C++11新特性
补充一下C++11新特性,被问到了
来源于:https://www.cnblogs.com/skyfsm/p/9038814.html
1,nullptr
nullptr 出现的目的是为了替代 NULL(某些编译器把NULL定义为0)。
专门用来区分空指针、0
nullptr 的类型为 nullptr_t
能够隐式的转换为任何指针或成员指针的类型,也能和他们进行相等或者不等的比较。
当需要使用 NULL 时候,养成直接使用 nullptr的习惯。
2,auto关键字
类型推导,注意个别的用法(不能推导数组)
常用于迭代器的类型推导
for(vector<int>::const_iterator itr = vec.cbegin(); itr != vec.cend(); ++itr)
我们用auto就比较简单了
// 由于 cbegin() 将返回 vector<int>::const_iterator // 所以 itr 也应该是 vector<int>::const_iterator 类型 for(auto itr = vec.cbegin(); itr != vec.cend(); ++itr); 也可以用begin()
3,区间迭代(范围for)就是foreach
// & 启用了引用 for(auto &i : arr) { std::cout << i << std::endl; }
4. Lambda 表达式
lambda 表达式,实际上就是提供了一个类似匿名函数的特性,而匿名函数则是在需要一个函数,但是又不想费力去命名一个函数的情况下去使用的。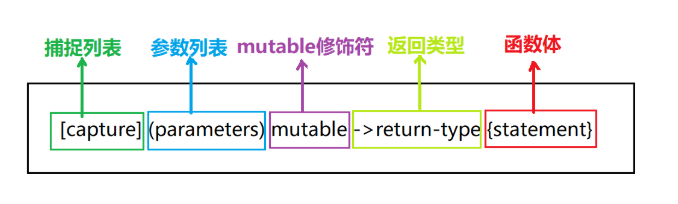
一般情况下参数修饰符和返回类型可以省略
[捕获区](参数区){代码区};
vector<int> vec = {1,3,2,34,2,11};
int m = [](int x) { return [](int y) { return y * 2; }(x)+6; }(5);
cout << m << endl;
auto func1 = [](int i) { return i + 4; }(2); // int i 这个i的值是2,
cout << func1 << endl; // 6
auto f5 = [](int a, int b) {return a + b; };
cout << f5(1,2);
// i 这个也可以从前面获取
sort(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](int a, int b){return a < b;});
for(auto it : vec) // 1 2 2 3 11 34
cout << it <<" ";
cout << endl;
// for_each 遍历
for_each(vec.begin(), vec.end(), [](int a){cout <<a << " ";});
// 1 2 2 3 11 34
- [a,&b] 其中 a 以复制捕获而 b 以引用捕获。
- [this] 以引用捕获当前对象(
*this) - [&] 以引用捕获所有用于 lambda 体内的自动变量,并以引用捕获当前对象,若存在
- [=] 以复制捕获所有用于 lambda 体内的自动变量,并以引用捕获当前对象,若存在
- [] 不捕获,大部分情况下不捕获就可以了
一般使用场景:sort等自定义比较函数、用thread起简单的线程。
详解
https://www.cnblogs.com/xiaokang01/p/12589505.html
5.列表初始化
使用{} 进行列表初始化
int a = {1};
6.=default和=delete
对于 C++ 的类,如果程序员没有为其定义特殊成员函数,那么在需要用到某个特殊成员函数的时候,编译器会隐式的自动生成一个默认的特殊成员函数,
比如拷贝构造函数,或者拷贝赋值操作符。
C++11允许我们使用=default来要求编译器生成一个默认构造函数,也允许我们使用=delete来告诉编译器我们虽然定义了它,但是不能使用它
class B { B() = default; //显示声明使用默认构造函数 B(const B&) = delete; //我们虽然定义了它,但是我们不能使用它 ~B() = default; //显示声明使用默认析构函数 B& operator=(const B&) = delete; //我们虽然定义了它,但是不能使用它。 B(int a); };
8.final和override
override对虚函数进行覆盖
原本希望派生类能够覆盖掉基类的虚函数,结果参数列表写错了,导致没有覆盖成功。
使用override可以防止这种情况出现(如果写了override但是列表写错了,就会报错)
struct B { virtual void f1(int) const; virtual void f2(); void f3(); }; struct D1 : public B { void f1(int) const override; //ok 覆盖基类的f1函数 void f2(int) override; //error,B中没有形如f2(int)的函数 (这个就是参数列表写错的情况) void f3() override; //error,f3不是虚函数 void f4() override; //error,B中无f4函数 };
struct D2 : public B { void f1(int) const final; //不许后续的其他类覆盖 }; struct D3 :public D2 { void f2(); void f1(int) const; //error,final函数不可覆盖 };
final还可以用于防止继承发生(我们不想让这个类发生继承)
class NoDerived final { }; class Bad :NoDerived //NoDerived不可做基类 { }; class Base { }; class Last final :Base { }; class Bad2 :Last //Last不可做基类 { }
9.std::array
std::array 会在编译时创建一个固定大小的数组,std::array 不能够被隐式的转换成指针,使用 std::array 很简单,只需指定其类型和大小即可
#include <array> void foo(int* p) { } int main() { std::array<int, 4> arr = {4,3,1,2}; foo(&arr[0]); //OK foo(arr.data()); //OK //foo(arr); //wrong std::sort(arr.begin(), arr.end()); //排序 return 0; }
初始化
array<int,10> a1; // 10个默认初始化的int
array<int,5>a2 = {1,3,4,5,6}; // 列表初始化
array<int,10>a3 = {0}; // a3[0] 为42剩余的为0
array支持拷贝,而内置数组类型不支持
int arr[5] = {2,3,4,6,7};
int cop[5] = arr; // 错误
array<int,5>a2 = {1,3,4,5,6};
