Mysql5.7 Linux安装教程
1.系统约定
安装文件下载目录:/data/software
Mysql目录安装位置:/usr/local/mysql
数据库保存位置:/data/mysql
日志保存位置:/data/log/mysql
2.下载mysql
在官网:http://dev.mysql.com/downloads/mysql/ 中,选择以下版本的mysql下载:
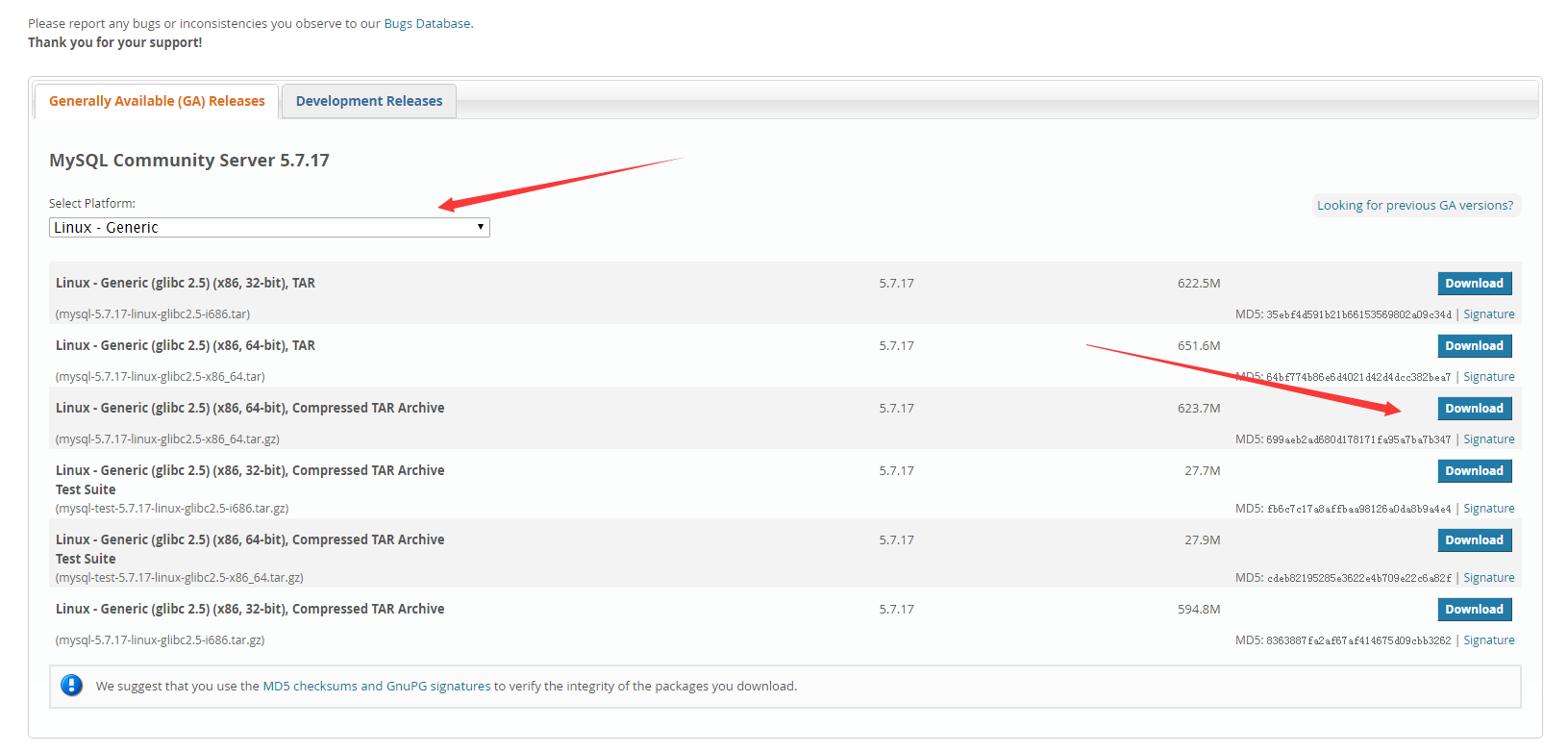
执行如下命名:
#mkdir /data/software
#cd /data/software
--下载安装包
--建议:在windows上使用迅雷下载,速度很快(我的是1M/s),然后用工具(Xftp)上传到 /data/software目录下;
#wget http://dev.mysql.com/get/Downloads/MySQL-5.7/mysql-5.7.17-linux-glibc2.5-x86_64.tar.gz
3解压压缩包到目标位置
#cd /data/software
--解压压缩包
#tar -xzvf /data/software/mysql-5.7.17-linux-glibc2.5-x86_64.tar.gz
--移动并修改文件名
#mv /data/software/mysql-5.7.17-linux-glibc2.5-x86_64 /usr/local/mysql
4.创建数据仓库目录
--/data/mysql 数据仓库目录
# mkdir /data/mysql
#ls /data/
5.新建mysql用户、组及目录
# ---新建一个msyql组
# useradd -r -s /sbin/nologin -g mysql mysql -d /usr/local/mysql ---新建msyql用户禁止登录shell
6.改变目录属有者
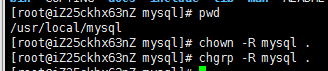
#cd /usr/local/mysql
#pwd
#chown -R mysql .
