0react
vscode
光标左击选中某个变量,然后CTRL+Shift+L 选中所有的目标变量 改名字
react开发依赖
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/react/16.13.1/umd/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/react-dom/16.13.1/umd/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/babel-standalone/6.26.0/babel.js"></script>
<script type="text/babel"></script>
初体验:切换文本
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<meta name="viewport" content="width=device-width, initial-scale=1.0">
<title>Document</title>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/react/16.13.1/umd/react.development.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/react-dom/16.13.1/umd/react-dom.development.js"></script>
<script src="https://cdn.bootcdn.net/ajax/libs/babel-standalone/6.26.0/babel.js"></script>
</head>
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
let flag = true
function render() {
const context = <div><h2>hello {flag ? 'world' : 'react'}</h2> <button onClick={changeText}>切换文字</button></div>
ReactDOM.render(context, document.getElementById('app'))
}
render()
function changeText() {
flag = !flag //改变数据,需要手动重新 调用ReactDOM.render
render()
}
</script>
</body>
</html>
class改进
- 响应数据要放在state里面。
- 更新state里面数据一定要调用this.setState()方法。这样react才会自动调用render函数。
- 所以永远不要手动调用render()函数。
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
// this.state控制响应式数据
this.state = {
flag: true,
}
}
// 永远不用手动调用render()函数,没有任何效果。
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>hello {this.state.flag ? 'world' : 'react'}</h2>
<button onClick={this.changeText}>切换文本</button>
</div>
)
}
changeText = () => {
// this.state.flag = !this.state.flag //state里面的flag确实改变,但是页面不会自动渲染更新,render函数不会执行
// 要想自动更新,需要调用setState方法。这样才会通知render函数去自动执行
this.setState({
flag: !this.state.flag //只会更新自己要改变的值。其他在state里的属性和值都不会丢失。保持原样
})
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App></App>, document.getElementById('app'))
</script>
</body>
jsx
jsx语法书写规范:
- jsx顶层只能有一个根元素
- render函数return 后面带一个小括号().小括号里面写任何的jsx语法。不带小括号就不能换行了。
- jsx里面HTML元素可以写单标签和双标签。如果是单标签,必须是带/闭合
- jsx注释{/注释注释注释/}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h3>{this.state.msg}</h3>
{/*
我是注释,可以一行
我是注释可以多行
*/}
<img src="" alt="" />
</div>
)
}
jsx变量
在{}中可以在页面正常显示的数据类型有:string|number|Array.
在{}中不会在页面显示的数据类型有:null|undefined|boolean.但是不会报错。如果想显示,转为字符串类型。
在{}中绝对不能放Object .
{/* 放变量,放变量表达式,放三目运算符,放函数*/}
<h3>hello world</h3>
<h3>hello {this.state.msg}</h3>
<h3>{this.state.demo1?'a':'b'}</h3>
<h3>{this.showInfo(this.state.user)}</h3>
绑定属性
<script type='text/babel'>
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
title: "I am title",
imgSrc: './imgs/logo192.png',
reactUrl: 'https://react.docschina.org/docs/introducing-jsx.html',
active: true,
marginRight: 30
}
}
render() {
let { title, imgSrc, reactUrl, active, marginRight } = this.state
return (
<div>
<h3 title={title}>绑定title</h3>
<img src={imgSrc} width="30"></img>
<a href={reactUrl}>react 官网</a>
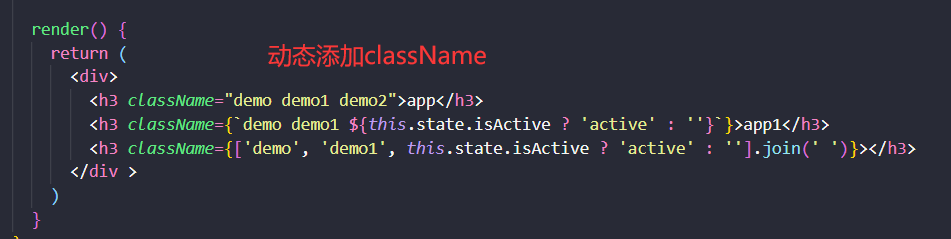
<h3 className="demo demo1 demo2">class样式是className 不是class避免es6 class关键字 </h3>
<h3 className={"demo0 demo1 " + (active ? 'active' : '')}>动态切换是否添加active class样式</h3>
<h3 className={['demo', 'demo', active ? 'active' : ''].join(' ')}>动态绑定class方式2</h3>
<h3 className={`demo0 demo1 ${active ? 'active' : ''}`}>动态绑定class方式3</h3>
<label htmlFor="aa">for在js中是关键字,所以label要避讳</label>
<h3 style={{ color: 'red', fontSize: '30px', marginRight:marginRight }}>绑定内联样式数字自动带px</h3>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'))
</script>
虚拟DOM
jsx语法本质是React.createElement()的语法糖,生成一个ReactElement对象树(js对象),这个对象数就是虚拟DOM对象,保存在内存中。然后通过ReactDOM.render()函数渲染成真实的DOM对象。
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
const message0 =
<div className="wrap">
<header className='header'>
<h2>i am header</h2>
</header>
<main className="content">
<h3>i am content</h3>
</main>
</div>
const message =
React.createElement("div", { className: "wrap" },
React.createElement("header", { className: "header" }, React.createElement("h2", null, "i am header")),
React.createElement("main", { className: "content" }, React.createElement("h3", null, "i am content")));
console.log(message);
ReactDOM.render(message, document.getElementById('app'))
</script>
</body>
react事件处理其传参
- React 事件的命名采用小驼峰式(camelCase),而不是纯小写。
- 使用 JSX 语法时你需要传入一个函数作为事件处理函数,而不是一个字符串。
<script type='text/babel'>
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
message: 'hello react',
num:300
}
// this.handleClick = this.handleClick.bind(this)
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{/*优选使用事件传参1 */}
<button onClick={(e) => { this.handleClick(e, 100) }}>事件传参方式1 this是render函数中的this</button>
<button onClick={this.handleClick1.bind(this, 100)}>事件传参方式2</button>
<button onClick={this.handleClick2(100)}>事件传参方式3</button>
</div>
)
}
handleClick(e, params) {
console.log(e, params);
}
handleClick1(num, e) {
console.log(num, e);
}
handleClick2 = (num) => {
return e => {
console.log(e);
console.log(num);
}
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'))
</script>