array<int 5>copy = a2; // 正确,只要数组类型匹配就合法
10.std::unordered_map和std::unordered_set
无序容器中的元素是不进行排序的,内部通过 Hash 表实现,插入和搜索元素的平均复杂度为 O(constant),
在不关心容器内部元素顺序时,能够获得显著的性能提升。
C++11 引入了两组无序容器:std::unordered_map/std::unordered_multimap 和 std::unordered_set/std::unordered_multiset。
下面给出unordered_map和unordered_set的使用方法。
#include <stdio.h> #include <algorithm> #include <iostream> #include <string> #include <unordered_map> #include <unordered_set> void foo(int* p) { } int main() { //unordered_map usage std::unordered_map<std::string, int> um = { {"2",2},{"1",1},{"3",3} }; //遍历 for (const auto &n : um) { std::cout << "key:" << n.first << " value:" << n.second << std::endl; } std::cout << "value:" << um["1"] << std::endl; //unordered_set usage std::unordered_set<int> us = { 2,3,4,1}; //遍历 for (const auto &n : us) { std::cout << "value:" << n << std::endl; } std::cout << "value:" << us.count(9) << std::endl; //判断一个数是否在集合内,1存在0不存在 std::cout << "value:" << *us.find(1) << std::endl; //查找一个特定的数是否在集合内,找到就返回该数的迭代器位置 return 0; }
11.智能指针
shared_ptr使用引用计数,每一个shared_ptr的拷贝都指向相同的内存。
每使用他一次,内部的引用计数加1,每析构一次,内部的引用计数减1,减为0时,删除所指向的堆内存。
shared_ptr内部的引用计数是安全的,但是对象的读取需要加锁。
#include <stdio.h> #include <memory> #include <iostream> int main() { //auto ptr = std::make_shared<int>(10); std::shared_ptr<int> ptr(new int(10)); std::shared_ptr<int> ptrC(ptr); auto ptr2 = ptr; { auto ptr3 = ptr2; std::cout << "pointer1.use_count() = " << ptr.use_count() << std::endl; //4 std::cout << "pointer2.use_count() = " << ptr2.use_count() << std::endl; //4 } std::cout << "pointer1.use_count() = " << ptr.use_count() << std::endl; //3 std::cout << "pointer2.use_count() = " << ptr2.use_count() << std::endl; //3 int *p = ptr.get(); //获取原始指针 std::cout << "pointer1.use_count() = " << ptr.use_count() << std::endl; //3 std::cout << "pointer2.use_count() = " << ptr2.use_count() << std::endl; //3 return 0; }
2. std::unique_ptr
std::unique_ptr 是一种独占的智能指针,它禁止其他智能指针与其共享同一个对象,从而保证代码的安全:
#include <stdio.h> #include <memory> #include <iostream> int main() { std::unique_ptr<int> ptr(new int(10)); //auto ptr2 = ptr; //非法 //虽说unique_ptr是不可复制的,但我们可以使用std::move将其独占权转移到其他的unique_ptr auto ptr2(std::move(ptr)); std::cout << *ptr2 << std::endl; return 0; }
std::weak_ptr
先观察下面的代码,如果我们在类father中使用的是shared_ptr son的话,father和son的实例并没有顺利回收,输出如下:
father !
son!
以上问题就是shared_ptr的环形引用问题。为了避免shared_ptr的环形引用问题,需要引入一个弱引用weak_ptr, weak_ptr是为了配合shared_ptr而引入的一种智能指针,弱引用不会引起引用计数增加,它更像是shared_ptr的一个助手而不是智能指针,因为它不具有普通指针的行为,没有重载operator*和->,它的最大作用在于协助shared_ptr工作,像旁观者那样观测资源的使用情况.
#include <iostream> #include <memory> using namespace std; class father; class son; class father { public: father() { cout << "father !" << endl; } ~father() { cout << "~~~~~father !" << endl; } void setSon(shared_ptr<son> s) { son = s; } private: //shared_ptr<son> son; weak_ptr<son> son; // 用weak_ptr来替换 }; class son { public: son() { cout << "son !" << endl; } ~son() { cout << "~~~~~~son !" << endl; } void setFather(shared_ptr<father> f) { father = f; } private: shared_ptr<father> father; }; void test() { shared_ptr<father> f(new father()); shared_ptr<son> s(new son()); f->setSon(s); s->setFather(f); } int main() { test(); return 0; }
father !
son !
~~~~~~son !
~~~~~father !



