Django Restful Framework【第三篇】认证、权限、限制访问频率
一、认证
认证请求头
views.py
#!/usr/bin/env python
# -*- coding:utf-8 -*-
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication
from rest_framework.permissions import BasePermission
from rest_framework.request import Request
from rest_framework import exceptions
token_list = [
'sfsfss123kuf3j123',
'asijnfowerkkf9812',
]
class TestAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
"""
用户认证,如果验证成功后返回元组: (用户,用户Token)
:param request:
:return:
None,表示跳过该验证;
如果跳过了所有认证,默认用户和Token和使用配置文件进行设置
self._authenticator = None
if api_settings.UNAUTHENTICATED_USER:
self.user = api_settings.UNAUTHENTICATED_USER() # 默认值为:匿名用户
else:
self.user = None
if api_settings.UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN:
self.auth = api_settings.UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN()# 默认值为:None
else:
self.auth = None
(user,token)表示验证通过并设置用户名和Token;
AuthenticationFailed异常
"""
val = request.query_params.get('token')
if val not in token_list:
raise exceptions.AuthenticationFailed("用户认证失败")
return ('登录用户', '用户token')
def authenticate_header(self, request):
"""
Return a string to be used as the value of the `WWW-Authenticate`
header in a `401 Unauthenticated` response, or `None` if the
authentication scheme should return `403 Permission Denied` responses.
"""
pass
class TestPermission(BasePermission):
message = "权限验证失败"
def has_permission(self, request, view):
"""
判断是否有权限访问当前请求
Return `True` if permission is granted, `False` otherwise.
:param request:
:param view:
:return: True有权限;False无权限
"""
if request.user == "管理员":
return True
# GenericAPIView中get_object时调用
def has_object_permission(self, request, view, obj):
"""
视图继承GenericAPIView,并在其中使用get_object时获取对象时,触发单独对象权限验证
Return `True` if permission is granted, `False` otherwise.
:param request:
:param view:
:param obj:
:return: True有权限;False无权限
"""
if request.user == "管理员":
return True
class TestView(APIView):
# 认证的动作是由request.user触发
authentication_classes = [TestAuthentication, ]
# 权限
# 循环执行所有的权限
permission_classes = [TestPermission, ]
def get(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
# self.dispatch
print(request.user)
print(request.auth)
return Response('GET请求,响应内容')
def post(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return Response('POST请求,响应内容')
def put(self, request, *args, **kwargs):
return Response('PUT请求,响应内容')
自定义认证功能
class MyAuthtication(BasicAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
token = request.query_params.get('token') #注意是没有GET的,用query_params表示
if token == 'zxxzzxzc':
return ('uuuuuu','afsdsgdf') #返回user,auth
# raise AuthenticationFailed('认证错误') #只要抛出认证错误这样的异常就会去执行下面的函数
raise APIException('认证错误')
def authenticate_header(self, request): #认证不成功的时候执行
return 'Basic reala="api"'
class UserView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [MyAuthtication,]
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
print(request.user)
print(request.auth)
return Response('用户列表')

二、权限
1、需求:Host是匿名用户和用户都能访问 #匿名用户的request.user = none;User只有注册用户能访问
urls.py
from app03 import views
from django.conf.urls import url
urlpatterns = [
# django rest framework
url('^auth/', views.AuthView.as_view()),
url(r'^hosts/', views.HostView.as_view()),
url(r'^users/', views.UsersView.as_view()),
url(r'^salary/', views.SalaryView.as_view()),
]
