALL & ~E_NOTICE & ~E_STRICT & ~E_DEPRECATED ; Development Value: E_ALL ; Production Value: E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT ; http://php.net/error-reporting error_reporting = E_ALL & ~E_DEPRECATED & ~E_STRICT ; This directive controls whether or not and where PHP will output errors, ; notices and warnings too. Error output is very useful during development, but ; it could be very dangerous in production environments. Depending on the code ; which is triggering the error, sensitive information could potentially leak ; out of your application such as database usernames and passwords or worse. ; For production environments, we recommend logging errors rather than ; sending them to STDOUT. ; Possible Values: ; Off = Do not display any errors ; stderr = Display errors to STDERR (affects only CGI/CLI binaries!) ; On or stdout = Display errors to STDOUT ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: Off ; http://php.net/display-errors display_errors = Off ; The display of errors which occur during PHP's startup sequence are handled ; separately from display_errors. PHP's default behavior is to suppress those ; errors from clients. Turning the display of startup errors on can be useful in ; debugging configuration problems. We strongly recommend you ; set this to 'off' for production servers. ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: Off ; http://php.net/display-startup-errors display_startup_errors = Off ; Besides displaying errors, PHP can also log errors to locations such as a ; server-specific log, STDERR, or a location specified by the error_log ; directive found below. While errors should not be displayed on productions ; servers they should still be monitored and logging is a great way to do that. ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: On ; http://php.net/log-errors log_errors = On ; Set maximum length of log_errors. In error_log information about the source is ; added. The default is 1024 and 0 allows to not apply any maximum length at all. ; http://php.net/log-errors-max-len log_errors_max_len = 1024 ; Do not log repeated messages. Repeated errors must occur in same file on same ; line unless ignore_repeated_source is set true. ; http://php.net/ignore-repeated-errors ignore_repeated_errors = Off ; Ignore source of message when ignoring repeated messages. When this setting ; is On you will not log errors with repeated messages from different files or ; source lines. ; http://php.net/ignore-repeated-source ignore_repeated_source = Off ; If this parameter is set to Off, then memory leaks will not be shown (on ; stdout or in the log). This has only effect in a debug compile, and if ; error reporting includes E_WARNING in the allowed list ; http://php.net/report-memleaks report_memleaks = On ; This setting is on by default. ;report_zend_debug = 0 ; Store the last error/warning message in $php_errormsg (boolean). Setting this value ; to On can assist in debugging and is appropriate for development servers. It should ; however be disabled on production servers. ; Default Value: Off ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: Off ; http://php.net/track-errors track_errors = Off ; Turn off normal error reporting and emit XML-RPC error XML ; http://php.net/xmlrpc-errors ;xmlrpc_errors = 0 ; An XML-RPC faultCode ;xmlrpc_error_number = 0 ; When PHP displays or logs an error, it has the capability of formatting the ; error message as HTML for easier reading. This directive controls whether ; the error message is formatted as HTML or not. ; Note: This directive is hardcoded to Off for the CLI SAPI ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: On ; Production value: On ; http://php.net/html-errors html_errors = On ; If html_errors is set to On *and* docref_root is not empty, then PHP ; produces clickable error messages that direct to a page describing the error ; or function causing the error in detail. ; You can download a copy of the PHP manual from http://php.net/docs ; and change docref_root to the base URL of your local copy including the ; leading '/'. You must also specify the file extension being used including ; the dot. PHP's default behavior is to leave these settings empty, in which ; case no links to documentation are generated. ; Note: Never use this feature for production boxes. ; http://php.net/docref-root ; Examples ;docref_root = "/phpmanual/" ; http://php.net/docref-ext ;docref_ext = .html ; String to output before an error message. PHP's default behavior is to leave ; this setting blank. ; http://php.net/error-prepend-string ; Example: ;error_prepend_string = "<span style='color: #ff0000'>" ; String to output after an error message. PHP's default behavior is to leave ; this setting blank. ; http://php.net/error-append-string ; Example: ;error_append_string = "</span>" ; Log errors to specified file. PHP's default behavior is to leave this value ; empty. ; http://php.net/error-log ; Example: ;error_log = php_errors.log ; Log errors to syslog (Event Log on Windows). ;error_log = syslog ;windows.show_crt_warning ; Default value: 0 ; Development value: 0 ; Production value: 0 ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Data Handling ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; The separator used in PHP generated URLs to separate arguments. ; PHP's default setting is "&". ; http://php.net/arg-separator.output ; Example: ;arg_separator.output = "&" ; List of separator(s) used by PHP to parse input URLs into variables. ; PHP's default setting is "&". ; NOTE: Every character in this directive is considered as separator! ; http://php.net/arg-separator.input ; Example: ;arg_separator.input = ";&" ; This directive determines which super global arrays are registered when PHP ; starts up. G,P,C,E & S are abbreviations for the following respective super ; globals: GET, POST, COOKIE, ENV and SERVER. There is a performance penalty ; paid for the registration of these arrays and because ENV is not as commonly ; used as the others, ENV is not recommended on productions servers. You ; can still get access to the environment variables through getenv() should you ; need to. ; Default Value: "EGPCS" ; Development Value: "GPCS" ; Production Value: "GPCS"; ; http://php.net/variables-order variables_order = "GPCS" ; This directive determines which super global data (G,P & C) should be ; registered into the super global array REQUEST. If so, it also determines ; the order in which that data is registered. The values for this directive ; are specified in the same manner as the variables_order directive, ; EXCEPT one. Leaving this value empty will cause PHP to use the value set ; in the variables_order directive. It does not mean it will leave the super ; globals array REQUEST empty. ; Default Value: None ; Development Value: "GP" ; Production Value: "GP" ; http://php.net/request-order request_order = "GP" ; This directive determines whether PHP registers $argv & $argc each time it ; runs. $argv contains an array of all the arguments passed to PHP when a script ; is invoked. $argc contains an integer representing the number of arguments ; that were passed when the script was invoked. These arrays are extremely ; useful when running scripts from the command line. When this directive is ; enabled, registering these variables consumes CPU cycles and memory each time ; a script is executed. For performance reasons, this feature should be disabled ; on production servers. ; Note: This directive is hardcoded to On for the CLI SAPI ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: Off ; Production Value: Off ; http://php.net/register-argc-argv register_argc_argv = Off ; When enabled, the ENV, REQUEST and SERVER variables are created when they're ; first used (Just In Time) instead of when the script starts. If these ; variables are not used within a script, having this directive on will result ; in a performance gain. The PHP directive register_argc_argv must be disabled ; for this directive to have any affect. ; http://php.net/auto-globals-jit auto_globals_jit = On ; Whether PHP will read the POST data. ; This option is enabled by default. ; Most likely, you won't want to disable this option globally. It causes $_POST ; and $_FILES to always be empty; the only way you will be able to read the ; POST data will be through the php://input stream wrapper. This can be useful ; to proxy requests or to process the POST data in a memory efficient fashion. ; http://php.net/enable-post-data-reading ;enable_post_data_reading = Off ; Maximum size of POST data that PHP will accept. ; Its value may be 0 to disable the limit. It is ignored if POST data reading ; is disabled through enable_post_data_reading. ; http://php.net/post-max-size post_max_size = 100M ; Automatically add files before PHP document. ; http://php.net/auto-prepend-file auto_prepend_file = ; Automatically add files after PHP document. ; http://php.net/auto-append-file auto_append_file = ; By default, PHP will output a media type using the Content-Type header. To ; disable this, simply set it to be empty. ; ; PHP's built-in default media type is set to text/html. ; http://php.net/default-mimetype default_mimetype = "text/html" ; PHP's default character set is set to UTF-8. ; http://php.net/default-charset default_charset = "UTF-8" ; PHP internal character encoding is set to empty. ; If empty, default_charset is used. ; http://php.net/internal-encoding ;internal_encoding = ; PHP input character encoding is set to empty. ; If empty, default_charset is used. ; http://php.net/input-encoding ;input_encoding = ; PHP output character encoding is set to empty. ; If empty, default_charset is used. ; See also output_buffer. ; http://php.net/output-encoding ;output_encoding = ; Always populate the $HTTP_RAW_POST_DATA variable. PHP's default behavior is ; to disable this feature and it will be removed in a future