条件渲染
模拟实现v-if
v-if作用1:显示不同内容
render() {
const { isLogin, flag, moiveList } = this.state
const txt = isLogin ? '登录' : '退出'
const isShowH3 = flag ? 'block' : 'none'
const h3Style = { color: 'red', display: isShowH3 }
return (
<div>
{/* v-if if控制显示内容方式1 判断逻辑放在外面*/}
<h3>{txt}</h3>
{/*v-if if控制显示内容方式2 三目表达式*/}
<h3>{isLogin ? '登录' : '退出'}</h3>
</div>
)
}
v-if作用2:控制是否渲染&&
render() {
const { isLogin, flag, moiveList } = this.state
const txt = isLogin ? '登录' : '退出'
const isShowH3 = flag ? 'block' : 'none'
const h3Style = { color: 'red', display: isShowH3 }
return (
<div>
{/* 这个h3标签不管是true/false都会渲染出*/}
<h3>{isLogin && '登录'}</h3>
{/* 这个最好; 只有当isLogin是true的时候还会渲染h3标签*/}
{isLogin && <h3>登录</h3>}
{/* 只有当moiveList列表长度>0才遍历渲染数组 */}
{moiveList.length > 0 &&
<ul>
{moiveList.map((item, index) => <li key={index}>{item}</li>)}
</ul>
}
</div>
)
}
模拟实现v-show css的display
render() {
const { isLogin, flag, moiveList } = this.state
const isShowH3 = flag ? 'block' : 'none'
const h3Style = { color: 'red', display: isShowH3 }
return (
<div>
{/*模拟实现v-show css的display属性*/}
<h3 style={h3Style}>hello react</h3>
</div>
)
}
列表和对象遍历&key
首先要明确对象不能在react遍历。需要变样遍历。
<script type='text/babel'>
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
message: 'hello world',
movieList: ['少年派', '变形金刚', '三国演义', '大话西游'],
user: { name: 'zs', age: 10 }
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h3>{this.state.message}</h3>
<h2>电影列表</h2>
<ul>//遍历列表
{
this.state.movieList.map((item, index) => {
return <li key={index}>{item}</li>
})
}
</ul>
<h3>user信息</h3>
<div>//遍历对象
{
Object.keys(this.state.user).map(key => {
return <p key={key}>{this.state.user[key]}</p>
})
}
</div>
</div>
)
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App />, document.getElementById('app'))
</script>
bookstore综合练习
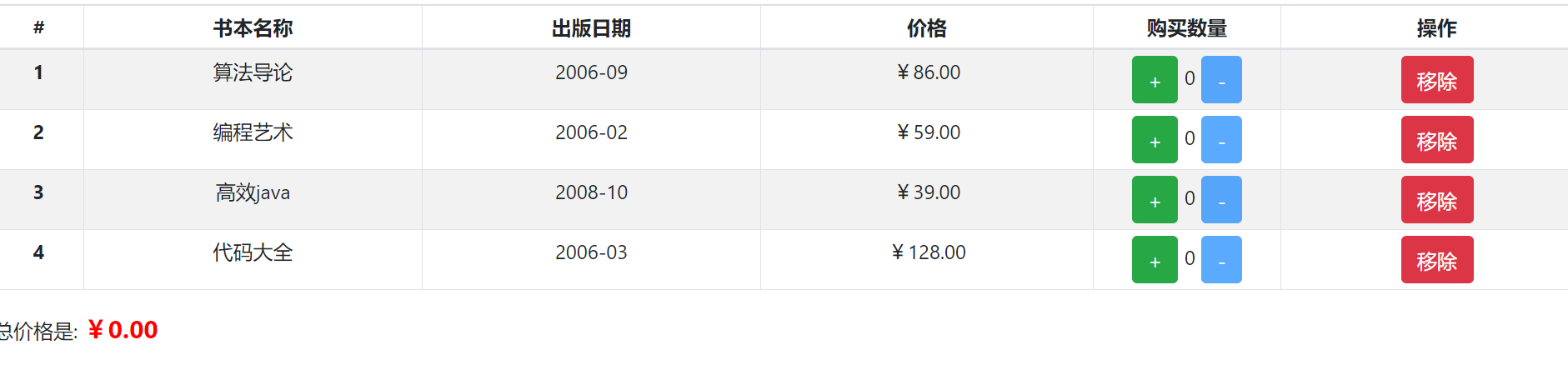
- 表格显示内容
- 底部显示总价格
- 点击+ -增加或者减少书数量。但是不能减少为负数
- 点击删除按钮移除一行数据,当移除所有书,显示购物车为空。
<body>
<div id="app"></div>
<script type="text/babel">
class App extends React.Component {
constructor() {
super()
this.state = {
bookStoreList: [
{ title: '算法导论', publicTime: '2006-09', price: 86.00, count: 0, },
{ title: '编程艺术', publicTime: '2006-02', price: 59.00, count: 0, },
{ title: '高效java', publicTime: '2008-10', price: 39, count: 0, },
{ title: '代码大全', publicTime: '2006-03', price: 128.00, count: 0 },
],
}
}
initTable() {
const { bookStoreList } = this.state
return (
<div>
<table className="table table-striped table-bordered table-sm">
<thead>
<tr>
<th scope="col">#</th>
<th scope="col">书本名称</th>
<th scope="col">出版日期</th>
<th scope="col">价格</th>
<th scope="col">购买数量</th>
<th scope="col">操作</th>
</tr>
</thead>
<tbody>
{bookStoreList.map((item, index) => {
return (
<tr key={item.title}>
<th scope="row">{index + 1}</th>
<td>{item.title}</td>
<td>{item.publicTime}</td>
<td>{this.formatPrice(item.price)}</td>
<td style={{ width: 150 }}>
<button type="button" className="btn btn-success" onClick={() => this.handleAdd(item.title,)}>+</button>
<span className="count">{item.count}</span>
<button type="button"
className="btn btn-primary"
disabled={item.count <= 0}
onClick={() => this.decrease(item.title,)}>-</button>
</td>
<td><button
type="button"
className="btn btn-danger"
onClick={() => this.deleteItem(item.title)}
>移除</button> </td>
</tr>
)
})}
</tbody>
</table>
{/*计算总价格*/}
{this.computeTotal()}
</div>
)
}
renderTips() {
return <p>购物车为空</p>
}
render() {
return this.state.bookStoreList.length > 0 ? this.initTable() : this.renderTips()
}
formatPrice(price) {
return typeof price === 'number' ? `¥${price.toFixed(2)}` : price
}
//计算总价格 注意:其他函数(非render函数)里面也可以使用jsx语法。
computeTotal() {
const totalPrice = this.formatPrice(this.state.bookStoreList.reduce((prev, next) => prev + next.price * next.count, 0))
return <p>总价格是: <span style={{ color: 'red', fontSize: 20, fontWeight: 700 }}>{totalPrice}</span></p>
}
//增加数量
handleAdd(title) {
{/*this.state.bookStoreList不要改动*/ }
this.setState({ bookStoreList: this.state.bookStoreList.map(item => item.title === title ? { ...item, count: ++item.count } : item) })
}
//减少数量
decrease(title) {
const res = this.state.bookStoreList.map(item => item.title === title ? { ...item, count: --item.count } : item)
this.setState({ bookStoreList: res })
}
// 移除
deleteItem(bookTitle) {
//react中设计原则:state数据不可变性。
this.setState({ bookStoreList: this.state.bookStoreList.filter(item => item.title !== bookTitle) })//filter函数不会修改this.state.bookStoreList的值
}
}
ReactDOM.render(<App></App>, document.getElementById('app'))
</script>
</body>
全局安装yarn
node 包管理工具
npm install yarn -g
yarn --version
yarn add package === npm i package -S 运行依赖
yarn add package -D ===npm i pageage -D 开发依赖
yarn remove package === npm uninstall package -S/D
yarn cache clean ===npm chahe clean
yarn upgrade
全局安装react手脚架
npm install create-react-app -g
create-react-app --version
创建react项目
create-react-app projectName 创建项目
cd projectName
yarn start
projectName不能使用大写字母,多个单词以-连接。eg: mail-store-h5
react vscode插件和快捷键
user.json加入。写标签自动闭合
"emmet.includeLanguages": {
"javascript": "javascriptreact"