#chgrp -R mysql .
#chown -R mysql /data/mysql
7.配置参数
# bin/mysqld --initialize --user=mysql --basedir=/usr/local/mysql --datadir=/data/mysql

此处需要注意记录生成的临时密码,如上文结尾处的:YLi>7ecpe;YP
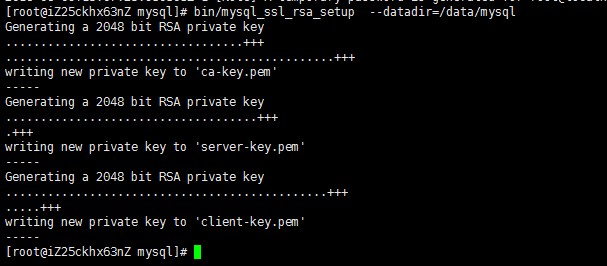
#bin/mysql_ssl_rsa_setup --datadir=/data/mysql
8.修改系统配置文件
#cd /usr/local/mysql/support-files
# cp my-default.cnf /etc/my.cnf
# cp mysql.server /etc/init.d/mysql
# vim /etc/init.d/mysql
修改以下内容:

9.启动mysql
# /etc/init.d/mysql start
--登陆
# mysql -hlocalhost -uroot -p
--如果出现:-bash: mysql: command not found
--就执行: # ln -s /usr/local/mysql/bin/mysql /usr/bin --没有出现就不用执行
--输入第6步生成的临时密码
--修改密码
mysql> set password=password('root');
--设置root账户的host地址(修改了才可以远程连接)
mysql>grant all privileges on *.* to 'root'@'%' identified by 'root';
mysql>flush privileges;
--查看表
mysql> use mysql;
mysql> select host,user from user;
--这里就可以使用远程连接测试了;
10.添加系统路径
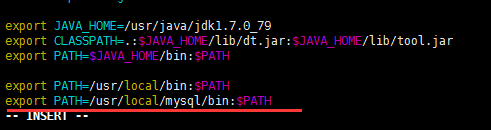
# vim /etc/profile
添加:
export PATH=/usr/local/mysql/bin:$PATH
如下:
# source /etc/profile
11.配置mysql自动启动
# chmod 755 /etc/init.d/mysql
# chkconfig --add mysql
# chkconfig --level 345 mysql on
以上就是linux环境Mysql 5.7.13安装教程,希望对大家的学习有所帮助。
补充:
--退出mysql命令窗口
#exit
--查看mysql状态
#service mysql status
--停止mysql
#service mysql stop
--启动mysql
#service mysql start
附my.cnf(这是一个配置mysql配置文件,暂时可以不用管,如你想钻研 你可以百度或google “mysql my.cnf 配置详情”)
/etc/my.cnf
# For advice on how to change settings please see
# http://dev.mysql.com/doc/refman/5.7/en/server-configuration-defaults.html
# *** DO NOT EDIT THIS FILE. It's a template which will be copied to the
# *** default location during install, and will be replaced if you
# *** upgrade to a newer version of MySQL.
[mysqld]
# Remove leading # and set to the amount of RAM for the most important data
# cache in MySQL. Start at 70% of total RAM for dedicated server, else 10%.
innodb_buffer_pool_size = 10G
# Remove leading # to turn on a very important data integrity option: logging
# changes to the binary log between backups.
log_bin
character-set-server=utf8
collation-server=utf8_bin
init-connect='SET NAMES utf8'
# These are commonly set, remove the # and set as required.
basedir = /usr/local/mysql
datadir = /export/mysql/var
port = 3306
server_id = 22206
socket = /export/mysql/mysql.sock
binlog_format = statement
# Remove leading # to set options mainly useful for reporting servers.
# The server defaults are faster for transactions and fast SELECTs.
# Adjust sizes as needed, experiment to find the optimal values.
join_buffer_size = 128M
sort_buffer_size = 2M
read_rnd_buffer_size = 2M
log_bin_trust_function_creators = on
sql_mode=NO_ENGINE_SUBSTITUTION,STRICT_TRANS_TABLES
lower_case_table_names=1
转载来源:https://www.cnblogs.com/dengshihuang/p/8029092.html