version. ; If post reading is disabled through enable_post_data_reading, ; $HTTP_RAW_POST_DATA is *NOT* populated. ; http://php.net/always-populate-raw-post-data ;always_populate_raw_post_data = -1 ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Paths and Directories ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; UNIX: "/path1:/path2" ;include_path = ".:/php/includes" ; ; Windows: "\path1;\path2" ;include_path = ".;c:\php\includes" ; ; PHP's default setting for include_path is ".;/path/to/php/pear" ; http://php.net/include-path ; The root of the PHP pages, used only if nonempty. ; if PHP was not compiled with FORCE_REDIRECT, you SHOULD set doc_root ; if you are running php as a CGI under any web server (other than IIS) ; see documentation for security issues. The alternate is to use the ; cgi.force_redirect configuration below ; http://php.net/doc-root doc_root = ; The directory under which PHP opens the script using /~username used only ; if nonempty. ; http://php.net/user-dir user_dir = ; Directory in which the loadable extensions (modules) reside. ; http://php.net/extension-dir ; extension_dir = "./" ; On windows: ; extension_dir = "ext" ; Directory where the temporary files should be placed. ; Defaults to the system default (see sys_get_temp_dir) ; sys_temp_dir = "/tmp" ; Whether or not to enable the dl() function. The dl() function does NOT work ; properly in multithreaded servers, such as IIS or Zeus, and is automatically ; disabled on them. ; http://php.net/enable-dl enable_dl = Off ; cgi.force_redirect is necessary to provide security running PHP as a CGI under ; most web servers. Left undefined, PHP turns this on by default. You can ; turn it off here AT YOUR OWN RISK ; **You CAN safely turn this off for IIS, in fact, you MUST.** ; http://php.net/cgi.force-redirect ;cgi.force_redirect = 1 ; if cgi.nph is enabled it will force cgi to always sent Status: 200 with ; every request. PHP's default behavior is to disable this feature. ;cgi.nph = 1 ; if cgi.force_redirect is turned on, and you are not running under Apache or Netscape ; (iPlanet) web servers, you MAY need to set an environment variable name that PHP ; will look for to know it is OK to continue execution. Setting this variable MAY ; cause security issues, KNOW WHAT YOU ARE DOING FIRST. ; http://php.net/cgi.redirect-status-env ;cgi.redirect_status_env = ; cgi.fix_pathinfo provides *real* PATH_INFO/PATH_TRANSLATED support for CGI. PHP's ; previous behaviour was to set PATH_TRANSLATED to SCRIPT_FILENAME, and to not grok ; what PATH_INFO is. For more information on PATH_INFO, see the cgi specs. Setting ; this to 1 will cause PHP CGI to fix its paths to conform to the spec. A setting ; of zero causes PHP to behave as before. Default is 1. You should fix your scripts ; to use SCRIPT_FILENAME rather than PATH_TRANSLATED. ; http://php.net/cgi.fix-pathinfo ;cgi.fix_pathinfo=1 ; if cgi.discard_path is enabled, the PHP CGI binary can safely be placed outside ; of the web tree and people will not be able to circumvent .htaccess security. ; http://php.net/cgi.dicard-path ;cgi.discard_path=1 ; FastCGI under IIS (on WINNT based OS) supports the ability to impersonate ; security tokens of the calling client. This allows IIS to define the ; security context that the request runs under. mod_fastcgi under Apache ; does not currently support this feature (03/17/2002) ; Set to 1 if running under IIS. Default is zero. ; http://php.net/fastcgi.impersonate ;fastcgi.impersonate = 1 ; Disable logging through FastCGI connection. PHP's default behavior is to enable ; this feature. ;fastcgi.logging = 0 ; cgi.rfc2616_headers configuration option tells PHP what type of headers to ; use when sending HTTP response code. If set to 0, PHP sends Status: header that ; is supported by Apache. When this option is set to 1, PHP will send ; RFC2616 compliant header. ; Default is zero. ; http://php.net/cgi.rfc2616-headers ;cgi.rfc2616_headers = 0 ; cgi.check_shebang_line controls whether CGI PHP checks for line starting with #! ; (shebang) at the top of the running script. This line might be needed if the ; script support running both as stand-alone script and via PHP CGI<. PHP in CGI ; mode skips this line and ignores its content if this directive is turned on. ; http://php.net/cgi.check-shebang-line ;cgi.check_shebang_line=1 ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; File Uploads ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Whether to allow HTTP file uploads. ; http://php.net/file-uploads file_uploads = On ; Temporary directory for HTTP uploaded files (will use system default if not ; specified). ; http://php.net/upload-tmp-dir ;upload_tmp_dir = ; Maximum allowed size for uploaded files. ; http://php.net/upload-max-filesize upload_max_filesize = 100M ; Maximum number of files that can be uploaded via a single request max_file_uploads = 20 ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Fopen wrappers ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Whether to allow the treatment of URLs (like http:// or ftp://) as files. ; http://php.net/allow-url-fopen allow_url_fopen = On ; Whether to allow include/require to open URLs (like http:// or ftp://) as files. ; http://php.net/allow-url-include allow_url_include = Off ; Define the anonymous ftp password (your email address). PHP's default setting ; for this is empty. ; http://php.net/from ;from="john@doe.com" ; Define the User-Agent string. PHP's default setting for this is empty. ; http://php.net/user-agent ;user_agent="PHP" ; Default timeout for socket based streams (seconds) ; http://php.net/default-socket-timeout default_socket_timeout = 60 ; If your scripts have to deal with files from Macintosh systems, ; or you are running on a Mac and need to deal with files from ; unix or win32 systems, setting this flag will cause PHP to ; automatically detect the EOL character in those files so that ; fgets() and file() will work regardless of the source of the file. ; http://php.net/auto-detect-line-endings ;auto_detect_line_endings = Off ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Dynamic Extensions ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; If you wish to have an extension loaded automatically, use the following ; syntax: ; ; extension=modulename.extension ; ; For example, on Windows: ; ; extension=msql.dll ; ; ... or under UNIX: ; ; extension=msql.so ; ; ... or with a path: ; ; extension=/path/to/extension/msql.so ; ; If you only provide the name of the extension, PHP will look for it in its ; default extension directory. ; ; Windows Extensions ; Note that ODBC support is built in, so no dll is needed for it. ; Note that many DLL files are located in the extensions/ (PHP 4) ext/ (PHP 5) ; extension folders as well as the separate PECL DLL download (PHP 5). ; Be sure to appropriately set the extension_dir directive. ; ;extension=php_bz2.dll ;extension=php_curl.dll ;extension=php_fileinfo.dll ;extension=php_gd2.dll ;extension=php_gettext.dll ;extension=php_gmp.dll ;extension=php_intl.dll ;extension=php_imap.dll ;extension=php_interbase.dll ;extension=php_ldap.dll ;extension=php_mbstring.dll ;extension=php_exif.dll ; Must be after mbstring as it depends on it ;extension=php_mysql.dll ;extension=php_mysqli.dll ;extension=php_oci8_12c.dll ; Use with Oracle Database 12c Instant Client ;extension=php_openssl.dll ;extension=php_pdo_firebird.dll ;extension=php_pdo_mysql.dll ;extension=php_pdo_oci.dll ;extension=php_pdo_odbc.dll ;extension=php_pdo_pgsql.dll ;extension=php_pdo_sqlite.dll ;extension=php_pgsql.dll ;extension=php_shmop.dll ; The MIBS data available in the PHP distribution must be installed. ; See http://www.php.net/manual/en/snmp.installation.php ;extension=php_snmp.dll ;extension=php_soap.dll ;extension=php_sockets.dll ;extension=php_sqlite3.dll ;extension=php_sybase_ct.dll ;extension=php_tidy.dll ;extension=php_xmlrpc.dll ;extension=php_xsl.dll ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Module Settings ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; [CLI Server] ; Whether the CLI web server uses ANSI color coding in its terminal output. cli_server.color = On [Date] ; Defines the default timezone used by the date functions ; http://php.net/date.timezone date.timezone = Asia/Shanghai ; http://php.net/date.default-latitude ;date.default_latitude = 31.7667 ; http://php.net/date.default-longitude ;date.default_longitude = 35.2333 ; http://php.net/date.sunrise-zenith ;date.sunrise_zenith = 90.583333 ; http://php.net/date.sunset-zenith ;date.sunset_zenith = 90.583333 [filter] ; http://php.net/filter.default ;filter.default = unsafe_raw ; http://php.net/filter.default-flags ;filter.default_flags = [iconv] ; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global input_encoding instead. ; If empty, default_charset or input_encoding or iconv.input_encoding is used. ; The precedence is: default_charset < intput_encoding < iconv.input_encoding ;iconv.input_encoding = ; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global internal_encoding instead. ; If empty, default_charset or internal_encoding or iconv.internal_encoding is used. ; The precedence is: default_charset < internal_encoding < iconv.internal_encoding ;iconv.internal_encoding = ; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global output_encoding instead. ; If empty, default_charset or output_encoding or iconv.output_encoding is used. ; The precedence is: default_charset < output_encoding < iconv.output_encoding ; To use an output encoding conversion, iconv's output handler must be set ; otherwise output encoding conversion cannot be performed. ;iconv.output_encoding = [intl] ;intl.default_locale = ; This directive allows you to produce PHP errors when some error ; happens within intl functions. The value is the level of the error produced. ; Default is 0, which does not produce any errors. ;intl.error_level = E_WARNING ;intl.use_exceptions = 0 [sqlite3] ;sqlite3.extension_dir = [Pcre] ;PCRE library backtracking limit. ; http://php.net/pcre.backtrack-limit ;pcre.backtrack_limit=100000 ;PCRE library recursion limit. ;Please note that if you set this value to a high number you may consume all ;the available process stack and eventually crash PHP (due to reaching the ;stack size limit imposed by the Operating System). ; http://php.net/pcre.recursion-limit ;pcre.recursion_limit=100000 [Pdo] ; Whether to pool ODBC connections. Can be one of "strict", "relaxed" or "off" ; http://php.net/pdo-odbc.connection-pooling ;pdo_odbc.connection_pooling=strict ;pdo_odbc.db2_instance_name [Pdo_mysql] ; If mysqlnd is used: Number of cache slots for the internal result set cache ; http://php.net/pdo_mysql.cache_size pdo_mysql.cache_size = 2000 ; Default socket name for local MySQL connects. If empty, uses the built-in ; MySQL defaults. ; http://php.net/pdo_mysql.default-socket pdo_mysql.default_socket= [Phar] ; http://php.net/phar.readonly ;phar.readonly = On ; http://php.net/phar.require-hash ;phar.require_hash = On ;phar.cache_list = [mail function] ; For Win32 only. ; http://php.net/smtp SMTP = localhost ; http://php.net/smtp-port smtp_port = 25 ; For Win32 only. ; http://php.net/sendmail-from ;sendmail_from = me@example.com ; For Unix only. You may supply arguments as well (default: "sendmail -t -i"). ; http://php.net/sendmail-path ;sendmail_path = ; Force the addition of the specified parameters to be passed as extra parameters ; to the sendmail binary. These parameters will always replace the value of ; the 5th parameter to mail(). ;mail.force_extra_parameters = ; Add X-PHP-Originating-Script: that will include uid of the script followed by the filename mail.add_x_header = On ; The path to a log file that will log all mail() calls. Log entries include ; the full path of the script, line number, To address and headers. ;mail.log = ; Log mail to syslog (Event Log on Windows). ;mail.log = syslog [SQL] ; http://php.net/sql.safe-mode sql.safe_mode = Off [ODBC] ; http://php.net/odbc.default-db ;odbc.default_db = Not yet implemented ; http://php.net/odbc.default-user ;odbc.default_user = Not yet implemented ; http://php.net/odbc.default-pw ;odbc.default_pw = Not yet implemented ; Controls the ODBC cursor model. ; Default: SQL_CURSOR_STATIC (default). ;odbc.default_cursortype ; Allow or prevent persistent links. ; http://php.net/odbc.allow-persistent odbc.allow_persistent = On ; Check that a connection is still valid before reuse. ; http://php.net/odbc.check-persistent odbc.check_persistent = On ; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/odbc.max-persistent odbc.max_persistent = -1 ; Maximum number of links (persistent + non-persistent). -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/odbc.max-links odbc.max_links = -1 ; Handling of LONG fields. Returns number of bytes to variables. 0 means ; passthru. ; http://php.net/odbc.defaultlrl odbc.defaultlrl = 4096 ; Handling of binary data. 0 means passthru, 1 return as is, 2 convert to char. ; See the documentation on odbc_binmode and odbc_longreadlen for an explanation ; of odbc.defaultlrl and odbc.defaultbinmode ; http://php.net/odbc.defaultbinmode odbc.defaultbinmode = 1 ;birdstep.max_links = -1 [Interbase] ; Allow or prevent persistent links. ibase.allow_persistent = 1 ; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit. ibase.max_persistent = -1 ; Maximum number of links (persistent + non-persistent). -1 means no limit. ibase.max_links = -1 ; Default database name for ibase_connect(). ;ibase.default_db = ; Default username for ibase_connect(). ;ibase.default_user = ; Default password for ibase_connect(). ;ibase.default_password = ; Default charset for ibase_connect(). ;ibase.default_charset = ; Default timestamp format. ibase.timestampformat = "%Y-%m-%d %H:%M:%S" ; Default date format. ibase.dateformat = "%Y-%m-%d" ; Default time format. ibase.timeformat = "%H:%M:%S" [MySQL] ; Allow accessing, from PHP's perspective, local files with LOAD DATA statements ; http://php.net/mysql.allow_local_infile mysql.allow_local_infile = On ; Allow or prevent persistent links. ; http://php.net/mysql.allow-persistent mysql.allow_persistent = On ; If mysqlnd is used: Number of cache slots for the internal result set cache ; http://php.net/mysql.cache_size mysql.cache_size = 2000 ; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/mysql.max-persistent mysql.max_persistent = -1 ; Maximum number of links (persistent + non-persistent). -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/mysql.max-links mysql.max_links = -1 ; Default port number for mysql_connect(). If unset, mysql_connect() will use ; the $MYSQL_TCP_PORT or the mysql-tcp entry in /etc/services or the ; compile-time value defined MYSQL_PORT (in that order). Win32 will only look ; at MYSQL_PORT. ; http://php.net/mysql.default-port mysql.default_port = ; Default socket name for local MySQL connects. If empty, uses the built-in ; MySQL defaults. ; http://php.net/mysql.default-socket mysql.default_socket = ; Default host for mysql_connect() (doesn't apply in safe mode). ; http://php.net/mysql.default-host mysql.default_host = ; Default user for mysql_connect() (doesn't apply in safe mode). ; http://php.net/mysql.default-user mysql.default_user = ; Default password for mysql_connect() (doesn't apply in safe mode). ; Note that this is generally a *bad* idea to store passwords in this file. ; *Any* user with PHP access can run 'echo get_cfg_var("mysql.default_password") ; and reveal this password! And of course, any users with read access to this ; file will be able to reveal the password as well. ; http://php.net/mysql.default-password mysql.default_password = ; Maximum time (in seconds) for connect timeout. -1 means no limit ; http://php.net/mysql.connect-timeout mysql.connect_timeout = 60 ; Trace mode. When trace_mode is active (=On), warnings for table/index scans and ; SQL-Errors will be displayed. ; http://php.net/mysql.trace-mode mysql.trace_mode = Off [MySQLi] ; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/mysqli.max-persistent mysqli.max_persistent = -1 ; Allow accessing, from PHP's perspective, local files with LOAD DATA statements ; http://php.net/mysqli.allow_local_infile ;mysqli.allow_local_infile = On ; Allow or prevent persistent links. ; http://php.net/mysqli.allow-persistent mysqli.allow_persistent = On ; Maximum number of links. -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/mysqli.max-links mysqli.max_links = -1 ; If mysqlnd is used: Number of cache slots for the internal result set cache ; http://php.net/mysqli.cache_size mysqli.cache_size = 2000 ; Default port number for mysqli_connect(). If unset, mysqli_connect() will use ; the $MYSQL_TCP_PORT or the mysql-tcp entry in /etc/services or the ; compile-time value defined MYSQL_PORT (in that order). Win32 will only look ; at MYSQL_PORT. ; http://php.net/mysqli.default-port mysqli.default_port = 3306 ; Default socket name for local MySQL connects. If empty, uses the built-in ; MySQL defaults. ; http://php.net/mysqli.default-socket mysqli.default_socket = ; Default host for mysql_connect() (doesn't apply in safe mode). ; http://php.net/mysqli.default-host mysqli.default_host = ; Default user for mysql_connect() (doesn't apply in safe mode). ; http://php.net/mysqli.default-user mysqli.default_user = ; Default password for mysqli_connect() (doesn't apply in safe mode). ; Note that this is generally a *bad* idea to store passwords in this file. ; *Any* user with PHP access can run 'echo get_cfg_var("mysqli.default_pw") ; and reveal this password! And of course, any users with read access to this ; file will be able to reveal the password as well. ; http://php.net/mysqli.default-pw mysqli.default_pw = ; Allow or prevent reconnect mysqli.reconnect = Off [mysqlnd] ; Enable / Disable collection of general statistics by mysqlnd which can be ; used to tune and monitor MySQL operations. ; http://php.net/mysqlnd.collect_statistics mysqlnd.collect_statistics = On ; Enable / Disable collection of memory usage statistics by mysqlnd which can be ; used to tune and monitor MySQL operations. ; http://php.net/mysqlnd.collect_memory_statistics mysqlnd.collect_memory_statistics = Off ; Records communication from all extensions using mysqlnd to the specified log ; file. ; http://php.net/mysqlnd.debug ;mysqlnd.debug = ; Defines which queries will be logged. ; http://php.net/mysqlnd.log_mask ;mysqlnd.log_mask = 0 ; Default size of the mysqlnd memory pool, which is used by result sets. ; http://php.net/mysqlnd.mempool_default_size ;mysqlnd.mempool_default_size = 16000 ; Size of a pre-allocated buffer used when sending commands to MySQL in bytes. ; http://php.net/mysqlnd.net_cmd_buffer_size ;mysqlnd.net_cmd_buffer_size = 2048 ; Size of a pre-allocated buffer used for reading data sent by the server in ; bytes. ; http://php.net/mysqlnd.net_read_buffer_size ;mysqlnd.net_read_buffer_size = 32768 ; Timeout for network requests in seconds. ; http://php.net/mysqlnd.net_read_timeout ;mysqlnd.net_read_timeout = 31536000 ; SHA-256 Authentication Plugin related. File with the MySQL server public RSA ; key. ; http://php.net/mysqlnd.sha256_server_public_key ;mysqlnd.sha256_server_public_key = [OCI8] ; Connection: Enables privileged connections using external ; credentials (OCI_SYSOPER, OCI_SYSDBA) ; http://php.net/oci8.privileged-connect ;oci8.privileged_connect = Off ; Connection: The maximum number of persistent OCI8 connections per ; process. Using -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/oci8.max-persistent ;oci8.max_persistent = -1 ; Connection: The maximum number of seconds a process is allowed to ; maintain an idle persistent connection. Using -1 means idle ; persistent connections will be maintained forever. ; http://php.net/oci8.persistent-timeout ;oci8.persistent_timeout = -1 ; Connection: The number of seconds that must pass before issuing a ; ping during oci_pconnect() to check the connection validity. When ; set to 0, each oci_pconnect() will cause a ping. Using -1 disables ; pings completely. ; http://php.net/oci8.ping-interval ;oci8.ping_interval = 60 ; Connection: Set this to a user chosen connection class to be used ; for all pooled server requests with Oracle 11g Database Resident ; Connection Pooling (DRCP). To use DRCP, this value should be set to ; the same string for all web servers running the same application, ; the database pool must be configured, and the connection string must ; specify to use a pooled server. ;oci8.connection_class = ; High Availability: Using On lets PHP receive Fast Application ; Notification (FAN) events generated when a database node fails. The ; database must also be configured to post FAN events. ;oci8.events = Off ; Tuning: This option enables statement caching, and specifies how ; many statements to cache. Using 0 disables statement caching. ; http://php.net/oci8.statement-cache-size ;oci8.statement_cache_size = 20 ; Tuning: Enables statement prefetching and sets the default number of ; rows that will be fetched automatically after statement execution. ; http://php.net/oci8.default-prefetch ;oci8.default_prefetch = 100 ; Compatibility. Using On means oci_close() will not close ; oci_connect() and oci_new_connect() connections. ; http://php.net/oci8.old-oci-close-semantics ;oci8.old_oci_close_semantics = Off [PostgreSQL] ; Allow or prevent persistent links. ; http://php.net/pgsql.allow-persistent pgsql.allow_persistent = On ; Detect broken persistent links always with pg_pconnect(). ; Auto reset feature requires a little overheads. ; http://php.net/pgsql.auto-reset-persistent pgsql.auto_reset_persistent = Off ; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/pgsql.max-persistent pgsql.max_persistent = -1 ; Maximum number of links (persistent+non persistent). -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/pgsql.max-links pgsql.max_links = -1 ; Ignore PostgreSQL backends Notice message or not. ; Notice message logging require a little overheads. ; http://php.net/pgsql.ignore-notice pgsql.ignore_notice = 0 ; Log PostgreSQL backends Notice message or not. ; Unless pgsql.ignore_notice=0, module cannot log notice message. ; http://php.net/pgsql.log-notice pgsql.log_notice = 0 [Sybase-CT] ; Allow or prevent persistent links. ; http://php.net/sybct.allow-persistent sybct.allow_persistent = On ; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/sybct.max-persistent sybct.max_persistent = -1 ; Maximum number of links (persistent + non-persistent). -1 means no limit. ; http://php.net/sybct.max-links sybct.max_links = -1 ; Minimum server message severity to display. ; http://php.net/sybct.min-server-severity sybct.min_server_severity = 10 ; Minimum client message severity to display. ; http://php.net/sybct.min-client-severity sybct.min_client_severity = 10 ; Set per-context timeout ; http://php.net/sybct.timeout ;sybct.timeout= ;sybct.packet_size ; The maximum time in seconds to wait for a connection attempt to succeed before returning failure. ; Default: one minute ;sybct.login_timeout= ; The name of the host you claim to be connecting from, for display by sp_who. ; Default: none ;sybct.hostname= ; Allows you to define how often deadlocks are to be retried. -1 means "forever". ; Default: 0 ;sybct.deadlock_retry_count= [bcmath] ; Number of decimal digits for all bcmath functions. ; http://php.net/bcmath.scale bcmath.scale = 0 [browscap] ; http://php.net/browscap ;browscap = extra/browscap.ini [Session] ; Handler used to store/retrieve data. ; http://php.net/session.save-handler session.save_handler = files ; Argument passed to save_handler. In the case of files, this is the path ; where data files are stored. Note: Windows users have to change this ; variable in order to use PHP's session functions. ; ; The path can be defined as: ; ; session.save_path = "N;/path" ; ; where N is an integer. Instead of storing all the session files in ; /path, what this will do is use subdirectories N-levels deep, and ; store the session data in those directories. This is useful if ; your OS has problems with many files in one directory, and is ; a more efficient layout for servers that handle many sessions. ; ; NOTE 1: PHP will not create this directory structure automatically. ; You can use the script in the ext/session dir for that purpose. ; NOTE 2: See the section on garbage collection below if you choose to ; use subdirectories for session storage ; ; The file storage module creates files using mode 600 by default. ; You can change that by using ; ; session.save_path = "N;MODE;/path" ; ; where MODE is the octal representation of the mode. Note that this ; does not overwrite the process's umask. ; http://php.net/session.save-path ;session.save_path = "/tmp" ; Whether to use strict session mode. ; Strict session mode does not accept uninitialized session ID and regenerate ; session ID if browser sends uninitialized session ID. Strict mode protects ; applications from session fixation via session adoption vulnerability. It is ; disabled by default for maximum compatibility, but enabling it is encouraged. ; https://wiki.php.net/rfc/strict_sessions session.use_strict_mode = 0 ; Whether to use cookies. ; http://php.net/session.use-cookies session.use_cookies = 1 ; http://php.net/session.cookie-secure ;session.cookie_secure = ; This option forces PHP to fetch and use a cookie for storing and maintaining ; the session id. We encourage this operation as it's very helpful in combating ; session hijacking when not specifying and managing your own session id. It is ; not the be-all and end-all of session hijacking defense, but it's a good start. ; http://php.net/session.use-only-cookies session.use_only_cookies = 1 ; Name of the session (used as cookie name). ; http://php.net/session.name session.name = PHPSESSID ; Initialize session on request startup. ; http://php.net/session.auto-start session.auto_start = 0 ; Lifetime in seconds of cookie or, if 0, until browser is restarted. ; http://php.net/session.cookie-lifetime session.cookie_lifetime = 0 ; The path for which the cookie is valid. ; http://php.net/session.cookie-path session.cookie_path = / ; The domain for which the cookie is valid. ; http://php.net/session.cookie-domain session.cookie_domain = ; Whether or not to add the httpOnly flag to the cookie, which makes it inaccessible to browser scripting languages such as JavaScript. ; http://php.net/session.cookie-httponly session.cookie_httponly = ; Handler used to serialize data. php is the standard serializer of PHP. ; http://php.net/session.serialize-handler session.serialize_handler = php ; Defines the probability that the 'garbage collection' process is started ; on every session initialization. The probability is calculated by using ; gc_probability/gc_divisor. Where session.gc_probability is the numerator ; and gc_divisor is the denominator in the equation. Setting this value to 1 ; when the session.gc_divisor value is 100 will give you approximately a 1% chance ; the gc will run on any give request. ; Default Value: 1 ; Development Value: 1 ; Production Value: 1 ; http://php.net/session.gc-probability session.gc_probability = 1 ; Defines the probability that the 'garbage collection' process is started on every ; session initialization. The probability is calculated by using the following equation: ; gc_probability/gc_divisor. Where session.gc_probability is the numerator and ; session.gc_divisor is the denominator in the equation. Setting this value to 1 ; when the session.gc_divisor value is 100 will give you approximately a 1% chance ; the gc will run on any give request. Increasing this value to 1000 will give you ; a 0.1% chance the gc will run on any give request. For high volume production servers, ; this is a more efficient approach. ; Default Value: 100 ; Development Value: 1000 ; Production Value: 1000 ; http://php.net/session.gc-divisor session.gc_divisor = 1000 ; After this number of seconds, stored data will be seen as 'garbage' and ; cleaned up by the garbage collection process. ; http://php.net/session.gc-maxlifetime session.gc_maxlifetime = 1440 ; NOTE: If you are using the subdirectory option for storing session files ; (see session.save_path above), then garbage collection does *not* ; happen automatically. You will need to do your own garbage ; collection through a shell script, cron entry, or some other method. ; For example, the following script would is the equivalent of ; setting session.gc_maxlifetime to 1440 (1440 seconds = 24 minutes): ; find /path/to/sessions -cmin +24 -type f | xargs rm ; Check HTTP Referer to invalidate externally stored URLs containing ids. ; HTTP_REFERER has to contain this substring for the session to be ; considered as valid. ; http://php.net/session.referer-check session.referer_check = ; How many bytes to read from the file. ; http://php.net/session.entropy-length ;session.entropy_length = 32 ; Specified here to create the session id. ; http://php.net/session.entropy-file ; Defaults to /dev/urandom ; On systems that don't have /dev/urandom but do have /dev/arandom, this will default to /dev/arandom ; If neither are found at compile time, the default is no entropy file. ; On windows, setting the entropy_length setting will activate the ; Windows random source (using the CryptoAPI) ;session.entropy_file = /dev/urandom ; Set to {nocache,private,public,} to determine HTTP caching aspects ; or leave this empty to avoid sending anti-caching headers. ; http://php.net/session.cache-limiter session.cache_limiter = nocache ; Document expires after n minutes. ; http://php.net/session.cache-expire session.cache_expire = 180 ; trans sid support is disabled by default. ; Use of trans sid may risk your users' security. ; Use this