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
from rest_framework.views import APIView #继承的view
from rest_framework.response import Response #友好的返回
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication #认证的类
from rest_framework.authentication import BasicAuthentication
from app01 import models
from rest_framework import exceptions
from rest_framework.permissions import AllowAny #权限在这个类里面
from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle,SimpleRateThrottle
# Create your views here.
# +++++++++++++++认证类和权限类========================
class MyAuthentication(BaseAuthentication):
def authenticate(self, request):
token = request.query_params.get('token')
obj = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if obj : #如果认证成功,返回用户名和auth
return (obj.username,obj)
return None #如果没有认证成功就不处理,进行下一步
def authenticate_header(self, request):
pass
class MyPermission(object):
message = '无权访问'
def has_permission(self,request,view): #has_permission里面的self是view视图对象
if request.user:
return True #如果不是匿名用户就说明有权限
return False #否则无权限
class AdminPermission(object):
message = '无权访问'
def has_permission(self, request, view): # has_permission里面的self是view视图对象
if request.user=='haiyun':
return True # 返回True表示有权限
return False #返回False表示无权限
# +++++++++++++++++++++++++++
class AuthView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [] #认证页面不需要认证
def get(self,request):
self.dispatch
return '认证列表'
class HostView(APIView):
'''需求:
Host是匿名用户和用户都能访问 #匿名用户的request.user = none
User只有注册用户能访问
'''
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication,]
permission_classes = [] #都能访问就没必要设置权限了
def get(self,request):
print(request.user)
print(request.auth)
return Response('主机列表')
class UsersView(APIView):
'''用户能访问,request.user里面有值'''
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication,]
permission_classes = [MyPermission,]
def get(self,request):
print(request.user,'111111111')
return Response('用户列表')
def permission_denied(self, request, message=None):
"""
If request is not permitted, determine what kind of exception to raise.
"""
if request.authenticators and not request.successful_authenticator:
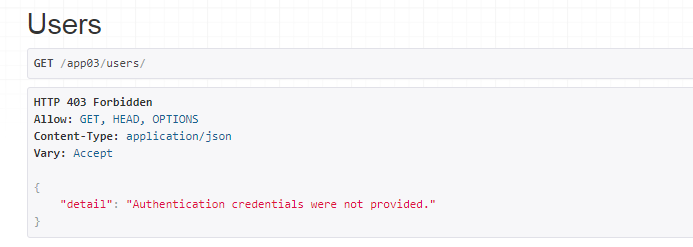
'''如果没有通过认证,并且权限中return False了,就会报下面的这个异常了'''
raise exceptions.NotAuthenticated(detail='无权访问')
raise exceptions.PermissionDenied(detail=message)
认证和权限配合使用
class SalaryView(APIView):
'''用户能访问'''
message ='无权访问'
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication,] #验证是不是用户
permission_classes = [MyPermission,AdminPermission,] #再看用户有没有权限,如果有权限在判断有没有管理员的权限
def get(self,request):
return Response('薪资列表')
def permission_denied(self, request, message=None):
"""
If request is not permitted, determine what kind of exception to raise.
"""
if request.authenticators and not request.successful_authenticator:
'''如果没有通过认证,并且权限中return False了,就会报下面的这个异常了'''
raise exceptions.NotAuthenticated(detail='无权访问')
raise exceptions.PermissionDenied(detail=message)
如果遇上这样的,还可以自定制,参考源码
def check_permissions(self, request):
"""
Check if the request should be permitted.
Raises an appropriate exception if the request is not permitted.
"""
for permission in self.get_permissions():
#循环每一个permission对象,调用has_permission
#如果False,则抛出异常
#True 说明有权访问
if not permission.has_permission(request, self):
self.permission_denied(
request, message=getattr(permission, 'message', None)
)
def permission_denied(self, request, message=None):
"""
If request is not permitted, determine what kind of exception to raise.
"""
if request.authenticators and not request.successful_authenticator:
'''如果没有通过认证,并且权限中return False了,就会报下面的这个异常了'''
raise exceptions.NotAuthenticated()
raise exceptions.PermissionDenied(detail=message)
那么我们可以重写permission_denied这个方法,如下:
views.py
class UsersView(APIView):
'''用户能访问,request.user里面有值'''
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication,]
permission_classes = [MyPermission,]
def get(self,request):
return Response('用户列表')
def permission_denied(self, request, message=None):
"""
If request is not permitted, determine what kind of exception to raise.
