pytorch随笔
pytorch中transform函数
一般用Compose把多个步骤整合到一起:
比如说
transforms.Compose([ transforms.CenterCrop(10), transforms.ToTensor(), ])
这样就把两个步骤整合到一起
接下来介绍transforms中的函数
Resize:把给定的图片resize到given size Normalize:Normalized an tensor image with mean and standard deviation ToTensor:convert a PIL image to tensor (H*W*C) in range [0,255] to a torch.Tensor(C*H*W) in the range [0.0,1.0] ToPILImage: convert a tensor to PIL image Scale:目前已经不用了,推荐用Resize CenterCrop:在图片的中间区域进行裁剪 RandomCrop:在一个随机的位置进行裁剪 RandomHorizontalFlip:以0.5的概率水平翻转给定的PIL图像 RandomVerticalFlip:以0.5的概率竖直翻转给定的PIL图像 RandomResizedCrop:将PIL图像裁剪成任意大小和纵横比 Grayscale:将图像转换为灰度图像 RandomGrayscale:将图像以一定的概率转换为灰度图像 FiceCrop:把图像裁剪为四个角和一个中心 TenCrop Pad:填充 ColorJitter:随机改变图像的亮度对比度和饱和度
torchvision.transforms.Normalize()
是对数据进行归一化的操作
image = (image - mean) / std
假设你数据的范围是图片的数据范围四[0,1],那么如果mean = [.5, .5, .5],std = [.5, .5, .5],根据上述式子计算
(0−0.5)/0.5=−1
(1−0.5)/0.5=1
就可将数据归一化到[-1,1]。
#逆向归一化 origin = x * 0.5 + 0.5
图像处理、转不同格式显示 cv2, PIL.Image
import torch import torchvision import torchvision.transforms as transforms import cv2 import numpy as np from PIL import Image img_path = "./data/timg.jpg" # transforms.ToTensor() transform1 = transforms.Compose([ transforms.ToTensor(), ]) ##numpy.ndarray img = cv2.imread(img_path) # 读取图像 3x1080x1920(通道*高*宽),数值[0, 255] print("img = ", img) img1 = transform1(img) # 归一化到 3x1080x1920(通道*高*宽),数值[0.0,1.0] print("img1 = ", img1) # 转化为numpy.ndarray并显示 img_1 = img1.numpy()*255 img_1 = img_1.astype('uint8') img_1 = np.transpose(img_1, (1,2,0)) cv2.imshow('img_1', img_1) cv2.waitKey() ##PIL img = Image.open(img_path).convert('RGB') # 读取图像, 数据格式 [h, w, c] img2 = transform1(img) # 归一化到 [0.0,1.0] # 转换到[c, h, w] print("img2 = ",img2) #转化为PILImage并显示 img_2 = transforms.ToPILImage()(img2).convert('RGB')
#等同于np.transpose(img2, (1, 2, 0)) print("img_2 = ",img_2) img_2.show()
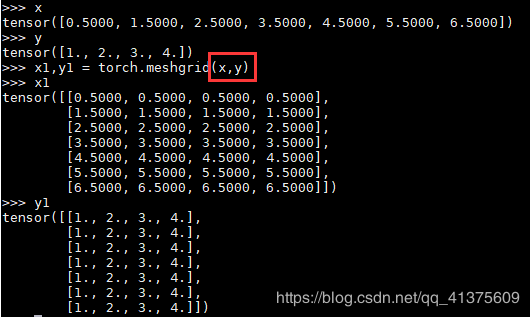
torch.meshgrid()
x1 ,y1 = torch.meshgrid(x,y)
参数是两个,第一个参数我们假设是x,第二个参数假设就是y
输出的是两个tensor,size就是x.size * y.size(行数是x的个数,列数是y的个数)
具体输出看下面
注意:两个参数的数据类型要相同,要么都是float,要么都是int,否则会报错。
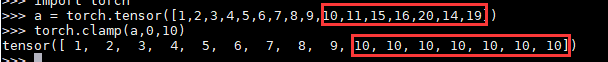
torch.clamp()
torch.clamp(input, min, max, out=None) → Tensor
将输入input张量每个元素的夹紧到区间 [min,max][min,max],并返回结果到一个新张量。
操作定义如下:
| min, if x_i < min y_i = | x_i, if min <= x_i <= max | max, if x_i > max
参数:
input (Tensor) – 输入张量
min (Number) – 限制范围下限
max (Number) – 限制范围上限
out (Tensor, optional) – 输出张量
示例:
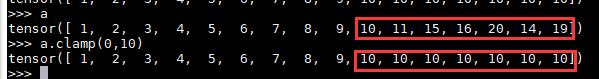
tensor.clamp()
tensor.clamp(min, max, out=None) → Tensor
跟上面是一样的作用,tensor就是input
参数:
min (Number) – 限制范围下限
max (Number) – 限制范围上限
out (Tensor, optional) – 输出张量
示例:
参考:https://blog.csdn.net/qq_41375609/article/details/102828154



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号