}
imrc -> import React, { Component } from 'react'
ccc ->快速生成类组件
rcc ->imrc+ccc
rconst ->constructor函数
rpcp -> proptypes
rfc ->函数式组件
//rpcp
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'
import PropTypes from 'prop-types'
export default class FileName extends PureComponent {
static propTypes = {}
render() {
return <div>$2</div>
}
}
react最开始的初始化
也就是删除一些文件而已
react组件化开发
组件思想:
数据逻辑和ui组件的分离
组件划分:
根据组件定义划分:函数组件(没有内部状态|没有生命周期)和类组件
根据组件内部是否有状态需要维护:无状态组件(stateless Component)和有状态组件(stateful Component)
根据组件的职责:展示性组件和容器类组件
异步组件、高阶组件等
类组件
- 定义组件时组件名大写字母开头,必须继承React.Component ;类组件必须实现render函数。
- eg: class News extends React.Component{}
- render函数的返回值:react元素(html元素|自定义react组件),数组(普通数组|jsx数组),基本数据类型(number|string|boolean(页面看不见))
- constructor()函数可选;this.state()里面放组件数据
- 作为组件使用:
而使用 是错的。
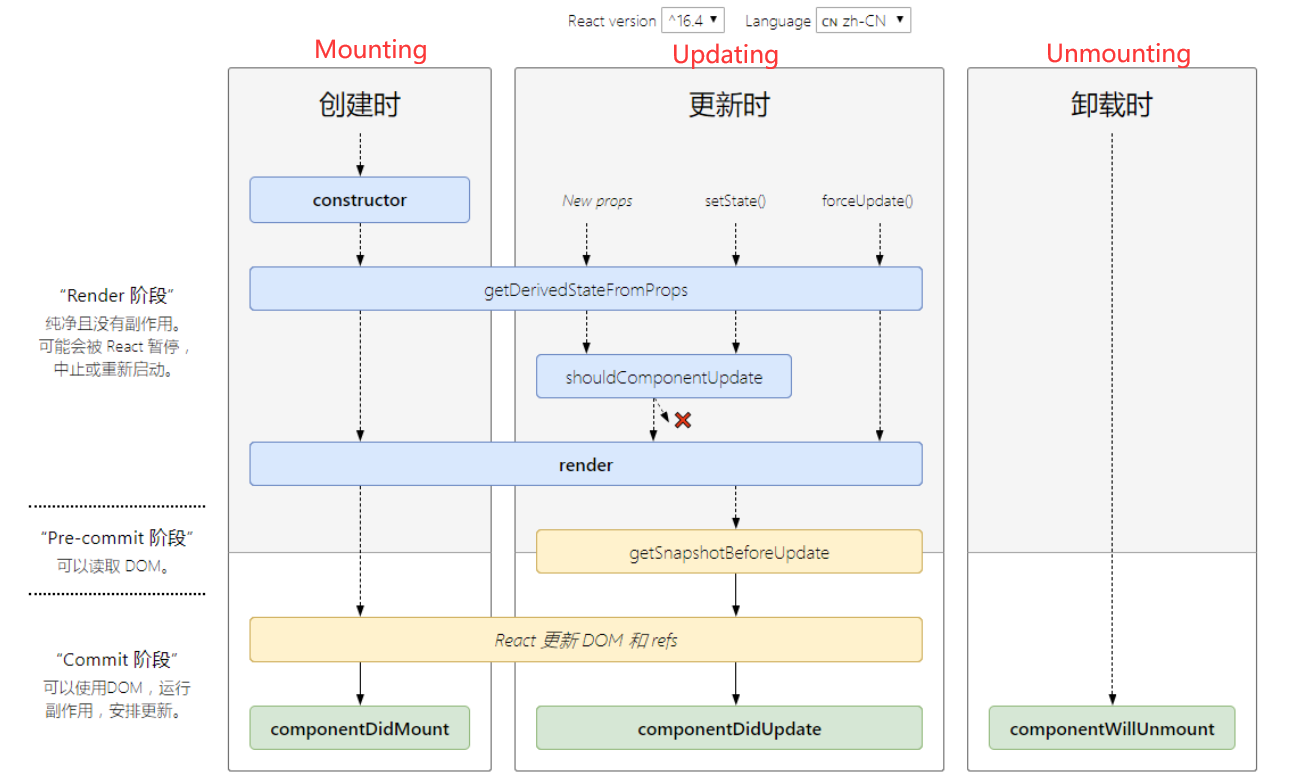
react 类组件生命周期
https://zh-hans.reactjs.org/docs/react-component.html
import React, { Component } from 'react';
export default class App extends Component {
constructor() {
super();
console.log('父组件的constructor');
this.state = {
message: 'hello world',
num: 10,
}
}
render() {
console.log('父组件的render');
const { message } = this.state;
return (
<div>
<h3>{message}</h3>
<button onClick={() => this.changeMessage()}>验证生命周期</button>
</div>
)
}
changeMessage() {
this.setState({
message: 'hello react'
})
}
componentDidMount() { //cdm
console.log('只会初始化时候执行唯一一次componentDidMount()');
console.log('constructor()函数执行->render()函数执行->componentDidMount()函数执行');
}
componentDidUpdate(prevProps, prevState) { //cdu
console.log(prevProps); //{}
console.log(prevState); //第一次点击{ message: 'hello world', num:10,}
console.log('componentDidUpdate初始化时不会执行,只有在state中数据发生改变时执行');
console.log('render()函数执行->componentDidUpdate()函数执行');
}
componentWillUnmount(){
console.log('组件卸载时候触发');
}
}
生命周期函数
componentDidMount
可以进行的数据操作有
1.真实dom操作,在ReactDOM.render()执行之后调用componentDidMount。这个时候虚拟dom已经渲染成真实的DOM
2. 网络请求,改变state里面数据
3. 添加一些订阅 (在componentWillUnmount手动取消订阅)
componentDidMount() {
fetchPosts().then(response => {
this.setState({
posts: response.posts
});//重新执行render函数,生成虚拟dom。
});
componetDidUpdate(prevProps,prevState)
组件初始化不会执行,只有当数据改变后才会执行。
可以进行的数据操作有
- 真实dom操作
- 通过前后props|state变化,判断是否发生网络请求。
componentDidUpdate(prevProps) {
// 典型用法(不要忘记比较 props):
if (this.props.userID !== prevProps.userID) {
this.fetchData(this.props.userID);
}
}
componentWillUnmount()
组件卸载和销毁之前调用。
可以进行的数据操作有
- 清除定时器
- 清除componentDidMount里面订阅的事件
数组通信 &&propTypes
rpcp快捷键
https://react.docschina.org/docs/typechecking-with-proptypes.html
//app.jsx
import React, { Component } from 'react';
import Header from './component/appComp/Header'
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
headerMessage: 'hello react',
headerMessage1: 100,
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h2>app</h2>
<Header
headerMessage={this.state.headerMessage}
headerMessage1={this.state.headerMessage1}
changeHeaderMessage={(newMessage) => { this.changeHeaderMessage(newMessage) }}>
</Header>
</div>
);
}
changeHeaderMessage(newMessage) {
this.setState({
headerMessage: newMessage
})
}
}
export default App;
//Header.jsx子组件 rpcp
import React, { Component } from 'react'
import propTypes from 'prop-types'
export default class Header extends Component {
//如果夫组件没有传属性,可以允许使用默认值。如果这个是属性是isRequired,但是父组件也没有传,如果设置了该值是默认值也不会有警告
static defaultProps = {
headerMessage: 'default value headerMessage ' //给headerMessage设置默认值
}
static propTypes = {
headerMessage: propTypes.string.isRequired, //string类型必选
headerMessage1: propTypes.oneOfType(
[propTypes.string, propTypes.number.isRequired] //任意类型之一,并且number必传
),
changeHeaderMessage: propTypes.func //函数类型
}
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<div className="header">{this.props.headerMessage}</div>
<div>{this.props.headerMessage1}</div>
//子组件给父组件传值。通过函数
<button onClick={() => { this.props.changeHeaderMessage('hello world') }}>改变父组件的header值</button>
</div>
)
}
}
本质是父组件传函数给子组件。子组件调用父组件函数时候会传递过来一些值。
react实现Vue插槽效果
首先明确一点:react没有插槽,需要自己手动实现
插槽:父组件向子组件传递HTML结构。props是向子组件传递数据。
1.this.props.children实现插槽
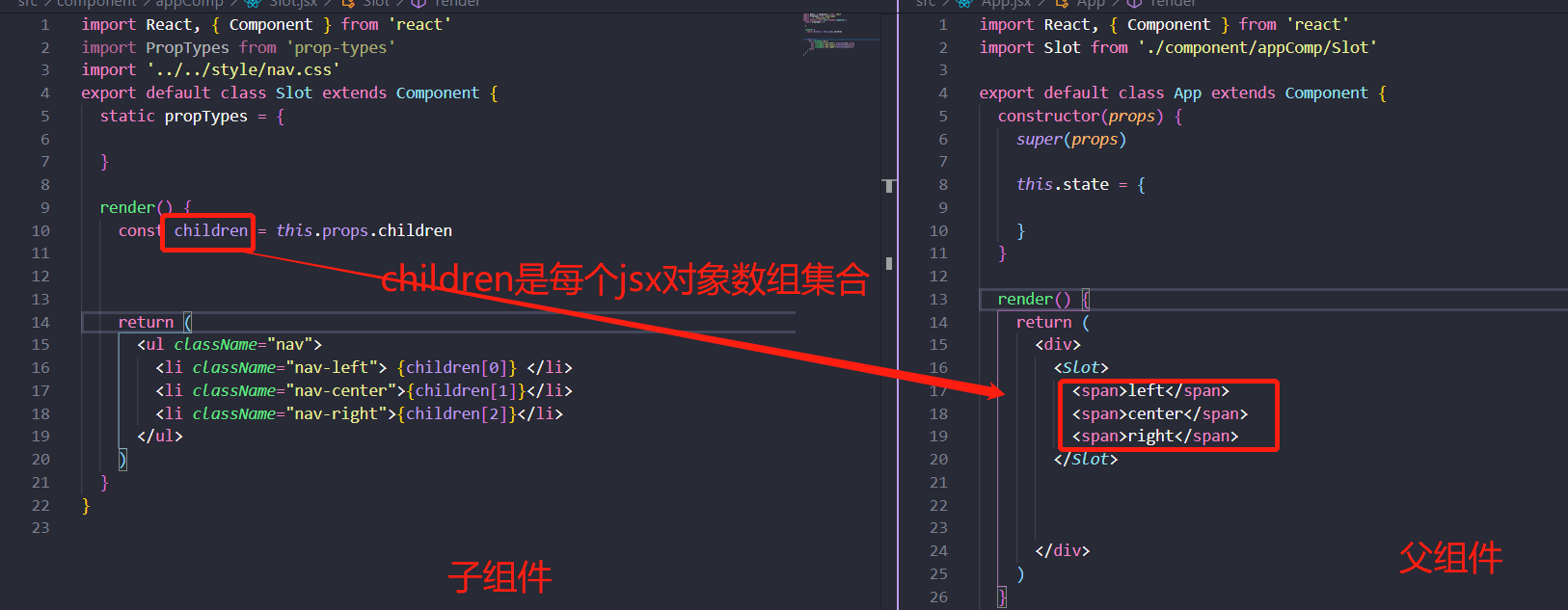
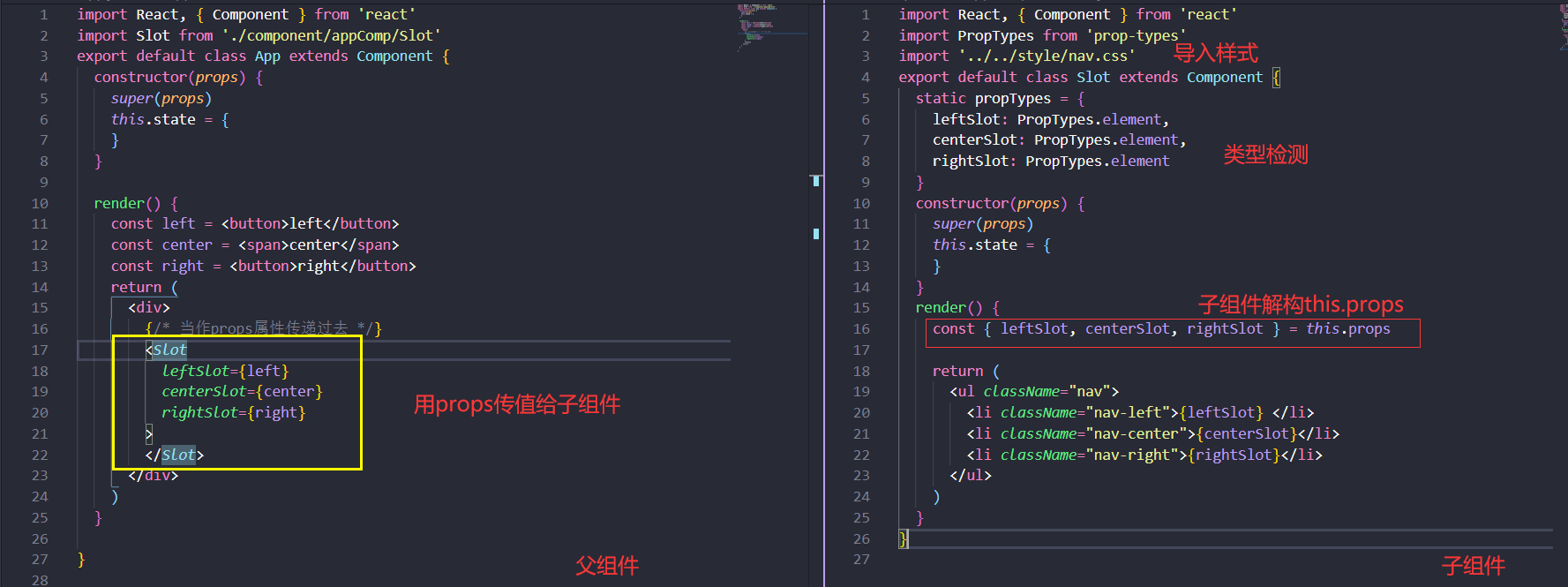
2.this.props直接实现插槽
综合建议:多多使用方式二 this.props实现插槽效果。
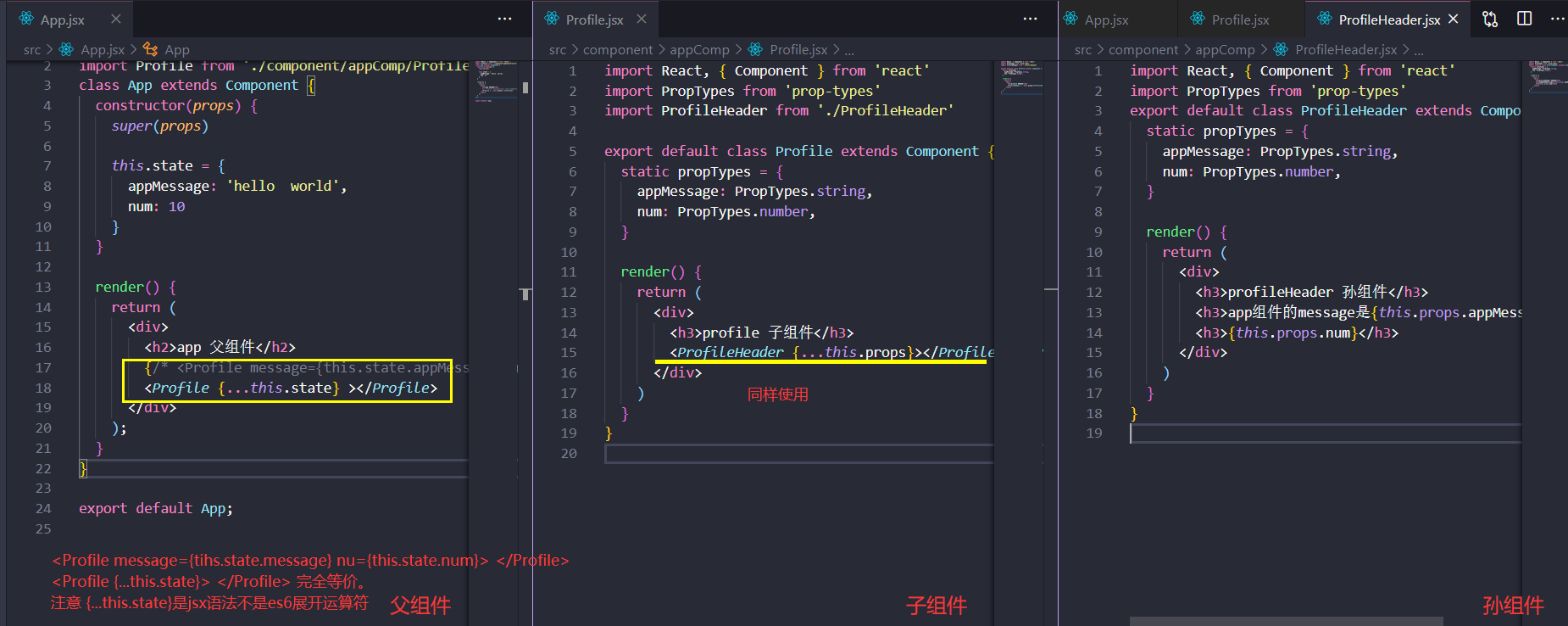
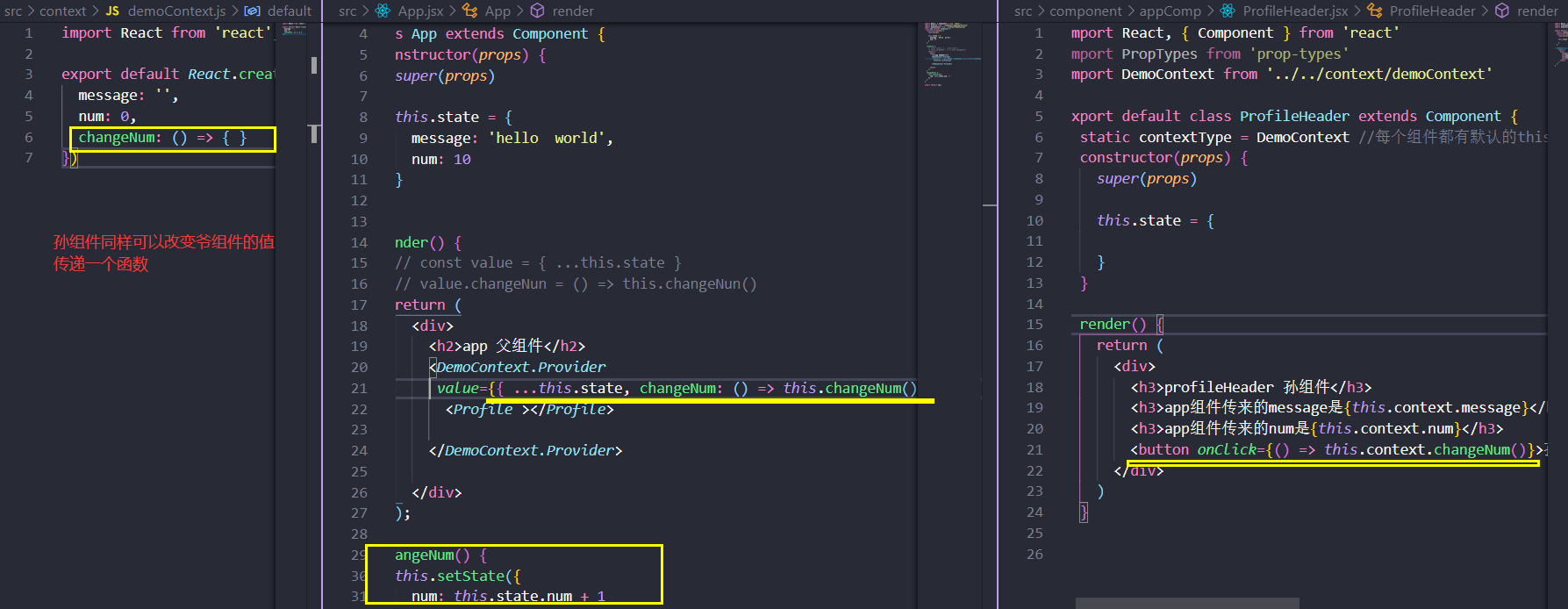
跨组件通信
app组件->子组件Profile->孙组件ProfileHeader.想要从app组件传值到孙组件ProfileHeader,就要通过props属性先传给子组件,然后子组件在做一次Props转发到子组件。这就是一层一层传递数据。
Context API
Context 提供了一个无需为每层组件手动添加 props,就能在组件树间进行数据传递的方法。
Context 设计目的是为了共享那些对于一个组件树而言是“全局”的数据,例如当前认证的用户、主题或首选语言。
React.createContext
const MyContext = React.createContext(defaultValue);
Context.Provider
<MyContext.Provider value={/* 某个值 */}>
每个 Context 对象都会返回一个 Provider React 组件,它允许消费组件订阅 context 的变化。
当 Provider 的 value 值发生变化时,它内部的所有消费组件都会重新渲染
多个 Provider 也可以嵌套使用,里层的会覆盖外层的数据。、
Class.contextType
和 static contextType = MyContext;等价.给this.context赋值操作。
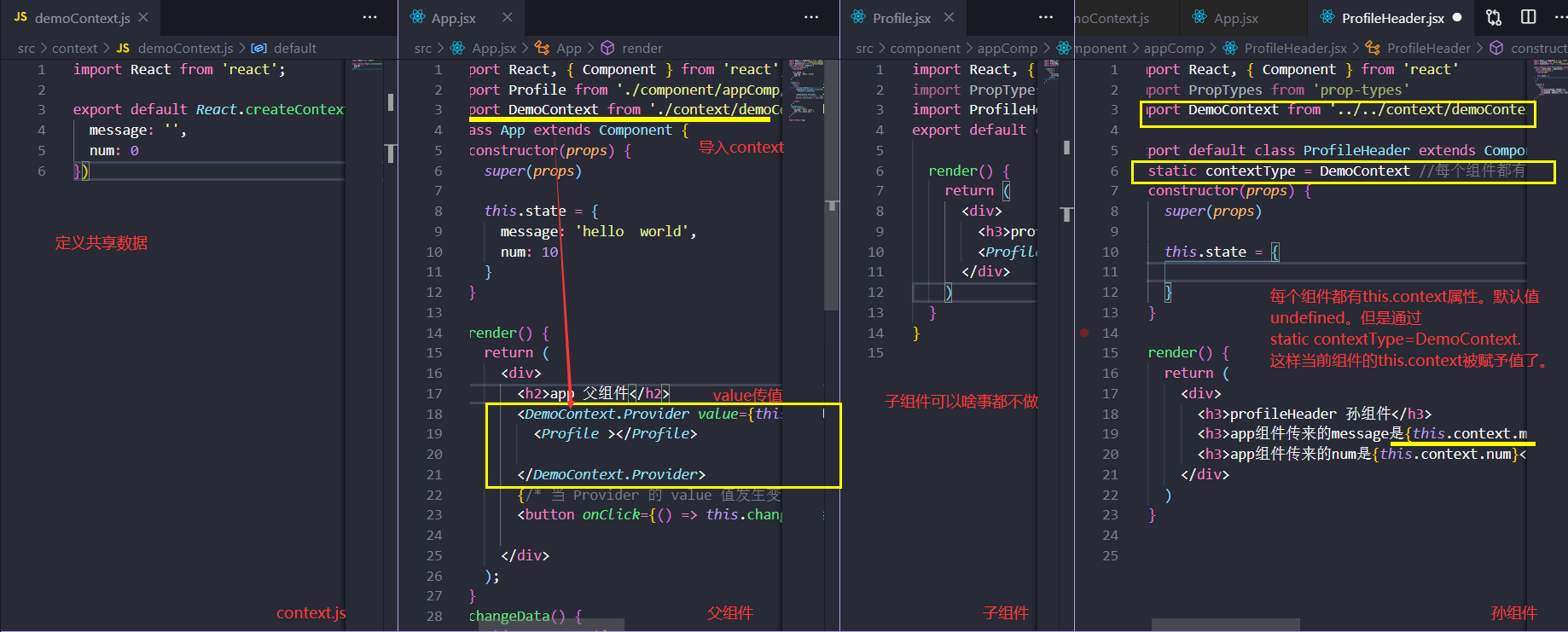
孙组件同样可以改变爷组件的值。传递函数
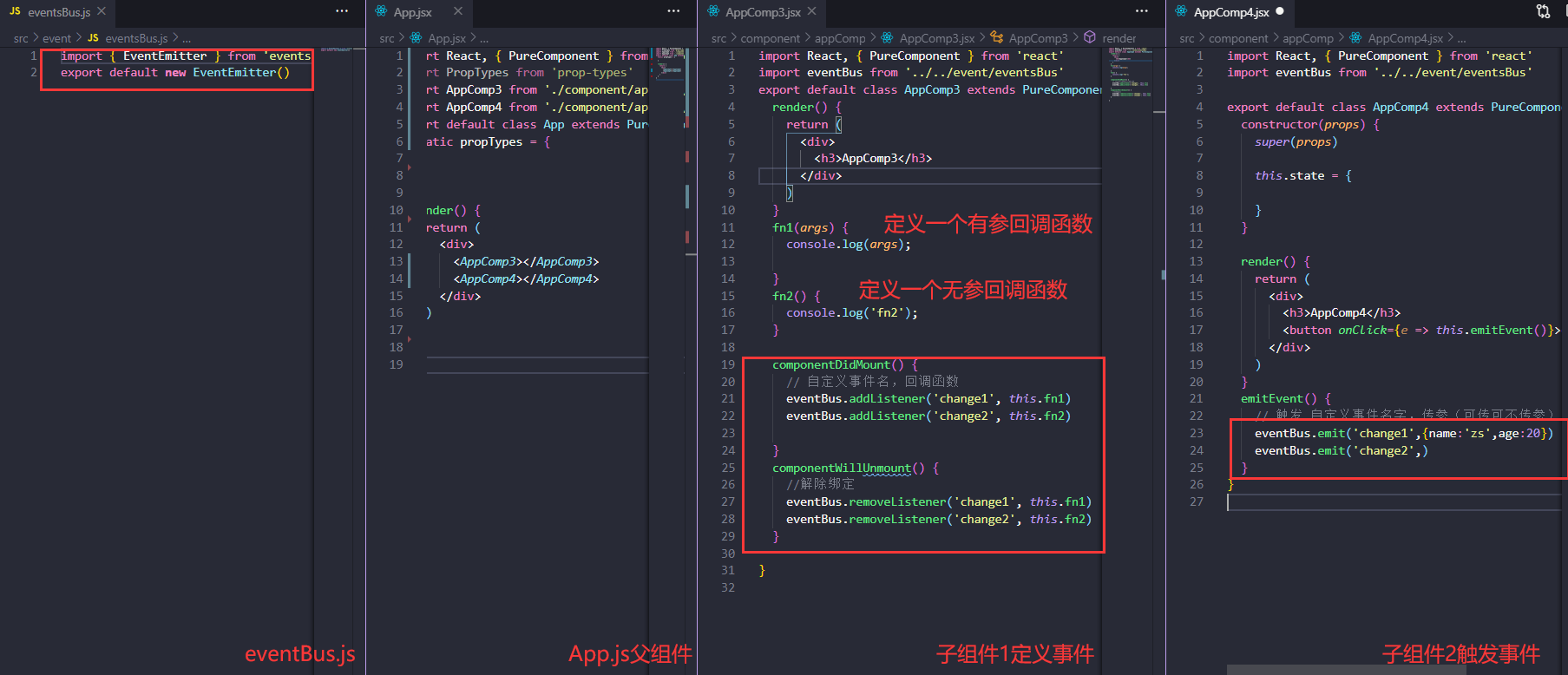
跨组件事件events
yarn add events
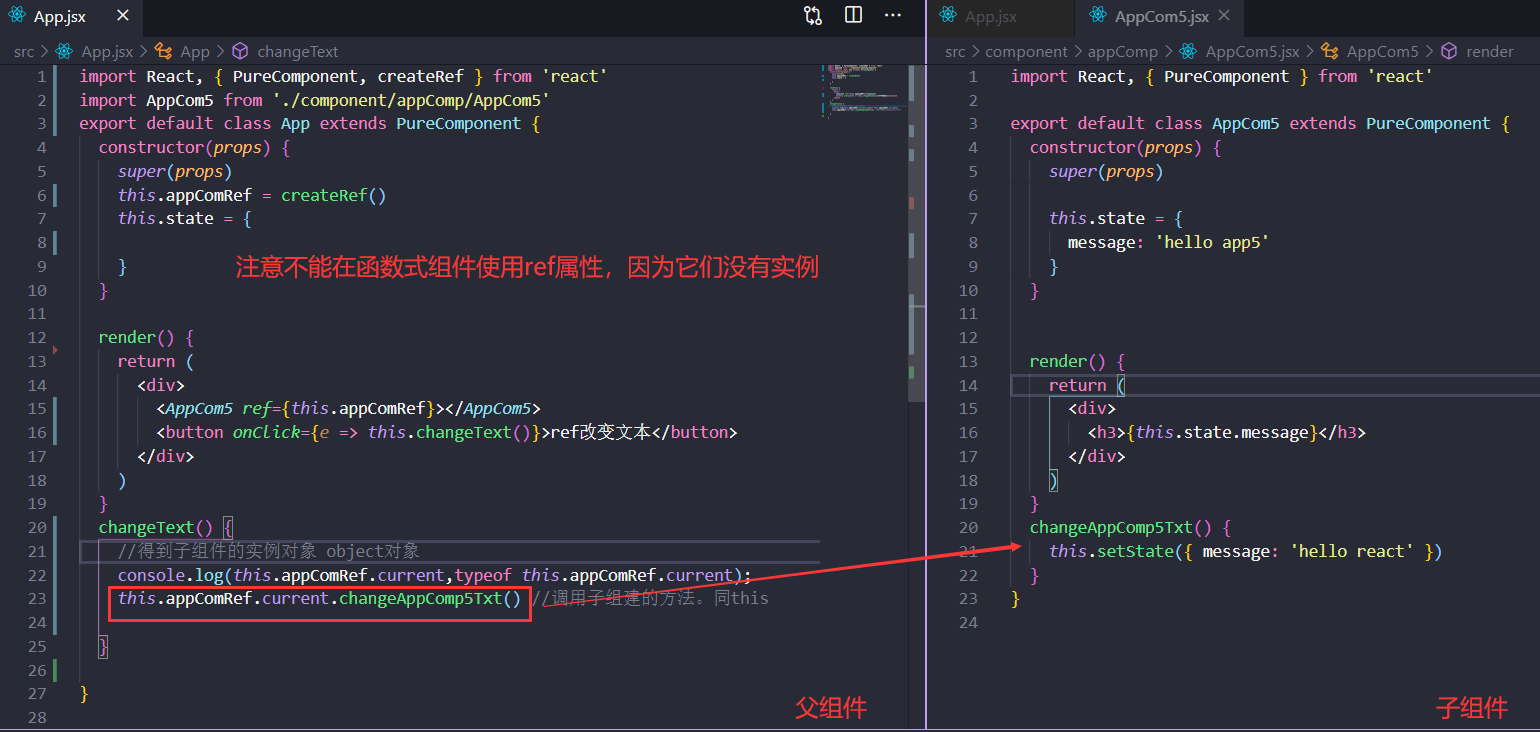