"""
if request.authenticators and not request.successful_authenticator:
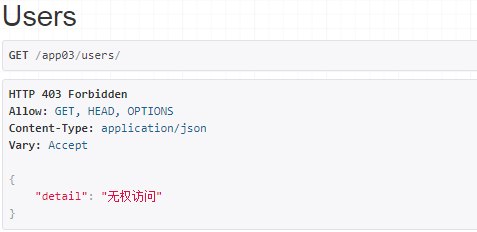
'''如果没有通过认证,并且权限中return False了,就会报下面的这个异常了'''
raise exceptions.NotAuthenticated(detail='无权访问')
raise exceptions.PermissionDenied(detail=message)
2. 全局使用
上述操作中均是对单独视图进行特殊配置,如果想要对全局进行配置,则需要再配置文件中写入即可。
settings.py
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'UNAUTHENTICATED_USER': None,
'UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN': None, #将匿名用户设置为None
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES": [
"app01.utils.MyAuthentication",
],
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES':[
"app03.utils.MyPermission",#设置路径,
]
}
Views.py
class AuthView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [] #认证页面不需要认证
def get(self,request):
self.dispatch
return '认证列表'
class HostView(APIView):
'''需求:
Host是匿名用户和用户都能访问 #匿名用户的request.user = none
User只有注册用户能访问
'''
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication,]
permission_classes = [] #都能访问就没必要设置权限了
def get(self,request):
print(request.user)
print(request.auth)
return Response('主机列表')
class UsersView(APIView):
'''用户能访问,request.user里面有值'''
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication,]
permission_classes = [MyPermission,]
def get(self,request):
print(request.user,'111111111')
return Response('用户列表')
def permission_denied(self, request, message=None):
"""
If request is not permitted, determine what kind of exception to raise.
"""
if request.authenticators and not request.successful_authenticator:
'''如果没有通过认证,并且权限中return False了,就会报下面的这个异常了'''
raise exceptions.NotAuthenticated(detail='无权访问')
raise exceptions.PermissionDenied(detail=message)
class SalaryView(APIView):
'''用户能访问'''
message ='无权访问'
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication,] #验证是不是用户
permission_classes = [MyPermission,AdminPermission,] #再看用户有没有权限,如果有权限在判断有没有管理员的权限
def get(self,request):
return Response('薪资列表')
def permission_denied(self, request, message=None):
"""
If request is not permitted, determine what kind of exception to raise.
"""
if request.authenticators and not request.successful_authenticator:
'''如果没有通过认证,并且权限中return False了,就会报下面的这个异常了'''
raise exceptions.NotAuthenticated(detail='无权访问')
raise exceptions.PermissionDenied(detail=message)
三、限流
1、为什么要限流呢?
答:防爬
2、限制访问频率源码分析
self.check_throttles(request)
self.check_throttles(request)
check_throttles
def check_throttles(self, request):
"""
Check if request should be throttled.
Raises an appropriate exception if the request is throttled.
"""
for throttle in self.get_throttles():
#循环每一个throttle对象,执行allow_request方法
# allow_request:
#返回False,说明限制访问频率
#返回True,说明不限制,通行
if not throttle.allow_request(request, self):
self.throttled(request, throttle.wait())
#throttle.wait()表示还要等多少秒就能访问了
get_throttles
def get_throttles(self):
"""
Instantiates and returns the list of throttles that this view uses.
"""
#返回对象
return [throttle() for throttle in self.throttle_classes]
找到类,可自定制类throttle_classes
throttle_classes = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES
BaseThrottle
class BaseThrottle(object):
"""
Rate throttling of requests.
"""
def allow_request(self, request, view):
"""
Return `True` if the request should be allowed, `False` otherwise.
"""
raise NotImplementedError('.allow_request() must be overridden')
def get_ident(self, request):
"""
Identify the machine making the request by parsing HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR
if present and number of proxies is > 0. If not use all of
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR if it is available, if not use REMOTE_ADDR.
"""
xff = request.META.get('HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR')
remote_addr = request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR')
num_proxies = api_settings.NUM_PROXIES
if num_proxies is not None:
if num_proxies == 0 or xff is None:
return remote_addr
addrs = xff.split(',')
client_addr = addrs[-min(num_proxies, len(addrs))]
return client_addr.strip()
return ''.join(xff.split()) if xff else remote_addr
def wait(self):
"""
Optionally, return a recommended number of seconds to wait before
the next request.
"""
return None
也可以重写allow_request方法
可自定制返回的错误信息throttled
def throttled(self, request, wait):
"""
If request is throttled, determine what kind of exception to raise.
