IO与NIO
'IO
IO流:理解为水流
传统IO:单向(输入/输出),面向流(byte)的。
NIO
建立通道:用于连接,本身不存储数据。
缓冲区:双向
IO与NIO区别
| IO | NIO |
|---|---|
| 面向流 | 面向缓冲区 |
| 阻塞IO | 非阻塞IO |
| 选择器 |
一、缓冲区:
一、底层是数组,用于存储不同类型的数据。根据数据类型的不同,提供不同的缓冲区。
ByteBuffer
CharBuffer
ShortBuffer
IntBuffer
LongBuffer
FloatBuffer
DoubleBuffer
二、通过allocation获取缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf = ByteBuffer.allocation(1024)
三、获取缓冲区的两个核心方法。
put()存入
get()获取
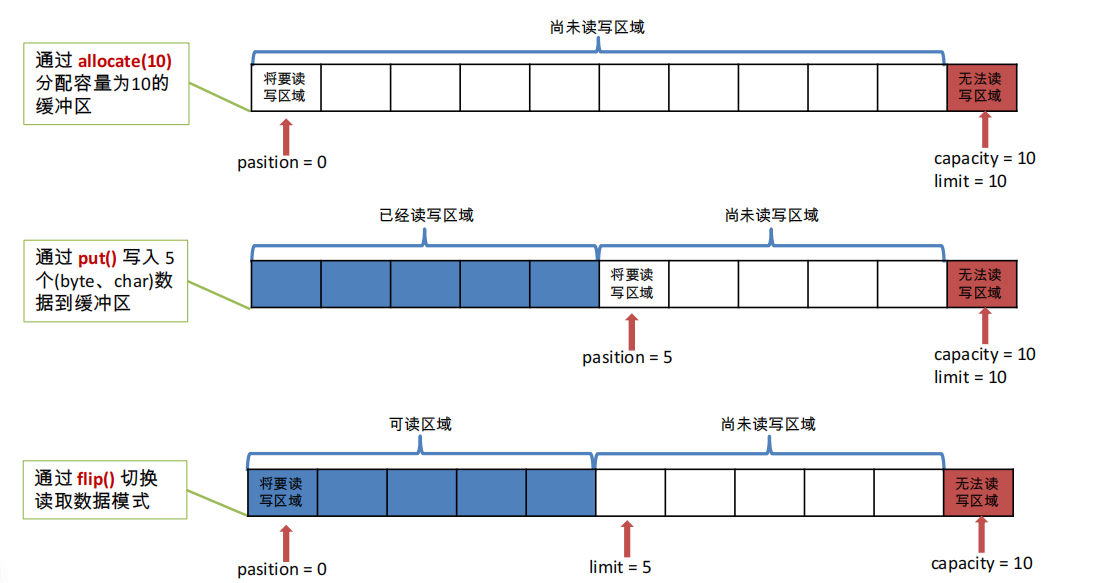
四、缓冲区的核心属性
capacity:容量,缓冲区最大存储数据的容量,一旦申明不能改变。
limit:界限。缓冲区可以操作的数据大小(limit中后,不能进行读写)
position:位置,当前缓冲区中正在操作数据的位置。
mark:标记,标记当前position位置,可通过reset回到标记的位置。
五、直接缓冲区\非直接缓冲区
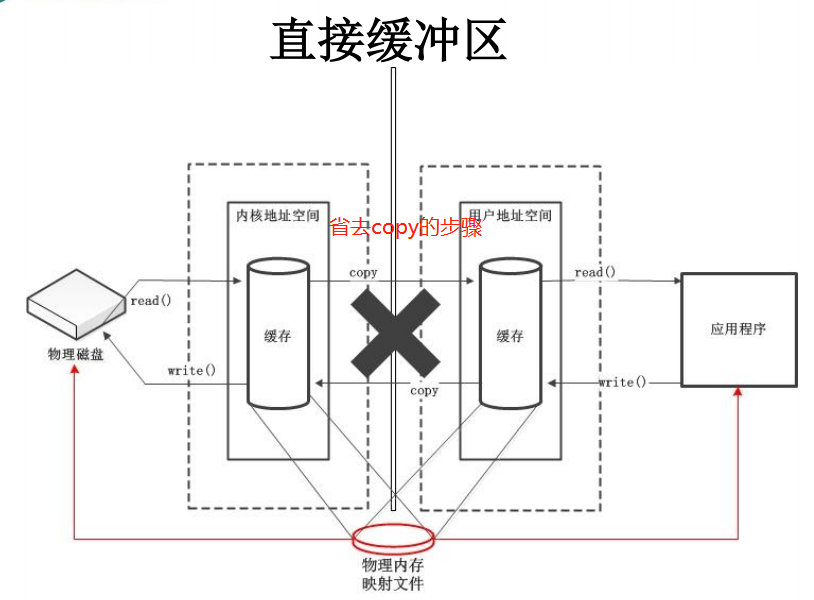
非直接缓冲区(传统IO):通过allocation方法分配缓冲区,将缓冲区建立在JVM内存中。
直接缓冲区(NIO):通过allocationDirect() 方法直接分配缓冲区,将缓冲区建立在物理内存中,提高效率。

六、通道(channel)
1、用于源节点和目标节点的连接,在NIO中负责缓冲区的传输,channel本身不存储数据,需要配合缓冲区进行传输。
2、通道的主要实现类java.nio.channels.Channel 接口
|--FileChannel
|--SocketChannel
|--ServerSocketChannel
|--DatagramChannel
3、获取通道
(1)、Java整对通道提供了getChannel()方法
本地IO:
FileInputStream/FileOutputStream
网络IO:
Socket
ServerSocket
DatagramSocket
(2)在JDK1.7中的NIO.2针对各个通道提供了静态方法open()
(3)在JDK1.7中的NIO.2 Files工具类的newByteChannel()
//利用通道完成文件的复制(非直接缓冲区)
@Test
public void test1(){
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
FileInputStream fis=null;
FileOutputStream fos=null;
FileChannel inChannel=null;
FileChannel outChannel=null;
try{
fis=new FileInputStream("d:/1.avi");
fos=new FileOutputStream("d:/2.avi");
//1.获取通道
inChannel=fis.getChannel();
outChannel=fos.getChannel();
//2.分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf= ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//3.将通道中的数据存入缓冲区中
while(inChannel.read(buf)!=-1){
buf.flip();//切换读取数据的模式
//4.将缓冲区中的数据写入通道中
outChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();//清空缓冲区
}
}catch(IOException e){
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(outChannel!=null){
try {
outChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(inChannel!=null){
try {
inChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fos!=null){
try {
fos.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(fis!=null){
try {
fis.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗费时间:"+(end-start));//耗费时间:1094
}
//使用直接缓冲区完成文件的复制(内存映射文件)
@Test
public void test2() {
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
FileChannel inChannel=null;
FileChannel outChannel=null;
try {
inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:/1.avi"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
outChannel=FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:/2.avi"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
//内存映射文件
MappedByteBuffer inMappedBuf=inChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_ONLY, 0, inChannel.size());
