python 003作业题:
# 1、分别打印100以内的所有偶数和奇数并存入不同的列表当中
# 2、请写一段Python代码实现删除一个list = [1, 3, 6, 9, 1, 8]# 里面的重复元素不能用set
# 3、将字符串类似:"k:1|k3:2|k2:9" 处理成key:value或json格式,比如{"k": "1", "k3": "2"}
# 4、把字符串user_controller转换为驼峰命名UserController大驼峰在java用作变量命名
# (前英文为大写后英文为小写) 小驼峰:作为变量命名
# 5、给一组无规律的数据从大到小或从小到大进行排序如:list = [2, 6, 9, 10, 18, 15, 1]
# 6、分析以下数字的规律, 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34用Python语言编程实现输出
# #分析题目:根据规律 1+1=2 2+1=3 2+3=5 3+5=8....
# #此为斐波那契数列 (考试题非常多次题目)
# 7、如有两个list:a =['a','b','c','d','e']
# b =[1,2,3,4,5] 将a中的元素作为key b中的元素作为value,将a,b合并为字典
# 8、有如下列表,统计列表中的字符串出现的次数
# # a = ['apple','banana','apple','tomao','orange','apple','banana','watermeton']
# 9、列表推导式求出列表所有奇数并构造新列表 a =[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
1、分别打印100以内的所有偶数和奇数并存入不同的列表当中
# o=[] #定义一个容器存放偶数
# j=[] #定义一个容器存放奇数
# a=0 #当前变量控制循环次数 0 1234567
# while a<=100:
# if a % 2 ==0: #0%2=0 1%2=1 2%2=0 3%2=1
# o.append(a)
# # 条件满足则进入执行:添加偶数
# # 否则添加奇数
# else:
# j.append(a)
# a+=1
# print(o)
# print(j)
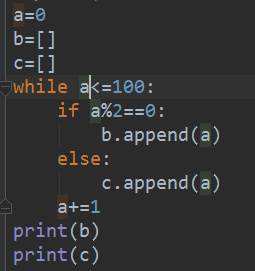
a=0
b=[]
c=[]
while a<=100:
if a%2==0:
b.append(a)
else:
c.append(a)
a+=1
print(b)
print(c)

# # 作业003第一题
# q=[]
# s=[]
# for i in range(0,100,2):
# s.append(i)
# for d in range(1, 100, 2):
# q.append(d)
# print("100以内的偶数:",s)
# print("100以内的奇数:",q)

a=[]
b=[]
for i in range(0,101):
if i%2==0:
a.append(i)
else:
b.append(i)
print(a)
print(b)
# # 2、请写一段Python代码实现删除一个list = [1, 3, 6, 9, 1, 8]# 里面的重复元素不能用set
#方案一:
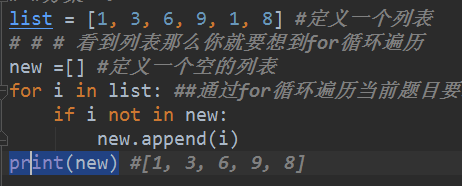
#list = [1, 3, 6, 9, 1, 8] #定义一个列表