"""
raise exceptions.Throttled(wait)
raise exceptions.Throttled(wait)错误信息详情
class Throttled(APIException):
status_code = status.HTTP_429_TOO_MANY_REQUESTS
default_detail = _('Request was throttled.')
extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
extra_detail_plural = 'Expected available in {wait} seconds.'
default_code = 'throttled'
def __init__(self, wait=None, detail=None, code=None):
if detail is None:
detail = force_text(self.default_detail)
if wait is not None:
wait = math.ceil(wait)
detail = ' '.join((
detail,
force_text(ungettext(self.extra_detail_singular.format(wait=wait),
self.extra_detail_plural.format(wait=wait),
wait))))
self.wait = wait
super(Throttled, self).__init__(detail, code)
下面来看看最简单的从源码中分析的示例,这只是举例说明了一下
urls.py
from django.conf.urls import url
from app04 import views
urlpatterns = [
url('limit/',views.LimitView.as_view()),
]
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework import exceptions
# from rest_framewor import
# Create your views here.
class MyThrottle(object):
def allow_request(self,request,view):
#返回False,限制
#返回True,不限制
pass
def wait(self):
return 1000
class LimitView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [] #不让认证用户
permission_classes = [] #不让验证权限
throttle_classes = [MyThrottle, ]
def get(self,request):
# self.dispatch
return Response('控制访问频率示例')
def throttled(self, request, wait):
'''可定制方法设置中文错误'''
# raise exceptions.Throttled(wait)
class MyThrottle(exceptions.Throttled):
default_detail = '请求被限制'
extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
extra_detail_plural = 'Expected available in {wait} seconds.'
default_code = '还需要再等{wait}秒'
raise MyThrottle(wait)
3、需求:对匿名用户进行限制,每个用户一分钟允许访问10次(只针对用户来说)
a、基于用户IP限制访问频率
流程分析:
- 先获取用户信息,如果是匿名用户,获取IP。如果不是匿名用户就可以获取用户名。
- 获取匿名用户IP,在request里面获取,比如IP= 1.1.1.1。
- 吧获取到的IP添加到到recode字典里面,需要在添加之前先限制一下。
- 如果时间间隔大于60秒,说明时间久远了,就把那个时间给剔除 了pop。在timelist列表里面现在留的是有效的访问时间段。
- 然后判断他的访问次数超过了10次没有,如果超过了时间就return False。
- 美中不足的是时间是固定的,我们改变他为动态的:列表里面最开始进来的时间和当前的时间进行比较,看需要等多久。
具体实现:
views初级版本
from django.shortcuts import render
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework import exceptions
from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle,SimpleRateThrottle #限制访问频率
import time
# Create your views here.
RECORD = {}
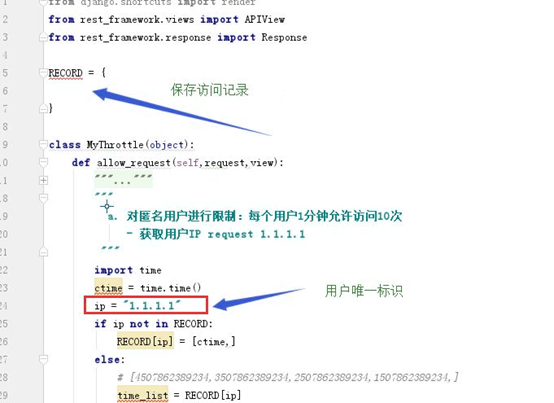
class MyThrottle(BaseThrottle):
def allow_request(self,request,view):
'''对匿名用户进行限制,每个用户一分钟访问10次 '''
ctime = time.time()
ip = '1.1.1.1'
if ip not in RECORD:
RECORD[ip] = [ctime]
else:
#[152042123,15204212,3152042,123152042123]
time_list = RECORD[ip] #获取ip里面的值
while True:
val = time_list[-1]#取出最后一个时间,也就是访问最早的时间
if (ctime-60)>val: #吧时间大于60秒的给剔除了
time_list.pop()
#剔除了之后timelist里面就是有效的时间了,在进行判断他的访问次数是不是超过10次
else:
break
if len(time_list) >10:
return False # 返回False,限制
time_list.insert(0, ctime)
return True #返回True,不限制
def wait(self):
ctime = time.time()
first_in_time = RECORD['1.1.1.1'][-1]
wt = 60-(ctime-first_in_time)
return wt
class LimitView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [] #不让认证用户
permission_classes = [] #不让验证权限
throttle_classes = [MyThrottle, ]
def get(self,request):
# self.dispatch
return Response('控制访问频率示例')
def throttled(self, request, wait):
'''可定制方法设置中文错误'''
# raise exceptions.Throttled(wait)
class MyThrottle(exceptions.Throttled):
default_detail = '请求被限制'
extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
extra_detail_plural = 'Expected available in {wait} seconds.'