ref
ref等于字符串|对象|函数。但是ref=字符串会被react抛弃。不建议使用
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'
export default class App extends PureComponent {
render() {
return (
<div>
//ref="字符串"
<h3 ref="titleRef">hello world!</h3>
<button onClick={e => this.changeText()}>ref改变文本</button>
</div>
)
}
changeText() {
//获取
this.refs.titleRef.innerHTML='hello react'
}
}
import React, { PureComponent, createRef } from 'react'
export default class App extends PureComponent {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.titleRef = createRef()
this.state = {
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
//ref=一个由createRef函数返回的对象。
<h3 ref={this.titleRef}>hello world!</h3>
<button onClick={e => this.changeText()}>ref改变文本</button>
</div>
)
}
changeText() {
this.titleRef.current.innerHTML ='hello react'
}
}
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'
export default class App extends PureComponent {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.titleEl = null
this.state = {
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
{/* args是h3dom元素,并且函数在初始化时候就执行 */}
<h3 ref={args => this.titleEl = args}>hello world</h3>
<button onClick={e => this.changeText()}>ref改变文本</button>
</div>
)
}
changeText() {
this.titleEl.innerHTML = 'hello react'
}
}
ref转发forwardRef
// 不能再函数式组件上面使用ref 。 要想获取函数式里面的元素 用forwardRef
const SS2=forwardRef(function (props,ref) {
return (
<div>
<h6 ref={ref}>ss2--{props.a}</h6>
</div>
)
})
export default class Son6 extends PureComponent {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.h4Ref = createRef()
this.ss1Ref=createRef()
this.ss2Ref=createRef()
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h4 ref={this.h4Ref}>son6</h4>
<SS1 ref={this.ss1Ref}></SS1>
<SS2 ref={this.ss2Ref} a='10'></SS2>
<button onClick={e=>this.showRef()}>打印ref</button>
</div>
)
}
showRef(){
console.log(this.h4Ref.current);
console.log(this.ss1Ref.current);
console.log(this.ss2Ref.current);
}
}
setState
react里面没有Vue2的Object.defineProperty或者Vue3 proxy监视数据变化。
必须手动调用setState来告知React数据已经发生了改变。
setState是继承过来的方法。
setState异步更新
为什么setState是异步更新?
- 设计为异步,可以显著提高性能。
- 如果设计为同步,每次调用setState都会触发调用render函数,界面将会重新渲染,最好的办法是获取到多个更新,批量更新
- 如果同步更新state,但是还没有执行render函数,render里面有子组件,子组件通过props传值。可能state和props不能保持同步(数据一致性)
获取到异步更新的数据
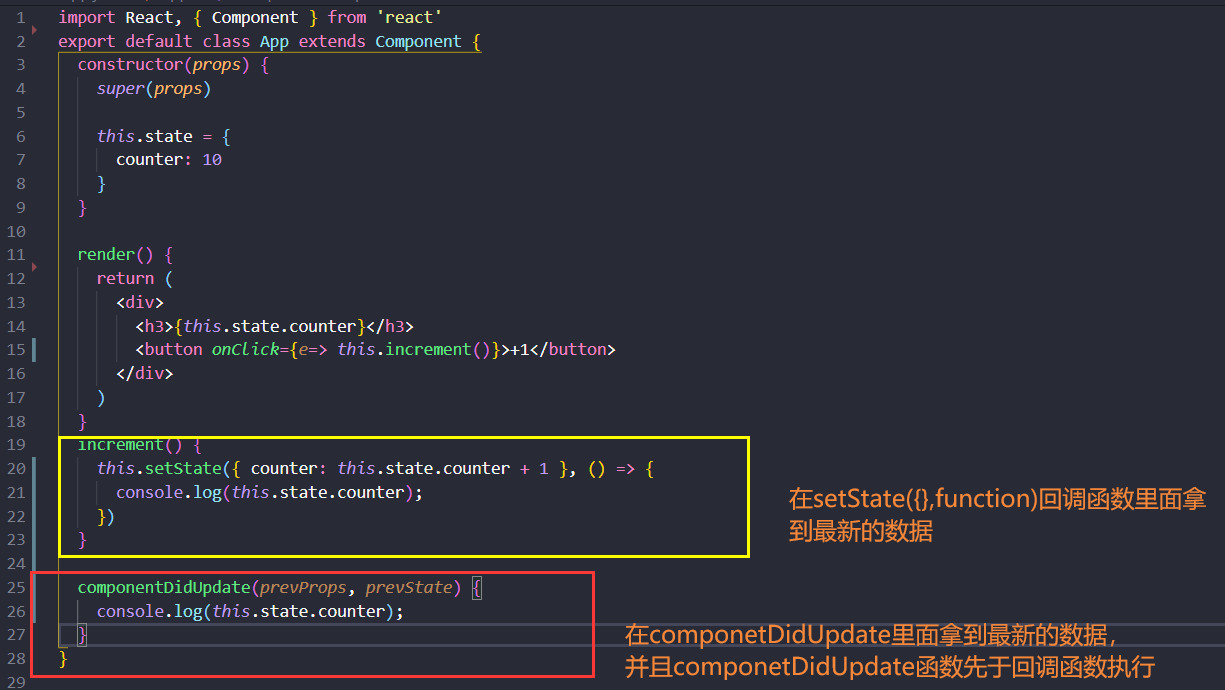
两种方式拿到最新的数据:
- setState({},function)回调函数里面拿到最新数据
- componentDidUpdate生命周期函数里面拿到最新数据
设计setState为同步更新方案
setState放入定时器中或者原生DOM事件中,setState将会变为同步
1将setState放入到定时器中执行,setState将会变为同步
render() {
return (
<div>
<h3>{this.state.counter}</h3>
<button onClick={e => this.increment()}>+1</button>
</div>
)
}
increment() {
setTimeout(() => {
this.setState({ counter: this.state.counter + 10 })
console.log(this.state.counter);
}, 0)
}
2.在dom原生事件中,setState是同步。
render() {
console.log('render');
return (
<div>
<h3>{this.state.counter}</h3>
{/* <button onClick={e => this.increment()}>+1</button> */}
<button id='btn'>+1</button>
</div>
)
}
componentDidMount() {
//原生事件方式1
document.getElementById('btn').onclick = () => {
this.setState({ counter: this.state.counter + 10 })
console.log(this.state.counter);
}
// 原生事件方式2
document.getElementById('btn').addEventListener('click', () => {
this.setState({ counter: this.state.counter + 10 })
console.log(this.state.counter);
})
}
setState数据的合并
state里面数据是合并的。源码是Object.assign({},this.state,新传入的对象)
setState本身的合并
setState本身合并导致的现象:
render函数只会执行一次。componentDidUpdate回调函数也只会执行一次。
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
num: 10,
message: 'hello world'
}
}
render() {
console.log(111);
return (
<div>
<h3>{this.state.num}</h3>
<button onClick={e => this.changeNum()}>改变num</button>
</div>
);
}
// setState会被合并,render函数只会执行一次,但是state里面的num变为10+40=50 message变为hello react
changeNum() {
this.setState({ num: this.state.num + 10 })
this.setState({ num: this.state.num + 20 })
this.setState({ num: this.state.num + 30 })
this.setState({ num: this.state.num + 40 })
this.setState({ message: 'hello react' })
}
}
export default App;
setState不让它本身合并
setState(function)传入函数。注意这个也是异步。
render函数也只会执行一次。componentDidUpdate回调函数也只会执行一次。
但是num是10+10+20+30=70
import React, { Component } from 'react';
class App extends Component {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
num: 10,
message: 'hello world'
}
}
render() {
console.log(111);
return (
<div>
<h3>{this.state.num}</h3>
<button onClick={e => this.changeNum()}>改变num</button>
</div>
);
}
// setState会被合并,render函数只会执行一次,但是state里面的num变为10+40=50 message变为hello react
changeNum() {
this.setState((preState) => {
console.log(preState);
return {
num: preState.num + 10
}
})
this.setState((preState) => {
console.log(preState);
return {
num: preState.num + 20
}
})
this.setState((preState) => {
console.log(preState);
return {
num: preState.num + 30
}
})
}
}
export default App;
setState传递的是不可变数据
换言之:setState不要改变原始this.state里面的数据。
this.setState()函数执行就会触发shouldComponentUpdate函数执行,只有shouldComponentUpdate函数返回true才会去执行render函数。shouldComponentUpdate返回false,render函数就不会被执行。默认情况下shouldComponentUpdate返回true 所以可以省略直接执行render函数.