option with caution. ; - User may send URL contains active session ID ; to other person via. email/irc/etc. ; - URL that contains active session ID may be stored ; in publicly accessible computer. ; - User may access your site with the same session ID ; always using URL stored in browser's history or bookmarks. ; http://php.net/session.use-trans-sid session.use_trans_sid = 0 ; Select a hash function for use in generating session ids. ; Possible Values ; 0 (MD5 128 bits) ; 1 (SHA-1 160 bits) ; This option may also be set to the name of any hash function supported by ; the hash extension. A list of available hashes is returned by the hash_algos() ; function. ; http://php.net/session.hash-function session.hash_function = 0 ; Define how many bits are stored in each character when converting ; the binary hash data to something readable. ; Possible values: ; 4 (4 bits: 0-9, a-f) ; 5 (5 bits: 0-9, a-v) ; 6 (6 bits: 0-9, a-z, A-Z, "-", ",") ; Default Value: 4 ; Development Value: 5 ; Production Value: 5 ; http://php.net/session.hash-bits-per-character session.hash_bits_per_character = 5 ; The URL rewriter will look for URLs in a defined set of HTML tags. ; form/fieldset are special; if you include them here, the rewriter will ; add a hidden <input> field with the info which is otherwise appended ; to URLs. If you want XHTML conformity, remove the form entry. ; Note that all valid entries require a "=", even if no value follows. ; Default Value: "a=href,area=href,frame=src,form=,fieldset=" ; Development Value: "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry" ; Production Value: "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry" ; http://php.net/url-rewriter.tags url_rewriter.tags = "a=href,area=href,frame=src,input=src,form=fakeentry" ; Enable upload progress tracking in $_SESSION ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: On ; http://php.net/session.upload-progress.enabled ;session.upload_progress.enabled = On ; Cleanup the progress information as soon as all POST data has been read ; (i.e. upload completed). ; Default Value: On ; Development Value: On ; Production Value: On ; http://php.net/session.upload-progress.cleanup ;session.upload_progress.cleanup = On ; A prefix used for the upload progress key in $_SESSION ; Default Value: "upload_progress_" ; Development Value: "upload_progress_" ; Production Value: "upload_progress_" ; http://php.net/session.upload-progress.prefix ;session.upload_progress.prefix = "upload_progress_" ; The index name (concatenated with the prefix) in $_SESSION ; containing the upload progress information ; Default Value: "PHP_SESSION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS" ; Development Value: "PHP_SESSION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS" ; Production Value: "PHP_SESSION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS" ; http://php.net/session.upload-progress.name ;session.upload_progress.name = "PHP_SESSION_UPLOAD_PROGRESS" ; How frequently the upload progress should be updated. ; Given either in percentages (per-file), or in bytes ; Default Value: "1%" ; Development Value: "1%" ; Production Value: "1%" ; http://php.net/session.upload-progress.freq ;session.upload_progress.freq = "1%" ; The minimum delay between updates, in seconds ; Default Value: 1 ; Development Value: 1 ; Production Value: 1 ; http://php.net/session.upload-progress.min-freq ;session.upload_progress.min_freq = "1" [MSSQL] ; Allow or prevent persistent links. mssql.allow_persistent = On ; Maximum number of persistent links. -1 means no limit. mssql.max_persistent = -1 ; Maximum number of links (persistent+non persistent). -1 means no limit. mssql.max_links = -1 ; Minimum error severity to display. mssql.min_error_severity = 10 ; Minimum message severity to display. mssql.min_message_severity = 10 ; Compatibility mode with old versions of PHP 3.0. mssql.compatibility_mode = Off ; Connect timeout ;mssql.connect_timeout = 5 ; Query timeout ;mssql.timeout = 60 ; Valid range 0 - 2147483647. Default = 4096. ;mssql.textlimit = 4096 ; Valid range 0 - 2147483647. Default = 4096. ;mssql.textsize = 4096 ; Limits the number of records in each batch. 0 = all records in one batch. ;mssql.batchsize = 0 ; Specify how datetime and datetim4 columns are returned ; On => Returns data converted to SQL server settings ; Off => Returns values as YYYY-MM-DD hh:mm:ss ;mssql.datetimeconvert = On ; Use NT authentication when connecting to the server mssql.secure_connection = Off ; Specify max number of processes. -1 = library default ; msdlib defaults to 25 ; FreeTDS defaults to 4096 ;mssql.max_procs = -1 ; Specify client character set. ; If empty or not set the client charset from freetds.conf is used ; This is only used when compiled with FreeTDS ;mssql.charset = "ISO-8859-1" [Assertion] ; Assert(expr); active by default. ; http://php.net/assert.active ;assert.active = On ; Issue a PHP warning for each failed assertion. ; http://php.net/assert.warning ;assert.warning = On ; Don't bail out by default. ; http://php.net/assert.bail ;assert.bail = Off ; User-function to be called if an assertion fails. ; http://php.net/assert.callback ;assert.callback = 0 ; Eval the expression with current error_reporting(). Set to true if you want ; error_reporting(0) around the eval(). ; http://php.net/assert.quiet-eval ;assert.quiet_eval = 0 [COM] ; path to a file containing GUIDs, IIDs or filenames of files with TypeLibs ; http://php.net/com.typelib-file ;com.typelib_file = ; allow Distributed-COM calls ; http://php.net/com.allow-dcom ;com.allow_dcom = true ; autoregister constants of a components typlib on com_load() ; http://php.net/com.autoregister-typelib ;com.autoregister_typelib = true ; register constants casesensitive ; http://php.net/com.autoregister-casesensitive ;com.autoregister_casesensitive = false ; show warnings on duplicate constant registrations ; http://php.net/com.autoregister-verbose ;com.autoregister_verbose = true ; The default character set code-page to use when passing strings to and from COM objects. ; Default: system ANSI code page ;com.code_page= [mbstring] ; language for internal character representation. ; This affects mb_send_mail() and mbstrig.detect_order. ; http://php.net/mbstring.language ;mbstring.language = Japanese ; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global internal_encoding instead. ; internal/script encoding. ; Some encoding cannot work as internal encoding. (e.g. SJIS, BIG5, ISO-2022-*) ; If empty, default_charset or internal_encoding or iconv.internal_encoding is used. ; The precedence is: default_charset < internal_encoding < iconv.internal_encoding ;mbstring.internal_encoding = ; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global input_encoding instead. ; http input encoding. ; mbstring.encoding_traslation = On is needed to use this setting. ; If empty, default_charset or input_encoding or mbstring.input is used. ; The precedence is: default_charset < intput_encoding < mbsting.http_input ; http://php.net/mbstring.http-input ;mbstring.http_input = ; Use of this INI entry is deprecated, use global output_encoding instead. ; http output encoding. ; mb_output_handler must be registered as output buffer to function. ; If empty, default_charset or output_encoding or mbstring.http_output is used. ; The precedence is: default_charset < output_encoding < mbstring.http_output ; To use an output encoding conversion, mbstring's output handler must be set ; otherwise output encoding conversion cannot be performed. ; http://php.net/mbstring.http-output ;mbstring.http_output = ; enable automatic encoding translation according to ; mbstring.internal_encoding setting. Input chars are ; converted to internal encoding by setting this to On. ; Note: Do _not_ use automatic encoding translation for ; portable libs/applications. ; http://php.net/mbstring.encoding-translation ;mbstring.encoding_translation = Off ; automatic encoding detection order. ; "auto" detect order is changed according to mbstring.language ; http://php.net/mbstring.detect-order ;mbstring.detect_order = auto ; substitute_character used when character cannot be converted ; one from another ; http://php.net/mbstring.substitute-character ;mbstring.substitute_character = none ; overload(replace) single byte functions by mbstring functions. ; mail(), ereg(), etc are overloaded by mb_send_mail(), mb_ereg(), ; etc. Possible values are 0,1,2,4 or combination of them. ; For example, 7 for overload everything. ; 0: No overload ; 1: Overload mail() function ; 2: Overload str*() functions ; 4: Overload ereg*() functions ; http://php.net/mbstring.func-overload ;mbstring.func_overload = 0 ; enable strict encoding detection. ; Default: Off ;mbstring.strict_detection = On ; This directive specifies the regex pattern of content types for which mb_output_handler() ; is activated. ; Default: mbstring.http_output_conv_mimetype=^(text/|application/xhtml\+xml) ;mbstring.http_output_conv_mimetype= [gd] ; Tell the jpeg decode to ignore warnings and try to create ; a gd image. The warning will then be displayed as notices ; disabled by default ; http://php.net/gd.jpeg-ignore-warning ;gd.jpeg_ignore_warning = 0 [exif] ; Exif UNICODE user comments are handled as UCS-2BE/UCS-2LE and JIS as JIS. ; With mbstring support this will automatically be converted into the encoding ; given by corresponding encode setting. When empty mbstring.internal_encoding ; is used. For the decode settings you can distinguish between motorola and ; intel byte order. A decode setting cannot be empty. ; http://php.net/exif.encode-unicode ;exif.encode_unicode = ISO-8859-15 ; http://php.net/exif.decode-unicode-motorola ;exif.decode_unicode_motorola = UCS-2BE ; http://php.net/exif.decode-unicode-intel ;exif.decode_unicode_intel = UCS-2LE ; http://php.net/exif.encode-jis ;exif.encode_jis = ; http://php.net/exif.decode-jis-motorola ;exif.decode_jis_motorola = JIS ; http://php.net/exif.decode-jis-intel ;exif.decode_jis_intel = JIS [Tidy] ; The path to a default tidy configuration file to use when using tidy ; http://php.net/tidy.default-config ;tidy.default_config = /usr/local/lib/php/default.tcfg ; Should tidy clean and repair output automatically? ; WARNING: Do not use this option if you are generating non-html content ; such as dynamic images ; http://php.net/tidy.clean-output tidy.clean_output = Off [soap] ; Enables or disables WSDL caching feature. ; http://php.net/soap.wsdl-cache-enabled soap.wsdl_cache_enabled=1 ; Sets the directory name where SOAP extension will put cache files. ; http://php.net/soap.wsdl-cache-dir soap.wsdl_cache_dir="/tmp" ; (time to live) Sets the number of second while cached file will be used ; instead of original one. ; http://php.net/soap.wsdl-cache-ttl soap.wsdl_cache_ttl=86400 ; Sets the size of the cache limit. (Max. number of WSDL files to cache) soap.wsdl_cache_limit = 5 [sysvshm] ; A default size of the shared memory segment ;sysvshm.init_mem = 10000 [ldap] ; Sets the maximum number of open links or -1 for unlimited. ldap.max_links = -1 [mcrypt] ; For more information about mcrypt settings see http://php.net/mcrypt-module-open ; Directory where to load mcrypt algorithms ; Default: Compiled in into libmcrypt (usually /usr/local/lib/libmcrypt) ;mcrypt.algorithms_dir= ; Directory where to load mcrypt modes ; Default: Compiled in into libmcrypt (usually /usr/local/lib/libmcrypt) ;mcrypt.modes_dir= [dba] ;dba.default_handler= [opcache] ; Determines if Zend OPCache is enabled opcache.enable=1 ; Determines if Zend OPCache is enabled for the CLI version of PHP opcache.enable_cli=0 ; The OPcache shared memory storage size. opcache.memory_consumption=128 ; The amount of memory for interned strings in Mbytes. opcache.interned_strings_buffer=8 ; The maximum number of keys (scripts) in the OPcache hash table. ; Only numbers between 200 and 100000 are allowed. opcache.max_accelerated_files=20000 ; The maximum percentage of "wasted" memory until a restart is scheduled. ;opcache.max_wasted_percentage=5 ; When this directive is enabled, the OPcache appends the current working ; directory to the script key, thus eliminating possible collisions between ; files with the same name (basename). Disabling the directive improves ; performance, but may break existing applications. opcache.use_cwd=1 ; When disabled, you must reset the OPcache manually or restart the ; webserver for changes to the filesystem to take effect. opcache.validate_timestamps=1 ; How often (in seconds) to check file timestamps for changes to the shared ; memory storage allocation. ("1" means validate once per second, but only ; once per request. "0" means always validate) opcache.revalidate_freq=0 ; Enables or disables file search in include_path optimization ;opcache.revalidate_path=0 ; If disabled, all PHPDoc comments are dropped from the code to reduce the ; size of the optimized code. ;opcache.save_comments=1 ; If disabled, PHPDoc comments are not loaded from SHM, so "Doc Comments" ; may be always stored (save_comments=1), but not loaded by applications ; that don't need them anyway. ;opcache.load_comments=1 ; If enabled, a fast shutdown sequence is used for the accelerated code ;opcache.fast_shutdown=0 ; Allow file existence override (file_exists, etc.) performance feature. ;opcache.enable_file_override=0 ; A bitmask, where each bit enables or disables the appropriate OPcache ; passes ;opcache.optimization_level=0xffffffff ;opcache.inherited_hack=1 ;opcache.dups_fix=0 ; The location of the OPcache blacklist file (wildcards allowed). ; Each OPcache blacklist file is a text file that holds the names of files ; that should not be accelerated. The file format is to add each filename ; to a new line. The filename may be a full path or just a file prefix ; (i.e., /var/www/x blacklists all the files and directories in /var/www ; that start with 'x'). Line starting with a ; are ignored (comments). ;opcache.blacklist_filename= ; Allows exclusion of large files from being cached. By default all files ; are cached. ;opcache.max_file_size=0 ; Check the cache checksum each N requests. ; The default value of "0" means that the checks are disabled. ;opcache.consistency_checks=0 ; How long to wait (in seconds) for a scheduled restart to begin if the cache ; is not being accessed. ;opcache.force_restart_timeout=180 ; OPcache error_log file name. Empty string assumes "stderr". ;opcache.error_log= ; All OPcache errors go to the Web server log. ; By default, only fatal errors (level 0) or errors (level 1) are logged. ; You can also enable warnings (level 2), info messages (level 3) or ; debug messages (level 4). ;opcache.log_verbosity_level=1 ; Preferred Shared Memory back-end. Leave empty and let the system decide. ;opcache.preferred_memory_model= ; Protect the shared memory from unexpected writing during script execution. ; Useful for internal debugging only. ;opcache.protect_memory=0 ; Validate cached file permissions. ; opcache.validate_permission=0 ; Prevent name collisions in chroot'ed environment. ; opcache.validate_root=0 [curl] ; A default value for the CURLOPT_CAINFO option. This is required to be an ; absolute path. ;curl.cainfo = [openssl] ; The location of a Certificate Authority (CA) file on the local filesystem ; to use when verifying the identity of SSL/TLS peers. Most users should ; not specify a value for this directive as PHP will attempt to use the ; OS-managed cert stores in its absence. If specified, this value may still ; be overridden on a per-stream basis via the "cafile" SSL stream context ; option. ;openssl.cafile= ; If openssl.cafile is not specified or if the CA file is not found, the ; directory pointed to by openssl.capath is searched for a suitable ; certificate. This value must be a correctly hashed certificate directory. ; Most users should not specify a value for this directive as PHP will ; attempt to use the OS-managed cert stores in its absence. If specified, ; this value may still be overridden on a per-stream basis via the "capath" ; SSL stream context option. ;openssl.capath= ; Local Variables: ; tab-width: 4 ; End:

;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; FPM Configuration ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; All relative paths in this configuration file are relative to PHP's install ; prefix (/usr/local/php). This prefix can be dynamically changed by using the ; '-p' argument from the command line. ; Include one or more files. If glob(3) exists, it is used to include a bunch of ; files from a glob(3) pattern. This directive can be used everywhere in the ; file. ; Relative path can also be used. They will be prefixed by: ; - the global prefix if it's been set (-p argument) ; - /usr/local/php otherwise ;include=etc/fpm.d/*.conf ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Global Options ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; [global] ; Pid file ; Note: the default prefix is /usr/local/php/var ; Default Value: none pid = /var/run/php-fpm.pid ; Error log file ; If it's set to "syslog", log is sent to syslogd instead of being written ; in a local file. ; Note: the default prefix is /usr/local/php/var ; Default Value: log/php-fpm.log error_log = /usr/local/php/log/php-fpm.log ; syslog_facility is used to specify what type of program is logging the ; message. This lets syslogd specify that messages from different facilities ; will be handled differently. ; See syslog(3) for possible values (ex daemon equiv LOG_DAEMON) ; Default Value: daemon ;syslog.facility = daemon ; syslog_ident is prepended to every message. If you have multiple FPM ; instances running on the same server, you can change the default value ; which must suit common needs. ; Default Value: php-fpm ;syslog.ident = php-fpm ; Log level ; Possible Values: alert, error, warning, notice, debug ; Default Value: notice log_level = warning ; If this number of child processes exit with SIGSEGV or SIGBUS within the time ; interval set by emergency_restart_interval then FPM will restart. A value ; of '0' means 'Off'. ; Default Value: 0 ;emergency_restart_threshold = 0 ; Interval of time used by emergency_restart_interval to determine when ; a graceful restart will be initiated. This can be useful to work around ; accidental corruptions in an accelerator's shared memory. ; Available Units: s(econds), m(inutes), h(ours), or d(ays) ; Default Unit: seconds ; Default Value: 0 emergency_restart_interval = 24h ; Time limit for child processes to wait for a reaction on signals from master. ; Available units: s(econds), m(inutes), h(ours), or d(ays) ; Default Unit: seconds ; Default Value: 0 process_control_timeout = 5s ; The maximum number of processes FPM will fork. This has been design to control ; the global number of processes when using dynamic PM within a lot of pools. ; Use it with caution. ; Note: A value of 0 indicates no limit ; Default Value: 0 ; process.max = 128 ; Specify the nice(2) priority to apply to the master process (only if set) ; The value can vary from -19 (highest priority) to 20 (lower priority) ; Note: - It will only work if the FPM master process is launched as root ; - The pool process will inherit the master process priority ; unless it specified otherwise ; Default Value: no set ; process.priority = -19 ; Send FPM to background. Set to 'no' to keep FPM in foreground for debugging. ; Default Value: yes daemonize = no ; Set open file descriptor rlimit for the master process. ; Default Value: system defined value rlimit_files = 10240 ; Set max core size rlimit for the master process. ; Possible Values: 'unlimited' or an integer greater or equal to 0 ; Default Value: system defined value ;rlimit_core = 0 ; Specify the event mechanism FPM will use. The following is available: ; - select (any POSIX os) ; - poll (any POSIX os) ; - epoll (linux >= 