MappedByteBuffer outMappedBuf=outChannel.map(FileChannel.MapMode.READ_WRITE, 0, inChannel.size());
//直接对缓冲区进行数据的读写操作
byte[] dst=new byte[inMappedBuf.limit()];
inMappedBuf.get(dst);
outMappedBuf.put(dst);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(outChannel!=null){
try {
outChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(inChannel!=null){
try {
inChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗费的时间为:"+(end-start));//耗费的时间为:200
}
4、通道之间的数据传输
transferFrom()
transferTo()
@Test
public void test3(){
long start=System.currentTimeMillis();
FileChannel inChannel=null;
FileChannel outChannel=null;
try {
inChannel = FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:/1.avi"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
outChannel=FileChannel.open(Paths.get("d:/2.avi"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.READ,StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
inChannel.transferTo(0, inChannel.size(), outChannel);
outChannel.transferFrom(inChannel, 0, inChannel.size());
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(outChannel!=null){
try {
outChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(inChannel!=null){
try {
inChannel.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
long end=System.currentTimeMillis();
System.out.println("耗费的时间为:"+(end-start));//耗费的时间为:147
}
5、分散与聚集
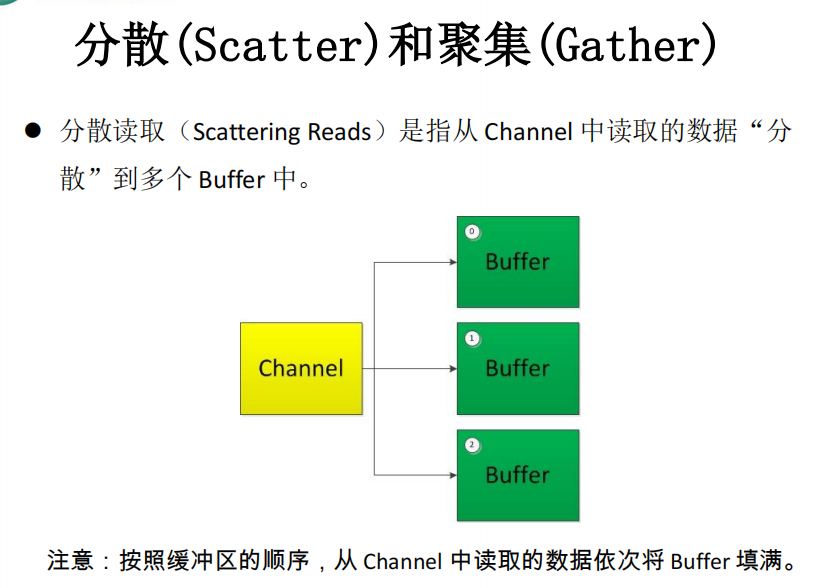
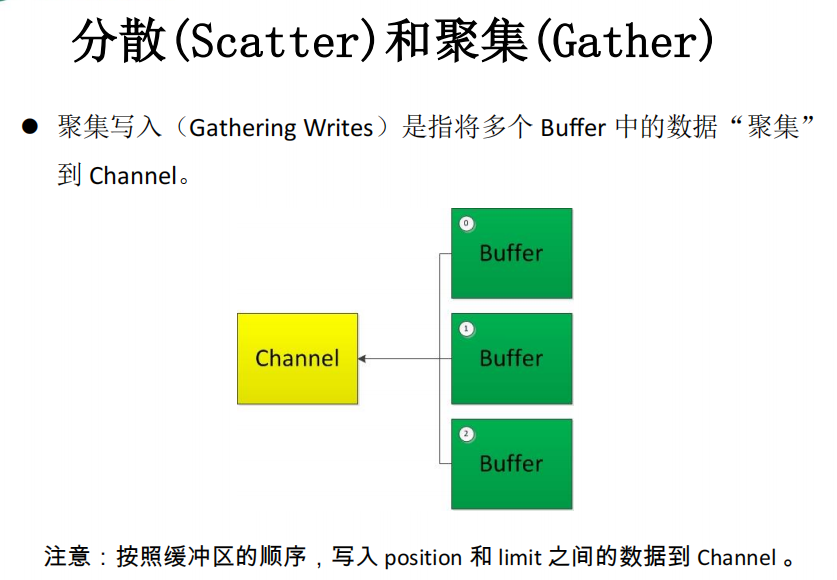
五、分散(Scatter)与聚集(Gather)
分散读取(Scattering Reads):将通道中的数据分散到多个缓冲区中
聚集写入(Gathering Writes):将多个缓冲区中的数据聚集到通道中
//分散和聚集
@Test
public void test4(){
RandomAccessFile raf1=null;
FileChannel channel1=null;
RandomAccessFile raf2=null;
FileChannel channel2=null;
try {
raf1=new RandomAccessFile("1.txt","rw");
//1.获取通道
channel1=raf1.getChannel();
//2.分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf1=ByteBuffer.allocate(100);
ByteBuffer buf2=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//3.分散读取
ByteBuffer[] bufs={buf1,buf2};
channel1.read(bufs);
for(ByteBuffer byteBuffer : bufs){
byteBuffer.flip();
}
System.out.println(new String(bufs[0].array(),0,bufs[0].limit()));
System.out.println("--------------------");
System.out.println(new String(bufs[1].array(),0,bufs[1].limit()));
//4.聚集写入
raf2=new RandomAccessFile("2.txt", "rw");
channel2=raf2.getChannel();
channel2.write(bufs);
}catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}finally{
if(channel2!=null){
try {
channel2.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(channel1!=null){
try {
channel1.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(raf2!=null){
try {
raf2.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
if(raf1!=null){
try {
raf1.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
6、字符集Charset
//字符集
@Test
public void test6(){