# # # 看到列表那么你就要想到for循环遍历
# new =[] #定义一个空的列表
# for i in list: ##通过for循环遍历当前题目要求的列表
# if i not in new:
# new.append(i)
# print(new) #[1, 3, 6, 9, 8]
#
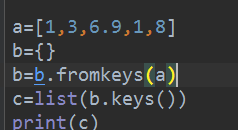
#方法二:使用字典函数
# a = [1, 3,6,9,1,8]
# b = {}
# b = b.fromkeys(a)
# c = list(b.keys())
# print( c)
#方法三:count,remove
# def delList(L):
# for i in L:
# if L.count(i) != 1:
# for x in range((L.count(i) - 1)):
# L.remove(i)
#
# return L
# print(delList([1, 3, 6, 9, 1, 8]))
方法四:
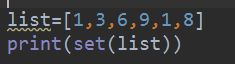
list=[1,3,6,9,1,8]
print(set(list))
方法五:
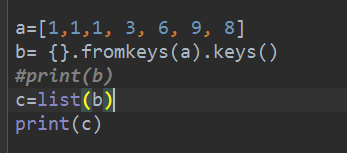
a=[1,1,1, 3, 6, 9, 8]
b= {}.fromkeys(a).keys()
#print(b)
c=list(b)
print(c)
# # 3、将字符串类似:"k:1|k3:2|k2:9" 处理成key:value或json格式,比如{"k": "1", "k3": "2"}
str ="k:1|k3:2|k2:9" #定义一个字符串
a =str.split("|") #将字符串中的|通过split进行分割
# print(a) #['k:1', 'k3:2', 'k2:9']返回一个列表
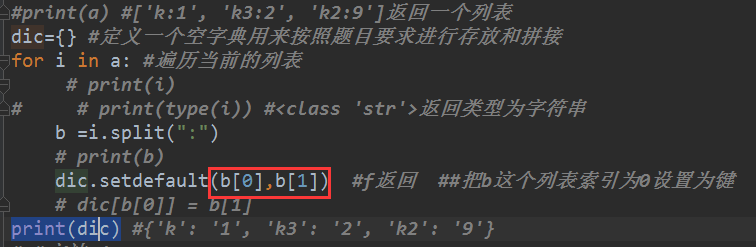
dic={} #定义一个空字典用来按照题目要求进行存放和拼接
for i in a: #遍历当前的列表
# print(i)
# print(type(i)) #<class 'str'>返回类型为字符串
b =i.split(":")
# print(b)
dic.setdefault(b[0],b[1]) #f返回
print(dic) #{'k': '1', 'k3': '2', 'k2': '9'}
方法二:
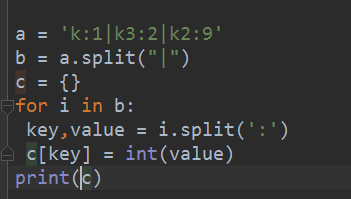
# a = 'k:1|k3:2|k2:9'
# b = a.split("|")
# c = {}
# for i in b:
# key,value = i.split(':')
# c[key] = int(value)
# print(c)
方法三:

print (dict([m.split(':') for m in str.split("|")]))
方法四:

dd = {k: int(v) for k, v in map(lambda x: x.split(':'), str.split('|'))}
print(dd)
#
# # 4、把字符串user_controller转换为驼峰命名UserController大驼峰在java用作变量命名
# # (前英文为大写后英文为小写) 小驼峰:作为变量命名
方法一:
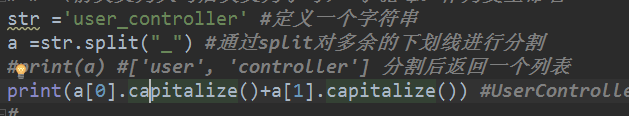
# str ='user_controller' #定义一个字符串
# a =str.split("_") #通过split对多余的下划线进行分割
# print(a) #['user', 'controller'] 分割后返回一个列表
# print(a[0].capitalize()+a[1].capitalize()) #UserController
方法二:
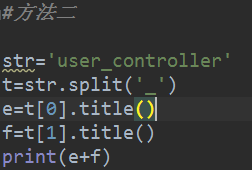
str='user_controller'
t=str.split('_')
e=t[0].title()
f=t[1].title()
print(e+f)
方法三:
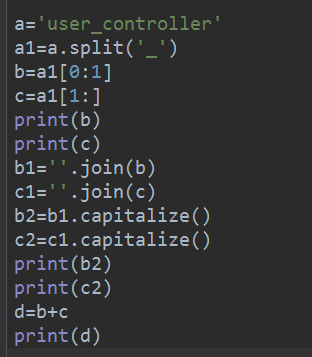
a='user_controller'
a1=a.split('_')
b=a1[0:1]
c=a1[1:]
print(b)
print(c)
b1=''.join(b)
c1=''.join(c)
b2=b1.capitalize()
c2=c1.capitalize()
print(b2)
print(c2)
d=b+c
print(d)
# # 5、给一组无规律的
数据从大到小或从小到大进行排序如:#冒泡排序
# list = [2, 6, 9, 10, 18, 15, 1]
# # 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
list = [2, 6, 9, 10, 18, 15, 1] #定义一个列表
# # 1 2 6 9 10 15 18
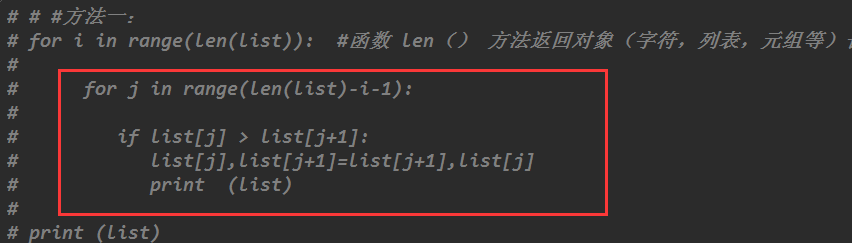
#方法一:
for i in range(len(list)):
for j in range(len(list)-i-1):
if list[j] > list[j+1]:
list[j],list[j+1]=list[j+1],list[j]
print (list)
print (list)
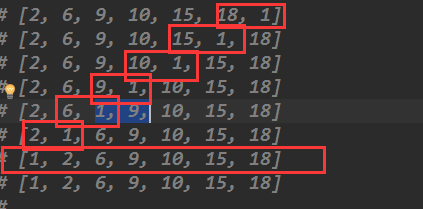
#打印结果:
[2, 6, 9, 10, 15, 18, 1]
[2, 6, 9, 10, 15, 1, 18]
[2, 6, 9, 10, 1, 15, 18]
[2, 6, 9, 1, 10, 15, 18]
[2, 6, 1, 9, 10, 15, 18]
[2, 1, 6, 9, 10, 15, 18]
[1, 2, 6, 9, 10, 15, 18]
[1, 2, 6, 9, 10, 15, 18]
#方法二:
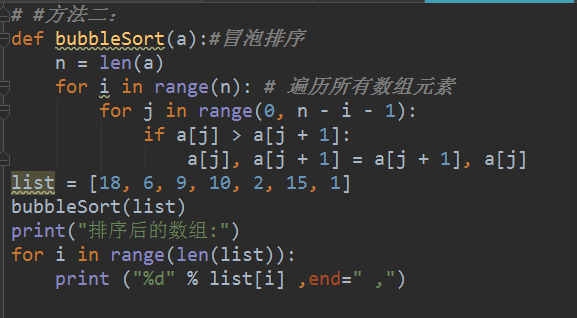
def bubbleSort(a):#冒泡排序
n = len(a)
for i in range(n): # 遍历所有数组元素
for j in range(0, n - i - 1):
if a[j] > a[j + 1]:
a[j], a[j + 1] = a[j + 1], a[j]
a = [64, 34, 25, 12, 22, 11, 90]
bubbleSort(a)
print("排序后的数组:")
for i in range(len(a)):
print ("%d" % a[i])
方法三:
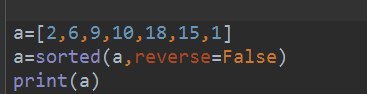
a=[2,6,9,10,18,15,1]
a=sorted(a,reverse=False)
print(a)
方法四:
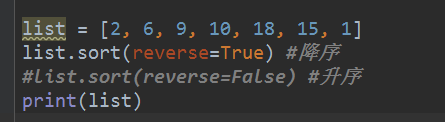
list = [2, 6, 9, 10, 18, 15, 1]
list.sort(reverse=True) #降序
#list.sort(reverse=False) #升序
print(list)
#函数 len() 方法返回对象(字符,列表,元组等)长度或项目的个数
语法:len(str)(计算字符串的长度)