default_code = '还需要再等{wait}秒'
raise MyThrottle(wait)
稍微做了改动
# from django.shortcuts import render
# from rest_framework.views import APIView
# from rest_framework.response import Response
# from rest_framework import exceptions
# from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle,SimpleRateThrottle #限制访问频率
# import time
# # Create your views here.
# RECORD = {}
# class MyThrottle(BaseThrottle):
#
# def allow_request(self,request,view):
# '''对匿名用户进行限制,每个用户一分钟访问10次 '''
# ctime = time.time()
# ip = '1.1.1.1'
# if ip not in RECORD:
# RECORD[ip] = [ctime]
# else:
# #[152042123,15204212,3152042,123152042123]
# time_list = RECORD[ip] #获取ip里面的值
# while True:
# val = time_list[-1]#取出最后一个时间,也就是访问最早的时间
# if (ctime-60)>val: #吧时间大于60秒的给剔除了
# time_list.pop()
# #剔除了之后timelist里面就是有效的时间了,在进行判断他的访问次数是不是超过10次
# else:
# break
# if len(time_list) >10:
# return False # 返回False,限制
# time_list.insert(0, ctime)
# return True #返回True,不限制
#
# def wait(self):
# ctime = time.time()
# first_in_time = RECORD['1.1.1.1'][-1]
# wt = 60-(ctime-first_in_time)
# return wt
#
#
# class LimitView(APIView):
# authentication_classes = [] #不让认证用户
# permission_classes = [] #不让验证权限
# throttle_classes = [MyThrottle, ]
# def get(self,request):
# # self.dispatch
# return Response('控制访问频率示例')
#
# def throttled(self, request, wait):
# '''可定制方法设置中文错误'''
# # raise exceptions.Throttled(wait)
# class MyThrottle(exceptions.Throttled):
# default_detail = '请求被限制'
# extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
# extra_detail_plural = 'Expected available in {wait} seconds.'
# default_code = '还需要再等{wait}秒'
# raise MyThrottle(wait)
from django.shortcuts import render
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework import exceptions
from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle,SimpleRateThrottle #限制访问频率
import time
# Create your views here.
RECORD = {}
class MyThrottle(BaseThrottle):
def allow_request(self,request,view):
'''对匿名用户进行限制,每个用户一分钟访问10次 '''
ctime = time.time()
self.ip =self.get_ident(request)
if self.ip not in RECORD:
RECORD[self.ip] = [ctime]
else:
#[152042123,15204212,3152042,123152042123]
time_list = RECORD[self.ip] #获取ip里面的值
while True:
val = time_list[-1]#取出最后一个时间,也就是访问最早的时间
if (ctime-60)>val: #吧时间大于60秒的给剔除了
time_list.pop()
#剔除了之后timelist里面就是有效的时间了,在进行判断他的访问次数是不是超过10次
else:
break
if len(time_list) >10:
return False # 返回False,限制
time_list.insert(0, ctime)
return True #返回True,不限制
def wait(self):
ctime = time.time()
first_in_time = RECORD[self.ip][-1]
wt = 60-(ctime-first_in_time)
return wt
class LimitView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [] #不让认证用户
permission_classes = [] #不让验证权限
throttle_classes = [MyThrottle, ]
def get(self,request):
# self.dispatch
return Response('控制访问频率示例')
def throttled(self, request, wait):
'''可定制方法设置中文错误'''
# raise exceptions.Throttled(wait)
class MyThrottle(exceptions.Throttled):
default_detail = '请求被限制'
extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
extra_detail_plural = 'Expected available in {wait} seconds.'
default_code = '还需要再等{wait}秒'
raise MyThrottle(wait)
b、用resetframework内部的限制访问频率(利于Django缓存)
源码分析:
from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle,SimpleRateThrottle #限制访问频率
BaseThrottle相当于一个抽象类
class BaseThrottle(object):
"""
Rate throttling of requests.
"""
def allow_request(self, request, view):
"""
Return `True` if the request should be allowed, `False` otherwise.
"""
raise NotImplementedError('.allow_request() must be overridden')
def get_ident(self, request): #唯一标识
"""
Identify the machine making the request by parsing HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR
if present and number of proxies is > 0. If not use all of
HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR if it is available, if not use REMOTE_ADDR.