Charset cs1= Charset.forName("GBK");
//获取编码器
CharsetEncoder ce=cs1.newEncoder();
//获取解码器
CharsetDecoder cd=cs1.newDecoder();
CharBuffer cBuf= CharBuffer.allocate(1024);
cBuf.put("尚硅谷威武");
cBuf.flip();
//编码
ByteBuffer bBuf=null;
try {
bBuf = ce.encode(cBuf);
} catch (CharacterCodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
for(int i=0;i<12;i++){
System.out.println(bBuf.get());//-64-78-64-78-71-2-7-2-80-55-80-55
}
//解码
bBuf.flip();
CharBuffer cBuf2=null;
try {
cBuf2 = cd.decode(bBuf);
} catch (CharacterCodingException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
System.out.println(cBuf2.toString());//啦啦哈哈吧吧
}
使用NIO完成网络通信的三个核心
1、通道(Channel):负责连接
-
java.nio.channels.Channel 接口: -
|--SelectableChannel -
|--SocketChannel -
|--ServerSocketChannel -
|--DatagramChannel -
|--Pipe.SinkChannel -
|--Pipe.SourceChannel
2、缓冲区:负责数据存取
3、选择器:是 SelectableChannel 的多路复用器。用于监控SelectableChannel的IO状况
七、网络通信
阻塞式
public class TestBlockingNIO {//没用Selector,阻塞型的
//客户端
@Test
public void client() throws IOException{
SocketChannel sChannel=SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1",9898));
FileChannel inChannel=FileChannel.open(Paths.get("1.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.READ);
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while(inChannel.read(buf)!=-1){
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
sChannel.shutdownOutput();//关闭发送通道,表明发送完毕
//接收服务端的反馈
int len=0;
while((len=sChannel.read(buf))!=-1){
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,len));
buf.clear();
}
inChannel.close();
sChannel.close();
}
//服务端
@Test
public void server() throws IOException{
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open();
FileChannel outChannel=FileChannel.open(Paths.get("2.jpg"), StandardOpenOption.WRITE,StandardOpenOption.CREATE);
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898));
SocketChannel sChannel=ssChannel.accept();
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
while(sChannel.read(buf)!=-1){
buf.flip();
outChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
//发送反馈给客户端
buf.put("服务端接收数据成功".getBytes());
buf.flip();//给为读模式
sChannel.write(buf);
sChannel.close();
outChannel.close();
ssChannel.close();
}
}
非阻塞式
public class TestNonBlockingNIO {
//客户端
@Test
public void client()throws IOException{
//1.获取通道
SocketChannel sChannel=SocketChannel.open(new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9898));
//2.切换非阻塞模式
sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//3.分配指定大小的缓冲区
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
//4.发送数据给服务端
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
while(scan.hasNext()){
String str=scan.next();
buf.put((new Date().toString()+"\n"+str).getBytes());
buf.flip();
sChannel.write(buf);
buf.clear();
}