# count =len(list) #将列表中的值的位数进行统计通过len()函数
# print(count) # 7
# for i in range(count): # 0 1 2 3 4 5 6
# # # 0
# # # 1
# for j in range(i+1,count):
# # # 0+1=1 ,7
# # # 123456
# # # 1+1=2 ,7
# # # 23456
# if list[i]>list[j]:
# # # i: 0
# # # i: 1
# # # 2, 6, 9, 10, 18, 15, 1
# # # j: 1 2 3 4 5 6
# # # j: 2 3 4 5 6
# # # 2:>6>9>10>18>15> 1
# # # 6:>9>10>18>15 2
# # # 1 6 9 10 18 15 2
# # # 1 2 9 10 18 15 6
# list[i],list[j]=list[j],list[i] #赋值语法
# print(list)
# #
#
# # 6、分析以下数字的规律, 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34用Python语言编程实现输出
# # #分析题目:根据规律 1+1=2 2+1=3 2+3=5 3+5=8....
# # #此为斐波那契数列 (考试题非常多次题目)
# l =[] #1 1#定义一个空的列表
# for i in range(10): #通过for循环来实现
# # i= 0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9
# if i ==0 or i ==1:
# # 1 1 2 3 5 8 13 21 34 55
# l.append(1)
# else:
# l.append(l[i-2]+l[i-1])
# # i=2 -2=0
# # l[0]+l[1]
# print(l)#[1, 1, 2, 3, 5, 8, 13, 21, 34, 55]
#
#讲解:
#斐波那契数列(Fibonacci sequence),又称黄金分割数列、因数学家列昂纳多·斐波那契(Leonardoda Fibonacci)以兔子繁殖为例子而引入,故又称为“兔子数列”,
# 指的是这样一个数列:1、1、2、3、5、8、13、21、34、……在数学上,斐波纳契数列以如下被以递归的方法定义:F(1)=1,F(2)=1, F(n)=F(n-1)+F(n-2)(n>=2,n∈N*)
#讲解
#递推法
##############################
# 使用`递推法`实现斐波那契数列 #
#############################
def fib_next(n):
first_number = 0
second_number = 1
for _ in range(n):
first_number, second_number = second_number, first_number+second_number
return first_number
if __name__ == '__main__':
[print(fib_next(i),end=',') for i in range(1,15)]
#生成器
def fib_generator(max):
first_number, second_number = 0, 1
while max > 0:
first_number, second_number = second_number, first_number+second_number
max -= 1
yield first_number
if __name__ == '__main__':
[print(i,end=',') for i in fib_generator(15)]
#2递归法
def fib_recursive(n):
assert n >= 0, "n must be larger than 0"
if n <= 1:
return n
return fib_recursive(n-1) + fib_recursive(n-2)
if __name__ == '__main__':
[print(fib_recursive(i),end=',') for i in range(1,15)]
方法三:
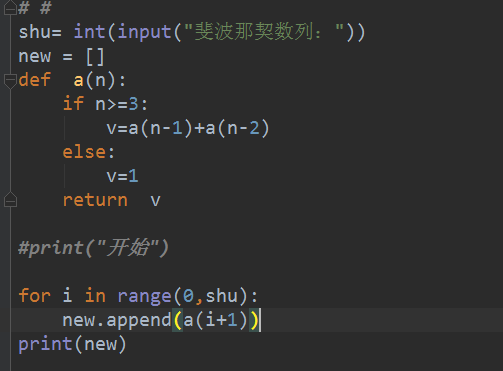
shu= int(input("斐波那契数列:"))
new = []
def a(n):
if n>=3:
v=a(n-1)+a(n-2)
else:
v=1
return v
#print("开始")
for i in range(0,shu):
new.append(a(i+1))
print(new)
# # 7、如有两个
list:
a =['a','b','c','d','e']
b =[1,2,3,4,5]
将a中的元素作为key b中的元素作为value,
# 将a,b合并为字典
#a =['a','b','c','d','e'] #定义一个列表
#b =[1,2,3,4,5] #定义一个列表
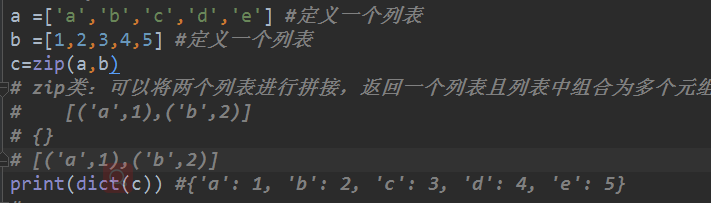