"""
xff = request.META.get('HTTP_X_FORWARDED_FOR')
remote_addr = request.META.get('REMOTE_ADDR') #获取IP等
num_proxies = api_settings.NUM_PROXIES
if num_proxies is not None:
if num_proxies == 0 or xff is None:
return remote_addr
addrs = xff.split(',')
client_addr = addrs[-min(num_proxies, len(addrs))]
return client_addr.strip()
return ''.join(xff.split()) if xff else remote_addr
def wait(self):
"""
Optionally, return a recommended number of seconds to wait before
the next request.
"""
return None
SimpleRateThrottle
class SimpleRateThrottle(BaseThrottle):
"""
一个简单的缓存实现,只需要` get_cache_key() `。被覆盖。
速率(请求/秒)是由视图上的“速率”属性设置的。类。该属性是一个字符串的形式number_of_requests /期。
周期应该是:(的),“秒”,“M”,“min”,“h”,“小时”,“D”,“一天”。
以前用于节流的请求信息存储在高速缓存中。
A simple cache implementation, that only requires `.get_cache_key()`
to be overridden.
The rate (requests / seconds) is set by a `rate` attribute on the View
class. The attribute is a string of the form 'number_of_requests/period'.
Period should be one of: ('s', 'sec', 'm', 'min', 'h', 'hour', 'd', 'day')
Previous request information used for throttling is stored in the cache.
"""
cache = default_cache
timer = time.time
cache_format = 'throttle_%(scope)s_%(ident)s'
scope = None
THROTTLE_RATES = api_settings.DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES
def __init__(self):
if not getattr(self, 'rate', None):
self.rate = self.get_rate()
self.num_requests, self.duration = self.parse_rate(self.rate)
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):#这个相当于是一个半成品,我们可以来补充它
"""
Should return a unique cache-key which can be used for throttling.
Must be overridden.
May return `None` if the request should not be throttled.
"""
raise NotImplementedError('.get_cache_key() must be overridden')
def get_rate(self):
"""
Determine the string representation of the allowed request rate.
"""
if not getattr(self, 'scope', None):
msg = ("You must set either `.scope` or `.rate` for '%s' throttle" %
self.__class__.__name__)
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg)
try:
return self.THROTTLE_RATES[self.scope]
except KeyError:
msg = "No default throttle rate set for '%s' scope" % self.scope
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg)
def parse_rate(self, rate):
"""
Given the request rate string, return a two tuple of:
<allowed number of requests>, <period of time in seconds>
"""
if rate is None:
return (None, None)
num, period = rate.split('/')
num_requests = int(num)
duration = {'s': 1, 'm': 60, 'h': 3600, 'd': 86400}[period[0]]
return (num_requests, duration)
#1、一进来会先执行他,
def allow_request(self, request, view):
"""
Implement the check to see if the request should be throttled.
On success calls `throttle_success`.
On failure calls `throttle_failure`.
"""
if self.rate is None:
return True
self.key = self.get_cache_key(request, view) #2、执行get_cache_key,这里的self.key就相当于我们举例ip
if self.key is None:
return True
self.history = self.cache.get(self.key, []) #3、得到的key,默认是一个列表,赋值给了self.history,
# 这时候self.history就是每一个ip对应的访问记录
self.now = self.timer()
# Drop any requests from the history which have now passed the
# throttle duration
while self.history and self.history[-1] <= self.now - self.duration:
self.history.pop()
if len(self.history) >= self.num_requests:
return self.throttle_failure()
return self.throttle_success()
def throttle_success(self):
"""
Inserts the current request's timestamp along with the key
into the cache.
"""
self.history.insert(0, self.now)
self.cache.set(self.key, self.history, self.duration)
return True
def throttle_failure(self):
"""
Called when a request to the API has failed due to throttling.
"""
return False
def wait(self):
"""
Returns the recommended next request time in seconds.
"""
if self.history:
remaining_duration = self.duration - (self.now - self.history[-1])
else:
remaining_duration = self.duration
available_requests = self.num_requests - len(self.history) + 1
if available_requests <= 0:
return None
return remaining_duration / float(available_requests)
请求一进来会先执行SimpleRateThrottle这个类的构造方法
__init__
def __init__(self):
if not getattr(self, 'rate', None):
self.rate = self.get_rate() #点进去看到需要些一个scope ,2/m
self.num_requests, self.duration = self.parse_rate(self.rate)
get_rate
def get_rate(self):
"""
Determine the string representation of the allowed request rate.