shouldComponentUpdate(nextProps, nextState) {
if (nextState.friends !== this.state.friends) {
return true //只有返回true 才会去执行render函数
}
return false
}
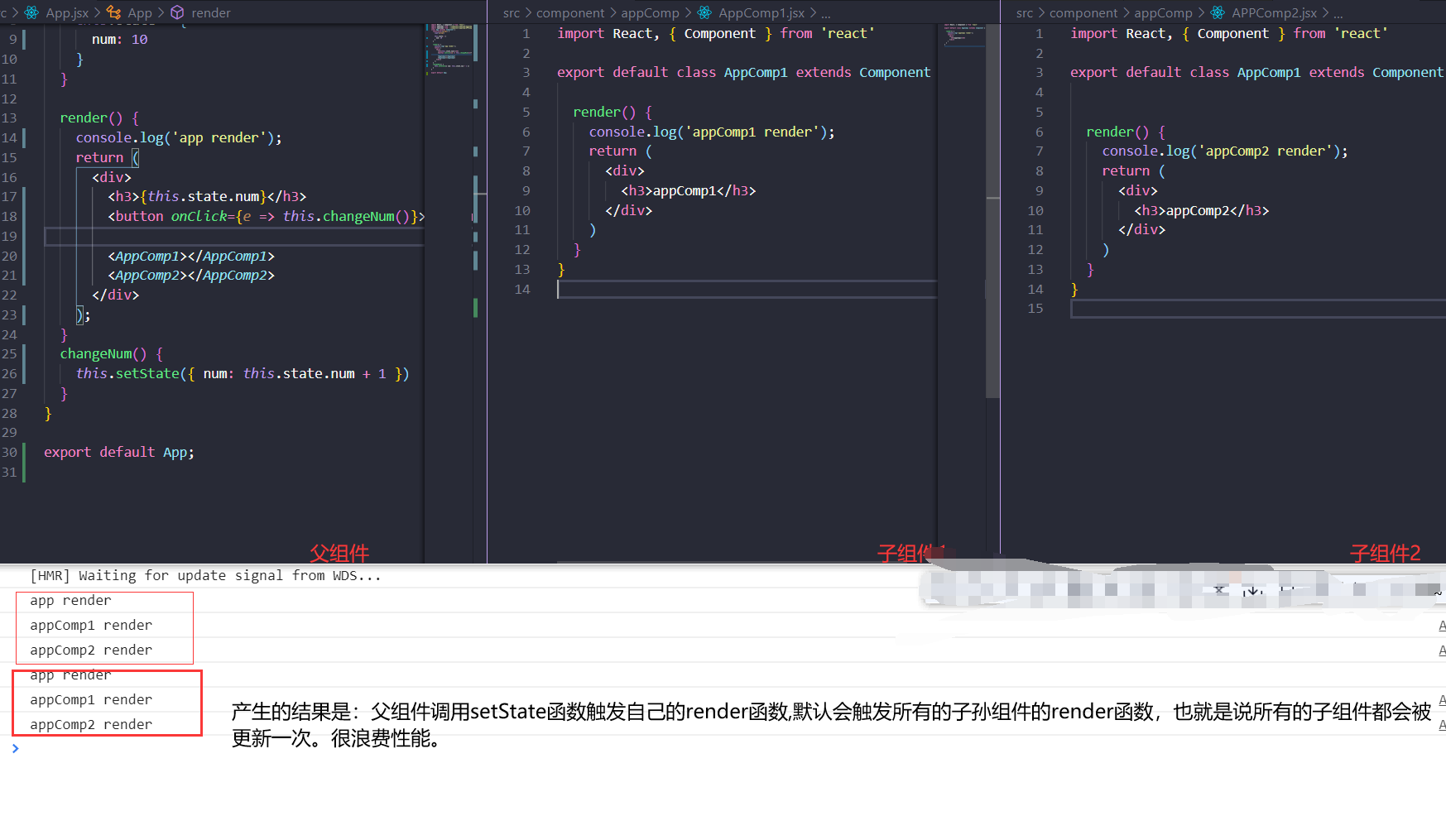
React更新机制
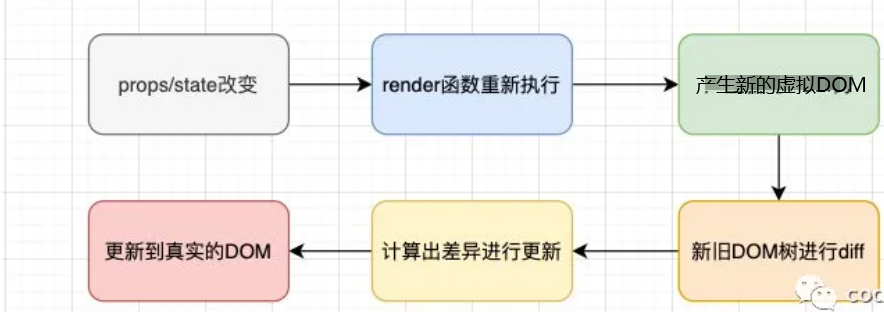



render函数
import { PureComponent } from 'react'
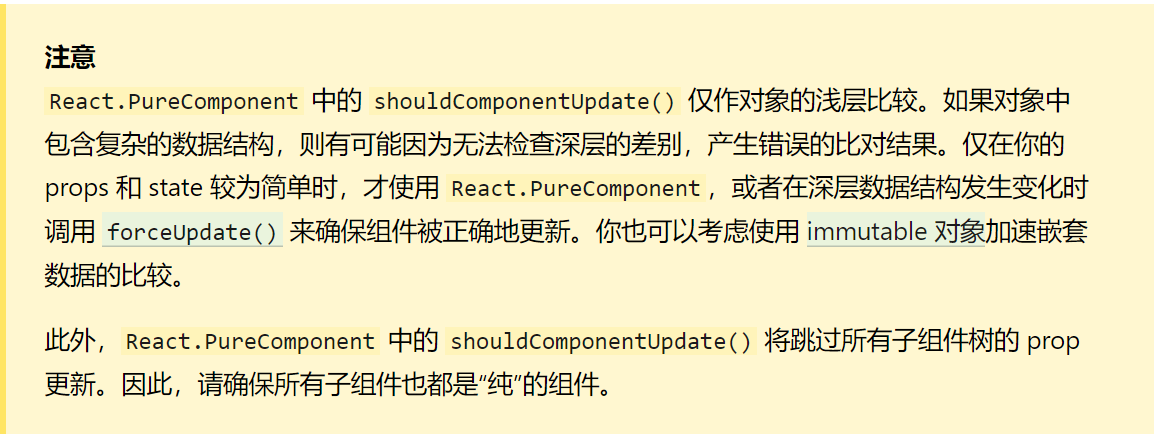
React.PureComponent 中以浅层对比 prop 和 state 的方式来实现了该函数。如果赋予 React 组件相同的 props 和 state,render() 函数会渲染相同的内容,那么在某些情况下使用 React.PureComponent 可提高性能。
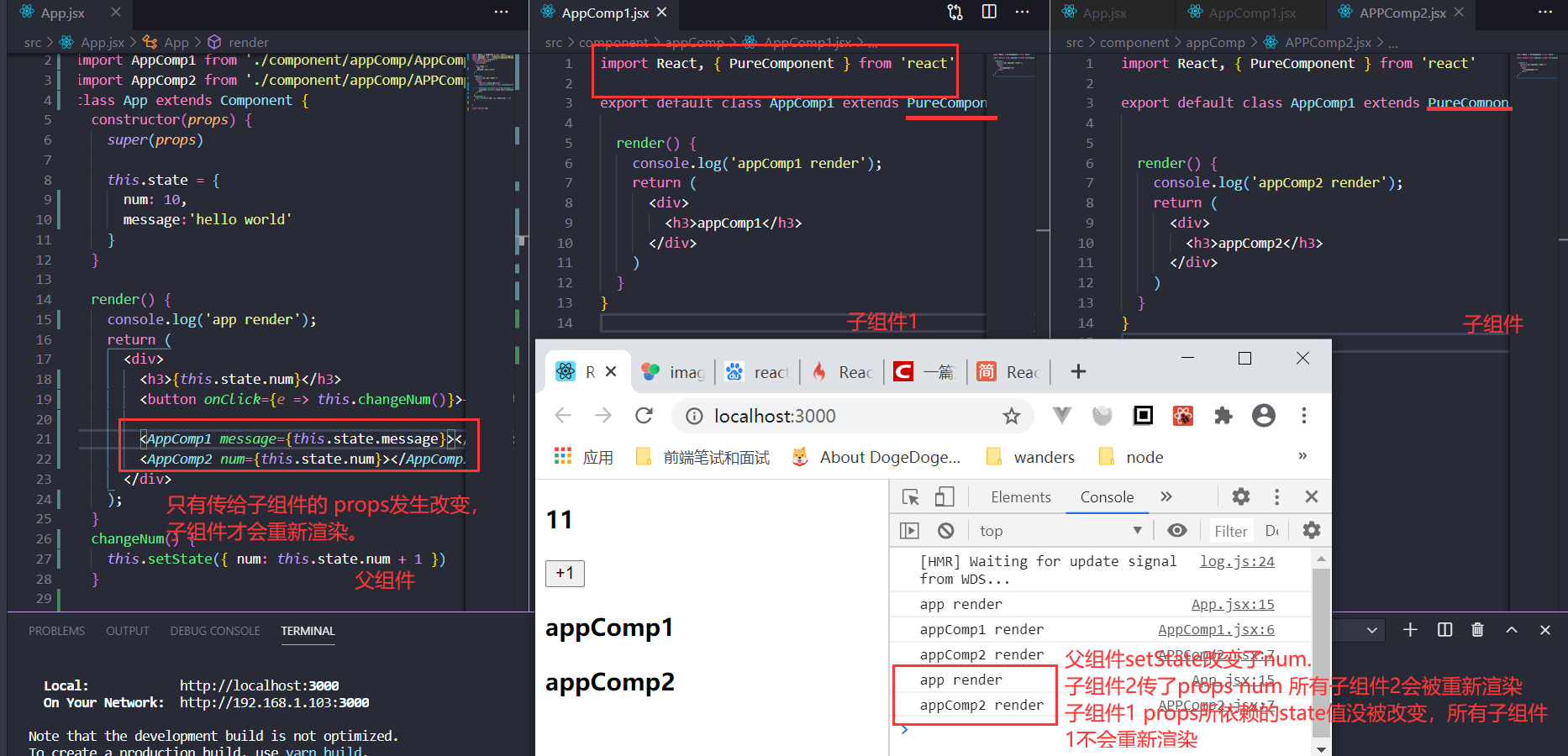
PureComponent&&memo
PureComponent对新旧state props进行浅层比较。如果没发生变化,就不会调用render函数
function checkShouldComponentUpdate(workInProgress, ctor, oldProps, newProps, oldState, newState, nextContext) {
// PureReactComponent 自带isPureReactComponent属性为true
if (ctor.prototype && ctor.prototype.isPureReactComponent) {
return !shallowEqual(oldProps, newProps) || !shallowEqual(oldState, newState); //结果返回false 表示不更新 即render函数不会执行
}
return true;
}
function shallowEqual(objA, objB) {
if (Object.is(objA, objB)) { //setState会返回一个新的对象 所以基本上 这个判断进不去
return true;
}
if (typeof objA !== 'object' || objA === null || typeof objB !== 'object' || objB === null) {
return false;
}
var keysA = Object.keys(objA);
var keysB = Object.keys(objB);
// 说明setState如果加了新属性或者减少 PureComponent也是会更新的
if (keysA.length !== keysB.length) {
return false;
} // Test for A's keys different from B.
for (var i = 0; i < keysA.length; i++) {
// 如果新的没有旧的key 或者新的旧的key对应的value不一样 也是会更新的 比较地址值
//注意点2: 只是对第一层数据的key进行比较,
if (!Object.prototype.hasOwnProperty.call(objB, keysA[i]) || !Object.is(objA[keysA[i]], objB[keysA[i]])) {
return false;
}
}
return true;
}
受控组件和非受控组件
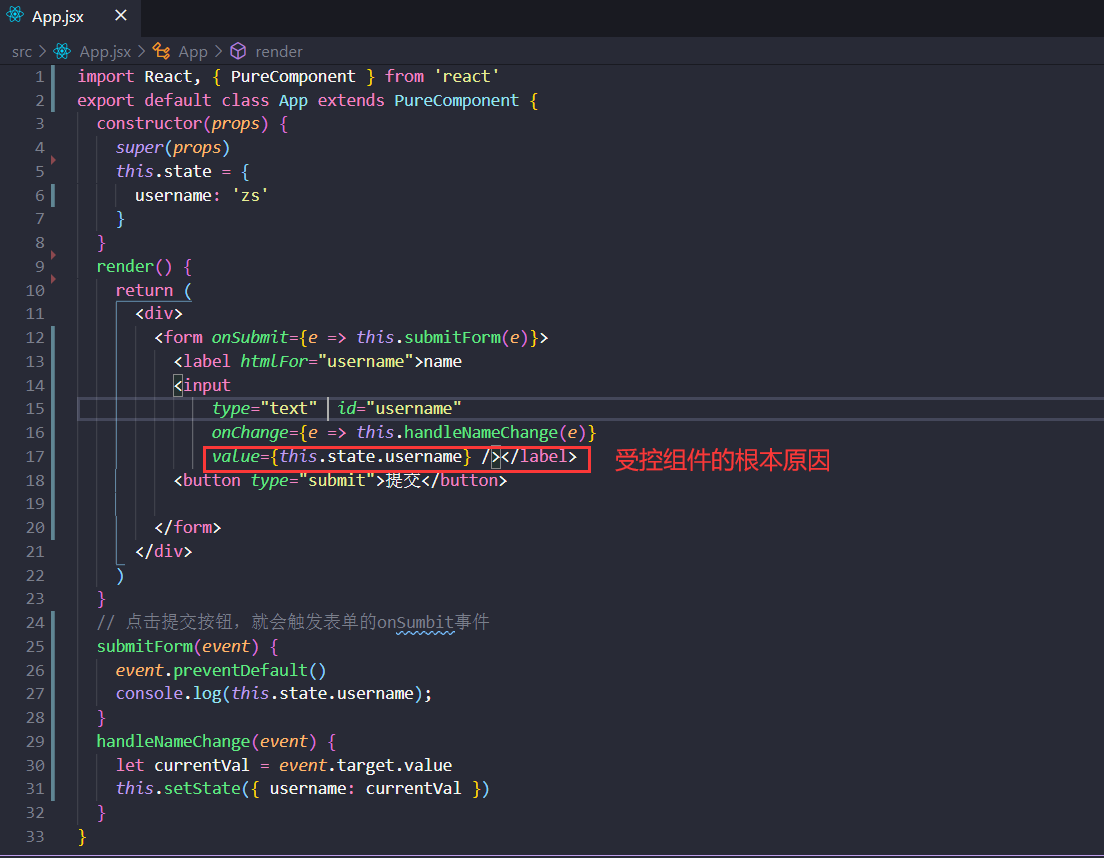
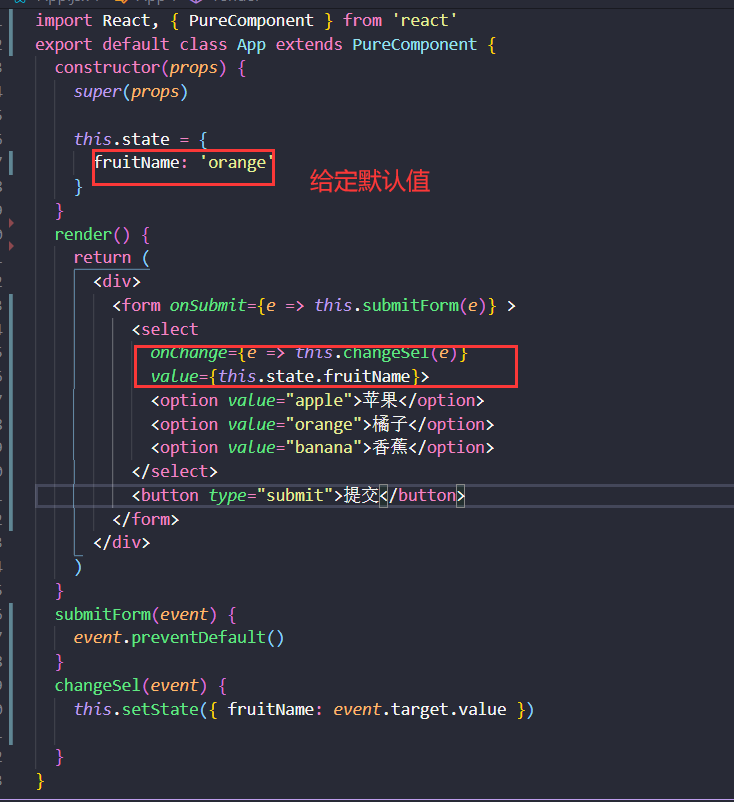
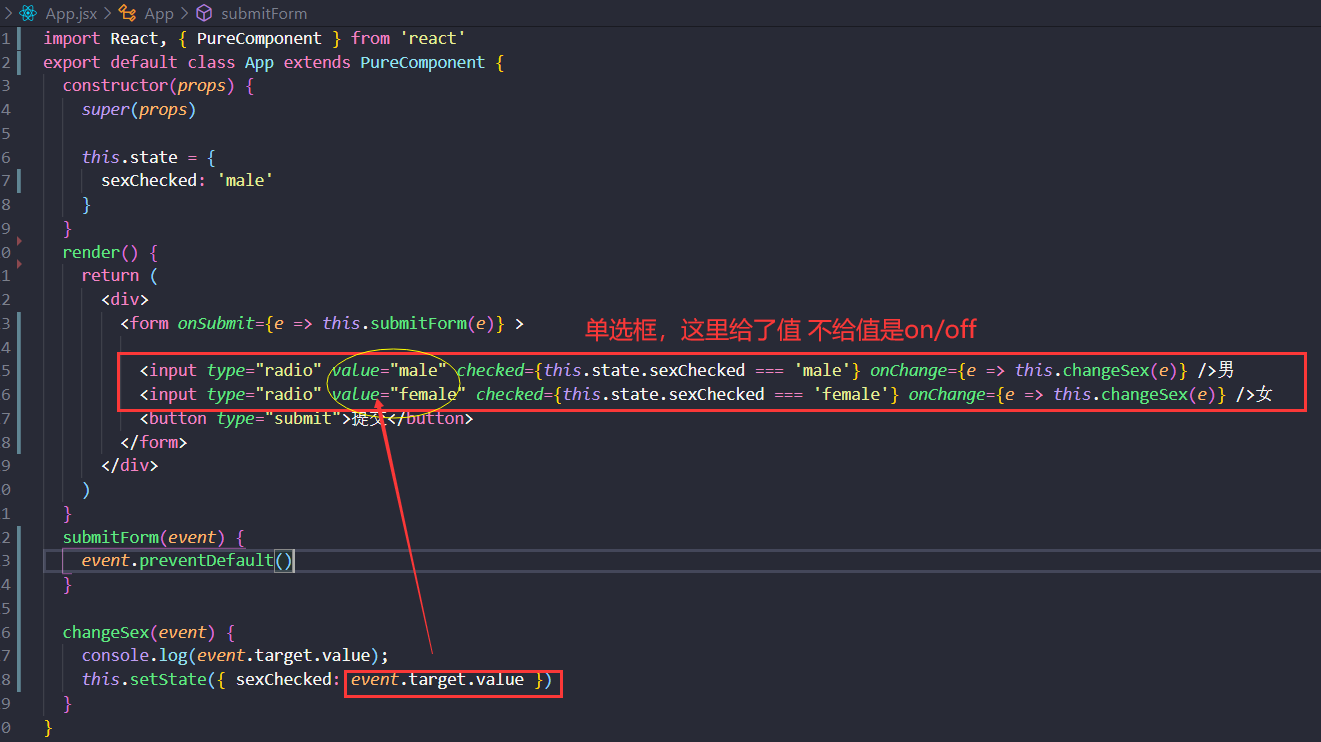
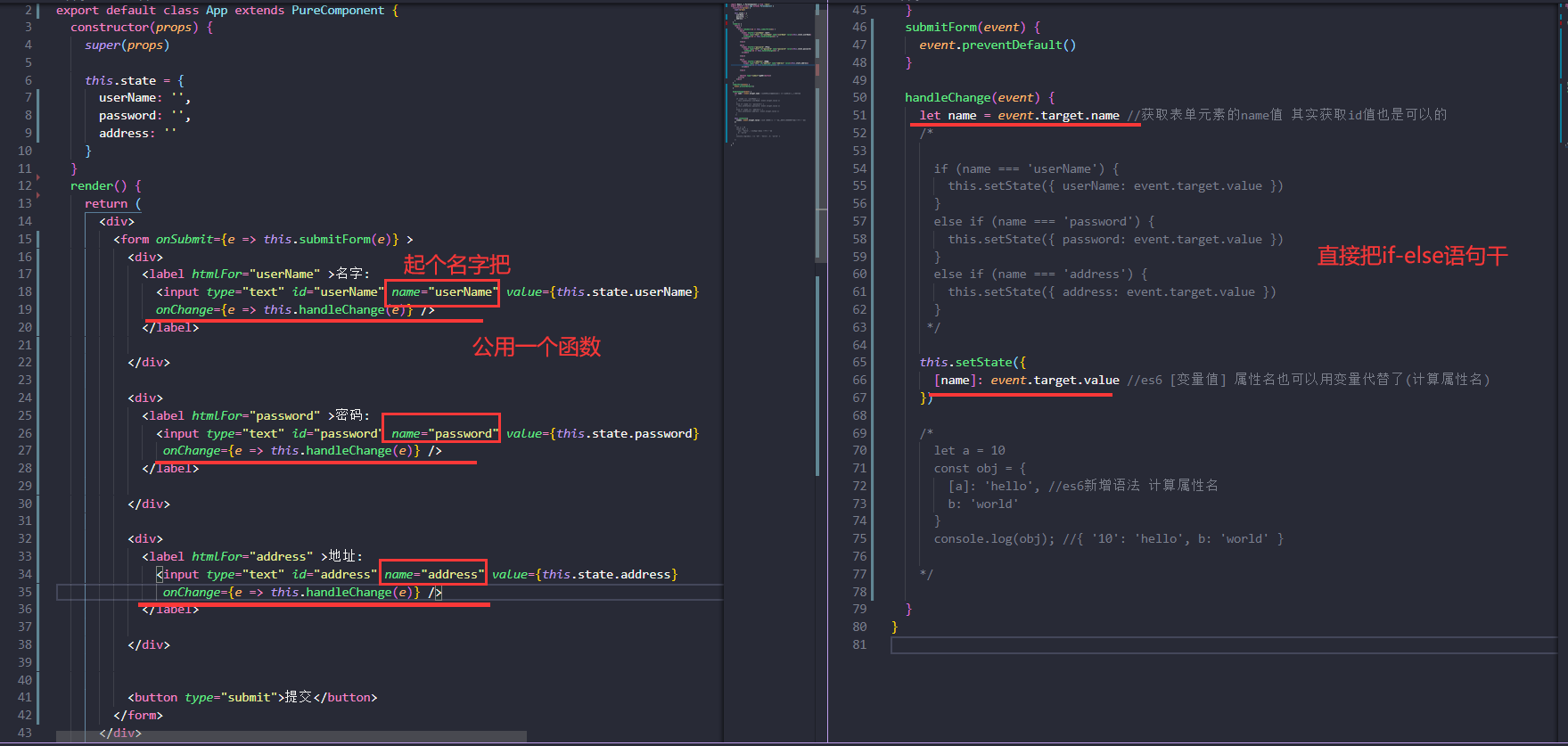
受控组件
在 HTML 中,表单元素(如<input>、 <textarea> 和 <select>)之类的表单元素通常自己维护 state,并根据用户输入进行更新。而在 React 中,可变状态(mutable state)通常保存在组件的 state 属性中,并且只能通过使用 setState()来更新。
我们可以把两者结合起来,使 React 的 state 成为“唯一数据源”。渲染表单的 React 组件还控制着用户输入过程中表单发生的操作。被 React 以这种方式控制取值的表单输入元素就叫做“受控组件”
大白话:由于在表单元素上设置了 value 属性,因此显示的值将始终为 this.state.value,这使得 React 的 state 成为唯一数据源。
多输入
高阶函数
知识待补充。。。
高阶组件HOC
higher-order Component 高阶组件(HOC)是 React 中用于复用组件逻辑的一种高级技巧。HOC 自身不是 React API 的一部分,它是一种基于 React 的组合特性而形成的设计模式。
高阶组件:高阶组件的参数是组件,返回值是新组件的函数。
注意:高阶组件本身不是一个组件而是一个函数。但是这个函数的参数是一个组件A,返回值也是一个组件B。组件B是组件A的父组件。
const EnhancedComponent = higherOrderComponent(WrappedComponent);
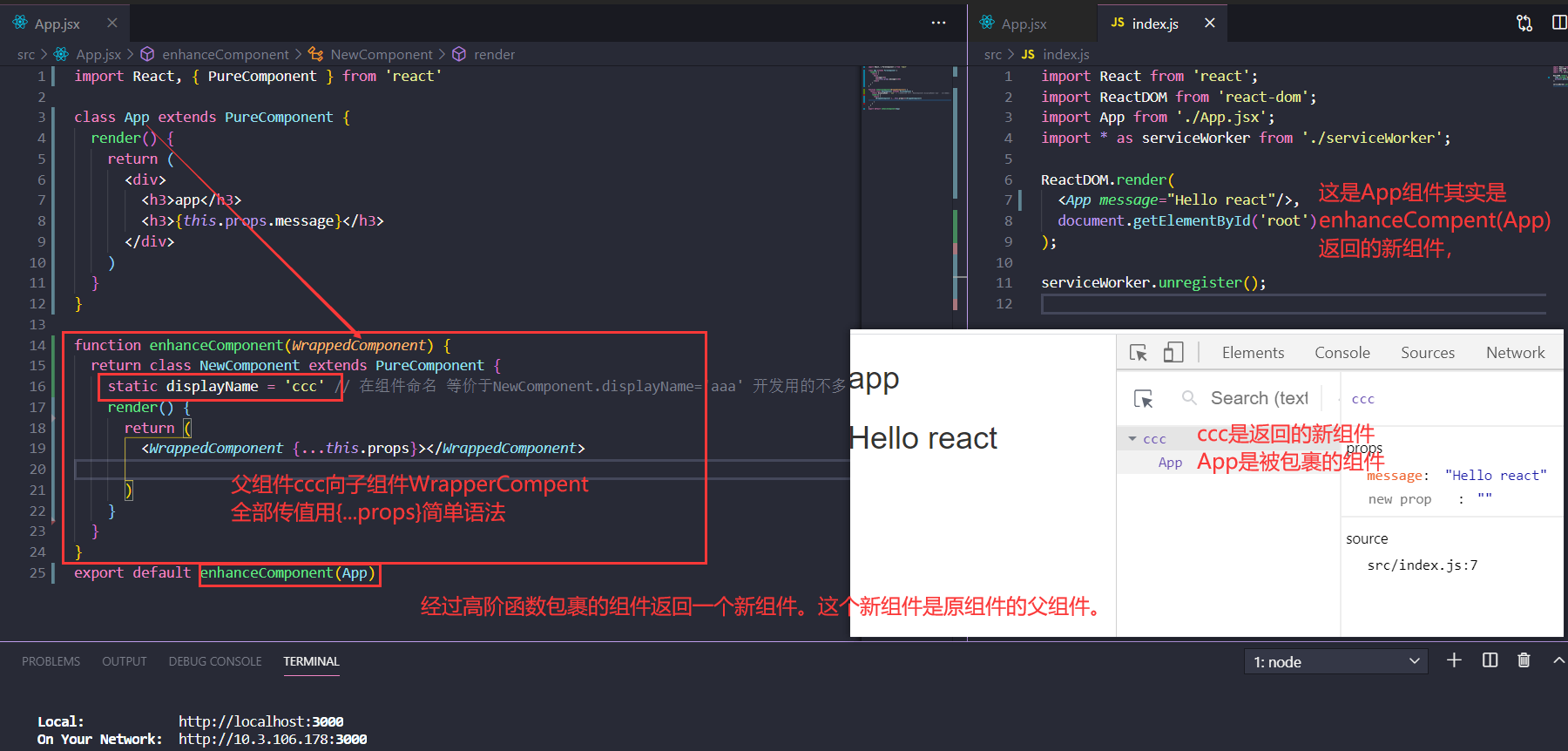
HOC高阶组件
本质就是一个函数highOrderComponent。入参是组件,返回值也是组件。起到了组件劫持的效果
const EnhanceComponent=highOrderComponent(WrapperComponent)
// hoc告诫组件定义形式1 类组件
function enhance(Wrapper) {
return class EnhanceComponent extends PureComponent {
render(){
return (
<div>
<Wrapper {...this.props} region='中国'></Wrapper>
</div>
)
}
}
}
//函数式组件 更清爽不是
function enhance1(Wrapper) {
return function EnhanceComponent(props) { //进化为箭头函数
return <Wrapper {...props} region='中国'></Wrapper> //实现props属性增强。
}
}
//函数式组件 变形 箭头函数形式
function enhance2(Wrapper){
return props=>{
return <Wrapper {...props} regin='中国'></Wrapper>
}
}
简化Context
原始写法。出现的问题是 Son3|Son4里面代码高度重复。
//Fa.jsx
<UserContext.Provider value={{nickName:'zs',level:90,region:'中国'}} >
<Son3 ></Son3>
<Son4 ></Son4>
</UserContext.Provider>
class Son3 extends PureComponent {
render() {
// UserContext.Consumer 比 ContextType 适用性更强 因为UserContext.Consumer在函数式组件和类组件里面都可以使用
return <UserContext.Consumer>
{value => {
return (
<div>
<h4>son3 --{value.nickName}---{value.level}---{value.region}</h4>
</div>
)
}}
</UserContext.Consumer>
}
}
class Son4 extends PureComponent {
render() {
return (
<UserContext.Consumer>
{
user => {
return (<div>
<h4>son4 --{user.nickName}---{user.level}---{user.region}</h4>
</div>)
}
}
</UserContext.Consumer>
)
}
}
Hoc增强做法
//fa.jsx 这个不变
<UserContext.Provider value={{nickName:'zs',level:90,region:'中国'}} >
<Son3 a='1' b='2' ></Son3>
<Son4 ></Son4>
</UserContext.Provider>
//精华在这里。 定义一个高阶组件withUser函数************************************************
export function withUser(Wrapper) {
return props => { //返回的是一个函数式组件
return <UserContext.Consumer>
{value => {
//这里看清楚 是把value属性展开 然后当作props属性来传递的 ==可以的==
return <Wrapper {...props} {...value}></Wrapper>
}}
</UserContext.Consumer>
}
}
//use
class Son3 extends PureComponent {
render() {
return (
<div>
//和普通组件使用的毫无感知一摸一样 ,也是props属性增强 写出更加优化的代码。
<h4>son3 --{this.props.nickName}---{this.props.level}---{this.props.region}</h4>
</div>
)
}
}
export default withUser(Son3) // 高阶函数调用*****************************88
鉴权
判断是否有权限进来这个页面。目的就是为了使用更加优雅 <Son5 isLogin={this.state.isLogin}></Son5>
class LoginPage extends PureComponent {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h4>去登录页面</h4>