//5.关闭通道
sChannel.close();
}
//服务端
@Test
public void server() throws IOException{
//1.获取通道
ServerSocketChannel ssChannel=ServerSocketChannel.open();
//2.切换非阻塞式模式
ssChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//3.绑定连接
ssChannel.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898));
//4.获取选择器
Selector selector=Selector.open();
//5.将通道注册到选择器上,并且指定“监听接收事件”
ssChannel.register(selector,SelectionKey.OP_ACCEPT);
//6.轮询式的获取选择器上已经“准备就绪”的事件
while(selector.select()>0){
//7.获取当前选择器中所有注册的“选择键(已就绪的监听事件)”
Iterator<SelectionKey> it=selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
//8.获取准备“就绪”的事件
SelectionKey sk=it.next();
//9.判断具体是什么时间准备就绪
if(sk.isAcceptable()){
//10.若“接收就绪”,获取客户端连接
SocketChannel sChannel=ssChannel.accept();
//11.切换非阻塞模式
sChannel.configureBlocking(false);
//12.将该通道注册到选择器上
sChannel.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
}else if(sk.isReadable()){
//13.获取当前选择器上“读就绪”状态的通道
SocketChannel sChannel=(SocketChannel)sk.channel();
//14.读取数据
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
int len=0;
while((len=sChannel.read(buf))>0){
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,len));
buf.clear();
}
}
//15.取消选择键SelectionKey
it.remove();
}
}
}
}
DatagramChannel:Java NIO中的DatagramChannel是一个能收发UDP包的通道。
public class TestNonBlockNIO2 {
@Test
public void send() throws IOException{
DatagramChannel dc=DatagramChannel.open();
dc.configureBlocking(false);
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Scanner scan=new Scanner(System.in);
while(scan.hasNext()){
String str=scan.next();
buf.put((new Date().toString()+"\n"+str).getBytes());
buf.flip();
dc.send(buf, new InetSocketAddress("127.0.0.1", 9898));
buf.clear();
}
dc.close();
}
@Test
public void receive() throws IOException{
DatagramChannel dc=DatagramChannel.open();
dc.configureBlocking(false);
dc.bind(new InetSocketAddress(9898));
Selector selector=Selector.open();
dc.register(selector, SelectionKey.OP_READ);
while(selector.select()>0){
Iterator<SelectionKey> it=selector.selectedKeys().iterator();
while(it.hasNext()){
SelectionKey sk=it.next();
if(sk.isReadable()){
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
dc.receive(buf)
;
buf.flip();
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,buf.limit()));
buf.clear();
}
}
it.remove();
}
}
}
管道
public class TestPipe {
@Test
public void test1()throws IOException{
//1.获取管道
Pipe pipe=Pipe.open();
//2.将缓冲区中的数据写入管道
ByteBuffer buf=ByteBuffer.allocate(1024);
Pipe.SinkChannel sinkChannel=pipe.sink();
buf.put("通过单向管道发送数据".getBytes());
buf.flip();
sinkChannel.write(buf);
//3.读取缓冲区中的数据
Pipe.SourceChannel sourceChannel=pipe.source();
buf.flip();
int len=sourceChannel.read(buf);
System.out.println(new String(buf.array(),0,len));
sourceChannel.close();
sinkChannel.close();
}
}