"""
if not getattr(self, 'scope', None): #检测必须有scope,没有就报错了
msg = ("You must set either `.scope` or `.rate` for '%s' throttle" %
self.__class__.__name__)
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg)
try:
return self.THROTTLE_RATES[self.scope]
except KeyError:
msg = "No default throttle rate set for '%s' scope" % self.scope
raise ImproperlyConfigured(msg)
parse_rate
def parse_rate(self, rate):
"""
Given the request rate string, return a two tuple of:
<allowed number of requests>, <period of time in seconds>
"""
if rate is None:
return (None, None)
num, period = rate.split('/')
num_requests = int(num)
duration = {'s': 1, 'm': 60, 'h': 3600, 'd': 86400}[period[0]]
return (num_requests, duration)
allow_request
#2、接下来会先执行他,
def allow_request(self, request, view):
"""
Implement the check to see if the request should be throttled.
On success calls `throttle_success`.
On failure calls `throttle_failure`.
"""
if self.rate is None:
return True
self.key = self.get_cache_key(request, view) #2、执行get_cache_key,这里的self.key就相当于我们举例ip
if self.key is None:
return True #不限制
# [114521212,11452121211,45212121145,21212114,521212]
self.history = self.cache.get(self.key, []) #3、得到的key,默认是一个列表,赋值给了self.history,
# 这时候self.history就是每一个ip对应的访问记录
self.now = self.timer()
# Drop any requests from the history which have now passed the
# throttle duration
while self.history and self.history[-1] <= self.now - self.duration:
self.history.pop()
if len(self.history) >= self.num_requests:
return self.throttle_failure()
return self.throttle_success()
wait
def wait(self):
"""
Returns the recommended next request time in seconds.
"""
if self.history:
remaining_duration = self.duration - (self.now - self.history[-1])
else:
remaining_duration = self.duration
available_requests = self.num_requests - len(self.history) + 1
if available_requests <= 0:
return None
return remaining_duration / float(available_requests)
代码实现:
views.py
###########用resetframework内部的限制访问频率##############
class MySimpleRateThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = 'xxx'
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
return self.get_ident(request) #返回唯一标识IP
class LimitView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [] #不让认证用户
permission_classes = [] #不让验证权限
throttle_classes = [MySimpleRateThrottle, ]
def get(self,request):
# self.dispatch
return Response('控制访问频率示例')
def throttled(self, request, wait):
'''可定制方法设置中文错误'''
# raise exceptions.Throttled(wait)
class MyThrottle(exceptions.Throttled):
default_detail = '请求被限制'
extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
extra_detail_plural = 'Expected available in {wait} seconds.'
default_code = '还需要再等{wait}秒'
raise MyThrottle(wait)
记得在settings里面配置
settings.py
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'UNAUTHENTICATED_USER': None,
'UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN': None, #将匿名用户设置为None
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES": [
"app01.utils.MyAuthentication",
],
'DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES':[
# "app03.utils.MyPermission",#设置路径,
],
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES':{
'xxx':'2/minute' #2分钟
}
}
#缓存:放在文件
CACHES = {
'default': {
'BACKEND': 'django.core.cache.backends.filebased.FileBasedCache',
'LOCATION': 'cache', #文件路径
}
}
4、对匿名用户进行限制,每个用户1分钟允许访问5次,对于登录的普通用户1分钟访问10次,VIP用户一分钟访问20次
- 比如首页可以匿名访问
- #先认证,只有认证了才知道是不是匿名的,
- #权限登录成功之后才能访问, ,index页面就不需要权限了
- If request.user #判断登录了没有
urls.py
from django.contrib import admin
from django.conf.urls import url, include
from app05 import views
urlpatterns = [
url('index/',views.IndexView.as_view()),
url('manage/',views.ManageView.as_view()),
]