2.5.44) ; - kqueue (FreeBSD >= 4.1, OpenBSD >= 2.9, NetBSD >= 2.0) ; - /dev/poll (Solaris >= 7) ; - port (Solaris >= 10) ; Default Value: not set (auto detection) ;events.mechanism = epoll ; When FPM is build with systemd integration, specify the interval, ; in second, between health report notification to systemd. ; Set to 0 to disable. ; Available Units: s(econds), m(inutes), h(ours) ; Default Unit: seconds ; Default value: 10 ;systemd_interval = 10 ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Pool Definitions ; ;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;;; ; Multiple pools of child processes may be started with different listening ; ports and different management options. The name of the pool will be ; used in logs and stats. There is no limitation on the number of pools which ; FPM can handle. Your system will tell you anyway :) ; Start a new pool named 'www'. ; the variable $pool can we used in any directive and will be replaced by the ; pool name ('www' here) [www] ; Per pool prefix ; It only applies on the following directives: ; - 'access.log' ; - 'slowlog' ; - 'listen' (unixsocket) ; - 'chroot' ; - 'chdir' ; - 'php_values' ; - 'php_admin_values' ; When not set, the global prefix (or /usr/local/php) applies instead. ; Note: This directive can also be relative to the global prefix. ; Default Value: none ;prefix = /path/to/pools/$pool ; Unix user/group of processes ; Note: The user is mandatory. If the group is not set, the default user's group ; will be used. user = nobody group = nobody ; The address on which to accept FastCGI requests. ; Valid syntaxes are: ; 'ip.add.re.ss:port' - to listen on a TCP socket to a specific IPv4 address on ; a specific port; ; '[ip:6:addr:ess]:port' - to listen on a TCP socket to a specific IPv6 address on ; a specific port; ; 'port' - to listen on a TCP socket to all IPv4 addresses on a ; specific port; ; '[::]:port' - to listen on a TCP socket to all addresses ; (IPv6 and IPv4-mapped) on a specific port; ; '/path/to/unix/socket' - to listen on a unix socket. ; Note: This value is mandatory. ;listen = 127.0.0.1:9000 listen = 0.0.0.0:9000 ; Set listen(2) backlog. ; Default Value: 65535 (-1 on FreeBSD and OpenBSD) ;listen.backlog = 65535 ; Set permissions for unix socket, if one is used. In Linux, read/write ; permissions must be set in order to allow connections from a web server. Many ; BSD-derived systems allow connections regardless of permissions. ; Default Values: user and group are set as the running user ; mode is set to 0660 listen.owner = nobody listen.group = nobody ;listen.mode = 0660 ; When POSIX Access Control Lists are supported you can set them using ; these options, value is a comma separated list of user/group names. ; When set, listen.owner and listen.group are ignored ;listen.acl_users = ;listen.acl_groups = ; List of addresses (IPv4/IPv6) of FastCGI clients which are allowed to connect. ; Equivalent to the FCGI_WEB_SERVER_ADDRS environment variable in the original ; PHP FCGI (5.2.2+). Makes sense only with a tcp listening socket. Each address ; must be separated by a comma. If this value is left blank, connections will be ; accepted from any ip address. ; Default Value: any ; listen.allowed_clients = 127.0.0.1 ; Specify the nice(2) priority to apply to the pool processes (only if set) ; The value can vary from -19 (highest priority) to 20 (lower priority) ; Note: - It will only work if the FPM master process is launched as root ; - The pool processes will inherit the master process priority ; unless it specified otherwise ; Default Value: no set ; process.priority = -19 ; Set the process dumpable flag (PR_SET_DUMPABLE prctl) even if the process user ; or group is differrent than the master process user. It allows to create process ; core dump and ptrace the process for the pool user. ; Default Value: no ; process.dumpable = yes ; Choose how the process manager will control the number of child processes. ; Possible Values: ; static - a fixed number (pm.max_children) of child processes; ; dynamic - the number of child processes are set dynamically based on the ; following directives. With this process management, there will be ; always at least 1 children. ; pm.max_children - the maximum number of children that can ; be alive at the same time. ; pm.start_servers - the number of children created on startup. ; pm.min_spare_servers - the minimum number of children in 'idle' ; state (waiting to process). If the number ; of 'idle' processes is less than this ; number then some children will be created. ; pm.max_spare_servers - the maximum number of children in 'idle' ; state (waiting to process). If the number ; of 'idle' processes is greater than this ; number then some children will be killed. ; ondemand - no children are created at startup. Children will be forked when ; new requests will connect. The following parameter are used: ; pm.max_children - the maximum number of children that ; can be alive at the same time. ; pm.process_idle_timeout - The number of seconds after which ; an idle process will be killed. ; Note: This value is mandatory. pm = dynamic ; The number of child processes to be created when pm is set to 'static' and the ; maximum number of child processes when pm is set to 'dynamic' or 'ondemand'. ; This value sets the limit on the number of simultaneous requests that will be ; served. Equivalent to the ApacheMaxClients directive with mpm_prefork. ; Equivalent to the PHP_FCGI_CHILDREN environment variable in the original PHP ; CGI. The below defaults are based on a server without much resources. Don't ; forget to tweak pm.* to fit your needs. ; Note: Used when pm is set to 'static', 'dynamic' or 'ondemand' ; Note: This value is mandatory. pm.max_children = 200 ; The number of child processes created on startup. ; Note: Used only when pm is set to 'dynamic' ; Default Value: min_spare_servers + (max_spare_servers - min_spare_servers) / 2 pm.start_servers = 50 ; The desired minimum number of idle server processes. ; Note: Used only when pm is set to 'dynamic' ; Note: Mandatory when pm is set to 'dynamic' pm.min_spare_servers = 50 ; The desired maximum number of idle server processes. ; Note: Used only when pm is set to 'dynamic' ; Note: Mandatory when pm is set to 'dynamic' pm.max_spare_servers = 100 ; The number of seconds after which an idle process will be killed. ; Note: Used only when pm is set to 'ondemand' ; Default Value: 10s ;pm.process_idle_timeout = 10s; ; The number of requests each child process should execute before respawning. ; This can be useful to work around memory leaks in 3rd party libraries. For ; endless request processing specify '0'. Equivalent to PHP_FCGI_MAX_REQUESTS. ; Default Value: 0 pm.max_requests = 51200 ; The URI to view the FPM status page. If this value is not set, no URI will be ; recognized as a status page. It shows the following informations: ; pool - the name of the pool; ; process manager - static, dynamic or ondemand; ; start time - the date and time FPM has started; ; start since - number of seconds since FPM has started; ; accepted conn - the number of request accepted by the pool; ; listen queue - the number of request in the queue of pending ; connections (see backlog in listen(2)); ; max listen queue - the maximum number of requests in the queue ; of pending connections since FPM has started; ; listen queue len - the size of the socket queue of pending connections; ; idle processes - the number of idle processes; ; active processes - the number of active processes; ; total processes - the number of idle + active processes; ; max active processes - the maximum number of active processes since FPM ; has started; ; max children reached - number of times, the process limit has been reached, ; when pm tries to start more children (works only for ; pm 'dynamic' and 'ondemand'); ; Value are updated in real time. ; Example output: ; pool: www ; process manager: static ; start time: 01/Jul/2011:17:53:49 +0200 ; start since: 62636 ; accepted conn: 190460 ; listen queue: 0 ; max listen queue: 1 ; listen queue len: 42 ; idle processes: 4 ; active processes: 11 ; total processes: 15 ; max active processes: 12 ; max children reached: 0 ; ; By default the status page output is formatted as text/plain. Passing either ; 'html', 'xml' or 'json' in the query string will return the corresponding ; output syntax. Example: ; http://www.foo.bar/status ; http://www.foo.bar/status?json ; http://www.foo.bar/status?html ; http://www.foo.bar/status?xml ; ; By default the status page only outputs short status. Passing 'full' in the ; query string will also return status for each pool process. ; Example: ; http://www.foo.bar/status?full ; http://www.foo.bar/status?json&full ; http://www.foo.bar/status?html&full ; http://www.foo.bar/status?xml&full ; The Full status returns for each process: ; pid - the PID of the process; ; state - the state of the process (Idle, Running, ...); ; start time - the date and time the process has started; ; start since - the number of seconds since the process has started; ; requests - the number of requests the process has served; ; request duration - the duration in µs of the requests; ; request method - the request method (GET, POST, ...); ; request URI - the request URI with the query string; ; content length - the content length of the request (only with POST); ; user - the user (PHP_AUTH_USER) (or '-' if not set); ; script - the main script called (or '-' if not set); ; last request cpu - the %cpu the last request consumed ; it's always 0 if the process is not in Idle state ; because CPU calculation is done when the request ; processing has terminated; ; last request memory - the max amount of memory the last request consumed ; it's always 0 if the process is not in Idle state ; because memory calculation is done when the request ; processing has terminated; ; If the process is in Idle