</div>
)
}
}
class Son5 extends PureComponent {
render() {
return (
<div>
<h4>son5</h4>
</div>
)
}
}
// use <Son5 isLogin={this.state.isLogin}></Son5>
function withAuth(Wrapper) {
return props => { //props就是外面传的自定义属性
const isLogin = props.isLogin;
if (isLogin) return <Wrapper {...props}></Wrapper>
else return <LoginPage></LoginPage>
}
}
export default withAuth(Son5)
react-css
内联样式
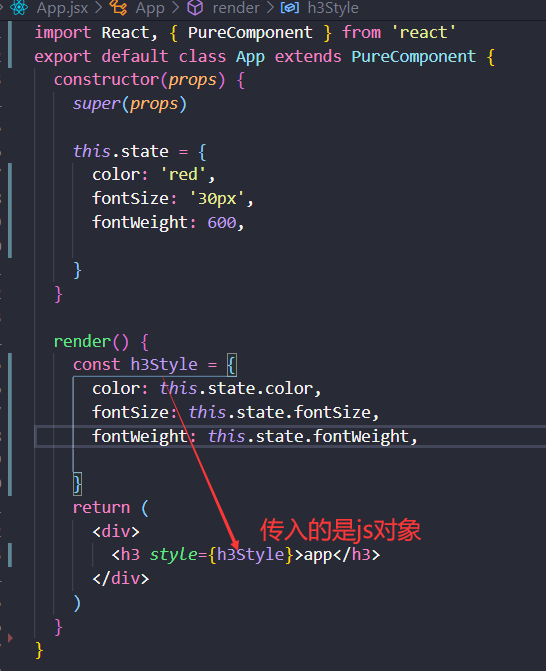
内联样式优点:不同组件之间,样式无论如何都不会发生冲突。可以动态获取到state中的状态。
缺点:写法上需要使用驼峰标识;大量内联样式出现代码混论;伪类和伪元素无法编写


css module
解决各个模块之间,样式不冲突问题。
但是最大的局限是:不能动态使用state状态值。
注意事项:文件命名必须是xxx.module.css;

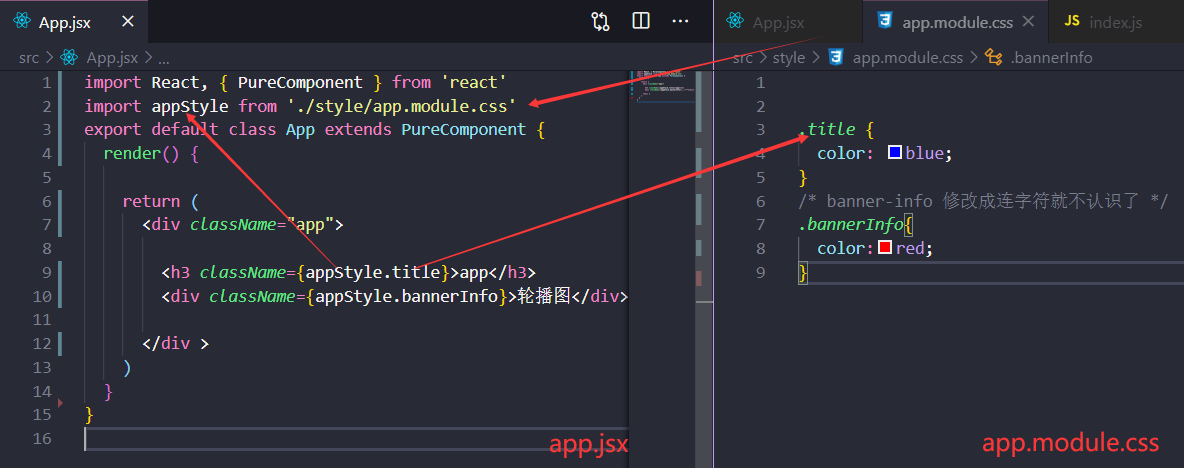
styled-components
函数调用标签模板字符串
const name = 'zs'
const age = 10
const message = `my name is ${name}, age is ${age}`
console.log(message);
// 标签模板字符串 函数调用标签模板字符串
function foo(...args) {
console.log(args);
}
foo`${message}` //[ [ '', '' ], 'my name is zs, age is 10' ]
foo`my name is ${name}, age is ${age}` //[ [ 'my name is ', ', age is ', '' ], 'zs', 10 ]
foo`
font-size:12px;
color:${props=>props.color};
`
css-in-js一种流行库 yarn add styled-components
styled.标签 本质是函数执行 ,返回值是react组件 并且这个组件自带了一些样式 。
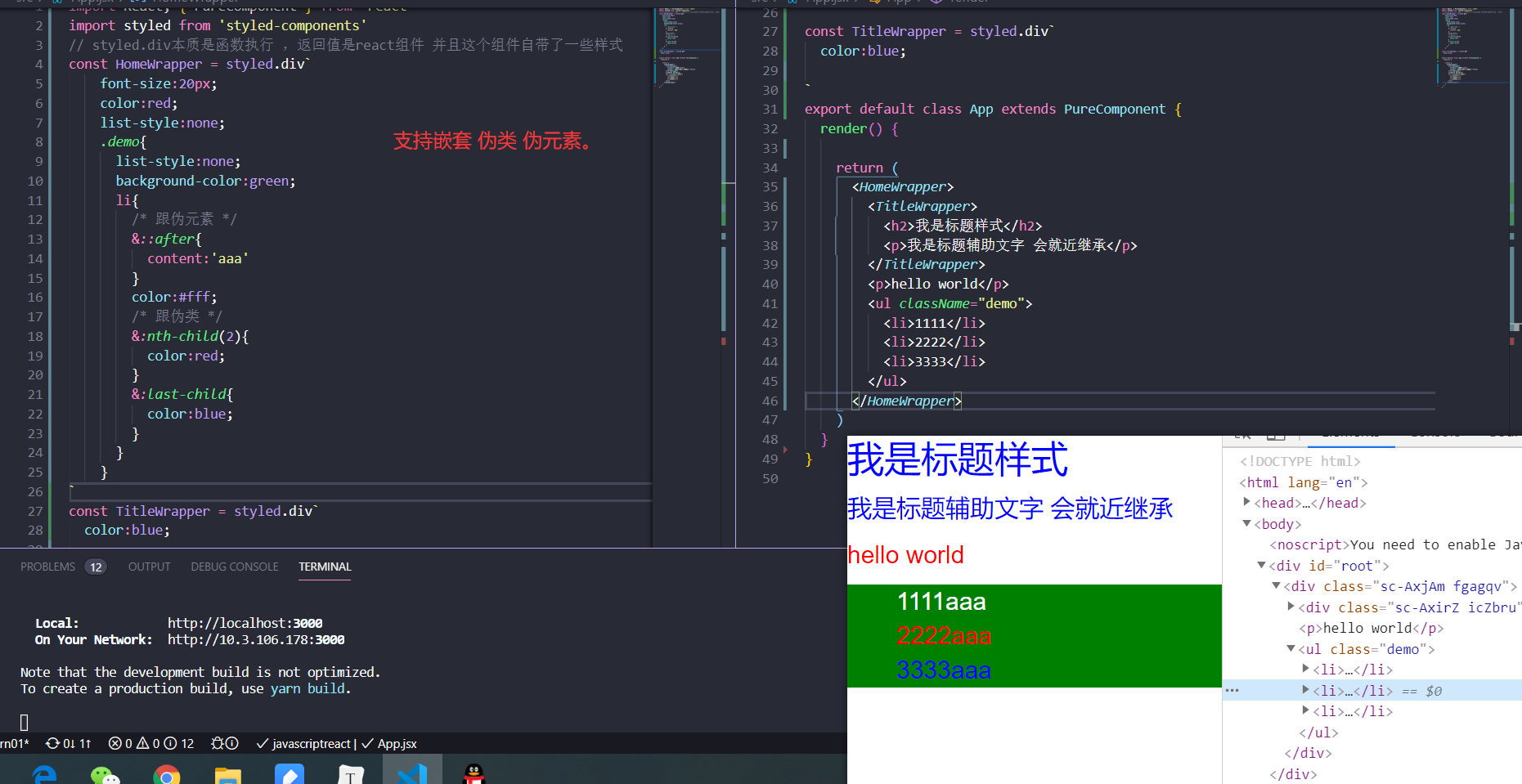
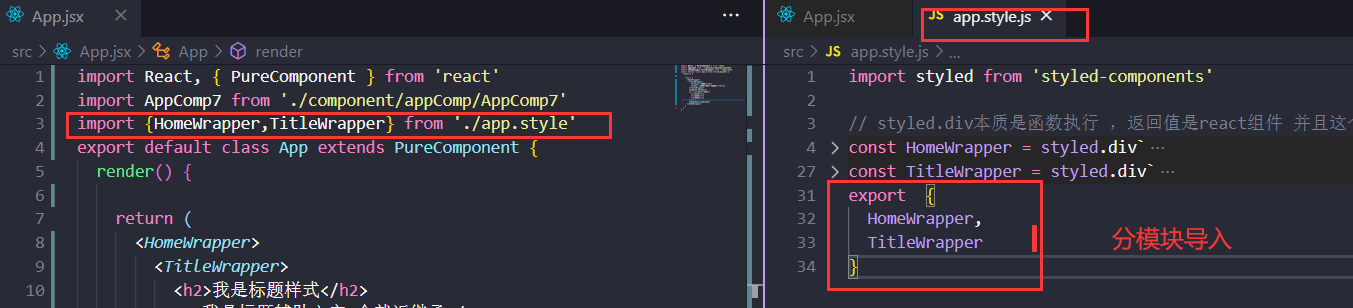
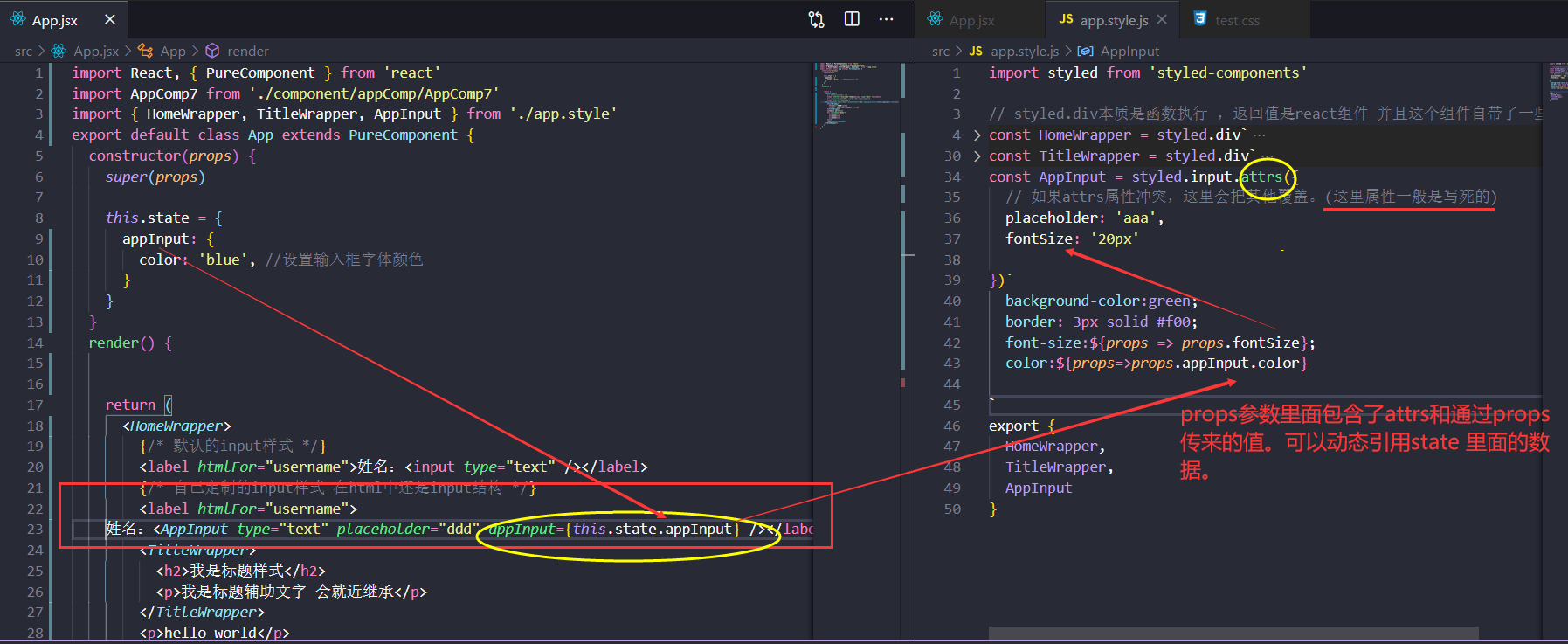
继承(不多)
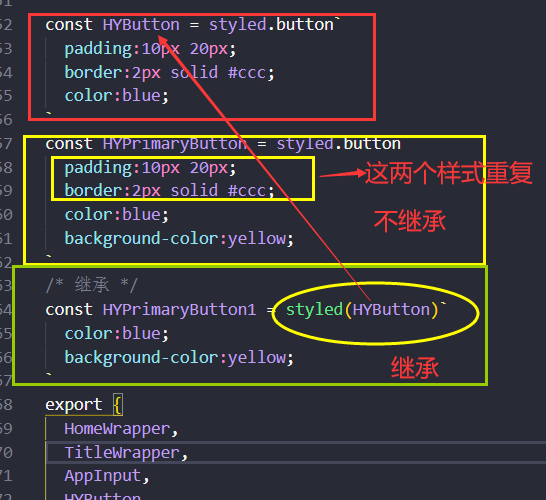
设置共享样式主题
也就是一些公共样式放在一起
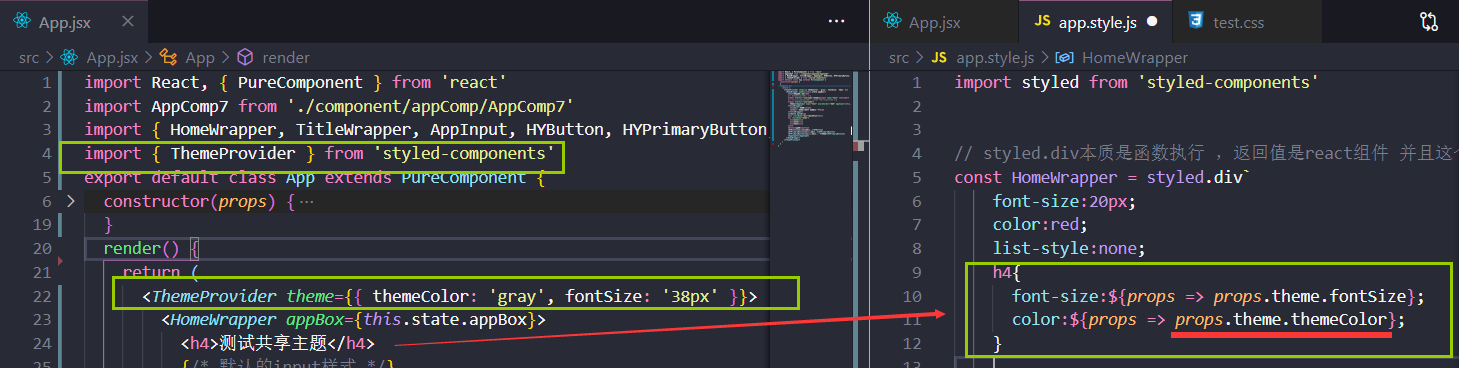
动态添加className
Ant Design of React(antd)
yarn add antd
按需加载
antd 的 JS 代码默认支持基于 ES modules 的 tree shaking。对于js部分,直接引入 import {Button,DataPicker} from "antd"就有按需加载的效果。
craco
https://ant.design/docs/react/use-with-create-react-app-cn
yarn run eject会暴露出来webpack配置进行修改。其实在开发中不建议直接修改webpack配置信息。
yarn add @craco/craco
修改package.json srcipt脚本文件
"scripts": {
"start": "set PORT=3000 && craco start",
"build": "set GENERATE_SOURCEMAP=false && craco build",
"test": "craco test"
},
修改antd内置主题颜色
1.安装 yarn add craco-less
2.新建 craro.config.js
const CracoLessPlugin = require('craco-less');
module.exports = {
plugins: [
{
plugin: CracoLessPlugin,
options: {
lessLoaderOptions: {
lessOptions: {
modifyVars: { '@primary-color': '#1DA57A' },
javascriptEnabled: true,
},
},
},
},
],
}
3.修改主入口文件index.js
// import 'antd/dist/antd.css';
import 'antd/dist/antd.less';
修改项目的别名
//craco.config.js
const CracoLessPlugin = require('craco-less');
const path = require('path');
const resolve = dir => path.resolve(__dirname, dir)
module.exports = {
plugins: [
{
plugin: CracoLessPlugin,
options: {
lessLoaderOptions: {
lessOptions: {
modifyVars: { '@primary-color': '#1DA57A' },
javascriptEnabled: true,
},
},
},
},
],
webpack: {
alias:{
"@":resolve("src"),
"components":resolve("src/components"),
"assets":resolve("src/assets"),
"pages":resolve("src/pages")
}
}
};
动画
yarn add react-transition-group
react-transition-group主要包含4个内置组件
Transition:用的不多
CSSTransition 过渡效果
SwitchTransition 两个组件的显示和隐藏切换效果
TransitionGroup包裹多个组件
CSSTransition:淡入淡出效果
classNames:自定义类名
unmountOnExit:隐藏是否卸载组件,默认不会卸载,
appear:首次进入是否加入动画,默认是不加的,其实不加动画也可以
render() {
return (
<div>
<Button type="primary" onClick={e => this.change()}>显示/隐藏(透明度opacity改变 scale大小缩放)</Button>
<CSSTransition in={this.state.isShow} classNames='demo-card' timeout={300} unmountOnExit={true} appear>
<Card
style={{ width: 300 }}
cover={
<img
alt="example"
src="https://gw.alipayobjects.com/zos/rmsportal/JiqGstEfoWAOHiTxclqi.png" />
}
actions={[
<SettingOutlined key="setting" />,
<EditOutlined key="edit" />,
<EllipsisOutlined key="ellipsis" />,
]}
>
<Meta
avatar={<Avatar src="https://zos.alipayobjects.com/rmsportal/ODTLcjxAfvqbxHnVXCYX.png" />}
title="Card title"
description="This is the description"
/>
</Card>
</CSSTransition>
<div>hhhaha</div>
</div>
)
}
//备注 transform-origin: 50% 50%;默认scale缩放是以中心点。但是根据效果可以改比如 transform-origin:0 0;以左上角缩放
.demo-card-enter,.demo-card-appear{
opacity: 0;
transform: scale(.6);
}
.demo-card-enter-active,.demo-card-appear-active{
opacity: 1;
transition: opacity 300ms, transform 300ms;
transform: scale(1);
}
.demo-card-enter-done,.demo-card-appear-done{
}
.demo-card-exit{
opacity: 1;
transform:scale(1);
}
.demo-card-exit-active{
opacity: 0;
transform:scale(.6);
transition: opacity 300ms, transform 300ms;
}
.demo-card-exit-done{
opacity: 0;
}
SwitchTransition:组件来回切换效果
SwitchTransition要配合CSSTransition使用。并且使用key
//isOn:true
render() {
return (
<div>
<h4>switchTransition</h4>
<span>nihioa</span>
<SwitchTransition mode="out-in">
<CSSTransition key={this.state.isOn ? 'on' : 'off'} classNames='btn' timeout={600}>
<Button type="primary"
onClick={e => this.setState({ isOn: !this.state.isOn })}
>{this.state.isOn ? 'on' : 'off'}</Button>
</CSSTransition>
</SwitchTransition>
</div>
)
}
//SwichTransition效果1
.btn-enter{