c=zip(a,b)
# zip类:可以将两个列表进行拼接,返回一个列表且列表中组合为多个元组
# [('a',1),('b',2)]
# {}
# [('a',1),('b',2)]
#print(dict(c)) #{'a': 1, 'b': 2, 'c': 3, 'd': 4, 'e': 5}
#
#方法二:
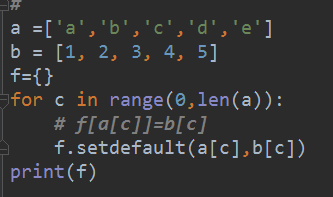
a =['a','b','c','d','e']
b = [1, 2, 3, 4, 5]
f={}
for c in range(0,len(a)):
# f[a[c]]=b[c]
f.setdefault(a[c],b[c])
print(f)
#
# # 8、有如下列表,统计列表中的字符串出现的次数
# # # a = ['apple','banana','apple','tomao','orange','apple','banana','watermeton']
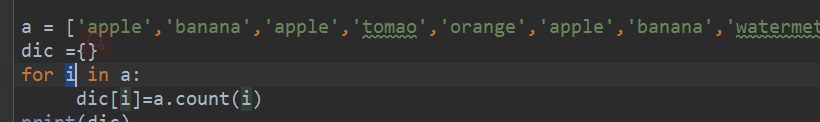
# a = ['apple','banana','apple','tomao','orange','apple','banana','watermeton']
# dic ={}
# for i in a:
# dic[i]=a.count(i)
# print(dic)
#拓展:
#方法二 2.1
# a= [1,2,5,6,7,1,1,3,4,5,5,6,7]
# b = set() #myset是另外一个列表,里面的内容是mylist里面的无重复项
# for i in a:
# print(" %s 出现 %s 次" %(i,a.count(i)))
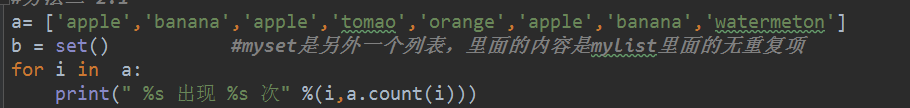
方法三:
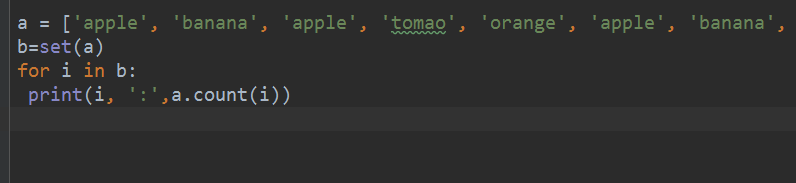
a = ['apple', 'banana', 'apple', 'tomao', 'orange', 'apple', 'banana', 'watermeton']
b=set(a)
for i in b:
print(i, ':',a.count(i))
# #方法2.2
# list = [1,2,3,4,5,4,3,7,2,8,1]
# num_count={}
# for i in list:
# if i not in num_count:
# num_count[i]=1
# else:
# num_count[i]+=1
# print(num_count)
#
# # 9、列表推导式求出列表所有奇数并构造新列表
# # a =[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
# a =[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10] # 定义一个列表
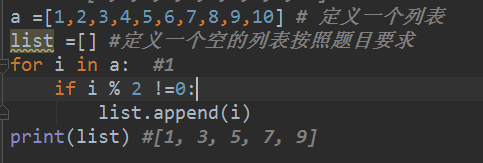
# list =[] #定义一个空的列表按照题目要求
# for i in a: #1
# if i % 2 !=0:
# list.append(i)
# print(list) #[1, 3, 5, 7, 9]
#10、列表推导式求出列表所有偶数并构造新列表
# # # a =[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10]
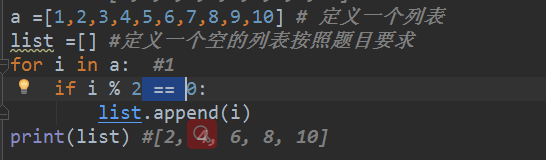
# a =[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10] # 定义一个列表
# list =[] #定义一个空的列表按照题目要求
# for i in a: #1
# if i % 2 == 0:
# list.append(i)
# print(list) #[2, 4, 6, 8, 10]




【推荐】国内首个AI IDE,深度理解中文开发场景,立即下载体验Trae
【推荐】编程新体验,更懂你的AI,立即体验豆包MarsCode编程助手
【推荐】抖音旗下AI助手豆包,你的智能百科全书,全免费不限次数
【推荐】轻量又高性能的 SSH 工具 IShell:AI 加持,快人一步
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语,封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· .NET Core 中如何实现缓存的预热?
· 从 HTTP 原因短语缺失研究 HTTP/2 和 HTTP/3 的设计差异
· AI与.NET技术实操系列:向量存储与相似性搜索在 .NET 中的实现
· 基于Microsoft.Extensions.AI核心库实现RAG应用
· 10年+ .NET Coder 心语 ── 封装的思维:从隐藏、稳定开始理解其本质意义
· 地球OL攻略 —— 某应届生求职总结
· 提示词工程——AI应用必不可少的技术
· Open-Sora 2.0 重磅开源!
· 周边上新:园子的第一款马克杯温暖上架