state, then informations are related to the ; last request the process has served. Otherwise informations are related to ; the current request being served. ; Example output: ; ************************ ; pid: 31330 ; state: Running ; start time: 01/Jul/2011:17:53:49 +0200 ; start since: 63087 ; requests: 12808 ; request duration: 1250261 ; request method: GET ; request URI: /test_mem.php?N=10000 ; content length: 0 ; user: - ; script: /home/fat/web/docs/php/test_mem.php ; last request cpu: 0.00 ; last request memory: 0 ; ; Note: There is a real-time FPM status monitoring sample web page available ; It's available in: /usr/local/php/share/php/fpm/status.html ; ; Note: The value must start with a leading slash (/). The value can be ; anything, but it may not be a good idea to use the .php extension or it ; may conflict with a real PHP file. ; Default Value: not set pm.status_path = /status ; The ping URI to call the monitoring page of FPM. If this value is not set, no ; URI will be recognized as a ping page. This could be used to test from outside ; that FPM is alive and responding, or to ; - create a graph of FPM availability (rrd or such); ; - remove a server from a group if it is not responding (load balancing); ; - trigger alerts for the operating team (24/7). ; Note: The value must start with a leading slash (/). The value can be ; anything, but it may not be a good idea to use the .php extension or it ; may conflict with a real PHP file. ; Default Value: not set ;ping.path = /ping ; This directive may be used to customize the response of a ping request. The ; response is formatted as text/plain with a 200 response code. ; Default Value: pong ;ping.response = pong ; The access log file ; Default: not set ;access.log = log/$pool.access.log ; The access log format. ; The following syntax is allowed ; %%: the '%' character ; %C: %CPU used by the request ; it can accept the following format: ; - %{user}C for user CPU only ; - %{system}C for system CPU only ; - %{total}C for user + system CPU (default) ; %d: time taken to serve the request ; it can accept the following format: ; - %{seconds}d (default) ; - %{miliseconds}d ; - %{mili}d ; - %{microseconds}d ; - %{micro}d ; %e: an environment variable (same as $_ENV or $_SERVER) ; it must be associated with embraces to specify the name of the env ; variable. Some exemples: ; - server specifics like: %{REQUEST_METHOD}e or %{SERVER_PROTOCOL}e ; - HTTP headers like: %{HTTP_HOST}e or %{HTTP_USER_AGENT}e ; %f: script filename ; %l: content-length of the request (for POST request only) ; %m: request method ; %M: peak of memory allocated by PHP ; it can accept the following format: ; - %{bytes}M (default) ; - %{kilobytes}M ; - %{kilo}M ; - %{megabytes}M ; - %{mega}M ; %n: pool name ; %o: output header ; it must be associated with embraces to specify the name of the header: ; - %{Content-Type}o ; - %{X-Powered-By}o ; - %{Transfert-Encoding}o ; - .... ; %p: PID of the child that serviced the request ; %P: PID of the parent of the child that serviced the request ; %q: the query string ; %Q: the '?' character if query string exists ; %r: the request URI (without the query string, see %q and %Q) ; %R: remote IP address ; %s: status (response code) ; %t: server time the request was received ; it can accept a strftime(3) format: ; %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S %z (default) ; %T: time the log has been written (the request has finished) ; it can accept a strftime(3) format: ; %d/%b/%Y:%H:%M:%S %z (default) ; %u: remote user ; ; Default: "%R - %u %t \"%m %r\" %s" ;access.format = "%R - %u %t \"%m %r%Q%q\" %s %f %{mili}d %{kilo}M %C%%" ; The log file for slow requests ; Default Value: not set ; Note: slowlog is mandatory if request_slowlog_timeout is set slowlog = log/$pool.log.slow ; The timeout for serving a single request after which a PHP backtrace will be ; dumped to the 'slowlog' file. A value of '0s' means 'off'. ; Available units: s(econds)(default), m(inutes), h(ours), or d(ays) ; Default Value: 0 request_slowlog_timeout = 10 ; The timeout for serving a single request after which the worker process will ; be killed. This option should be used when the 'max_execution_time' ini option ; does not stop script execution for some reason. A value of '0' means 'off'. ; Available units: s(econds)(default), m(inutes), h(ours), or d(ays) ; Default Value: 0 request_terminate_timeout = 600 ; Set open file descriptor rlimit. ; Default Value: system defined value rlimit_files = 10240 ; Set max core size rlimit. ; Possible Values: 'unlimited' or an integer greater or equal to 0 ; Default Value: system defined value ;rlimit_core = 0 ; Chroot to this directory at the start. This value must be defined as an ; absolute path. When this value is not set, chroot is not used. ; Note: you can prefix with '$prefix' to chroot to the pool prefix or one ; of its subdirectories. If the pool prefix is not set, the global prefix ; will be used instead. ; Note: chrooting is a great security feature and should be used whenever ; possible. However, all PHP paths will be relative to the chroot ; (error_log, sessions.save_path, ...). ; Default Value: not set ;chroot = ; Chdir to this directory at the start. ; Note: relative path can be used. ; Default Value: current directory or / when chroot ;chdir = /var/www ; Redirect worker stdout and stderr into main error log. If not set, stdout and ; stderr will be redirected to /dev/null according to FastCGI specs. ; Note: on highloaded environement, this can cause some delay in the page ; process time (several ms). ; Default Value: no ;catch_workers_output = yes ; Clear environment in FPM workers ; Prevents arbitrary environment variables from reaching FPM worker processes ; by clearing the environment in workers before env vars specified in this ; pool configuration are added. ; Setting to "no" will make all environment variables available to PHP code ; via getenv(), $_ENV and $_SERVER. ; Default Value: yes ;clear_env = no ; Limits the extensions of the main script FPM will allow to parse. This can ; prevent configuration mistakes on the web server side. You should only limit ; FPM to .php extensions to prevent malicious users to use other extensions to ; exectute php code. ; Note: set an empty value to allow all extensions. ; Default Value: .php ;security.limit_extensions = .php .php3 .php4 .php5 ; Pass environment variables like LD_LIBRARY_PATH. All $VARIABLEs are taken from ; the current environment. ; Default Value: clean env ;env[HOSTNAME] = $HOSTNAME ;env[PATH] = /usr/local/bin:/usr/bin:/bin ;env[TMP] = /tmp ;env[TMPDIR] = /tmp ;env[TEMP] = /tmp ; Additional php.ini defines, specific to this pool of workers. These settings ; overwrite the values previously defined in the php.ini. The directives are the ; same as the PHP SAPI: ; php_value/php_flag - you can set classic ini defines which can ; be overwritten from PHP call 'ini_set'. ; php_admin_value/php_admin_flag - these directives won't be overwritten by ; PHP call 'ini_set' ; For php_*flag, valid values are on, off, 1, 0, true, false, yes or no. ; Defining 'extension' will load the corresponding shared extension from ; extension_dir. Defining 'disable_functions' or 'disable_classes' will not ; overwrite previously defined php.ini values, but will append the new value ; instead. ; Note: path INI options can be relative and will be expanded with the prefix ; (pool, global or /usr/local/php) ; Default Value: nothing is defined by default except the values in php.ini and ; specified at startup with the -d argument ;php_admin_value[sendmail_path] = /usr/sbin/sendmail -t -i -f www@my.domain.com ;php_flag[display_errors] = off ;php_admin_value[error_log] = /var/log/fpm-php.www.log ;php_admin_flag[log_errors] = on ;php_admin_value[memory_limit] = 32M
docker build -t php:v1 -f Dockerfile-php . # 使用 Dockerfile-nginx 文件构建一个基础镜像 php:v1
docker images #确认 php:v1镜像是否构建成功
docker run -d --name php01 php:v1 # 使用php:v1镜像启动一个容器 php01
docker ps -l # 确认 容器php01是否可以成功启动
docker exec -it php01 bash # 进入容器php01 bash环境,确定一下php是否安装成功
2、dockerfile的作用
docker可以根据Dockerfile中的指令来构建docker镜像。
Dockerfile是一个文本文件,其应当包含用户想要构建一个镜像的所有指令。
FROM # build是基于哪个镜像来构建新的镜像
ENV PATH $PATH:/usr/local/nginx/sbin # 配置环境变量,注意此配置会在container中生效
COPY src dest # docker内部文件系统中拷贝
ADD src dest # 将宿主机本地文件拷贝到docker中
RUN command # 执行linux命令
CMD ["sh","/code/start.sh"] # 启动服务
EXPOSE 8080 # 暴露端口
WORKDIR /path #在此指令之后的操作,以及container的默认进入路径都将时 /path目录
VOLUME ['/path1', '/path2'] # 基于此镜像创建的container都将拥有VOLUME中指定的挂在目录
3、Dockerfile编写优化
1. 一个docker image只负责一个职责。当有多个服务时,请将服务分别docker化,然后组合使用这些docker images。
2. 就像编程一样,当一个字符串出现多次时,请用ARG来声明变量取代hard code。
3. 拷贝文件到镜像时,ADD负责网络资源的拷贝,COPY负责本地文件的COPY。
4. 尽量使用cache,docker在build镜像时可以利用缓存,缓存的原则时:当重复构建时,如果单个指令的内容没有变化,则docker会默认使用cache。
5. 将相同变化频率的RUN指令合并成一个。注意,一定要是相同变化频率的RUN命令才能合并成一个,不然缓存的特性就无法使用了。
6. 合理使用.dockerignore,减少images的体积。
7. 尽量使用CMD,VOLUME将image进行服务化。
8. 使用LABEL对image进行元信息的描述。
9. 单一服务的基础镜像如何可以请使用alpine版本的镜像来减少image的体积。
1.10 使用docker简单部署django项目
1、初始化一个django项目并用docker启动
[root@linux-node1 ~]# django-admin startproject demo [root@linux-node1 demo]# cd demo [root@linux-node1 demo]# python3 manage.py runserver 0.0.0.0:8000 # 测试项目是否可以启动
[root@linux-node1 demo]# vim Dockerfile # dockerfile内容如下,路径放到django项目根路径
[root@linux-node1 demo]# vim requirements.txt # django需要安装的包,路径放到django项目根路径 [root@linux-node1 demo]# docker build -t dj_demo:v1 -f Dockerfile . [root@linux-node1 demo]# docker run -d -p 192.168.56.11:8000:8000 dj_demo:v1

Django==2.0.4
mysqlclient==1.4.6

FROM python:3.6 MAINTAINER xiaonq RUN mkdir /code WORKDIR /code ADD . /code/ RUN pip install -r requirements.txt -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple EXPOSE 8000 CMD ["python", "manage.py", "runserver", "0:8000"]
作者:学无止境
出处:https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaonq
生活不只是眼前的苟且,还有诗和远方。


 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号