opacity: 0;
}
.btn-enter-active{
opacity: 1;
transition:opacity 600ms;
}
.btn-exit{
opacity: 1;
}
.btn-exit-active{
opacity: 0;
transition:opacity 600ms;
}
//SwitchTransition效果2
.btn-enter{
opacity: 0;
transform:translateX(100%)
}
.btn-enter-active{
opacity: 1;
transform:translateX(0);
transition:opacity 600ms,transform 600ms;
}
.btn-exit{
opacity: 1;
transform:translateX(0)
}
.btn-exit-active{
opacity: 0;
transform:translateX(-100%);
transition:opacity 600ms,transform 600ms;
}
TransitionGroup
TransitionGroup添加列表动画
export default class Son3 extends PureComponent {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
list: ['zs', 'lisi', 'wangwu']
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h4>son3</h4>
<button onClick={e => this.addNames()}>addName</button>
<TransitionGroup>
{this.state.list.map((v, i) => {
return (
<CSSTransition key={i} timeout={300} classNames='demo-item'>
<div>{v}</div>
</CSSTransition>
)
})}
</TransitionGroup>
</div>
)
}
addNames() {
this.setState({
list: [...this.state.list, 'shunzi']
})
}
}
.demo-item-enter {
opacity: 0;
transform: scale(.6);
transform-origin:0 0;
}
.demo-item-enter-active {
opacity: 1;
transform: scale(1);
transition: opacity 300ms, transform 300ms;
transform-origin:0 0;
}
.demo-item-enter-done {
/* color:red; */
}
.demo-item-exit {
opacity: 1;
transform: scale(1)
}
.demo-item-exit-active {
opacity: 0;
transform: scale(.6);
transition: opacity 300ms, transform 300ms;
}
.demo-item-exit-done {
opacity: 0;
}
纯函数
纯函数:函数返回值只依赖它的参数(不依赖外部变量),并且在函数执行过程中没有任何的副作用。
副作用:是说函数在执行过程中产生了外部可观察变化。
比如:发送HTTP请求;操作DOM;修改外部数据;console.log()输出打印;调用Date.now和Math.random函数。
所有的React组件都必须像纯函数一样,保护它们的props不被修改(不能修改外部数据)。
redux
redux最基本的使用
redux最基本的使用,已经实现了核心 dispatch->reducer->subscribe(callback)
// import redux from 'redux';
import { createStore } from 'redux'
const initialState = {
counter: 0
}
// reducer 很类似reduce函数啊
function reducer(state = initialState, action) { //state给个默认值
switch (action.type) {
case 'INCREMENT':
return { ...state, counter: state.counter + 1 } //返回新的state
case 'DECREMENT':
return { ...state, counter: state.counter - 1 }
case 'ADD_NUMBER':
return { ...state, counter: state.counter + action.num }
case 'SUB_NUMBER':
return { ...state, counter: state.counter - action.num }
default:
return state //如果没有匹配就把state原路返回
}
}
const store = createStore(reducer)
//订阅在定义dispatch之前 dispatch->reducer->subscribe(callback)
store.subscribe(() => {
console.log(store.getState());
console.log(store.getState().counter);
console.log('------------------------------');
})
//定义action action是普通对象
const action1 = { type: 'INCREMENT' } //递增1
const action2 = { type: 'DECREMENT' } //递减1
const action3 = { type: 'ADD_NUMBER', num: 10 }
const action4 = { type: 'SUB_NUMBER', num: 20 }
//每次派发action,都会触发reducer函数
store.dispatch(action1) //执行reducer
store.dispatch(action2)
store.dispatch(action3)
store.dispatch(action4)
redux目录划分

redux在react里面的简单使用
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'
import store from './store'
import { subAction } from './store/actionCreators'
export default class S2 extends PureComponent {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
counter: store.getState().counter //绑定store里面的值
}
}
render() {
return (
<div>
<h4>son2</h4>
{/* 改变store里面的值 */}
<button onClick={e => store.dispatch(subAction(20))}>-20</button>
<h4>{this.state.counter}</h4>
</div>
)
}
componentDidMount() {
// store里面的值一旦改变,subscribe里面回调函数执行。执行调用setState保持与store值同步
this.unsubscribe = store.subscribe(() => {
this.setState({
counter: store.getState().counter
})
})
}
componentWillUnmount() {
this.unsubscribe() //取消订阅 返回一个函数
}
}
封装connect函数简化代码
//connect.js
import { PureComponent } from "react"
import store from '../08redux/store'
//react 和connect连接在一起
export function connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps) {
return function enhanceHOC(Wrapper) {
return class extends PureComponent {
constructor(props) {
super(props)
this.state = {
storeState: mapStateToProps(store.getState())
}
}
render() {
return (
<Wrapper
{...this.props}
{...mapStateToProps(store.getState())}
{...mapDispatchToProps(store.dispatch)} ></Wrapper>
)
}
componentDidMount() {
this.unsubscribe = store.subscribe(() => {
this.setState({
storeState: mapStateToProps(store.getState())
})
})
}
componentWillUnmount() {
this.unsubscribe()
}
}
}
}
//use connect
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'
import { connect } from '../utils/connect'
import { addAction } from './store/actionCreators'
function S1(props) {
return (
<div>
<h4>son1</h4>
<h4>'state.counter'--????{props.counter}</h4>
<button onClick={e => props.addTen(10)}>+10</button>
</div>
)
}
const mapStateToProps = state => {