views.py
from django.shortcuts import render
from rest_framework.views import APIView
from rest_framework.response import Response
from rest_framework.authentication import BaseAuthentication #认证需要
from rest_framework.throttling import BaseThrottle,SimpleRateThrottle #限流处理
from rest_framework.permissions import BasePermission
from rest_framework import exceptions
from app01 import models
# Create your views here.
###############3##认证#####################
class MyAuthentcate(BaseAuthentication):
'''检查用户是否存在,如果存在就返回user和auth,如果没有就返回'''
def authenticate(self, request):
token = request.query_params.get('token')
obj = models.UserInfo.objects.filter(token=token).first()
if obj:
return (obj.username,obj.token)
return None #表示我不处理
##################权限#####################
class MyPermission(BasePermission):
message='无权访问'
def has_permission(self, request, view):
if request.user:
return True #true表示有权限
return False #false表示无权限
class AdminPermission(BasePermission):
message = '无权访问'
def has_permission(self, request, view):
if request.user=='haiyan':
return True # true表示有权限
return False # false表示无权限
############3#####限流##################3##
class AnonThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = 'wdp_anon' #相当于设置了最大的访问次数和时间
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
if request.user:
return None #返回None表示我不限制,登录用户我不管
#匿名用户
return self.get_ident(request) #返回一个唯一标识IP
class UserThrottle(SimpleRateThrottle):
scope = 'wdp_user'
def get_cache_key(self, request, view):
#登录用户
if request.user:
return request.user
return None #返回NOne表示匿名用户我不管
##################视图#####################
#首页支持匿名访问,
#无需要登录就可以访问
class IndexView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentcate,] #认证判断他是不是匿名用户
permission_classes = [] #一般主页就不需要权限验证了
throttle_classes = [AnonThrottle,UserThrottle,] #对匿名用户和普通用户的访问限制
def get(self,request):
# self.dispatch
return Response('访问首页')
def throttled(self, request, wait):
'''可定制方法设置中文错误'''
# raise exceptions.Throttled(wait)
class MyThrottle(exceptions.Throttled):
default_detail = '请求被限制'
extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
extra_detail_plural = 'Expected available in {wait} seconds.'
default_code = '还需要再等{wait}秒'
raise MyThrottle(wait)
#需登录就可以访问
class ManageView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentcate, ] # 认证判断他是不是匿名用户
permission_classes = [MyPermission,] # 一般主页就不需要权限验证了
throttle_classes = [AnonThrottle, UserThrottle, ] # 对匿名用户和普通用户的访问限制
def get(self, request):
# self.dispatch
return Response('管理人员访问页面')
def throttled(self, request, wait):
'''可定制方法设置中文错误'''
# raise exceptions.Throttled(wait)
class MyThrottle(exceptions.Throttled):
default_detail = '请求被限制'
extra_detail_singular = 'Expected available in {wait} second.'
extra_detail_plural = 'Expected available in {wait} seconds.'
default_code = '还需要再等{wait}秒'
raise MyThrottle(wait)
四、总结
1、认证:就是检查用户是否存在;如果存在返回(request.user,request.auth);不存在request.user/request.auth=None
2、权限:进行职责的划分
3、限制访问频率
认证
- 类:authenticate/authenticate_header ##验证不成功的时候执行的
- 返回值:
- return None,
- return (user,auth),
- raise 异常
- 配置:
- 视图:
class IndexView(APIView):
authentication_classes = [MyAuthentication,]
- 全局:
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
'UNAUTHENTICATED_USER': None,
'UNAUTHENTICATED_TOKEN': None,
"DEFAULT_AUTHENTICATION_CLASSES": [
# "app02.utils.MyAuthentication",
],
}
权限
- 类:has_permission/has_object_permission
- 返回值:
- True、#有权限
- False、#无权限
- exceptions.PermissionDenied(detail="错误信息") #异常自己随意,想抛就抛,错误信息自己指定
- 配置:
- 视图:
class IndexView(APIView):
permission_classes = [MyPermission,]
- 全局:
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_PERMISSION_CLASSES": [
# "app02.utils.MyAuthentication",
],
}
限流
- 类:allow_request/wait PS: scope = "wdp_user"
- 返回值:
return True、#不限制
return False #限制
- 配置:
- 视图:
class IndexView(APIView):
throttle_classes=[AnonThrottle,UserThrottle,]
def get(self,request,*args,**kwargs):
self.dispatch
return Response('访问首页')
- 全局
REST_FRAMEWORK = {
"DEFAULT_THROTTLE_CLASSES":[
],
'DEFAULT_THROTTLE_RATES':{
'wdp_anon':'5/minute',
'wdp_user':'10/minute',
}
}



 浙公网安备 33010602011771号
浙公网安备 33010602011771号