return {
counter: state.counter
}
}
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({ //return简写方式 还是返回一个对象而已
addTen(num) {
dispatch(addAction(num))
}
})
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(S1) //重点是这里
react-redux
//1使用Provider
import store from './08redux/store'
import { Provider } from 'react-redux'
import App from './08redux/Fa'
ReactDOM.render(
<Provider store={store}>
<App />
</Provider>,
document.getElementById('root')
);
//2
import React, { PureComponent } from 'react'
// import { connect } from '../utils/connect' //把自己写的注释掉
import {connect} from 'react-redux' //直接用react-redux的connect函数 其他都不变
import { addAction } from './store/actionCreators'
function S1(props) {
return (
<div>
<h4>son1</h4>
<h4>'state.counter'--????{props.counter}</h4>
<button onClick={e => props.addTen(10)}>+10</button>
</div>
)
}
const mapStateToProps = state => {
return {
counter: state.counter
}
}
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({
addTen(num) {
dispatch(addAction(num))
}
})
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(S1)
redux结合异步操作
中间件Middleware
使用中间件:在redux的dispatch和reducer之间,扩展;一些额外的功能。比如异步数据接口,日志,添加代码调试逻辑等
redux-thunk
//store.js/index.js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import thunkMiddleware from 'redux-thunk' //异步请求middleware
import reducer from './reducer'
// 中间件 applyMiddleware(中1,中2,中3)
const storeEnhancer = applyMiddleware(thunkMiddleware)
const store = createStore(reducer, storeEnhancer)
export default store
//store/actionCreators.js 定义getHomeMultiDataAction发送网络请求
import axios from 'axios'
//dispatch是redux-thunk传的参数
export const getHomeMultiDataAction = (dispatch, getState) => {
// console.log(getState()); 上一次的getState
axios({
url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata'
}).then(res => {
const data = res.data.data
dispatch(changeBannerAction(data.banner.list))
dispatch(changeRecommendAction(data.recommend.list))
})
}
//use
import { getHomeMultiDataAction } from './store/actionCreators'
//class组件
componentDidMount() {
this.props.getHomeMultiData()
}
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({
//看这里
getHomeMultiData(){
dispatch(getHomeMultiDataAction) //看清楚 传入getHomeMultiDataAction函数,而不是将它执行
}
})
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(S3)
redux-devtools-extension
调试工具而已
//store.js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import { composeWithDevTools } from 'redux-devtools-extension';
import thunkMiddleware from 'redux-thunk' //异步请求middleware
import reducer from './reducer'
// 中间件 applyMiddleware(中1,中2,中3)
const storeEnhancer = applyMiddleware(thunkMiddleware)
const store=createStore(reducer,composeWithDevTools(storeEnhancer))
export default store
generator结合promise
function* bar() {
const result = yield new Promise((resolve, reject) => {
setTimeout(() => {
resolve(100);
}, 3000)
})
console.log(result); //3000
}
const iter1 = bar()
iter1.next().value.then(res => {
iter1.next(res)
})
redux-saga 异步请求
其实也是拦截dispatch->reducer中间的步骤加入redux-sage的逻辑
//store.js
import { createStore, applyMiddleware } from 'redux'
import { composeWithDevTools } from 'redux-devtools-extension';
import createSagaMiddleware from 'redux-saga' //异步请求middleware
import reducer from './reducer'
import saga from './saga'
const sagaMiddleware = createSagaMiddleware()
// 中间件 applyMiddleware(中1,中2,中3)
const storeEnhancer = applyMiddleware( sagaMiddleware)
const store = createStore(reducer, composeWithDevTools(storeEnhancer))
sagaMiddleware.run(saga)
export default store
//cpnstansant.js
export const FETCH_HOME_NUMTIDATA= 'FETCH_HOME_NUMTIDATA'
//actionCreators
import { FETCH_HOME_NUMTIDATA } from './constants'
export const fetchHomeMultiDataAction = {
type: FETCH_HOME_NUMTIDATA
}
//saga.js
//导出一个生成器函数
import axios from 'axios'
import { takeEvery, put, all, takeLatest } from 'redux-saga/effects'
import { FETCH_HOME_NUMTIDATA } from './constants'
import { changeBannerAction, changeRecommendAction } from './actionCreators'
//自定义迭代器函数
function* fetchHomeNumtiData(action) {
const res = yield axios({
url: 'http://123.207.32.32:8000/home/multidata'
})
const data = res.data.data
yield all([
yield put(changeBannerAction(data.banner.list)),
yield put(changeRecommendAction(data.recommend.list))
])
}
//主函数
export default function* saga() {
yield takeEvery(FETCH_HOME_NUMTIDATA, fetchHomeNumtiData)
}
//use
import { fetchHomeMultiDataAction } from './store/actionCreators'
const mapDispatchToProps = dispatch => ({
fetchHomeMultiData(){
dispatch(fetchHomeMultiDataAction)
}
})
export default connect(mapStateToProps, mapDispatchToProps)(S3)
componentDidMount() {
this.props.fetchHomeMultiData()
}



